drain JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 644 of 2199

(2) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Disconnect the left headlamp and dash wire harness
connector for the rear washer pump/motor unit from
the pump/motor unit connector receptacle. Check for
continuity between the ground circuit cavity of the
left headlamp and dash wire harness connector for
the rear washer pump/motor unit and a good ground.
There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 3. If not
OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground (G106)
as required.
(3) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Push the right
multi-function switch control stalk toward the instru-
ment panel to actuate the rear washer switch. With
the rear washer switch actuated, check for battery
voltage at the rear washer switch output circuit cav-
ity of the left headlamp and dash wire harness con-
nector for the rear washer pump/motor unit. If OK,
replace the faulty rear washer pump/motor unit. If
not OK, repair the open rear washer switch output
circuit between the rear washer pump/motor unit
and the right multi-function switch as required.
CLEANING - REAR WIPER & WASHER SYSTEM
WIPER SYSTEM
The squeegee of a wiper blade exposed to the ele-
ments for a long time tends to lose its wiping effec-
tiveness. Periodic cleaning of the squeegee is
suggested to remove any deposits of salt or road film.
The wiper blade, arm, and liftgate glass should only
be cleaned using a sponge or soft cloth and wind-
shield washer fluid, a mild detergent, or a non-abra-
sive cleaner. If the wiper blade continues to leave
streaks, smears, hazing, or beading on the glass after
thorough cleaning of the squeegees and the glass, the
entire wiper blade assembly must be replaced.
CAUTION: Protect the rubber squeegee of the wiper
blade from any petroleum-based cleaners, solvents,
or contaminants. These products can rapidly deteri-
orate the rubber squeegee.
WASHER SYSTEM
If the washer system is contaminated with foreign
material, drain the washer reservoir by removing the
front washer pump/motor from the reservoir. Clean
foreign material from the inside of the washer reser-
voir using clean washer fluid, a mild detergent, or a
non-abrasive cleaner. Flush foreign material from the
washer system plumbing by first disconnecting the
washer hose from the washer nozzle, then running
the washer pump/motor to run clean washer fluid or
water through the system. A plugged or restricted
washer nozzle should be carefully back-flushed usingcompressed air. If the washer nozzle obstruction can-
not be cleared, replace the washer nozzle.
CAUTION: Never introduce petroleum-based clean-
ers, solvents, or contaminants into the washer sys-
tem. These products can rapidly deteriorate the
rubber seals and hoses of the washer system, as
well as the rubber squeegee of the wiper blade.
CAUTION: Never use compressed air to flush the
washer system plumbing. Compressed air pres-
sures are too great for the washer system plumbing
components and will result in further system dam-
age. Never use sharp instruments to clear a
plugged washer nozzle or damage to the nozzle ori-
fice and improper nozzle spray patterns will result.
INSPECTION - REAR WIPER & WASHER
SYSTEM
WIPER SYSTEM
The rear wiper blade and wiper arm should be
inspected periodically, not just when wiper perfor-
mance problems are experienced. This inspection
should include the following points:
(1) Inspect the wiper arm for any indications of
damage, or contamination. If the wiper arm is con-
taminated with any foreign material, clean as
required. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/REAR WIPERS/
WASHERS - CLEANING). If a wiper arm is damaged
or corrosion is evident, replace the wiper arm with a
new unit. Do not attempt to repair a wiper arm that
is damaged or corroded.
(2) Carefully lift the wiper arm off of the ramp.
Note the action of the wiper arm hinge. The wiper
arm should pivot freely at the hinge, but with no lat-
eral looseness evident. If there is any binding evident
in the wiper arm hinge, or there is evident lateral
play in the wiper arm hinge, replace the wiper arm.
CAUTION: Do not allow the wiper arm to spring
back against the glass without the wiper blade in
place or the glass may be damaged.
(3) Once proper hinge action of the wiper arm is
confirmed, check the hinge for proper spring tension.
The spring tension of the wiper arm should be suffi-
cient to cause the rubber squeegee to conform to the
curvature of the glass. Replace a wiper arm if it has
low or no spring tension.
(4) Inspect the wiper blade and squeegee for any
indications of damage, contamination, or rubber dete-
rioration (Fig. 1). If the wiper blade or squeegee is
contaminated with any foreign material, clean them
and the glass as required. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
WJREAR WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 37
REAR WIPERS/WASHERS (Continued)
Page 646 of 2199
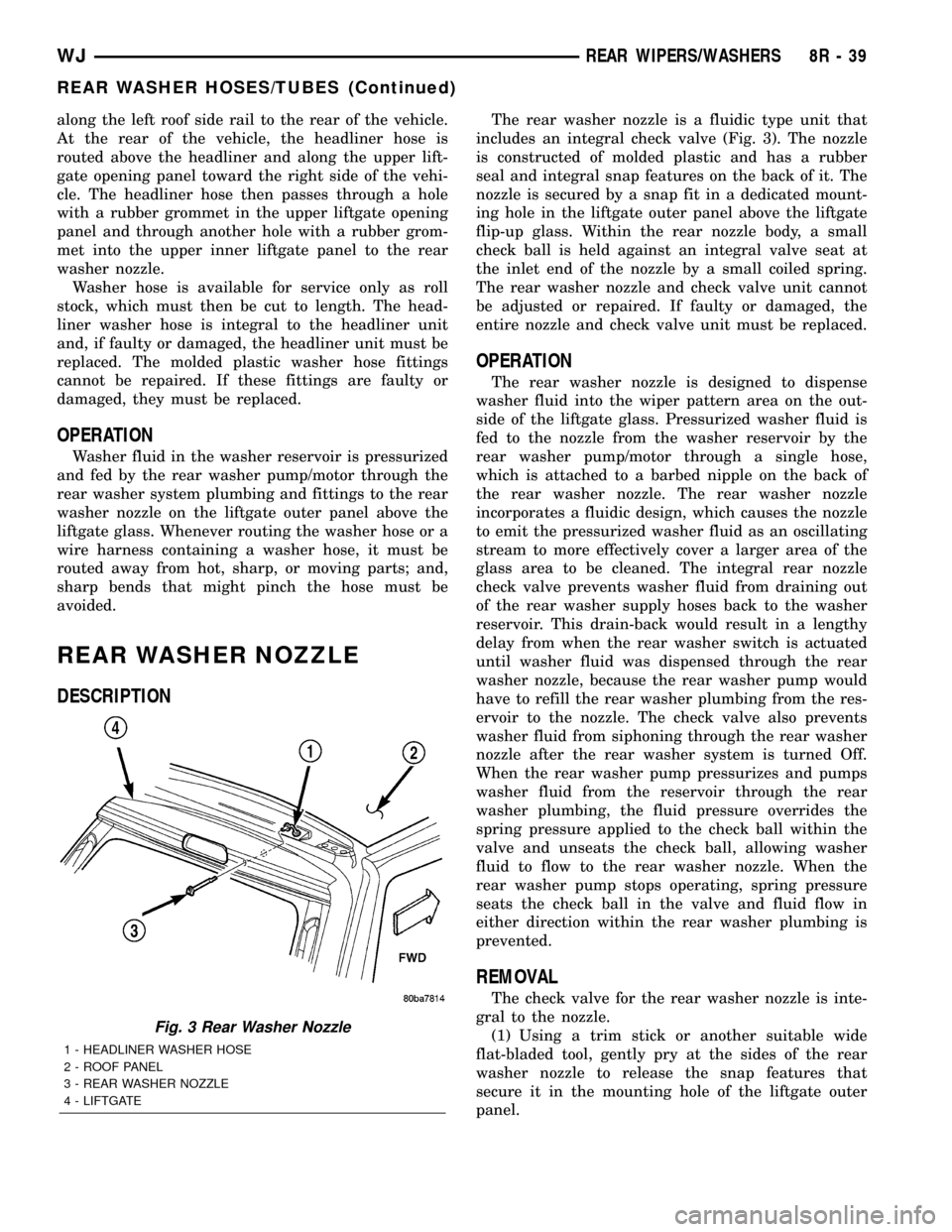
along the left roof side rail to the rear of the vehicle.
At the rear of the vehicle, the headliner hose is
routed above the headliner and along the upper lift-
gate opening panel toward the right side of the vehi-
cle. The headliner hose then passes through a hole
with a rubber grommet in the upper liftgate opening
panel and through another hole with a rubber grom-
met into the upper inner liftgate panel to the rear
washer nozzle.
Washer hose is available for service only as roll
stock, which must then be cut to length. The head-
liner washer hose is integral to the headliner unit
and, if faulty or damaged, the headliner unit must be
replaced. The molded plastic washer hose fittings
cannot be repaired. If these fittings are faulty or
damaged, they must be replaced.
OPERATION
Washer fluid in the washer reservoir is pressurized
and fed by the rear washer pump/motor through the
rear washer system plumbing and fittings to the rear
washer nozzle on the liftgate outer panel above the
liftgate glass. Whenever routing the washer hose or a
wire harness containing a washer hose, it must be
routed away from hot, sharp, or moving parts; and,
sharp bends that might pinch the hose must be
avoided.
REAR WASHER NOZZLE
DESCRIPTION
The rear washer nozzle is a fluidic type unit that
includes an integral check valve (Fig. 3). The nozzle
is constructed of molded plastic and has a rubber
seal and integral snap features on the back of it. The
nozzle is secured by a snap fit in a dedicated mount-
ing hole in the liftgate outer panel above the liftgate
flip-up glass. Within the rear nozzle body, a small
check ball is held against an integral valve seat at
the inlet end of the nozzle by a small coiled spring.
The rear washer nozzle and check valve unit cannot
be adjusted or repaired. If faulty or damaged, the
entire nozzle and check valve unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The rear washer nozzle is designed to dispense
washer fluid into the wiper pattern area on the out-
side of the liftgate glass. Pressurized washer fluid is
fed to the nozzle from the washer reservoir by the
rear washer pump/motor through a single hose,
which is attached to a barbed nipple on the back of
the rear washer nozzle. The rear washer nozzle
incorporates a fluidic design, which causes the nozzle
to emit the pressurized washer fluid as an oscillating
stream to more effectively cover a larger area of the
glass area to be cleaned. The integral rear nozzle
check valve prevents washer fluid from draining out
of the rear washer supply hoses back to the washer
reservoir. This drain-back would result in a lengthy
delay from when the rear washer switch is actuated
until washer fluid was dispensed through the rear
washer nozzle, because the rear washer pump would
have to refill the rear washer plumbing from the res-
ervoir to the nozzle. The check valve also prevents
washer fluid from siphoning through the rear washer
nozzle after the rear washer system is turned Off.
When the rear washer pump pressurizes and pumps
washer fluid from the reservoir through the rear
washer plumbing, the fluid pressure overrides the
spring pressure applied to the check ball within the
valve and unseats the check ball, allowing washer
fluid to flow to the rear washer nozzle. When the
rear washer pump stops operating, spring pressure
seats the check ball in the valve and fluid flow in
either direction within the rear washer plumbing is
prevented.
REMOVAL
The check valve for the rear washer nozzle is inte-
gral to the nozzle.
(1) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry at the sides of the rear
washer nozzle to release the snap features that
secure it in the mounting hole of the liftgate outer
panel.
Fig. 3 Rear Washer Nozzle
1 - HEADLINER WASHER HOSE
2 - ROOF PANEL
3 - REAR WASHER NOZZLE
4 - LIFTGATE
WJREAR WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 39
REAR WASHER HOSES/TUBES (Continued)
Page 648 of 2199

the washer fluid and forces it through the pump out-
let nipple, the rear washer plumbing, and the rear
washer nozzle onto the liftgate glass.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the liner from the left front fender
wheel house.
(4) Disconnect the left headlamp and dash wire
harness connector for the rear washer pump/motor
from the motor connector receptacle (Fig. 6).
(5) Disconnect the washer hose from the barbed
outlet nipple of the rear washer pump/motor and
allow the washer fluid to drain into a clean container
for reuse.
(6) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry the barbed inlet nipple of
the washer pump out of the rubber grommet seal in
the reservoir. Care must be taken not to damage the
reservoir.
(7) Remove the rubber grommet seal from the
washer pump mounting hole in the washer reservoir
and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new rubber grommet seal into the
washer pump mounting hole in the washer reservoir.
Always use a new rubber grommet seal on the reser-
voir.(2) Position the barbed inlet nipple of the washer
pump to the rubber grommet seal in the reservoir
(Fig. 6).
(3) Press firmly and evenly on the washer pump
until the barbed inlet nipple is fully seated in the
rubber grommet seal in the washer reservoir mount-
ing hole.
(4) Reconnect the washer hose to the barbed outlet
nipple of the washer pump.
(5) Reconnect the left headlamp and dash wire
harness connector for the rear washer pump/motor
unit to the motor connector receptacle.
(6) Reinstall the liner into the left front fender
wheel house.
(7) Lower the vehicle.
(8) Refill the washer reservoir with the washer
fluid drained from the reservoir during the removal
procedure.
(9) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
REAR WIPER ARM
DESCRIPTION
The rear wiper arm is the rigid member located
between the rear wiper motor output shaft that pro-
trudes from the outer liftgate panel near the base of
the liftgate glass opening and the rear wiper blade
(Fig. 7). This wiper arm features an over-center
hinge that allows easy access to the liftgate and lift-
gate glass for cleaning. The wiper arm has a die cast
metal pivot end. This pivot end has a hole in it with
internal serrations and a plastic pivot cover is
Fig. 6 Washer Pumps (Viewed from Bottom of
Reservoir)
1 - REAR WASHER PUMP/MOTOR
2 - FRONT WASHER PUMP/MOTOR
3 - WASHER FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
Fig. 7 Rear Wiper Arm
1 - LIFTGATE
2 - REAR WIPER MOTOR OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - PARK RAMP
4 - PIVOT COVER
5 - REAR WIPER ARM
6 - NUT
WJREAR WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 41
REAR WASHER PUMP/MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1229 of 2199

of the preparation procedures performed just prior to
new vehicle delivery.
The PDC has a molded plastic cover that can be
removed to provide service access to all of the fuses
and relays in the PDC. An integral latch and hinges
are molded into the PDC cover for easy removal. A
fuse layout map is integral to the underside of the
PDC cover to ensure proper fuse and relay identifica-
tion. The IOD fuse is a 50 ampere maxi-type car-
tridge fuse and, when removed, it is stored in a spare
fuse cavity within the PDC.
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal con-
dition where power is being drained from the battery
with the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD
fuse feeds the memory and sleep mode functions for
some of the electronic modules in the vehicle as well
as various other accessories that require battery cur-
rent when the ignition switch is in the Off position,
including the clock. The only reason the IOD fuse is
removed is to reduce the normal IOD of the vehicle
electrical system during new vehicle transportation
and pre-delivery storage to reduce battery depletion,
while still allowing vehicle operation so that the
vehicle can be loaded, unloaded and moved as needed
by both vehicle transportation company and dealer
personnel.
The IOD fuse is removed from PDC fuse cavity 15
when the vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant.
Dealer personnel must install the IOD fuse when the
vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation. Once the
vehicle is prepared for delivery, the IOD function of
this fuse becomes transparent and the fuse that has
been assigned the IOD designation becomes only
another Fused B(+) circuit fuse. The IOD fuse serves
no useful purpose to the dealer technician in the ser-
vice or diagnosis of any vehicle system or condition,
other than the same purpose as that of any other
standard circuit protection device.
The IOD fuse can be used by the vehicle owner as
a convenient means of reducing battery depletion
when a vehicle is to be stored for periods not toexceed about thirty days. However, it must be
remembered that removing the IOD fuse will not
eliminate IOD, but only reduce this normal condition.
If a vehicle will be stored for more than about thirty
days, the battery negative cable should be discon-
nected to eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery
should be tested and recharged at regular intervals
during the vehicle storage period to prevent the bat-
tery from becoming discharged or damaged. Refer to
Battery Systemfor additional service information.
REMOVAL
The Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) fuses normal installa-
tion location is cavity 15 in the power distribution
center. When the vehicle is shipped from the assem-
bly plant the fuse is removed to maintain proper bat-
tery voltage during vehicle storage (in some cases).
Dealer personnel must install the IOD fuse when the
vehicle is being prepared for customer delivery in
order to restore full electrical system operation.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) Unlatch and open the cover of the power distri-
bution center.
(3) Remove the IOD fuse from fusecavity 15of
the power distribution center (Fig. 2).
(4) Store the removed IOD fuse by installing it in
the unused fuse storagecavity 11of the PDC (Fig.
2).
(5) Close and latch the power distribution center
cover.
INSTALLATION
(1) Be certain the ignition switch is in the Off posi-
tion.
(2) Unlatch and open the cover of the power distri-
bution center.
(3) Remove the stored IOD fuse from fuse storage
cavity 11of the power distribution center.
(4) Use a thumb to press the IOD fuse firmly down
into power distribution center fusecavity 15.
(5) Close and latch the power distribution center
cover.
8W - 97 - 4 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONWJ
IOD FUSE (Continued)
Page 1240 of 2199

ground at all times. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit to ground as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the steering column opening cover
from the instrument panel. Refer toSteering Col-
umn Opening Coverin Body for the procedure.
(3) The power outlet / cigar lighter relay is located
on the left side of the combination flasher in the
junction block.
(4) Remove the power outlet / cigar lighter relay
from the junction block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the power outlet / cigar lighter relay in
the proper receptacle in the junction block.
(2) Align the power outlet / cigar lighter relay ter-
minals with the terminal cavities in the junction
block receptacle.
(3) Push in firmly on the power outlet / cigar
lighter relay until the terminals are fully seated in
the terminal cavities in the junction block receptacle.
(4) Install the steering column opening cover onto
the instrument panel. Refer toSteering Column
Opening Coverin Body for the procedure.
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
IOD WIRE HARNESS
CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) connector that is located in a molded
connector receptacle on the lower rear surface of the
Junction Block (JB) housing (Fig. 17). The JB is con-
cealed above the molded plastic instrument panel
fuse cover. Integral latches molded into the fuse
cover secure it the JB, the Body Control Module
(BCM) and the 16-way data link connector tab of the
instrument panel steering column support bracket.
The fuse cover can be pulled downward to disengage
the latches and provide service access to all of the
fuses, relays and wire harness connectors of the JB.
Refer toInstrument Panel Fuse Coverin the
index of this service manual for the location of addi-
tional service information covering the fuse cover.
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal con-
dition where power is being drained from the battery
with the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD
connector feeds the memory and sleep mode func-
tions for some of the electronic modules in the vehicleas well as various other accessories that require bat-
tery current when the ignition switch is in the Off
position, including the clock.
The IOD connector can be used by the vehicle
owner as a convenient means of reducing battery
depletion when a vehicle is to be stored for periods
not to exceed about twenty days (short-term storage).
Simply disconnect the IOD connector from the JB
receptacle. However, it must be remembered that dis-
connecting the IOD connector will not eliminate IOD,
but only reduce this normal condition. When a vehi-
cle will not be used for more than twenty days, but
less than thirty days, remove the IOD fuse from the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). If a vehicle will be
stored for more than about thirty days, the battery
negative cable should be disconnected to eliminate
normal IOD; and, the battery should be tested and
recharged at regular intervals during the vehicle
storage period to prevent the battery from becoming
discharged or damaged. Refer toIgnition-Off Draw
Fig. 17 Ignition-Off Draw Connector
1 - SNAP CLIPS
2 - SCREW
3 - CONNECTOR
4 - LEFT BODY WIRE HARNESS
5 - IOD CONNECTOR
6 - FUSED B+ CONNECTOR
7 - RIGHT BODY WIRE HARNESS
8 - SCREW
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - JUNCTION BLOCK
WJ8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 15
POWER OUTLET RELAY (Continued)
Page 1249 of 2199
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐ ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
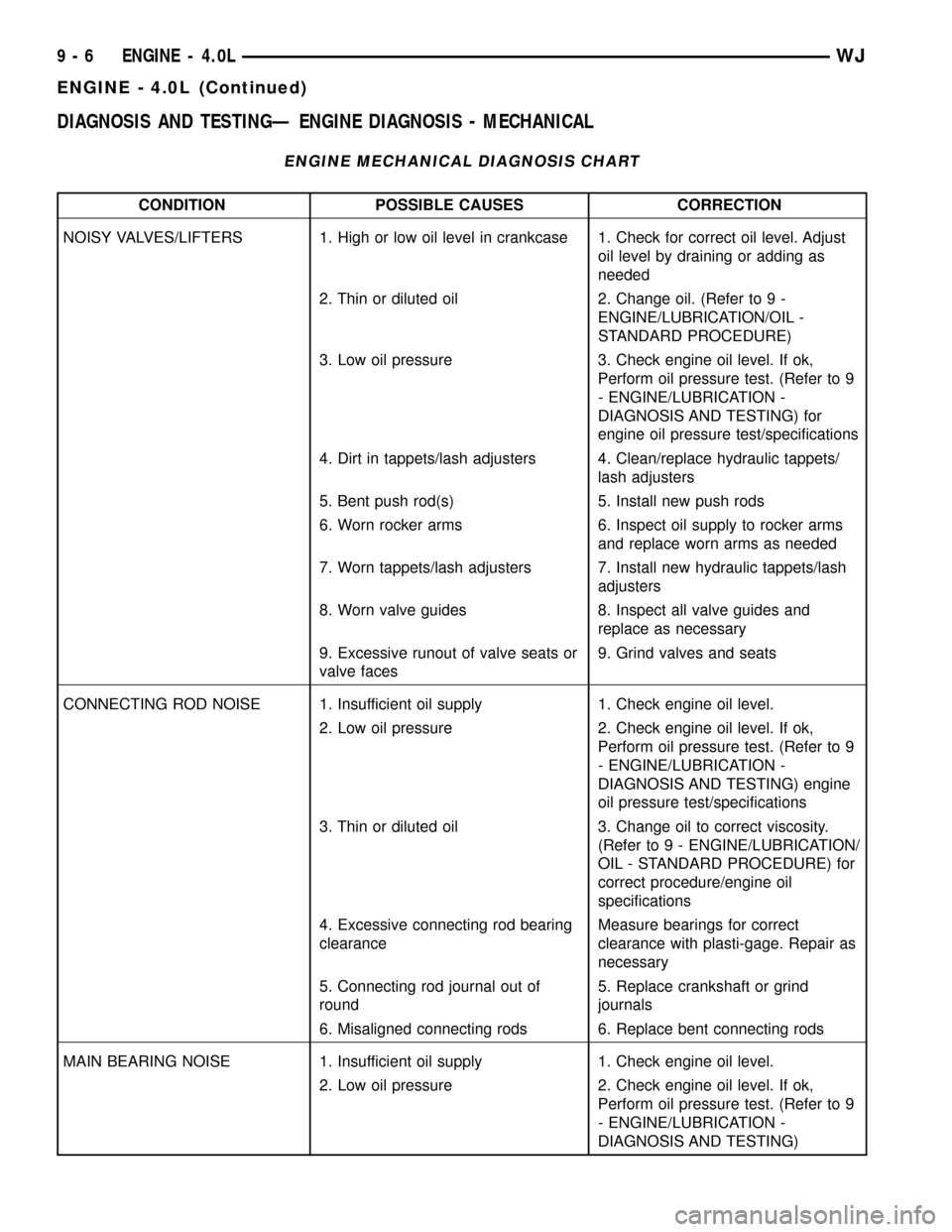
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES/LIFTERS 1. High or low oil level in crankcase 1. Check for correct oil level. Adjust
oil level by draining or adding as
needed
2. Thin or diluted oil 2. Change oil. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
3. Low oil pressure 3. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
engine oil pressure test/specifications
4. Dirt in tappets/lash adjusters 4. Clean/replace hydraulic tappets/
lash adjusters
5. Bent push rod(s) 5. Install new push rods
6. Worn rocker arms 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms
and replace worn arms as needed
7. Worn tappets/lash adjusters 7. Install new hydraulic tappets/lash
adjusters
8. Worn valve guides 8. Inspect all valve guides and
replace as necessary
9. Excessive runout of valve seats or
valve faces9. Grind valves and seats
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) engine
oil pressure test/specifications
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/
OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE) for
correct procedure/engine oil
specifications
4. Excessive connecting rod bearing
clearanceMeasure bearings for correct
clearance with plasti-gage. Repair as
necessary
5. Connecting rod journal out of
round5. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals
6. Misaligned connecting rods 6. Replace bent connecting rods
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
9 - 6 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1253 of 2199

FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gaskets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1)
Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round, as well as removing light scuff-
ing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few strokes will
clean up a bore and maintain the required limits.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60
strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing
oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, available from
major oil distributors.
9 - 10 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1254 of 2199

CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 40É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 4).CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Mark the hinge locations on the hood panel for
alignment reference during installation. Remove the
engine compartment lamp. Remove the hood.
(3) Remove the radiator drain cock and radiator
cap to drain the coolant. DO NOT waste usable cool-
ant. If the solution is clean, drain the coolant into a
clean container for reuse.
(4) Remove the upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
(5) Remove the lower radiator hose.
(6) Remove upper radiator support retaining bolts
and remove radiator support.
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
Fig. 4 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 11
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1255 of 2199

(7) Remove the fan assembly from the water pump
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the fan shroud.
(9) Disconnect the transmission fluid cooler lines
(automatic transmission).
(10) Discharge the A/C system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Remove the service valves and cap the com-
pressor ports.
(12) Remove the radiator or radiator/condenser (if
equipped with A/C).
(13) Disconnect the heater hoses at the engine
thermostat housing and water pump.
(14) Disconnect the accelerator cable, transmission
line pressure cable and speed control cable (if
equipped) from the throttle body.
(15) Remove cables from the bracket and secure
out of the way.
(16) Disconnect the body ground at the engine.
(17) Disconnect the following connectors and
secure their harness out of the way.
²Power steering pressure switch
²Coolant temperature sensor
²Six (6) fuel injector connectors
²Intake air temperature sensor
²Throttle position sensor
²Map sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Oxygen sensor
²Camshaft position sensor
²Generator connector and B+ terminal wire
(18) Disconnect the coil rail electrical connections
and the oil pressure switch connector.
(19) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(20) Disconnect the fuel supply line at the injector
rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/
QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(21) Remove the fuel line bracket from the intake
manifold.
(22) Remove the air cleaner assembly (Fig. 5).
(23) Disconnect the hoses from the fittings at the
steering gear.
(24) Drain the pump reservoir.
(25) Cap the fittings on the hoses and steering
gear to prevent foreign objects from entering the sys-
tem.
(26) Raise and support the vehicle.
(27) Disconnect the wires from the engine starter
motor solenoid.(28) Remove the engine starter motor (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR -
REMOVAL).
(29) Disconnect the oxygen sensor from the
exhaust pipe.
(30) Disconnect the exhaust pipe from the mani-
fold.
(31) Remove the exhaust pipe support.
(32) Remove the bending brace (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCT SUPPORT -
REMOVAL).
(33) Remove the engine flywheel/converter housing
access cover.
(34) Mark the converter and drive plate location.
(35) Remove the converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(36) Remove the upper engine flywheel/converter
housing bolts and loosen the bottom bolts.
(37) Remove the engine mount cushion-to-engine
compartment bracket bolts.
(38) Lower the vehicle.
(39) Attach a lifting device to the engine.
(40) Raise the engine off the front supports.
(41) Place a support or floor jack under the con-
verter (or engine flywheel) housing.
(42) Remove the remaining converter (or engine
flywheel) housing bolts.
(43) Lift the engine out of the engine compart-
ment.
Fig. 5 Air Cleaner Assembly
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP
2 - AIR CLEANER ASSEMBLY
9 - 12 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1260 of 2199
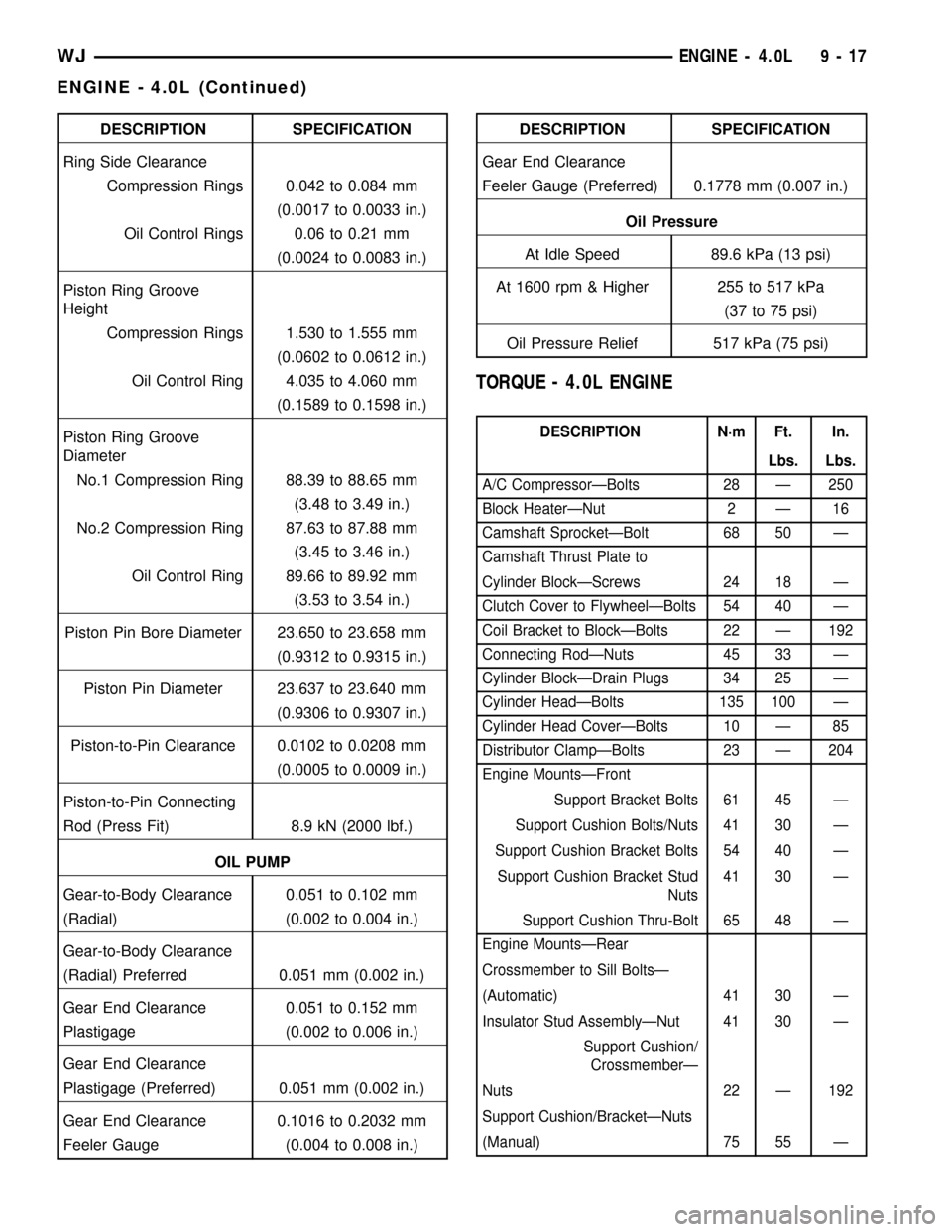
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Ring Side Clearance
Compression Rings 0.042 to 0.084 mm
(0.0017 to 0.0033 in.)
Oil Control Rings 0.06 to 0.21 mm
(0.0024 to 0.0083 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Height
Compression Rings 1.530 to 1.555 mm
(0.0602 to 0.0612 in.)
Oil Control Ring 4.035 to 4.060 mm
(0.1589 to 0.1598 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Diameter
No.1 Compression Ring 88.39 to 88.65 mm
(3.48 to 3.49 in.)
No.2 Compression Ring 87.63 to 87.88 mm
(3.45 to 3.46 in.)
Oil Control Ring 89.66 to 89.92 mm
(3.53 to 3.54 in.)
Piston Pin Bore Diameter 23.650 to 23.658 mm
(0.9312 to 0.9315 in.)
Piston Pin Diameter 23.637 to 23.640 mm
(0.9306 to 0.9307 in.)
Piston-to-Pin Clearance 0.0102 to 0.0208 mm
(0.0005 to 0.0009 in.)
Piston-to-Pin Connecting
Rod (Press Fit) 8.9 kN (2000 lbf.)
OIL PUMP
Gear-to-Body Clearance 0.051 to 0.102 mm
(Radial) (0.002 to 0.004 in.)
Gear-to-Body Clearance
(Radial) Preferred 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Gear End Clearance 0.051 to 0.152 mm
Plastigage (0.002 to 0.006 in.)
Gear End Clearance
Plastigage (Preferred) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Gear End Clearance 0.1016 to 0.2032 mm
Feeler Gauge (0.004 to 0.008 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Gear End Clearance
Feeler Gauge (Preferred) 0.1778 mm (0.007 in.)
Oil Pressure
At Idle Speed 89.6 kPa (13 psi)
At 1600 rpm & Higher 255 to 517 kPa
(37 to 75 psi)
Oil Pressure Relief 517 kPa (75 psi)
TORQUE - 4.0L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
A/C CompressorÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Block HeaterÐNut 2 Ð 16
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 68 50 Ð
Camshaft Thrust Plate to
Cylinder BlockÐScrews 24 18 Ð
Clutch Cover to FlywheelÐBolts 54 40 Ð
Coil Bracket to BlockÐBolts 22 Ð 192
Connecting RodÐNuts 45 33 Ð
Cylinder BlockÐDrain Plugs 34 25 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts 135 100 Ð
Cylinder Head CoverÐBolts 10 Ð 85
Distributor ClampÐBolts 23 Ð 204
Engine MountsÐFront
Support Bracket Bolts 61 45 Ð
Support Cushion Bolts/Nuts 41 30 Ð
Support Cushion Bracket Bolts 54 40 Ð
Support Cushion Bracket Stud
Nuts41 30 Ð
Support Cushion Thru-Bolt 65 48 Ð
Engine MountsÐRear
Crossmember to Sill BoltsÐ
(Automatic) 41 30 Ð
Insulator Stud AssemblyÐNut 41 30 Ð
Support Cushion/
CrossmemberÐ
Nuts 22 Ð 192
Support Cushion/BracketÐNuts
(Manual) 75 55 Ð
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 17
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)