engine systems JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 1654 of 1803

DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT
The two refrigerant system service ports are used
to charge, recover/recycle, evacuate, and test the air
conditioning refrigerant system. Unique service port
coupler sizes are used on the R-134a system, to
ensure that the refrigerant system is not accidentally
contaminated by the use of the wrong refrigerant
(R-12), or refrigerant system service equipment.
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
The heater and optional air conditioner are blend-
air type systems. In a blend-air system, a blend door
controls the amount of unconditioned air (or cooled
air from the evaporator on models with air condition-
ing) that is allowed to flow through, or around, the
heater core. A temperature control knob on the A/C
Heater control panel determines the discharge air
temperature by controlling an electric actuator,
which moves the blend door. This allows an almost
immediate control of the output air temperature of
the system.
The mode control knob on the heater-only or A/C
Heater control panel is used to direct the conditioned
air to the selected system outlets. Both mode control
switches use engine vacuum to control the mode
doors, which are operated by vacuum actuators.
On all vehicles, the outside air intake can be shut
off by selecting the Recirculation Mode with the
mode control knob. This will operate a vacuum actu-
ated recirculation door that closes off the outside
fresh air intake and recirculates the air that is
already inside the vehicle.
The optional air conditioner for all models is
designed for the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant.
The air conditioning system has an evaporator to cool
and dehumidify the incoming air prior to blending it
with the heated air. This air conditioning system
uses a fixed orifice tube in the liquid line near the
condenser outlet tube to meter refrigerant flow to the
evaporator coil. To maintain minimum evaporator
temperature and prevent evaporator freezing, the
A/C low pressure switch on the accumulator cycles
the compressor clutch.
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
PORT
The high pressure service port is located on the
refrigerant line, near the discharge port of the com-
pressor. The low pressure service port is located on
the liquid line at the side of the engine compartment,
near the condensor.Each of the service ports has a threaded plastic
protective cap installed over it from the factory. After
servicing the refrigerant system, always reinstall
both of the service port caps.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to provide
the passenger compartment with low temperature
and low humidity air. The evaporator, located in the
HVAC housing on the dash panel below the instru-
ment panel, is cooled to temperatures near the freez-
ing point. As warm damp air passes through the
cooled evaporator, the air transfers its heat to the
refrigerant in the evaporator and the moisture in the
air condenses on the evaporator fins. During periods
of high heat and humidity, an air conditioning sys-
tem will be more effective in the Recirculation Mode.
With the system in the Recirculation Mode, only air
from the passenger compartment passes through the
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, the air conditioning system performance
levels improve.
Humidity has an important bearing on the temper-
ature of the air delivered to the interior of the vehi-
cle. It is important to understand the effect that
humidity has on the performance of the air condition-
ing system. When humidity is high, the evaporator
has to perform a double duty. It must lower the air
temperature, and it must lower the temperature of
the moisture in the air that condenses on the evapo-
rator fins. Condensing the moisture in the air trans-
fers heat energy into the evaporator fins and tubing.
This reduces the amount of heat the evaporator can
absorb from the air. High humidity greatly reduces
the ability of the evaporator to lower the temperature
of the air.
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Remov-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from the
air conditioning system on humid days. A perfor-
mance test is the best way to determine whether the
system is performing up to standard. This test also
provides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the air conditioning system.
Before proceeding, (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION). The air temperature in
the test room and in the vehicle must be a minimum
of 21É C (70É F) for this test.
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1687 of 1803

STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(8) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
(9) Install the instrument panel in the vehicle(Re-
fer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL - INSTAL-
LATION).
(10) Connect the battery negative cable.
(11) Start the engine and check for proper opera-
tion of the heating and air conditioning systems.
BLEND DOOR
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Remove and disassemble the HVAC housing.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - DISASSEMBLY)
(2) Lift the blend door pivot shaft out of the pivot
hole in the bottom of the lower half of the HVAC
housing (Fig. 6).
INSTALLATION
(1) Place the blend door pivot shaft in of the pivot
hole in the bottom of the lower half of the HVAC
housing.
(2) Assemble the HVAC housing. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - ASSEMBLY)
(3) Install the HVAC housing in the vehicle. (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRI-
BUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLATION)
MODE DOOR
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - DEFROST DOOR
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
Fig. 6 Blend Door
1 - DEFROSTER DOOR
2- HEATER CORE
3- BLEND DOORS
4- BLOWER MOTOR HOUSING
5- EVAPORATOR (A/C ONLY)
6- LOWER HVAC CASE ASSEMBLY
KJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 35
HVAC HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1707 of 1803

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM.............................1
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES..............................2DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER.........17
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS . . . 17
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION........19
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS . . 19
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED
CIRCUITS...........................20
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS . . . 20
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE...........20
OPERATION - TASK MANAGER............21
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS................24
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a
problem with a monitored circuit often enough to
indicate an actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the
code applies to a non-emissions related component or
system, and the problem is repaired or ceases to
exist, the PCM cancels the code after 40 warm-up
cycles. Diagnostic trouble codes that affect vehicle
emissions illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL). The MIL is displayed as an engine icon on the
instrument panel. Refer to Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) in this section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine RPM, engine temperature,
and/or input voltage to the PCM.
The PCM might not store a DTC for a monitored
circuit even though a malfunction has occurred. This
may happen because one of the DTC criteria for the
circuit has not been met.For example, assume the
diagnostic trouble code criteria requires the PCM to
monitor the circuit only when the engine operates
between 750 and 2000 RPM. Suppose the sensor's
output circuit shorts to ground when engine operates
above 2400 RPM (resulting in 0 volt input to the
PCM). Because the condition happens at an engine
speed above the maximum threshold (2000 rpm), the
PCM will not store a DTC.There are several operating conditions for which
the PCM monitors and sets DTC's. Refer to Moni-
tored Systems, Components, and Non-Monitored Cir-
cuits in this section.
Technicians must retrieve stored DTC's by connect-
ing the DRB scan tool (or an equivalent scan tool) to
the 16±way data link connector (Fig. 1).
NOTE: Various diagnostic procedures may actually
cause a diagnostic monitor to set a DTC. For
instance, pulling a spark plug wire to perform a
spark test may set the misfire code. When a repair
is completed and verified, connect the DRB scan
tool to the 16±way data link connector to erase all
DTC's and extinguish the MIL.
Fig. 1 DATA LINK CONNECTOR LOCATION
KJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 1
Page 1721 of 1803
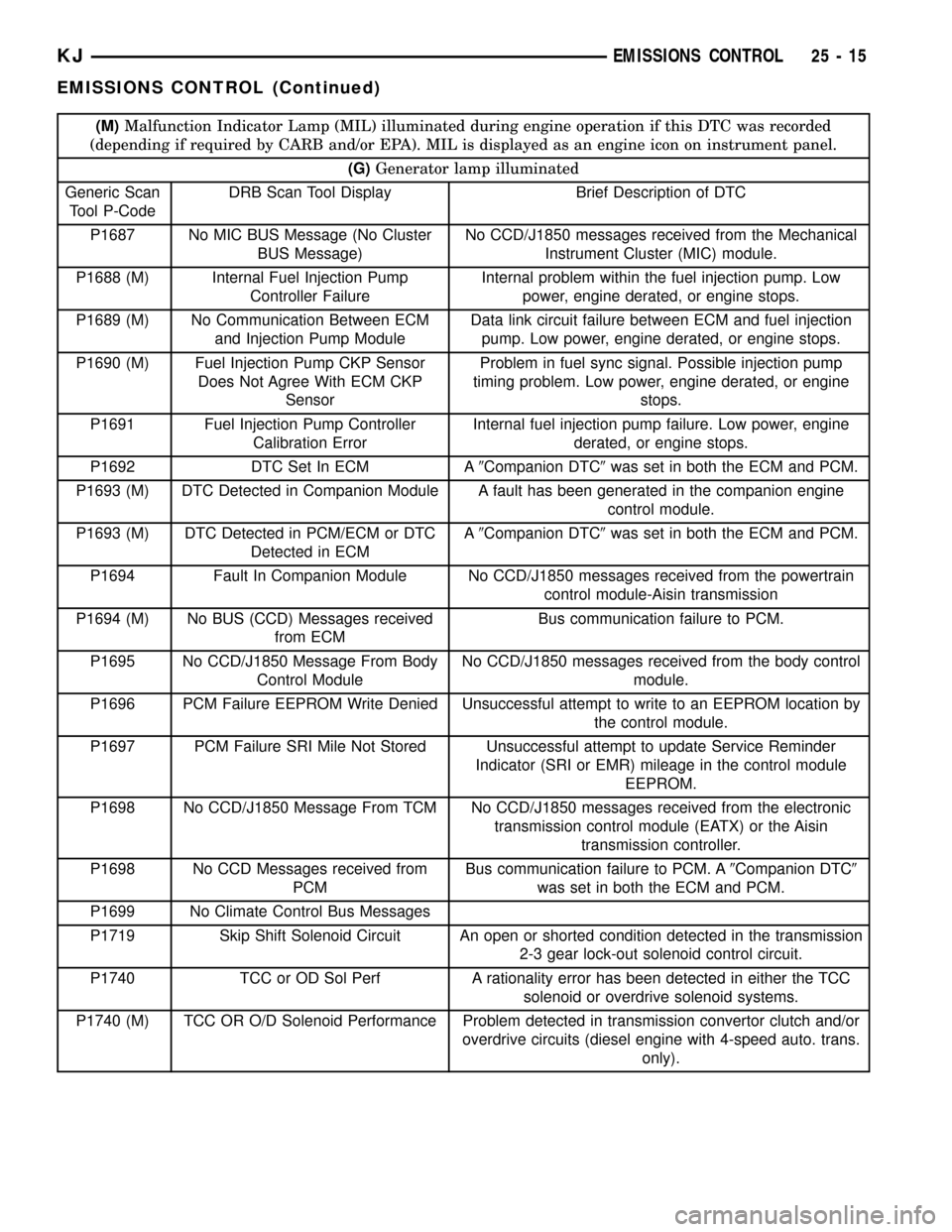
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1687 No MIC BUS Message (No Cluster
BUS Message)No CCD/J1850 messages received from the Mechanical
Instrument Cluster (MIC) module.
P1688 (M) Internal Fuel Injection Pump
Controller FailureInternal problem within the fuel injection pump. Low
power, engine derated, or engine stops.
P1689 (M) No Communication Between ECM
and Injection Pump ModuleData link circuit failure between ECM and fuel injection
pump. Low power, engine derated, or engine stops.
P1690 (M) Fuel Injection Pump CKP Sensor
Does Not Agree With ECM CKP
SensorProblem in fuel sync signal. Possible injection pump
timing problem. Low power, engine derated, or engine
stops.
P1691 Fuel Injection Pump Controller
Calibration ErrorInternal fuel injection pump failure. Low power, engine
derated, or engine stops.
P1692 DTC Set In ECM A9Companion DTC9was set in both the ECM and PCM.
P1693 (M) DTC Detected in Companion Module A fault has been generated in the companion engine
control module.
P1693 (M) DTC Detected in PCM/ECM or DTC
Detected in ECMA9Companion DTC9was set in both the ECM and PCM.
P1694 Fault In Companion Module No CCD/J1850 messages received from the powertrain
control module-Aisin transmission
P1694 (M) No BUS (CCD) Messages received
from ECMBus communication failure to PCM.
P1695 No CCD/J1850 Message From Body
Control ModuleNo CCD/J1850 messages received from the body control
module.
P1696 PCM Failure EEPROM Write Denied Unsuccessful attempt to write to an EEPROM location by
the control module.
P1697 PCM Failure SRI Mile Not Stored Unsuccessful attempt to update Service Reminder
Indicator (SRI or EMR) mileage in the control module
EEPROM.
P1698 No CCD/J1850 Message From TCM No CCD/J1850 messages received from the electronic
transmission control module (EATX) or the Aisin
transmission controller.
P1698 No CCD Messages received from
PCMBus communication failure to PCM. A9Companion DTC9
was set in both the ECM and PCM.
P1699 No Climate Control Bus Messages
P1719 Skip Shift Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
2-3 gear lock-out solenoid control circuit.
P1740 TCC or OD Sol Perf A rationality error has been detected in either the TCC
solenoid or overdrive solenoid systems.
P1740 (M) TCC OR O/D Solenoid Performance Problem detected in transmission convertor clutch and/or
overdrive circuits (diesel engine with 4-speed auto. trans.
only).
KJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 15
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1723 of 1803

DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER
The PCM is responsible for efficiently coordinating
the operation of all the emissions-related compo-
nents. The PCM is also responsible for determining if
the diagnostic systems are operating properly. The
software designed to carry out these responsibilities
is referred to as the 'Task Manager'.
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS
There are new electronic circuit monitors that
check fuel, emission, engine and ignition perfor-
mance. These monitors use information from various
sensor circuits to indicate the overall operation of the
fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems and thus
the emissions performance of the vehicle.
The fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems
monitors do not indicate a specific component prob-
lem. They do indicate that there is an implied prob-
lem within one of the systems and that a specific
problem must be diagnosed.
If any of these monitors detect a problem affecting
vehicle emissions, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated. These monitors generate
Diagnostic Trouble Codes that can be displayed with
the MIL or a scan tool.
The following is a list of the system monitors:
²Misfire Monitor
²Fuel System Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
All these system monitors require two consecutive
trips with the malfunction present to set a fault.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnos-
tics Procedures manual for diagnostic proce-
dures.
The following is an operation and description of
each system monitor:
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S can fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²slow response rate
²reduced output voltage
²dynamic shift
²shorted or open circuits
Response rate is the time required for the sensor to
switch from lean to rich once it is exposed to a richer
than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As the sen-
sor starts malfunctioning, it could take longer to
detect the changes in the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas.
The output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1
volt. A good sensor can easily generate any output
voltage in this range as it is exposed to different con-
centrations of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F
mixture (lean or rich), the output voltage has to
change beyond a threshold value. A malfunctioning
sensor could have difficulty changing beyond the
threshold value.
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR
If there is an oxygen sensor (O2S) shorted to volt-
age DTC, as well as a O2S heater DTC, the O2S
fault MUST be repaired first. Before checking the
O2S fault, verify that the heater circuit is operating
correctly.
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572 É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S sensor
are very temperature sensitive. The readings are not
accurate below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S sensor is
done to allow the engine controller to shift to closed
loop control as soon as possible. The heating element
used to heat the O2S sensor must be tested to ensure
that it is heating the sensor properly.
The O2S sensor circuit is monitored for a drop in
voltage. The sensor output is used to test the heater
by isolating the effect of the heater element on the
O2S sensor output voltage from the other effects.
KJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 17
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1726 of 1803

an associated limp in will take two trips to illumi-
nate the MIL.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
causing driveability problems. The PCM might not
store diagnostic trouble codes for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause the
PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other sys-
tems or components. For example, a fuel pressure
problem will not register a fault directly, but could
cause a rich/lean condition or misfire. This could
cause the PCM to store an oxygen sensor or misfire
diagnostic trouble code
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system, although it may set a fuel
system fault.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injectoris installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIRFLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
VACUUM ASSIST
The PCM cannot detect leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices. However, these could cause the PCM
to store a MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code and
cause a high idle condition.
PCM SYSTEM GROUND
The PCM cannot determine a poor system ground.
However, one or more diagnostic trouble codes may
be generated as a result of this condition. The mod-
ule should be mounted to the body at all times, also
during diagnostic.
PCM CONNECTOR ENGAGEMENT
The PCM may not be able to determine spread or
damaged connector pins. However, it might store
diagnostic trouble codes as a result of spread connec-
tor pins.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for
the device. If the input voltage is not within limits
and other criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnos-
tic trouble code in memory. Other diagnostic trouble
code criteria might include engine RPM limits or
input voltages from other sensors or switches that
must be present before verifying a diagnostic trouble
code condition.
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE
ENGINE IDLE/NEUTRAL 2500 RPM/NEUTRAL
All Engines 2% to 8% of Maximum Load 9% to 17% of Maximum Load
25 - 20 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1728 of 1803

²Priority4ÐTwotrip failure or matured fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) and misfire or one trip cat-
alyst damaging misfire.
Non-emissions related failures have no priority.
One trip failures of two trip faults have low priority.
Two trip failures or matured faults have higher pri-
ority. One and two trip failures of fuel system and
misfire monitor take precedence over non-fuel system
and non-misfire failures.
DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within 375
RPM and load is within 10% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up Cycles
Specific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfire
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
25 - 22 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1747 of 1803

DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK - CLEANING . . 3-109,
3-77
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK -
DISASSEMBLY...................3-107,3-75
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK -
INSPECTION....................3-109,3-77
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS -
INSTALLATION...............3-110,3-44,3-79
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS -
REMOVAL..................3-110,3-43,3-79
DIMENSIONS - SPECIFICATIONS, FRAME . . . 13-3
DIMENSIONS - SPECIFICATIONS,
OPENING..........................23-111
DIODE - INSTALLATION............8W-01-14
DIODE - REMOVAL................8W-01-14
DIODE REPLACEMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE.........................24-9
DISASSEMBLY - POWER DISTRIBUTION
CENTER DISASSEMBLY.............8W-97-7
DISASSEMBLY, 4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD . 21-122
DISASSEMBLY, DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................21-83
DISASSEMBLY, DIFFERENTIAL......3-105,3-41
DISASSEMBLY, DIFFERENTIAL -
TRAC-LOK......................3-107,3-75
DISASSEMBLY, DISASSEMBLY - POWER
DISTRIBUTION CENTER.............8W-97-7
DISASSEMBLY, DISC BRAKE CALIPERS....5-14
DISASSEMBLY, HVAC HOUSING.........24-34
DISASSEMBLY, INPUT CLUTCH
ASSEMBLY.........................21-135
DISASSEMBLY, INSTRUMENT CLUSTER....8J-9
DISASSEMBLY, LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH . . 21-145
DISASSEMBLY, MANUAL - NV1500........21-4
DISASSEMBLY, MANUAL - NV3550.......21-35
DISASSEMBLY, OIL PUMP...............9-65
DISASSEMBLY, OIL PUMP.............21-149
DISASSEMBLY, PLANETARY GEARTRAIN . 21-159
DISASSEMBLY, SINGLE CARDAN
UNIVERSAL JOINTS....................3-8
DISASSEMBLY, TRANSFER CASE -
NV231............................21-182
DISASSEMBLY, TRANSFER CASE -
NV242............................21-218
DISASSEMBLY, VALVE BODY...........21-173
DISASSEMBLY, WHEEL CYLINDERS.......5-28
DISC - INSTALLATION, CLUTCH...........6-6
DISC - REMOVAL, CLUTCH...............6-6
DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER -
INSTALLATION........................5-18
DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER -
REMOVAL...........................5-18
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - ASSEMBLY......5-16
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - CLEANING......5-16
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - DESCRIPTION....5-13
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - DISASSEMBLY . . . 5-14
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - INSPECTION.....5-16
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION . . . 5-17
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - OPERATION.....5-14
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL.......5-14
DISC BRAKE ROTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................5-18
DISC BRAKE ROTOR - STANDARD
PROCEDURE.........................5-19
DISCHARGE (ESD) SENSITIVE DEVICES -
STANDARD PROCEDURE,
ELECTROSTATIC...................8W-01-8
DISCHARGE LINE - INSTALLATION, A/C . . . 24-47
DISCHARGE LINE - REMOVAL, A/C.......24-46
DISPLAY TEST MODE - DESCRIPTION,
STATE ..............................25-2
DISTRIBUTION - DESCRIPTION, POWER . 8W-97-1
DISTRIBUTION - OPERATION, POWER . . 8W-97-1
DISTRIBUTION CENTER - DESCRIPTION,
POWER..........................8W-97-6
DISTRIBUTION CENTER - OPERATION,
POWER..........................8W-97-7
DISTRIBUTION CENTER - REMOVAL,
POWER..........................8W-97-7
DISTRIBUTION CENTER ASSEMBLY,
ASSEMBLY - POWER
..............8W-97-10
DISTRIBUTION CENTER DISASSEMBLY,
DISASSEMBLY - POWER
............8W-97-7
DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS, SPECIAL
TOOLS - POWER
...................8W-97-2
DOO - INSTALLATION, FLOOR -
DEFROST
...........................24-37
DOOR - INSTALLATION
.........23-122,23-129DOOR - INSTALLATION, BLEND.........24-35
DOOR - INSTALLATION, PANEL..........24-36
DOOR - INSTALLATION, PASSENGER
AIRBAG............................8O-30
DOOR - INSTALLATION, RECIRC.........24-37
DOOR - REMOVAL.............23-122,23-129
DOOR - REMOVAL, BLEND.............24-35
DOOR - REMOVAL, DEFROST...........24-35
DOOR - REMOVAL, FLOOR - DEFROST....24-36
DOOR - REMOVAL, PASSENGER AIRBAG . . 8O-29
DOOR - REMOVAL, RECIRC............24-37
DOOR ACTUATOR - INSTALLATION,
BLEND.............................24-20
DOOR ACTUATOR - INSTALLATION,
FLOOR - DEFROST...................24-25
DOOR ACTUATOR - INSTALLATION,
PANEL.............................24-25
DOOR ACTUATOR - INSTALLATION,
RECIRCULATION.....................24-26
DOOR ACTUATOR - REMOVAL, BLEND....24-20
DOOR ACTUATOR - REMOVAL, FLOOR -
DEFROST...........................24-24
DOOR ACTUATOR - REMOVAL, PANEL....24-24
DOOR ACTUATOR - REMOVAL,
RECIRCULATION.....................24-26
DOOR AJAR INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION . . 8J-17
DOOR AJAR INDICATOR - OPERATION....8J-17
DOOR AJAR SWITCH - DESCRIPTION....8L-77
DOOR AJAR SWITCH - OPERATION........8L-77
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION........................8Q-9
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.............8Q-10
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH -
INSTALLATION......................8Q-10
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH -
OPERATION.........................8Q-10
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH -
REMOVAL..........................8Q-10
DOOR GLASS - INSTALLATION . . 23-122,23-129,
23-172
DOOR GLASS - REMOVAL......23-122,23-129,
23-172
DOOR LOCK / UNLOCK SWITCH -
INSTALLATION.......................8N-5
DOOR LOCK / UNLOCK SWITCH -
REMOVAL...........................8N-4
DOOR LOCK MOTOR - DESCRIPTION......8N-5
DOOR LOCK MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................8N-5
DOOR LOCK MOTOR - OPERATION.......8N-5
DOOR LOCK RELAY - DESCRIPTION......8N-6
DOOR LOCK RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................8N-6
DOOR LOCK RELAY - INSTALLATION......8N-7
DOOR LOCK RELAY - OPERATION........8N-6
DOOR LOCK RELAY - REMOVAL.........8N-6
DOOR LOCK/UNLOCK SWITCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............8N-4
DOOR LOWER WEATHERSTRIP -
INSTALLATION......................23-186
DOOR LOWER WEATHERSTRIP -
REMOVAL.........................23-186
DOOR OUTER BELT MOLDING -
INSTALLATION, FRONT...............23-186
DOOR OUTER BELT MOLDING -
INSTALLATION, REAR................23-186
DOOR OUTER BELT MOLDING -
REMOVAL, FRONT...................23-186
DOOR OUTER BELT MOLDING -
REMOVAL, REAR....................23-186
DOOR PRIMARY WEATHERSTRIP -
INSTALLATION......................23-185
DOOR PRIMARY WEATHERSTRIP -
REMOVAL.........................23-185
DOOR SCUFF PLATE - INSTALLATION,
REAR.............................23-160
DOOR SCUFF PLATE - REMOVAL, REAR . . 23-160
DOOR SILL SCUFF PLATE -
INSTALLATION......................23-157
DOOR SILL SCUFF PLATE - REMOVAL
. . . 23-157
DOOR/HOUSING - INSTALLATION, FUEL
FILL
..............................23-141
DOOR/HOUSING - REMOVAL, FUEL FILL
. 23-141
DOUBLE INVERTED FLARING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE
.................5-8
DRAIN AND FILL - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, FLUID
...........21-208,21-246DRAIN TUBE - INSTALLATION..........23-181
DRAIN TUBE - REMOVAL.............23-180
DRAINAGE AND WIND NOISE
DIAGNOSIS, DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- WATER ..........................23-176
DRAINING COOLING SYSTEM 3.7L
ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE........7-12
DRAW TEST - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
IGNITION-OFF.......................8F-14
DRIVE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
VISCOUS FAN........................7-28
DRIVE BELT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
SERPENTINE.........................7-15
DRIVE MOTOR - INSTALLATION........23-182
DRIVE MOTOR - REMOVAL............23-182
DRIVER AIRBAG - DESCRIPTION........8O-17
DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION.......8O-20
DRIVER AIRBAG - OPERATION..........8O-18
DRIVER AIRBAG - REMOVAL...........8O-19
DRIVER SEAT HEATER SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION.......................8G-11
DRIVER SEAT HEATER SWITCH -
INSTALLATION......................8G-13
DRIVER SEAT HEATER SWITCH -
OPERATION.........................8G-12
DRIVER SEAT HEATER SWITCH -
REMOVAL..........................8G-13
DRIVER SIDE BEZELS - INSTALLATION,
INSTRUMENT PANEL.................23-154
DRIVER SIDE BEZELS - REMOVAL,
INSTRUMENT PANEL.................23-153
DROP - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
TESTING FOR A VOLTAGE...........8W-01-10
DRUM - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BRAKE..............................5-27
DRUM BRAKE - ADJUSTMENT, REAR......5-12
DRUM BRAKE - DESCRIPTION, REAR.....5-10
DRUM BRAKE - OPERATION, REAR.......5-11
DRUM BRAKE SHOES - INSTALLATION....5-11
DRUM BRAKE SHOES - REMOVAL........5-11
DRUM MACHINING - STANDARD
PROCEDURES, BRAKE.................5-27
DUCT - INSTALLATION, DEFROST/
DEMISTER..........................24-32
DUCT - INSTALLATION, FLOOR..........24-32
DUCT - INSTALLATION, FLOOR CONSOLE . 24-31
DUCT - REMOVAL, FLOOR.............24-32
DUCT - REMOVAL, FLOOR CONSOLE.....24-31
DUCT/DEMISTER ADAPTOR - REMOVAL,
DEFROST...........................24-32
EFFECTS OF INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING............21-125
ELECTRIC - DESCRIPTION, RADIATOR
FAN ................................7-26
ELECTRIC - INSTALLATION, RADIATOR
FAN ................................7-27
ELECTRIC - INSTALLATION, WINDOW
REGULATOR.................23-126,23-134
ELECTRIC - OPERATION, RADIATOR FAN . . . 7-26
ELECTRIC - REMOVAL, RADIATOR FAN....7-26
ELECTRIC - REMOVAL, WINDOW
REGULATOR.................23-126,23-134
ELECTRICAL - DESCRIPTION............5-34
ELECTRICAL - OPERATION..............5-34
ELECTRICAL TESTER - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, USING MIDTRONICS.......8F-15
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD)
SENSITIVE DEVICES - STANDARD
PROCEDURE......................8W-01-8
ELEMENT - DESCRIPTION, HEATED SEAT . 8G-13
ELEMENT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
HEATED SEAT .......................8G-13
ELEMENT - OPERATION, HEATED SEAT . . . 8G-13
EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
(VECI) LABEL - DESCRIPTION,
VEHICLE..........................Intro.-8
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM -
DESCRIPTION........................25-1
END - INSTALLATION, TIE ROD.........19-16
END - REMOVAL, TIE ROD.............19-16
END CAP - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL
............................23-153
END CAP - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT
PANEL
............................23-153
END REMOVAL TOOL, SPECIAL TOOLS -
OUTER TIE ROD
.....................19-15
ENGINE - 3.7L - DESCRIPTION
............9-3
ENGINE - DESCRIPTION, 3.7L
............7-21
8 INDEXKJ
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page
Page 1755 of 1803

LOW PRESSURE SWITCH - OPERATION,
A/C................................24-18
LOW PRESSURE SWITCH - REMOVAL,
A/C................................24-19
LOWER BALL JOINT - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................2-10
LOWER CONTROL ARM - DESCRIPTION . . . 2-21
LOWER CONTROL ARM - INSTALLATION . . 2-10,
2-21
LOWER CONTROL ARM - OPERATION.....2-21
LOWER CONTROL ARM - REMOVAL . . 2-10,2-21
LOWER TRIM - INSTALLATION,
B-PILLAR..........................23-157
LOWER TRIM - REMOVAL, B-PILLAR....23-157
LOWER WEATHERSTRIP -
INSTALLATION, DOOR................23-186
LOWER WEATHERSTRIP - REMOVAL,
DOOR............................23-186
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH - ASSEMBLY....21-146
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH - CLEANING....21-146
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH - DISASSEMBLY . 21-145
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH - INSPECTION . . 21-146
LUBRICATION - DESCRIPTION...........9-57
LUBRICATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, ENGINE DIAGNOSIS............9-7
LUBRICATION - OPERATION.............9-58
LUBRICATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
BODY...............................23-3
LUGGAGE RACK - INSTALLATION.......23-144
LUGGAGE RACK - REMOVAL............23-144
MACHINING - STANDARD PROCEDURES,
BRAKE DRUM........................5-27
MAIN BEARING, FITTING................9-45
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES -
DESCRIPTION.........................0-4
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) -
DESCRIPTION.......................8J-24
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) -
OPERATION.........................8J-24
MANAGEMENT VALVE - DESCRIPTION,
FLOW...............................14-6
MANAGEMENT VALVE - INSTALLATION,
FLOW...............................14-7
MANAGEMENT VALVE - OPERATION,
FLOW...............................14-6
MANAGEMENT VALVE - REMOVAL,
FLOW...............................14-6
MANAGER - DESCRIPTION, TASK........25-17
MANAGER - OPERATION, TASK.........25-21
MANIFOLD - DESCRIPTION, EXHAUST.....9-69
MANIFOLD - DESCRIPTION, INTAKE.......9-68
MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION, EXHAUST....9-70
MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION, INTAKE......9-69
MANIFOLD - REMOVAL, EXHAUST........9-69
MANIFOLD - REMOVAL, INTAKE..........9-68
MANIFOLD LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, INTAKE.....................9-68
MANUAL - INSTALLATION, WINDOW
REGULATOR............23-126,23-133 21-34
MANUAL - REMOVAL, WINDOW
REGULATOR.................23-126,23-133
MANUAL BLEEDING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE..........................5-6
MANUAL, NV1500....................21-30
MANUAL, NV3550....................21-71
MANUAL SEAT RISER - INSTALLATION . . 23-168
MANUAL SEAT RISER - REMOVAL......23-167
MANUAL TRANSMISSION -
DESCRIPTION.........................0-2
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING...................21-2,21-33
MAP SENSOR - DESCRIPTION..........14-38
MAP SENSOR - INSTALLATION..........14-40
MAP SENSOR - OPERATION............14-38
MAP SENSOR - REMOVAL.............14-39
MASTER CYLINDER - DESCRIPTION......5-24
MASTER CYLINDER - INSPECTION.........6-9
MASTER CYLINDER - INSTALLATION......5-25
MASTER CYLINDER - OPERATION........5-24
MASTER CYLINDER - REMOVAL
..........5-25
MASTER CYLINDER BLEEDING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE
................5-24
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL -
STANDARD PROCEDURES
...............5-26
MASTER CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
..........5-21,5-24
MATCH MOUNTING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE
.........................22-3MATS - INSTALLATION, CARPETS AND
FLOOR............................23-158
MATS - REMOVAL, CARPETS AND
FLOOR............................23-158
MEASUREMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, HEIGHT...................2-4
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN WEAR,
STANDARD PROCEDURE................9-71
MECHANICAL - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, ENGINE DIAGNOSIS............9-6
MECHANISM - DESCRIPTION, SHIFT....21-160
MECHANISM - INSTALLATION, SHIFT....21-160
MECHANISM - OPERATION, SHIFT......21-160
MECHANISM - REMOVAL, SHIFT.......21-160
METRIC SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION......Intro.-5
MICRO-RELAY - DESCRIPTION.......8W-97-14
MICRO-RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING........................8W-97-14
MICRO-RELAY - INSTALLATION......8W-97-14
MICRO-RELAY - OPERATION........8W-97-14
MICRO-RELAY - REMOVAL..........8W-97-14
MIDTRONICS ELECTRICAL TESTER -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, USING........8F-15
MINI-TRIP COMPUTER - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, COMPASS..............8M-6
MINI-TRIP ILLUMINATION BULB -
INSTALLATION, COMPASS.............8L-75
MINI-TRIP ILLUMINATION BULB -
REMOVAL, COMPASS.................8L-74
MIRROR - INSTALLATION, SIDE VIEW . . . 23-145
MIRROR - REMOVAL, REAR VIEW......23-161
MIRROR - REMOVAL, SIDE VIEW.......23-145
MIRROR - REMOVAL, SIDEVIEW........8N-13
MIRROR SUPPORT BRACKET -
INSTALLATION, REARVIEW............23-161
MIRROR SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, POWER....................8N-12
MIRROR SWITCH - INSTALLATION,
POWER............................8N-13
MIRROR SWITCH - REMOVAL, POWER . . . 8N-13
MIRRORS - DESCRIPTION, HEATED.......8G-1
MIRRORS - DESCRIPTION, POWER......8N-11
MIRRORS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
HEATED.............................8G-1
MIRRORS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
POWER............................8N-11
MIRRORS - OPERATION, HEATED........8G-1
MIRRORS - OPERATION, POWER........8N-11
MODE - DESCRIPTION, CIRCUIT
ACTUATION TEST.....................25-2
MODE - DESCRIPTION, STATE DISPLAY
TEST...............................25-2
MODE INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, FOUR
LOW...............................8J-29
MODE INDICATOR - OPERATION, FOUR
LOW...............................8J-30
MODES OF OPERATION - DESCRIPTION . . . 8E-11
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, AIRBAG
CONTROL...........................8O-9
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, BODY
CONTROL...........................8E-2
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, FRONT WIPER . 8R-15
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, FUEL PUMP....14-18
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, HEATED SEAT . . 8E-21
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, INTRUSION
TRANSCEIVER.......................8Q-14
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, REMOTE
KEYLESS ENTRY......................8N-7
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, SENTRY KEY
IMMOBILIZER.......................8E-15
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, SIDE IMPACT
AIRBAG CONTROL...................8O-43
MODULE - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSMISSION CONTROL.............8E-18
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BODY CONTROL......................8E-7
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
HEATED SEAT .......................8E-22
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY..............8N-7
MODULE - INSTALLATION, AIRBAG
CONTROL
..........................8O-12
MODULE - INSTALLATION, BODY
CONTROL
...........................8E-7
MODULE - INSTALLATION, CONTROL
....23-183
MODULE - INSTALLATION, FRONT
WIPER
.............................8R-16
MODULE - INSTALLATION, FUEL PUMP
. . . 14-19MODULE - INSTALLATION, HEATED SEAT . . 8E-24
MODULE - INSTALLATION, INTRUSION
TRANSCEIVER.......................8Q-16
MODULE - INSTALLATION, REMOTE
KEYLESS ENTRY......................8N-7
MODULE - INSTALLATION, SENTRY KEY
IMMOBILIZER.......................8E-18
MODULE - INSTALLATION, SIDE IMPACT
AIRBAG CONTROL...................8O-45
MODULE - OPERATION, AIRBAG
CONTROL..........................8O-10
MODULE - OPERATION, BODY CONTROL . . . 8E-5
MODULE - OPERATION, FRONT WIPER . . . 8R-15
MODULE - OPERATION, FUEL PUMP.....14-18
MODULE - OPERATION, HEATED SEAT....8E-21
MODULE - OPERATION, INTRUSION
TRANSCEIVER.......................8Q-15
MODULE - OPERATION, REMOTE
KEYLESS ENTRY......................8N-7
MODULE - OPERATION, SENTRY KEY
IMMOBILIZER.......................8E-16
MODULE - OPERATION, SIDE IMPACT
AIRBAG CONTROL...................8O-43
MODULE - OPERATION, TRANSMISSION
CONTROL..........................8E-18
MODULE - REMOVAL, AIRBAG CONTROL . 8O-11
MODULE - REMOVAL, BODY CONTROL....8E-7
MODULE - REMOVAL, CONTROL.......23-183
MODULE - REMOVAL, FRONT WIPER....8R-16
MODULE - REMOVAL, FUEL PUMP.......14-18
MODULE - REMOVAL, HEATED SEAT.....8E-24
MODULE - REMOVAL, INTRUSION
TRANSCEIVER.......................8Q-15
MODULE - REMOVAL, REMOTE KEYLESS
ENTRY..............................8N-7
MODULE - REMOVAL, SENTRY KEY
IMMOBILIZER.......................8E-17
MODULE - REMOVAL, SIDE IMPACT
AIRBAG CONTROL...................8O-44
MODULE ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION . . . 23-181
MODULE ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL.......23-181
MOLDING - INSTALLATION, FRONT
DOOR OUTER BELT..................23-186
MOLDING - INSTALLATION, REAR DOOR
OUTER BELT.......................23-186
MOLDING - REMOVAL, FRONT DOOR
OUTER BELT.......................23-186
MOLDING - REMOVAL, REAR DOOR
OUTER BELT.......................23-186
MOLDINGS - INSTALLATION, BODY SIDE . 23-140
MOLDINGS - INSTALLATION, FRONT
WHEEL OPENING FLARE..............23-145
MOLDINGS - INSTALLATION, REAR
WHEEL OPENING FLARE..............23-145
MOLDINGS - REMOVAL, BODY SIDE....23-140
MOLDINGS - REMOVAL, FRONT WHEEL
OPENING FLARE....................23-145
MOLDINGS - REMOVAL, REAR WHEEL
OPENING FLARE....................23-145
MONITORED SYSTEMS - DESCRIPTION . . . 25-17
MONITORS - DESCRIPTION,
COMPONENT........................25-19
MOTOR - DESCRIPTION, BLOWER.......24-30
MOTOR - DESCRIPTION, DOOR LOCK.....8N-5
MOTOR - DESCRIPTION, HEADLAMP
LEVELING..........................8L-35
MOTOR - DESCRIPTION, IDLE AIR
CONTROL..........................14-35
MOTOR - DESCRIPTION, REAR WIPER
. . . 8R-41
MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BLOWER
...........................24-30
MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
DOOR LOCK
.........................8N-5
MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
STARTER
...........................8F-39
MOTOR - INSTALLATION, BLOWER
......24-31
MOTOR - INSTALLATION, DRIVE
........23-182
MOTOR - INSTALLATION, HEADLAMP
LEVELING
..........................8L-36
MOTOR - INSTALLATION, IDLE AIR
CONTROL
..........................14-36
MOTOR - INSTALLATION, REAR WIPER
. . . 8R-42
MOTOR - INSTALLATION, STARTER
......8F-41
MOTOR - OPERATION, BLOWER
.........24-30
MOTOR - OPERATION, DOOR LOCK
.......8N-5
MOTOR - OPERATION, HEADLAMP
LEVELING
..........................8L-36
16 INDEXKJ
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page
Page 1758 of 1803
PLATE LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION,
LICENSE...........................8L-46
PLATE LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, LICENSE . . 8L-45
PLATES - INSTALLATION, EXTERIOR
NAME............................23-141
PLATES - REMOVAL, EXTERIOR NAME . . . 23-140
PLUG - CLEANING SPARK PLUGS,
SPARK .............................8I-15
PLUG - DESCRIPTION, SPARK...........8I-12
PLUG - INSTALLATION, SPARK..........8I-15
PLUG - OPERATION, SPARK............8I-12
PLUG - REMOVAL, SPARK..............8I-15
PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE, 2.4L - SPARK . . . 8I-3
PLUG CONDITIONS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, SPARK.....................8I-13
PLUGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
ENGINE CORE AND OIL GALLERY........9-10
PLUGS, SPARK PLUG - CLEANING
SPARK .............................8I-15
PLUGS, SPECIFICATIONS - SPARK........8I-3
POLISHING - DESCRIPTION, FINESSE
SANDING/BUFFING..................23-163
PORT - DESCRIPTION, REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE.....................24-2
PORT - OPERATION, REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE.....................24-2
POSITION LAMP BULB - INSTALLATION,
FRONT.............................8L-28
POSITION LAMP BULB - REMOVAL,
FRONT.............................8L-28
POSITION SENSOR - DESCRIPTION . 21-209,21-247
POSITION SENSOR - DESCRIPTION,
CRANKSHAFT.......................14-30
POSITION SENSOR - DESCRIPTION,
THROTTLE..........................14-47
POSITION SENSOR - INSTALLATION....21-210,
21-247
POSITION SENSOR - INSTALLATION,
CRANKSHAFT.......................14-32
POSITION SENSOR - INSTALLATION,
THROTTLE..........................14-48
POSITION SENSOR - OPERATION . 21-209,21-247
POSITION SENSOR - OPERATION,
CRANKSHAFT.......................14-31
POSITION SENSOR - OPERATION,
THROTTLE..........................14-47
POSITION SENSOR - REMOVAL . . 21-210,21-247
POSITION SENSOR - REMOVAL,
CRANKSHAFT.......................14-31
POSITION SENSOR - REMOVAL,
THROTTLE..........................14-47
POSITION SWITCH - DESCRIPTION,
CLUTCH PEDAL.......................6-11
POSITION SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, CLUTCH PEDAL...............6-11
POSITION SWITCH - OPERATION,
CLUTCH PEDAL.......................6-11
POTENTIAL - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
TESTING OF VOLTAGE..............8W-01-9
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER -
DESCRIPTION........................5-21
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER -
INSTALLATION........................5-23
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER - OPERATION . . . 5-21
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER - REMOVAL.....5-22
POWER DISTRIBUTION - DESCRIPTION . 8W-97-1
POWER DISTRIBUTION - OPERATION . . 8W-97-1
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER -
DESCRIPTION.....................8W-97-6
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER -
OPERATION.......................8W-97-7
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER -
REMOVAL........................8W-97-7
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
ASSEMBLY, ASSEMBLY.............8W-97-10
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
DISASSEMBLY, DISASSEMBLY........8W-97-7
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS,
SPECIAL TOOLS...................8W-97-2
POWER GROUNDS - DESCRIPTION......8E-13
POWER LOCKS - DESCRIPTION
..........8N-1
POWER LOCKS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING
............................8N-3
POWER LOCKS - OPERATION
............8N-3
POWER MIRROR SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING
.......................8N-12
POWER MIRROR SWITCH -
INSTALLATION
......................8N-13POWER MIRROR SWITCH - REMOVAL . . . 8N-13
POWER MIRRORS - DESCRIPTION......8N-11
POWER MIRRORS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8N-11
POWER MIRRORS - OPERATION........8N-11
POWER OUTLET - DESCRIPTION.....8W-97-11
POWER OUTLET - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING........................8W-97-11
POWER OUTLET - INSTALLATION....8W-97-13
POWER OUTLET - OPERATION.......8W-97-11
POWER OUTLET - REMOVAL........8W-97-12
POWER SEAT SWITCH - DESCRIPTION,
LEFT..............................8N-16
POWER SEAT SWITCH - DESCRIPTION,
RIGHT.............................8N-19
POWER SEAT SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, LEFT..................8N-17
POWER SEAT SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, RIGHT.................8N-19
POWER SEAT SWITCH - INSTALLATION,
LEFT..............................8N-18
POWER SEAT SWITCH - INSTALLATION,
RIGHT.............................8N-20
POWER SEAT SWITCH - OPERATION,
LEFT..............................8N-17
POWER SEAT SWITCH - OPERATION,
RIGHT.............................8N-19
POWER SEAT SWITCH - REMOVAL, LEFT . 8N-18
POWER SEAT SWITCH - REMOVAL,
RIGHT.............................8N-20
POWER SEATS - DESCRIPTION...........8N-14
POWER SEATS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8N-15
POWER SEATS - OPERATION...........8N-15
POWER STEERING FLOW AND
PRESSURE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................19-3
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION.......................19-22
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH -
INSTALLATION.......................19-22
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH -
OPERATION.........................19-22
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH -
REMOVAL..........................19-22
POWER STEERING PUMP - INITIAL
OPERATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE . . . 19-18
POWER STEERING PUMP, SPECIAL
TOOLS.............................19-20
POWER STEERING SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............19-1
POWER WINDOWS - DESCRIPTION......8N-21
POWER WINDOWS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8N-21
POWER WINDOWS - OPERATION........8N-21
POWERED - STARTER MOTOR, GAS......8F-39
POWERED - TORQUE, GAS.............8F-38
POWERING SEVERAL LOADS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, TESTING
FOR A SHORT TO GROUND ON FUSES . 8W-01-9
PRECAUTIONS - CAUTION,
REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
......24-40
PRECAUTIONS - OPERATION, SERVICE
....19-5
PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS,
WARNING - SAFETY
...................23-1
PRECAUTIONS, WARNING -
WINDSHIELD SAFETY
................23-173
PREFERENCES - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, RKE TRANSMITTER
CUSTOMER
..........................8N-8
PRELIMINARY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING
...........................21-78
PRELIMINARY CHECKS - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING
.........................7-3
PREPARATION - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, ENGINE GASKET
SURFACE
.............................9-9
PRESS CONTAINER - DESCRIPTION,
COOLANT RECOVERY
..................7-19
PRESS CONTAINER - OPERATION,
COOLANT RECOVERY
..................7-19
PRESSURE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
...............9-8
PRESSURE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
ENGINE OIL
..........................9-60
PRESSURE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
POWER STEERING FLOW
...............19-3PRESSURE BLEEDING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE..........................5-5
PRESSURE CAP - CLEANING, RADIATOR . . . 7-25
PRESSURE CAP - DESCRIPTION,
RADIATOR...........................7-25
PRESSURE CAP - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, RADIATOR...................7-25
PRESSURE CAP - INSPECTION,
RADIATOR...........................7-25
PRESSURE CAP - OPERATION,
RADIATOR...........................7-25
PRESSURE HOSE - INSTALLATION.......19-21
PRESSURE HOSE - REMOVAL..........19-21
PRESSURE INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION,
LOW OIL ...........................8J-23
PRESSURE INDICATOR - OPERATION,
LOW OIL ...........................8J-23
PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, FUEL.........14-3
PRESSURE LEAKAGE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, CYLINDER COMBUSTION........9-8
PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION, LINE.................21-144
PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR -
INSTALLATION, LINE.................21-144
PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR - OPERATION,
LINE..............................21-144
PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR - REMOVAL,
LINE..............................21-144
PRESSURE REGULATOR - DESCRIPTION,
FUEL..............................14-13
PRESSURE REGULATOR -
INSTALLATION, FUEL...................14-14
PRESSURE REGULATOR - OPERATION,
FUEL..............................14-14
PRESSURE REGULATOR - REMOVAL,
FUEL..............................14-14
PRESSURE RELEASE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, FUEL SYSTEM.............14-4
PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE -
DESCRIPTION, HIGH..................24-42
PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE - OPERATION,
HIGH..............................24-42
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION, OIL....................9-65
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
INSTALLATION, OIL....................9-65
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
OPERATION, OIL......................9-65
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
REMOVAL, OIL.......................9-65
PRESSURE, SPECIFICATIONS - FUEL
SYSTEM............................14-5
PRESSURE SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, A/C
HIGH..............................24-17
PRESSURE SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, A/C
LOW ..............................24-18
PRESSURE SWITCH - DESCRIPTION,
POWER STEERING...................19-22
PRESSURE SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, A/C HIGH...................24-18
PRESSURE SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, A/C LOW
...................24-19
PRESSURE SWITCH - INSTALLATION,
A/C HIGH
...........................24-18
PRESSURE SWITCH - INSTALLATION,
A/C LOW
...........................24-19
PRESSURE SWITCH - INSTALLATION,
POWER STEERING
...................19-22
PRESSURE SWITCH - OPERATION, A/C
HIGH
..............................24-18
PRESSURE SWITCH - OPERATION, A/C
LOW
..............................24-18
PRESSURE SWITCH - OPERATION,
POWER STEERING
...................19-22
PRESSURE SWITCH - REMOVAL, A/C
HIGH
..............................24-18
PRESSURE SWITCH - REMOVAL, A/C
LOW
..............................24-19
PRESSURE SWITCH - REMOVAL,
POWER STEERING
...................19-22
PRESSURE TEST - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, FUEL PUMP
.................14-15
PRESSURE TEST - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, HYDRAULIC
.................21-79
PRIMARY WEATHERSTRIP -
INSTALLATION, DOOR
................23-185
KJINDEX 19
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page