automatic transmission fluid level JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 16 of 2199

ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. The designation of ENERGY CON-
SERVING is located on the label of an engine oil con-
tainer.
CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 6).
DESCRIPTION
A multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant which con-
forms to MIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifi-
cations should be used. Mopar Hypoid Gear
Lubricant conforms to these specifications.
FRONT AXLE
²Lubricant is SAE 75W-140 SYNTHETIC.
REAR AXLE
²Lubricant is a thermally stable SAE 80W-90
gear lubricant.
²Lubricant for heavy-duty or trailer tow use is
SAE 75W-140 SYNTHETIC.
NOTE: Trac-lokTand Vari-lokTequipped axles
require a friction modifier be added to the lubricant.
DESCRIPTION - TRANSFER CASE - NV242
Recommended lubricant for the NV242 transfer
case is MopartATF+4, type 9602 Automatic Trans-
mission Fluid.
DESCRIPTION - TRANSFER CASE - NV247
MopartTransfer Case Lubricant (P/N 05016796) is
the only lubricant recommended for the NV247
transfer case.
DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
FLUID
NOTE: Refer to Service Procedures in this group for
fluid level checking procedures.
MopartATF +4, type 9602, Automatic Transmis-
sion Fluid is the recommended fluid for
DaimlerChrysler automatic transmissions.
Dexron II fluid IS NOT recommended. Clutch
chatter can result from the use of improper
fluid.
MopartATF +4, type 9602, Automatic Transmis-
sion Fluid when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed
red so it can be identified from other fluids used in
the vehicle such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red
color is not permanent and is not an indicator of fluid
condition. As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin
to look darker in color and may eventually become
brown.This is normal.ATF+4 also has a unique
odor that may change with age. Consequently, odor
and color cannot be used to indicate the fluid condi-
tion or the need for a fluid change.
FLUID ADDITIVES
DaimlerChrysler strongly recommends against the
addition of any fluids to the transmission, other than
those automatic transmission fluids listed above.
Exceptions to this policy are the use of special dyes
to aid in detecting fluid leaks.
Various ªspecialº additives and supplements exist
that claim to improve shift feel and/or quality. These
additives and others also claim to improve converter
clutch operation and inhibit overheating, oxidation,
varnish, and sludge. These claims have not been sup-
ported to the satisfaction of DaimlerChrysler and
these additivesmust not be used.The use of trans-
mission ªsealersº should also be avoided, since they
may adversely affect the integrity of transmission
seals.
Fig. 5 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity - 4.0L
Fig. 6 API Symbol
WJLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 5
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
Page 17 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - ENGINE OIL - DIESEL
ENGINES
Use only Diesel Engine Oil meeting standardMIL-
2104Cor API ClassificationCD or higherorCCML
D4, D5.
SAE VISCOSITY GRADE
CAUTION: Low viscosity oils must have the proper
API quality or the CCMC G5 designation.
To assure of properly formulated engine oils, it is
recommended that SAE Grade 10W-40 engine oils
that meet Chrysler material standard MS-6395, be
used. European Grade 10W-40 oils are also accept-
able.
Oils of the SAE 5W-40 or 8W-80 grade number are
preferred when minimum temperatures consistently
fall below -12ÉC.
OPERATION - AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
FLUID
The automatic transmission fluid is selected based
upon several qualities. The fluid must provide a high
level of protection for the internal components by
providing a lubricating film between adjacent metal
components. The fluid must also be thermally stable
so that it can maintain a consistent viscosity through
a large temperature range. If the viscosity stays con-
stant through the temperature range of operation,
transmission operation and shift feel will remain con-
sistent. Transmission fluid must also be a good con-
ductor of heat. The fluid must absorb heat from the
internal transmission components and transfer that
heat to the transmission case.
FLUID FILL/CHECK
LOCATIONS
INSPECTION - FLUID FILL/CHECK LOCATIONS
The fluid fill/check locations and lubrication points
are located in each applicable group.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
DESCRIPTION
9Maintenance Schedule Information not included in
this section, is located in the appropriate Owner's
Manual.9
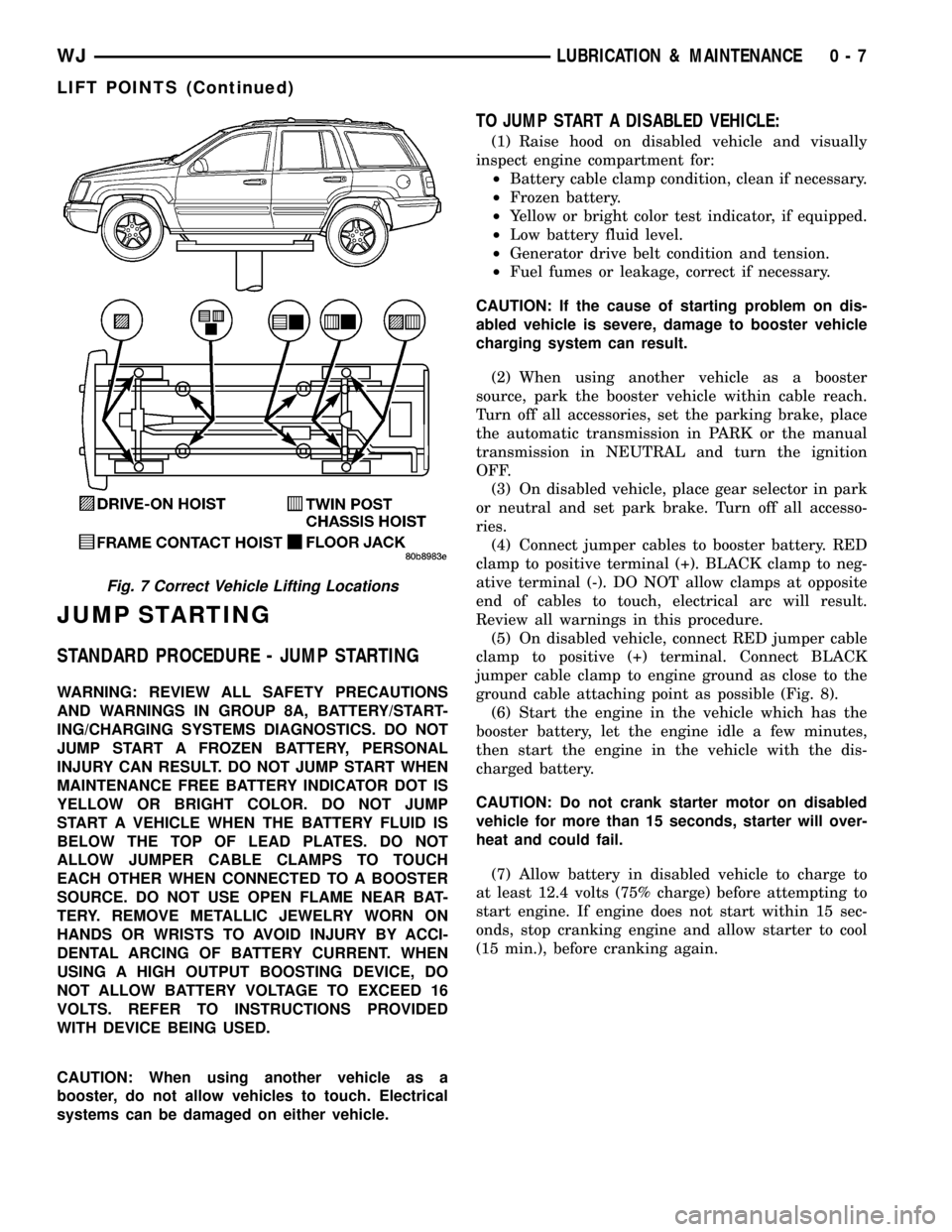
LIFT POINTS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HOISTING AND
JACKING RECOMMENDATIONS
FLOOR JACK
When properly positioned, a floor jack can be used
to lift a WJ vehicle (Fig. 7). Support the vehicle in
the raised position with jack stands at the front and
rear ends of the frame rails.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to lift a vehicle with a
floor jack positioned under:
²An axle tube.
²Aluminum differential.
²A body side sill.
²A steering linkage component.
²A drive shaft.
²The engine or transmission oil pan.
²The fuel tank.
²A front suspension arm.
HOIST
A vehicle can be lifted with:
²A single-post, frame-contact hoist.
²A twin-post, chassis hoist.
²A ramp-type, drive-on hoist.
NOTE: When a frame-contact type hoist is used,
verify that the lifting pads are positioned properly
(Fig. 7).
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN A CHASSIS OR DRIVETRAIN COMPO-
NENT IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE
CENTER OF GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME
HOISTING CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY
SUPPORT OR SECURE VEHICLE TO HOISTING
DEVICE WHEN THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.
0 - 6 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEWJ
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
Page 18 of 2199
JUMP STARTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - JUMP STARTING
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN GROUP 8A, BATTERY/START-
ING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS. DO NOT
JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY, PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT JUMP START WHEN
MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERY INDICATOR DOT IS
YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR. DO NOT JUMP
START A VEHICLE WHEN THE BATTERY FLUID IS
BELOW THE TOP OF LEAD PLATES. DO NOT
ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO TOUCH
EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A BOOSTER
SOURCE. DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY. REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON
HANDS OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCI-
DENTAL ARCING OF BATTERY CURRENT. WHEN
USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING DEVICE, DO
NOT ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO EXCEED 16
VOLTS. REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED
WITH DEVICE BEING USED.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually
inspect engine compartment for:
²Battery cable clamp condition, clean if necessary.
²Frozen battery.
²Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
²Low battery fluid level.
²Generator drive belt condition and tension.
²Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, park the booster vehicle within cable reach.
Turn off all accessories, set the parking brake, place
the automatic transmission in PARK or the manual
transmission in NEUTRAL and turn the ignition
OFF.
(3) On disabled vehicle, place gear selector in park
or neutral and set park brake. Turn off all accesso-
ries.
(4) Connect jumper cables to booster battery. RED
clamp to positive terminal (+). BLACK clamp to neg-
ative terminal (-). DO NOT allow clamps at opposite
end of cables to touch, electrical arc will result.
Review all warnings in this procedure.
(5) On disabled vehicle, connect RED jumper cable
clamp to positive (+) terminal. Connect BLACK
jumper cable clamp to engine ground as close to the
ground cable attaching point as possible (Fig. 8).
(6) Start the engine in the vehicle which has the
booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes,
then start the engine in the vehicle with the dis-
charged battery.
CAUTION: Do not crank starter motor on disabled
vehicle for more than 15 seconds, starter will over-
heat and could fail.
(7) Allow battery in disabled vehicle to charge to
at least 12.4 volts (75% charge) before attempting to
start engine. If engine does not start within 15 sec-
onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 min.), before cranking again.
Fig. 7 Correct Vehicle Lifting Locations
WJLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
LIFT POINTS (Continued)
Page 421 of 2199

The VFD is diagnosed using the EMIC self-diag-
nostic actuator test. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IN-
STRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). Proper testing of the PCI data bus and
the data bus message inputs to the EMIC that con-
trol the VFD functions requires the use of a DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation. Specific operation details for the odometer
and trip odometer functions of the VFD may be found
elsewhere in this service information.
INDICATORS
Indicators are located in various positions within
the EMIC and are all connected to the EMIC circuit
board. The turn signal indicators are hard wired. The
brake indicator is controlled by PCI data bus mes-
sages from the Controller Antilock Brake (CAB) as
well as by hard wired park brake switch and brake
fluid level switch inputs to the EMIC. The Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp (MIL) is normally controlled by
PCI data bus messages from the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM); however, if the EMIC loses PCI data
bus communication, the EMIC circuitry will automat-
ically turn the MIL on until PCI data bus communi-
cation is restored. The EMIC uses PCI data bus
messages from the Airbag Control Module (ACM), the
BCM, the PCM, the CAB, the Sentry Key Immobi-
lizer Module (SKIM), and the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) to control all of the remaining indica-
tors.
The various indicators are controlled by different
strategies; some receive fused ignition switch output
from the EMIC circuitry and have a switched ground,
others are grounded through the EMIC circuitry and
have a switched battery feed, while still others are
completely controlled by the EMIC microprocessor
based upon various hard wired and electronic mes-
sage inputs. Some indicators are illuminated at a
fixed intensity, while the illumination intensity of
others is synchronized with that of the EMIC general
illumination lamps.
The hard wired indicators are diagnosed using con-
ventional diagnostic methods. The EMIC and PCI
bus message controlled indicators are diagnosed
using the EMIC self-diagnostic actuator test. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). Proper testing of the
PCI data bus and the electronic data bus message
inputs to the EMIC that control each indicator
require the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information. Specific details of
the operation for each indicator may be found else-
where in this service information.CLUSTER ILLUMINATION
Two types of general cluster illumination are avail-
able in this model. Base versions of the EMIC have
several incandescent illumination lamps, while pre-
mium versions of the EMIC have a single electro-lu-
minescent lamp. Both types of lamps provide cluster
back lighting whenever the exterior lighting is
turned On with the control knob on the left (lighting)
multi-function switch control stalk. The illumination
intensity of these lamps is adjusted by the EMIC
microprocessor based upon electronic dimming level
messages received from the Body Control Module
(BCM) over the PCI data bus. The BCM provides
electronic dimming level messages to the EMIC
based upon internal programming and inputs it
receives when the control ring on the left (lighting)
multi-function switch control stalk is rotated (down
to dim, up to brighten) to one of six available minor
detent positions.
The incandescent illumination lamps receive bat-
tery current at all times, while the ground for these
lamps is controlled by a 12-volt Pulse Width Modu-
lated (PWM) output of the EMIC electronic circuitry.
The illumination intensity of these bulbs and of the
vacuum-fluorescent electronic display are controlled
by the instrument cluster microprocessor based upon
dimming level messages received from the Body Con-
trol Module (BCM) over the PCI data bus. The BCM
uses inputs from the headlamp and panel dimmer
switches within the left (lighting) multi-function
switch control stalk and internal programming to
decide what dimming level message is required. The
BCM then sends the proper dimming level messages
to the EMIC over the PCI data bus.
The electro-luminescent lamp unit consists of lay-
ers of phosphor, carbon, idium tin oxide, and dielec-
tric applied by a silk-screen process between two
polyester membranes and includes a short pigtail
wire and connector. The lamp pigtail wire is con-
nected to a small connector receptacle on the EMIC
circuit board through a small clearance hole in the
cluster housing rear cover. The EMIC electronic cir-
cuitry also uses a PWM strategy to control the illu-
mination intensity of this lamp; however, the EMIC
powers this lamp with an Alternating Current (AC)
rated at 80 volts rms (root mean squared) and 415
Hertz, which excites the phosphor particles causing
them to luminesce.
The BCM also has several hard wired panel lamp
driver outputs and sends the proper panel lamps
dimming level messages over the PCI data bus to
coordinate the illumination intensity of all of the
instrument panel lighting and the VFDs of other
electronic modules on the PCI data bus. Vehicles
equipped with the Auto Headlamps option have an
automatic parade mode. In this mode, the BCM uses
8J - 6 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERWJ
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 490 of 2199

for door and liftgate open indications and to show if a
turn signal has been left on. The EVIC messages and
displays are coordinated with warning indicators in
the instrument cluster to avoid duplication.
The EVIC module contains a central processing
unit and interfaces with other electronic modules in
the vehicle over the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network. The PCI data bus
network allows the sharing of sensor information.
This helps to reduce wire harness complexity, reduce
internal controller hardware, and reduce component
sensor current loads. At the same time, this system
provides increased reliability, enhanced diagnostics,
and allows the addition of many new feature capabil-
ities.
The EVIC module includes the following display
options:
²Compass and Temperature- provides the out-
side temperature and one of eight compass readings
to indicate the direction the vehicle is facing.
²Average fuel economy- shows the average
fuel economy since the last trip computer reset.
²Distance to empty- shows the estimated dis-
tance that can be travelled with the fuel remaining
in the fuel tank. This estimated distance is computed
using the average miles-per-gallon from the last 30
gallons of fuel used.
²Instant fuel economy- shows the present fuel
economy based upon the current vehicle distance and
fuel used information.
²Trip distance- shows the distance travelled
since the last trip computer reset.
²Elapsed time- shows the accumulated igni-
tion-on time since the last trip computer reset.
²Distance to service- shows the distance
remaining until the next scheduled service interval.
²Tire Pressure- shows the tire pressure in each
tire.
²Blank screen- the EVIC compass/temperature/
trip computer VFD is turned off.
The EVIC is capable of displaying the following
alert messages, which are accompanied by an audible
announcement consisting of a series of beeps:
²TURN SIGNALS ON (with vehicle graphic)-
Indicates that a turn signal has remained on for
about 1.6 kilometers (one mile).
²PERFORM SERVICE- Indicates that a cus-
tomer programmable service interval distance has
been reached.
²DOOR OPEN (one or more, with vehicle
graphic)- Indicates that a door is open or not fully
closed.
²LIFTGATE OPEN (with vehicle graphic)-
Indicates that the liftgate is open or not fully closed.
²LIFTGLASS OPEN (with vehicle graphic)-
Indicates that the liftglass is open or not fully closed.²COOLANT LEVEL LOW (with vehicle
graphic)- Indicates that the coolant level in the
engine coolant reservoir is low.
²XX LOW PRESSURE (with vehicle graphic)
- Indicates that the air pressure in the selected tire
is low.
²WASHER FLUID LOW (with vehicle
graphic)- Indicates that the fluid level in the
washer fluid reservoir is low.
The EVIC ªMenuº push button provides the vehicle
operator with a user interface, which allows the
selection of several optional customer programmable
electronic features to suit individual preferences.
Refer toELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFORMA-
TION CENTER PROGRAMMINGin the Service
Procedures section of this group for more information
on the customer programmable feature options.
If the vehicle is equipped with the optional mem-
ory system, the EVIC will display the following mem-
ory system messages:
²MEMORY #X POSITION SET (X = Driver 1
or Driver 2)- This message appears in the EVIC
display each time the memory system is successfully
programmed. It is accompanied by an audible
announcement chime tone.
²MEMORY SYSTEM DISABLED- The memory
system is automatically disabled while the driver
side seat belt is fastened and/or while the automatic
transmission gear selector is in any position except
Park or Neutral. This message appears in the EVIC
display as a reminder when a memory switch push
button is depressed while the memory system is dis-
abled. If the REMOTE LINKED TO MEMORY cus-
tomer programmable feature has been selected, this
message will also appear when the Unlock button of
the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitter is
depressed while the memory system is disabled.
If the vehicle is equipped with the optional Univer-
sal Transmitter transceiver, the EVIC will also dis-
play messages and an icon indicating when the
Universal Transmitter is being trained, which of the
three transmitter buttons is transmitting, and when
the transceiver is cleared.
If the vehicle is equipped with the optionalTire
Pressure Monitoring System, the EVIC will also
display messages and an icon indicating when the
tire air pressure falls below a given set-point, and
which of the five tires is transmitting the low pres-
sure warning, and when the condition is cleared.
Refer to the Tires/Wheels section of this manual for
complete Tire Pressure Monitoring System descrip-
tion. Refer to this section of the service manual for
EVIC modules function description for the Tire Pres-
sure Monitoring.
Data input for all EVIC functions, including VFD
dimming level, is received through PCI data bus
WJMESSAGE SYSTEMS 8M - 7
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER (Continued)
Page 742 of 2199
8W-15 GROUND DISTRIBUTION
Component Page
A/C Compressor Clutch.................. 8W-15-4
Adjustable Pedals Module............. 8W-15-17, 21
Airbag Control Module.................. 8W-15-16
Ash Receiver Lamp.................... 8W-15-14
Automatic Day/Night Mirror.............. 8W-15-19
Automatic Zone Control Module........... 8W-15-15
Battery............................ 8W-15-2, 3
Blower Motor Controller................. 8W-15-15
Body Control Module.............. 8W-15-12, 13, 15
Brake Lamp Switch................. 8W-15-17, 22
Center High Mounted Stop Lamp.......... 8W-15-20
Cigar Lighter........................ 8W-15-14
Cigar Lighter Relay.................... 8W-15-12
Controller Antilock Brake................ 8W-15-12
Coolant Level Sensor............... 8W-15-9, 10, 11
Crankcase Heater...................... 8W-15-4
Data Link Connector.................. 8W-15-2, 3
Driver Cylinder Lock Switch.............. 8W-15-16
Driver Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch........ 8W-15-16
Driver Door Module.................... 8W-15-16
Driver Heated Seat Switch............... 8W-15-14
Driver Lumbar Switch............... 8W-15-18, 21
Driver Power Seat Switch............. 8W-15-18, 21
Driver Rear Power Window Switch....... 8W-15-18, 21
Electric Brake........................ 8W-15-17
Electronic Speed Control Servo.......... 8W-15-9, 10
Engine Control Module.................. 8W-15-3
Front Power Outlet.................... 8W-15-14
Front Washer Pump................... 8W-15-6, 7
Front Wiper Motor.................... 8W-15-6, 7
Fuel Pump Module.................... 8W-15-19
G100............................. 8W-15-2, 3
G101............................. 8W-15-2, 3
G102............................... 8W-15-2
G103............................. 8W-15-2, 3
G104............................... 8W-15-4
G105............................... 8W-15-4
G106............................. 8W-15-6, 7
G107.............................. 8W-15-12
G108.......................... 8W-15-9, 10, 11
G200......................... 8W-15-13, 14, 15
G201.............................. 8W-15-16
G300......................... 8W-15-16, 17, 18
G301......................... 8W-15-19, 21, 22
Headlamp Leveling Switch............... 8W-15-15
Hood Ajar Switch..................... 8W-15-6, 7
Horn No. 1...................... 8W-15-9, 10, 11
Horn No. 2...................... 8W-15-9, 10, 11
Hydraulic Cooling Module........... 8W-15-9, 10, 11
Ignition Switch....................... 8W-15-15
Instrument Cluster.................. 8W-15-13, 14
Intake Port Swirl Actuator................ 8W-15-3
Intrusion Transceiver Module.......... 8W-15-21, 22
Junction Block.................. 8W-15-12, 13, 15
Left Fog Lamp...................... 8W-15-6, 7
Left Front Park Lamp................... 8W-15-5
Left Front Park/Turn Signal Lamp.......... 8W-15-5
Left Front Turn Signal Lamp.............. 8W-15-5
Left Headlamp Leveling Motor............. 8W-15-5
Left High Beam Headlamp................ 8W-15-5
Component Page
Left Liftgate Ajar Switch................ 8W-15-20
Left Low Beam Headlamp................ 8W-15-5
Left Multi-Function Switch............... 8W-15-15
Left Rear Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch.... 8W-15-21, 22
Left Rear Lamp Assembly............... 8W-15-19
Left Side Repeater Lamp............... 8W-15-6, 7
License Lamp No. 1.................... 8W-15-20
License Lamp No. 2.................... 8W-15-20
Liftgate Flip-Up Ajar Switch.............. 8W-15-20
Liftgate Flip-Up Release Solenoid.......... 8W-15-20
Line Pressure Sensor.................... 8W-15-2
Low Beam/Daytime Running Lamp Relay.... 8W-15-12
Manual Temperature Control........... 8W-15-13, 15
Oxygen Sensor 1/2 Downstream............ 8W-15-4
Oxygen Sensor 2/2 Downstream............ 8W-15-4
Park Lamp Relay..................... 8W-15-12
Passenger Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch...... 8W-15-16
Passenger Door Module................. 8W-15-16
Passenger Heated Seat Switch............ 8W-15-14
Passenger Lumbar Switch............. 8W-15-17, 22
Passenger Power Seat Switch.......... 8W-15-17, 22
Passenger Rear Power Window Switch.... 8W-15-16, 22
Power Amplifier.................... 8W-15-17, 18
Power Connector...................... 8W-15-15
Powertrain Control Module............... 8W-15-2
Radio........................... 8W-15-17, 18
Rain Sensor....................... 8W-15-21, 22
Rear Power Outlet.................. 8W-15-17, 18
Rear Washer Pump................... 8W-15-6, 7
Rear Window Defogger.................. 8W-15-20
Rear Wiper Motor..................... 8W-15-20
Remote Keyless Module................. 8W-15-16
Right Fog Lamp.................. 8W-15-9, 10, 11
Right Front Park Lamp.................. 8W-15-8
Right Front Park/Turn Signal Lamp......... 8W-15-8
Right Front Turn Signal Lamp............. 8W-15-8
Right Headlamp Leveling Motor............ 8W-15-8
Right High Beam Headlamp............... 8W-15-8
Right Low Beam Headlamp............... 8W-15-8
Right Rear Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch . . 8W-15-16, 18
Right Rear Lamp Assembly............ 8W-15-17, 18
Right Side Repeater Lamp........... 8W-15-9, 10, 11
Seat Module...................... 8W-15-18, 21
Sentry Key Immobilizer Module........... 8W-15-13
Shifter Assembly................... 8W-15-14, 15
Siren............................. 8W-15-6, 7
Sunroof Control Module................. 8W-15-19
Sunroof Motor........................ 8W-15-19
Sunroof Switch....................... 8W-15-19
Temperature Valve Actuator.............. 8W-15-13
Trailer Tow Brake Lamp Relay............ 8W-15-19
Trailer Tow Connector.................. 8W-15-19
Trailer Tow Left Turn Relay.............. 8W-15-19
Trailer Tow Right Turn Relay............. 8W-15-19
Transmission Control Module.............. 8W-15-2
Transmission Control Relay............ 8W-15-9, 10
Underhood Lamp..................... 8W-15-6, 7
Vehicle Information Center............ 8W-15-21, 22
Viscous/Cabin Heater................... 8W-15-4
Washer Fluid Level Switch.............. 8W-15-6, 7
WJ8W-15 GROUND DISTRIBUTION 8W - 15 - 1
Page 1510 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PUMP LEAKAGE
(1) Possible areas of pump leakage (Fig. 3).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INITIAL OPERATION
- 4.0L
WARNING: THE FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE
CHECKED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING COMPONENTS.
CAUTION: Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid or
equivalent. Do not use automatic transmission fluid
and do not overfill.
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal ambient temperature.
(1) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds
then turn engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops at least 20 times.(6) Check the fluid level add if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle, start the engine and turn
the steering wheel slowly from lock to lock.
(8) Stop the engine and check the fluid level and
refill as required.
(9) If the fluid is extremely foamy or milky look-
ing, allow the vehicle to stand a few minutes and
repeat the procedure.
CAUTION: Do not run a vehicle with foamy fluid for
an extended period. This may cause pump damage.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INITIAL OPERATION
- 4.7L
WARNING: THE FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE
CHECKED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING COMPONENTS.
NOTE: Remove as much of the old fluid out of the
system as possible with a suction tool or by remov-
ing a hose, When a component has failed. Then
refill it with fresh fluid until it is clean. This may
have to be done more than once.
CAUTION: Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid or
equivalent. Do not use automatic transmission fluid
and do not overfill.
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal ambient temperature.
(1) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds
then turn engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops at least 20 times.
(6) Check the fluid level add if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle, start the engine, and use
the DRB III to activate the hydraulic fan on full fan
operation.
(8)
Turn the steering wheel slowly from lock to lock.
(9) Stop the engine, check the fluid level and refill
as required and repeat the process
CAUTION: Do not run a vehicle with foamy fluid for
an extended period. This may cause pump damage.
(10) If the fluid is extremely foamy or milky look-
ing, allow the vehicle to stand a few minutes and
repeat the procedure.
Fig. 3 4.0L Power Steering Pump
WJPUMP 19 - 33
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1520 of 2199

TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE..........1
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE......177TRANSFER CASE - NV242................280
TRANSFER CASE - NV247................315
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION......................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY . 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING............................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST.....................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH AND BAND
OPERATION.........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK.................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIAGNOSIS
CHARTS............................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR......................26
REMOVAL.............................27
DISASSEMBLY.........................29
CLEANING............................34
INSPECTION..........................34
ASSEMBLY............................34
INSTALLATION.........................41
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS..............43
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION......................55
SPECIAL TOOLS
RE TRANSMISSIONS..................57
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................60
OPERATION...........................60
INSPECTION..........................60BANDS
DESCRIPTION.........................61
OPERATION...........................61
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - BANDS................62
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION.........................63
OPERATION...........................63
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK.......63
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK....................64
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION.........................65
OPERATION...........................65
REMOVAL.............................67
INSTALLATION.........................67
EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................68
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL.............................69
INSTALLATION.........................69
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL..............69
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID........................69
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION.....................70
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK.............................70
WJTRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE 21 - 1
Page 1524 of 2199

IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan gas-
ket surface (Fig. 2). Refer to this information when
ordering replacement parts.
GEAR RATIOS The 42RE gear ratios are:
1st.................................2.74:1
2nd................................1.54:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th.................................0.69:1
Rev.................................2.21:1
OPERATION
The application of each driving or holding compo-
nent is controlled by the valve body based upon the
manual lever position, throttle pressure, and gover-
nor pressure. The governor pressure is a variable
pressure input to the valve body and is one of the
signals that a shift is necessary. First through fourth
gear are obtained by selectively applying and releas-
ing the different clutches and bands. Engine power is
thereby routed to the various planetary gear assem-
blies which combine with the overrunning clutch
assemblies to generate the different gear ratios. The
torque converter clutch is hydraulically applied and
is released when fluid is vented from the hydraulic
circuit by the torque converter control (TCC) solenoid
on the valve body. The torque converter clutch is con-
trolled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The
torque converter clutch engages in fourth gear, and
in third gear under various conditions, such as when
the O/D switch is OFF, when the vehicle is cruising
on a level surface after the vehicle has warmed up.
The torque converter clutch will disengage momen-
tarily when an increase in engine load is sensed by
the PCM, such as when the vehicle begins to go
uphill or the throttle pressure is increased. The
torque converter clutch feature increases fuel econ-
omy and reduces the transmission fluid temperature.
Since the overdrive clutch is applied in fourth gear
only and the direct clutch is applied in all ranges
except fourth gear, the transmission operation for
park, neutral, and first through third gear will be
described first. Once these powerflows are described,
the third to fourth shift sequence will be described.
1 - CONVERTER CLUTCH 15 - HOUSING
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER 16 - REAR BEARING
3 - OIL PUMP AND REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT ASSEMBLY 17 - OUTPUT SHAFT
4 - FRONT BAND 18 - SEAL
5 - FRONT CLUTCH 19 - OVERDRIVE OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
6 - DRIVING SHELL 20 - OVERDRIVE PLANETARY GEAR
7 - REAR BAND 21 - DIRECT CLUTCH SPRING
8 - TRANSMISSION OVERRUNNING CLUTCH 22 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH PISTON
9 - OVERDRIVE UNIT 23 - VALVE BODY ASSEMBLY
10 - PISTON RETAINER 24 - FILTER
11 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH 25 - FRONT PLANETARY GEAR
12 - DIRECT CLUTCH 26 - REAR CLUTCH
13 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT 27 - TRANSMISSION
14 - FRONT BEARING 28 - REAR PLANETARY GEAR
Fig. 2 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
1 - PART NUMBER
2 - BUILD DATE
3 - SERIAL NUMBER
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 5
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1530 of 2199

FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
overdrive control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
valve moves the overdrive piston into contact with
the overdrive clutch. The direct clutch is disengaged
before the overdrive clutch is engaged. The boost
valve provides increased fluid apply pressure to the
overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts, and when accel-
erating in fourth gear. The 3-4 accumulator cushions
overdrive clutch engagement to smooth 3-4 upshifts.
The accumulator is charged at the same time as
apply pressure acts against the overdrive piston.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Automatic transmission problems can be a result of
poor engine performance, incorrect fluid level, incor-
rect linkage or cable adjustment, band or hydraulic
control pressure adjustments, hydraulic system mal-
functions or electrical/mechanical component mal-
functions. Begin diagnosis by checking the easily
accessible items such as: fluid level and condition,
linkage adjustments and electrical connections. A
road test will determine if further diagnosis is neces-
sary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVEABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust throttle and gearshift linkage if com-
plaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift or
throttle linkage.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that diagnostic trouble
codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, band or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is advanced, an overhaul will be necessary
to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart provides a basis for analyzing road test
results.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 11
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)