water pump JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 1227 of 1803
(35) Install the mechanical cooling fan.
(36) Install the fan shroud with the electric fan
assembly.
(37) Install the radiator core support bracket.
(38) Install the air cleaner assembly.
(39) Refill the engine cooling system.
(40) Install the hood.
(41) Check and fill engine oil.
(42) Connect the battery negative cable.
(43) Start the engine and check for leaks.
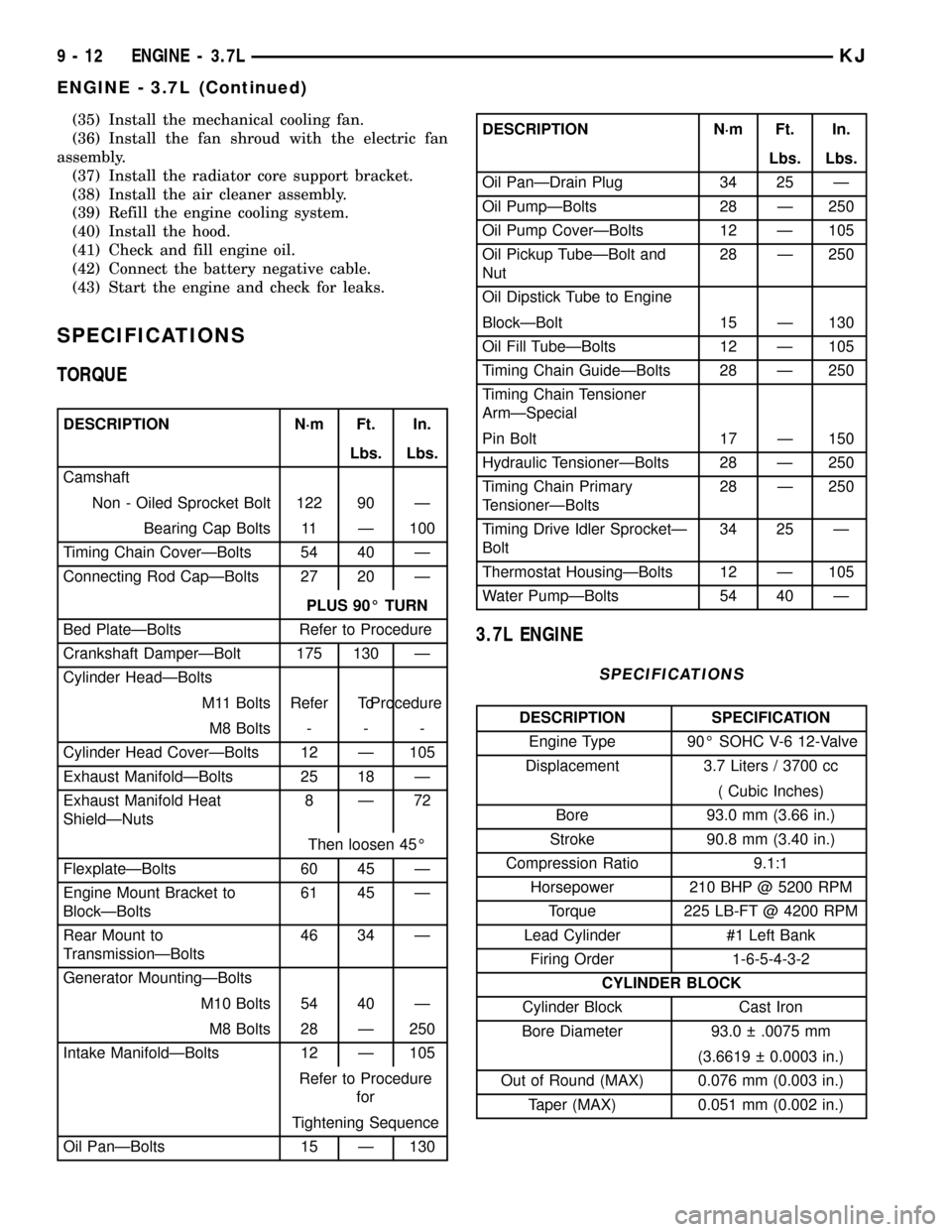
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Camshaft
Non - Oiled Sprocket Bolt 122 90 Ð
Bearing Cap Bolts 11 Ð 100
Timing Chain CoverÐBolts 54 40 Ð
Connecting Rod CapÐBolts 27 20 Ð
PLUS 90É TURN
Bed PlateÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Crankshaft DamperÐBolt 175 130 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts
M11 Bolts Refer ToProcedure
M8 Bolts - - -
Cylinder Head CoverÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Exhaust ManifoldÐBolts 25 18 Ð
Exhaust Manifold Heat
ShieldÐNuts8Ð72
Then loosen 45É
FlexplateÐBolts 60 45 Ð
Engine Mount Bracket to
BlockÐBolts61 45 Ð
Rear Mount to
TransmissionÐBolts46 34 Ð
Generator MountingÐBolts
M10 Bolts 54 40 Ð
M8 Bolts 28 Ð 250
Intake ManifoldÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Refer to Procedure
for
Tightening Sequence
Oil PanÐBolts 15 Ð 130
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Oil PanÐDrain Plug 34 25 Ð
Oil PumpÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Oil Pump CoverÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Pickup TubeÐBolt and
Nut28 Ð 250
Oil Dipstick Tube to Engine
BlockÐBolt 15 Ð 130
Oil Fill TubeÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Timing Chain GuideÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Timing Chain Tensioner
ArmÐSpecial
Pin Bolt 17 Ð 150
Hydraulic TensionerÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Timing Chain Primary
TensionerÐBolts28 Ð 250
Timing Drive Idler SprocketÐ
Bolt34 25 Ð
Thermostat HousingÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Water PumpÐBolts 54 40 Ð
3.7L ENGINE
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Engine Type 90É SOHC V-6 12-Valve
Displacement 3.7 Liters / 3700 cc
( Cubic Inches)
Bore 93.0 mm (3.66 in.)
Stroke 90.8 mm (3.40 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.1:1
Horsepower 210 BHP @ 5200 RPM
Torque 225 LB-FT @ 4200 RPM
Lead Cylinder #1 Left Bank
Firing Order 1-6-5-4-3-2
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Block Cast Iron
Bore Diameter 93.0 .0075 mm
(3.6619 0.0003 in.)
Out of Round (MAX) 0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Taper (MAX) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
9 - 12 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1234 of 1803

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 3.7L
Housing removal is not necessary for element (fil-
ter) replacement.
(1) Pry up 2 spring clips (Fig. 3) from front of
housing cover (spring clips retain cover to housing).
(2) Release housing cover from 4 locating tabs
located on rear of housing, and remove cover.
(3) Remove air cleaner element (filter) from hous-
ing.
(4) Clean inside of housing before replacing ele-
ment.
INSTALLATION - 3.7L
(1) Install element into housing.
(2) Position housing cover into housing locating
tabs.
(3) Pry up spring clips and lock cover to housing.
If any air filter, air resonator, air intake tubes or
air filter housing clamps had been loosened or
removed, tighten them to 5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
CYLINDER HEAD - LEFT
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powered metal and
are pressed into the cylinder head. The guides are
not replaceable or serviceable, and valve guide ream-
ing is not recommended. If the guides are worn
beyond acceptable limits, replace the cylinder heads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.
²Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
²Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
²Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Fig. 3 AIR CLEANER ELEMENT - 3.7L
1 - AIR INTAKE HOSE
2 - HOSE CLAMP
3 - COVER
4 - CLIPS (2)
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 19
Page 1235 of 1803

Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the left side
exhaust manifold.
(4) Drain the engine coolant. Refer to COOLING
SYSTEM.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the intake manifold. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
(7) Remove the cylinder head cover. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
(8) Remove the fan shroud and fan blade assembly.
Refer to COOLING SYSTEM.
(9) Remove accessory drive belt. Refer to COOL-
ING SYSTEM.
(10) Remove the power steering pump and set
aside.
(11) Rotate the crankshaft until the damper timing
mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark (Fig. 4).
(12) Verify the V6 mark on the camshaft sprocket
is at the 12 o'clock position (Fig. 5). Rotate the crank-
shaft one turn if necessary.
(13) Remove the crankshaft damper. Refer to Pro-
cedure.
(14) Remove the timing chain cover. Refer to pro-
cedure.
Fig. 4 Engine Top Dead Center
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - CRANKSHAFT TIMING MARKS
9 - 20 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
CYLINDER HEAD - LEFT (Continued)
Page 1245 of 1803

(9) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, install the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(10) Install the cylinder head cover. Refer to Cylin-
der Head Cover in this Section.
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD
The cylinder heads are made of an aluminum alloy.
The cylinder head features two valves per cylinder
with pressed in powdered metal valve guides. The
cylinder heads also provide enclosures for the timing
chain drain, necessitating unique left and right cylin-
der heads.
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powered metal and
are pressed into the cylinder head. The guides are
not replaceable or serviceable, and valve guide ream-
ing is not recommended. If the guides are worn
beyond acceptable limits, replace the cylinder heads.
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel and
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Each
valve is actuated by a roller rocker arm which pivots
on a stationary lash adjuster. All valves use three
bead lock keepers to retain the springs and promote
valve rotation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.
²Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
²Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
²Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
9 - 30 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 1283 of 1803

INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold (Fig. 86) is made of a compos-
ite material and features 300 mm (11.811 in.) long
runners which maximizes low end torque. The intake
manifold uses single plane sealing which consist of
six individual press in place port gaskets to prevent
leaks. The throttle body attaches directly to the
intake manifold. Eight studs and two bolts are used
to fasten the intake to the head.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If engine RPM'S change, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove resonator assembly and air inlet hose.
(3) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
(4) Disconnect electrical connectors for the follow-
ing components: Refer to FUEL SYSTEM for compo-
nent locations.
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
(5) Disconnect vapor purge hose, brake booster
hose, speed control servo hose, positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) hose.
(6) Disconnect generator electrical connections.
(7) Disconnect air conditioning compressor electri-
cal connections.
(8) Disconnect left and right radio suppressor
straps.
(9) Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers.
(10) Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt
and ground strap.
Fig. 85 Oil Pump and Primary Timing Chain
Tensioner Tightening Sequence
Fig. 86 INTAKE MANIFOLD
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - INTAKE PORT GASKETS
9 - 68 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1286 of 1803

(1) Position the engine exhaust manifold and gas-
ket on the two studs located on the cylinder head.
Install conical washers and nuts on these studs.
(2) Install remaining conical washers. Starting at
the center arm and working outward, tighten the
bolts and nuts to 25 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the exhaust heat shields.
(4) Raise and support the vehicle.
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(5) Assemble exhaust pipe to manifold and secure
with bolts, nuts and retainers. Tighten the bolts and
nuts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
LEFT EXHAUST MANIFOLD
CAUTION: If the studs came out with the nuts when
removing the engine exhaust manifold, install new
studs. Apply sealer on the coarse thread ends.
Water leaks may develop at the studs if this precau-
tion is not taken.
(1) Position the engine exhaust manifold and gas-
ket on the two studs located on the cylinder head.
Install conical washers and nuts on these studs.
(2) Install remaining conical washers. Starting at
the center arm and working outward, tighten the
bolts and nuts to 25 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the exhaust heat shields.
(4) Raise and support the vehicle.
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(5) Assemble exhaust pipe to manifold and secure
with bolts, nuts and retainers. Tighten the bolts and
nuts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTION
The timing drive system has been designed to pro-
vide quiet performance and reliability to support a
non-free wheelingengine. Specifically the intake
valves are non-free wheeling and can be easily dam-
aged with forceful engine rotation if camshaft-to-
crankshaft timing is incorrect. The timing drive
system consists of a primary chain, two secondary
timing chain drives and a counterbalance shaft drive.
OPERATION
The primary timing chain is a single inverted tooth
chain type. The primary chain drives the large 40
tooth idler sprocket directly from a 20 tooth crank-shaft sprocket. Primary chain motion is controlled by
a pivoting leaf spring tensioner arm and a fixed
guide. The arm and the guide both use nylon plastic
wear faces for low friction and long wear. The pri-
mary chain receives oil splash lubrication from the
secondary chain drive and designed oil pump leak-
age. The idler sprocket assembly connects the pri-
mary chain drive, secondary chain drives, and the
counterbalance shaft. The idler sprocket assembly
consists of two integral 26 tooth sprockets a 40 tooth
sprocket and a helical gear that is press-fit to the
assembly. The spline joint for the 40 tooth sprocket is
a non ± serviceable press fit anti rattle type. A spiral
ring is installed on the outboard side of the fifty
tooth sprocket to prevent spline disengagement. The
idler sprocket assembly spins on a stationary idler
shaft. The idler shaft is a light press-fit into the cyl-
inder block. A large washer on the idler shaft bolt
and the rear flange of the idler shaft are used to con-
trol sprocket thrust movement. Pressurized oil is
routed through the center of the idler shaft to pro-
vide lubrication for the two bushings used in the
idler sprocket assembly.
There are two secondary drive chains, both are
roller type, one to drive the camshaft in each SOHC
cylinder head. There are no shaft speed changes in
the secondary chain drive system. Each secondary
chain drives a 26 tooth cam sprocket directly from
the 26 tooth sprocket on the idler sprocket assembly.
A fixed chain guide and a hydraulic oil damped ten-
sioner are used to maintain tension in each second-
ary chain system. The hydraulic tensioners for the
secondary chain systems are fed pressurized oil from
oil reservoir pockets in the block. Each tensioner
incorprates a controled leak path through a device
known as a vent disc located in the nose of the piston
to manage chain loads. Each tensioner also has a
mechanical ratchet system that limits chain slack if
the tensioner piston bleeds down after engine shut
down. The tensioner arms and guides also utilize
nylon wear faces for low friction and long wear. The
secondary timing chains receive lubrication from a
small orifice in the tensioners. This orifice is pro-
tected from clogging by a fine mesh screen which is
located on the back of the hydraulic tensioners.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN WEAR
NOTE: This procedure must be performed with the
timing chain cover removed.
(1) Remove the timing chain cover. Refer to Timing
Chain Cover in this section for procedure.
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 71
EXHAUST MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1290 of 1803

(7) Remove accessory drive belt tensioner assembly
(Fig. 98).
(8) Remove crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(9) Remove the generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove A/C compressor (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - REMOVAL).
CAUTION: The 3.7L engine uses an anerobic sealer
instead of a gasket to seal the front cover to the
engine block, from the factory. For service, MoparT
Engine RTV sealant must be substituted.
NOTE: It is not necessary to remove the water
pump for timing cover removal.
(11) Remove the bolts holding the timing cover to
engine block. (Fig. 99).
(12) Remove the timing cover.
Fig. 96 COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT RETAINING
PLATE
1 - IDLER SHAFT
2 - COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT THRUST PLATE
3 - COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT DRIVE GEAR
4 - RETAINING BOLT
Fig. 97 COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION TOOL
1 - COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TOOL
2 - COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT THRUST PLATE
Fig. 98 Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner
1 - TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
2 - FASTENER TENSIONER TO FRONT COVER
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 75
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) (Continued)
Page 1317 of 1803

Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.(Refer to 14 -FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - SPECIFICA-
TIONS)
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(4) Remove air filter housing and inlet tube.
(5) Remove intake manifold.
(6) Remove heater tube support bracket from cyl-
inder head.
(7) Disconnect radiator upper and heater supply
hoses from water outlet connections.
(8) Remove accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL)
(9) Raise vehicle and remove exhaust pipe from
manifold.
(10) Remove power steering pump and set aside.
Do not disconnect lines.
(11) Remove accessory drive bracket
(12) Remove ignition coil and wires from engine.
(13) Disconnect cam sensor and fuel injector wir-
ing connectors.
(14) Remove timing belt and camshaft sprockets.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL)
(15) Remove timing belt idler pulley and rear tim-
ing belt cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIM-
ING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) -
REMOVAL)
(16) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(17) Remove camshafts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Identify rocker arm position to ensure cor-
rect re-installation in original position, if reused.
(18) Remove rocker arms. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove cylinder head bolts in REVERSE
sequence of tightening.
(20) Remove cylinder head from engine block.
(21) Inspect and clean cylinder head. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSPECTION) (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - CLEANING)
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
9s - 20 ENGINEKJ
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1354 of 1803

(1) Set crankshaft sprocket to TDC by aligning the
sprocket with the arrow on the oil pump housing.
(2) Set camshafts timing marks so that the
exhaust camshaft sprocket is a 1/2 notch below the
intake camshaft sprocket (Fig. 99).
CAUTION: Ensure that the arrows on both camshaft
sprockets are facing up.
(3) Install timing belt. Starting at the crankshaft,
go around the water pump sprocket, idler pulley,
camshaft sprockets and then around the tensioner
(Fig. 100).
(4) Move the exhaust camshaft sprocket counter-
clockwise (Fig. 100) to align marks and take up belt
slack.
(5) Inserta6mmAllen wrench into the hexagon
opening located on the top plate of the belt tensioner
pulley. Rotate the top plateCOUNTERCLOCK-
WISE. The tensioner pulley will move against the
belt and the tensioner setting notch will eventually
start to move clockwise. Watching the movement of
the setting notch, continue rotating the top plate
counterclockwise until the setting notch is aligned
with the spring tang (Fig. 101). Using the allen
wrench to prevent the top plate from moving, torque
the tensioner lock nut to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.). Setting
notch and spring tang should remain aligned after
lock nut is torqued.
(6) Remove allen wrench and torque wrench.NOTE: Repositioning the crankshaft to the TDC
position must be done only during the CLOCKWISE
rotation movement. If TDC is missed, rotate a fur-
ther two revolutions until TDC is achieved. DO NOT
rotate crankshaft counterclockwise as this will
make verification of proper tensioner setting impos-
sible.
(7) Once the timing belt has been installed and
tensioner adjusted, rotate the crankshaft CLOCK-
WISE two complete revolutions manually for seating
of the belt, until the crankshaft is repositioned at the
TDC position. Verify that the camshaft and crank-
shaft timing marks are in proper position (Fig. 102).
Fig. 99 Camshaft Sprocket Alignment
1 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET-EXHAUST
2 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET-INTAKE
3 - 1/2 NOTCH LOCATION
Fig. 100 Timing Belt - Installation - Typical
1 - ROTATE CAMSHAFT SPROCKET TO TAKE UP BELT SLACK
2 - CAMSHAFT TIMING MARKS 1/2 NOTCH LOCATION
3 - CRANKSHAFT AT TDC
4 - INSTALL BELT IN THIS DIRECTION
KJENGINE9s-57
TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S) (Continued)
Page 1431 of 1803
STEERING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STEERING
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING SYSTEM....................1DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING FLOW AND PRESSURE........3
COLUMN...............................5
GEAR.................................13
LINKAGE..............................16
PUMP.................................17
STEERING
DESCRIPTION
Power steering systems consist of:
²Steering column & Intermediate Shaft
²Rack and pinion steering gear
²Belt driven hydraulic steering pump
²Pump pressure, supply and return hoses
²Oil Cooler
OPERATION
The steering column intermediate shaft attaches
the steering column to the gear pinion. The rotation
of the pinion moves the gear rack from side-to-side.
This lateral action of the rack pushes and pulls the
tie rods to change the direction of the front wheels.
Power assist is provided by an engine mounted
hydraulic pump. The pump supplies hydraulic fluid
to the steering gear. All vehicles are equipped with
an oil cooler.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
STEERING NOISE
There is some noise in all power steering systems. One of the most common is a hissing sound evident at a
standstill/parking, or when the steering is at the end of it's travel. Hiss is a high frequency noise similar to that
of a water tap being closed slowly. The noise is present in all valves that have a high velocity fluid passing through
an orifice. There is no relationship between this noise and steering performance.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONAL HISS OR
WHISTLE1. Steering intermediate shaft to dash panel
seal.1. Check and repair seal at dash
panel.
2. Noisy valve in power steering gear. 2. Replace steering gear.
1. Gear mounting bolts loose. 1. Tighten bolts to specification.
2. Loose or damaged suspension
components.2. Inspect and repair suspension.
3. Internal gear noise. 3. Replace steering gear.
4. Loose or damaged intermediate shaft or
column.4. Inspect and repair or replace.
MOAN Pressure hose in contact with other
components.Reposition hose.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL 1. Loose belt. 1. Adjust or replace.
KJSTEERING 19 - 1