vent JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 271 of 1803

(8) Disconnect the power steering cooler line from
cooler.
(9) Disconnect the radiator upper and lower hoses.
(10) Disconnect the overflow hose from radiator.
(11) The lower part of radiator is equipped with
two alignment dowel pins (Fig. 8). They are located
on the bottom of radiator tank and fit into rubber
grommets. These rubber grommets are pressed into
the radiator lower crossmember.
WARNING: THE AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM (IF
EQUIPPED) IS UNDER A CONSTANT PRESSURE
EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF. REFER TO REFRIG-
ERANT WARNINGS IN, HEATING AND AIR CONDI-
TIONING BEFORE HANDLING ANY AIR
CONDITIONING COMPONENT.
NOTE: The radiator and radiator cooling fan can be
removed as an assembly. It is not necessary to
remove the cooling fan before removing or install-
ing the radiator.
(12) Gently lift up and remove radiator from vehi-
cle. Be careful not to scrape the radiator fins against
any other component. Also be careful not to disturb
the air conditioning condenser (if equipped).CLEANING
Clean radiator fins With the engine cold, apply cold
water and compressed air to the back (engine side) of
the radiator to flush the radiator and/or A/C con-
denser of debris.
INSPECTION
The radiator cooling fins should be checked for
damage or deterioration. Inspect cooling fins to make
sure they are not bent or crushed, these areas result
in reduced heat exchange causing the cooling system
to operate at higher temperatures. Inspect the plastic
end tanks for cracks, damage or leaks.
Inspect the radiator neck for damage or distortion.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Before installing the radiator or A/C con-
denser, be sure the radiator-to-body and radiator-to-
A/C condenser rubber air seals are properly
fastened to their original positions. These are used
at the top, bottom and sides of the radiator and A/C
condenser. To prevent overheating, these seals
must be installed to their original positions.
(1) Gently lower the radiator and fan shroud into
the vehicle. Guide the two radiator alignment dowels
into the rubber grommets located in lower radiator
crossmember.
(2) Connect the radiator upper and lower hoses
and hose clamps to radiator.
CAUTION: The tangs on the hose clamps must be
positioned straight down.
(3) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank hose at
radiator.
(4) Connect both transmission cooler lines at the
radiator.
(5) Install both radiator mounting bolts.
(6) Reconnect the electric cooling fan.
(7) Install the grill (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/GRILLE - INSTALLATION).
(8) Reinstall the cooling fan to the engine.
(9) Rotate the fan blades (by hand) and check for
interference at fan shroud.
(10) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Connect battery cable at battery.
(12) Start and warm engine. Check for leaks.
Fig. 8 Radiator Alignment Dowels - Typical
1 - RADIATOR
2 - ALIGNMENT DOWEL
3 - RADIATOR LOWER ISOLATOR
4 - RADIATOR LOWER CROSSMEMBER
7s - 24 ENGINEKJ
RADIATOR (Continued)
Page 272 of 1803

RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION
The cooling system cap is located on the coolant
pressure bottle. The cap construction includes; stain-
less steel swivel top, rubber seals and retainer, main
spring, and a spring loaded valve (Fig. 9).
OPERATION
The pressure cap allows the cooling system to oper-
ate at higher than atmospheric pressure which raises
the coolant boiling point, thus allowing increased
radiator cooling capacity. The pressure cap releases
pressure at some point within a range of 110 kPa
14 kPa (16 psi 2 psi).
A spring-loaded vent valve in the center of the cap
allows the system to pressurize and depressurize
without creating a vacuum. If the valve is stuck
open, coolant will escape to the overflow hose. There
is also a gasket in the cap to seal to the top of the
filler neck.
CAUTION: Use only the pressure cap specified for
this vehicle. Use of other pressure caps can lead to
coolant loss and overheating.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP
Remove cap from radiator. Be sure that sealing
surfaces are clean. Moisten rubber gasket with water
and install the cap on pressure tester (tool 7700 or
an equivalent) (Fig. 10).Operate the tester pump and observe the gauge
pointer at its highest point. The cap release pressure
should be 124 to 145 kPa (18 to 21 psi). The cap is
satisfactory when the pressure holds steady. It is also
good if it holds pressure within the 124 to 145 kPa
(18 to 21 psi) range for 30 seconds or more. If the
pointer drops quickly, replace the cap.
CAUTION: Radiator pressure testing tools are very
sensitive to small air leaks, which will not cause
cooling system problems. A pressure cap that does
not have a history of coolant loss should not be
replaced just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to tool. Turn tool upside
down and recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap
needs replacement.
CLEANING
Clean the radiator pressure cap using a mild soap
and water only.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the pressure valve gasket on the
cap. Replace cap if the gasket is swollen, torn or
worn. Inspect the area around radiator filler neck for
white deposits that indicate a leaking cap.
Fig. 9 PRESSURE CAP
1 - MAIN SPRING
2 - GASKET RETAINER
3 - STAINLESS STEEL SWIVEL TOP
4 - RUBBER SEALS
5 - SPRING LOADED VALVE
6 - COOLANT PRESSURE BOTTLE
7 - FILLER NECK
8 - OVERFLOW NIPPLEFig. 10 Pressure Testing Radiator Pressure Cap -
Typical
1 - PRESSURE CAP
2 - TYPICAL COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER
KJENGINE7s-25
Page 277 of 1803

TRANSMISSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANS COOLER
DESCRIPTION.........................30STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING
COOLERS AND TUBES.................30
TRANS COOLER
DESCRIPTION
An internal high capacity/high efficiency cooler is
used on all vehicles, these coolers are an oil-to-cool-
ant type, which consists of plates mounted in the
radiator outlet tank.Because the internal oil cooler is
so efficient, no auxiliary oil cooler is offered. The
cooler is not serviceable separately from the radiator.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING
COOLERS AND TUBES
When a transmission failure has contaminated the
fluid, the oil cooler(s) must be flushed. The torque
converter must also be replaced. This will insure that
metal particles or sludged oil are not later trans-
ferred back into the reconditioned (or replaced) trans-
mission.
The only recommended procedure for flushing cool-
ers and lines is to use Tool 6906-B Cooler Flusher.
WARNING: WEAR PROTECTIVE EYEWEAR THAT
MEETS THE REQUIREMENTS OF OSHA AND ANSI
Z87.1±1968. WEAR STANDARD INDUSTRIAL RUB-
BER GLOVES. KEEP LIGHTED CIGARETTES,
SPARKS, FLAMES, AND OTHER IGNITION
SOURCES AWAY FROM THE AREA TO PREVENT
THE IGNITION OF COMBUSTIBLE LIQUIDS AND
GASES. KEEP A CLASS (B) FIRE EXTINGUISHER IN
THE AREA WHERE THE FLUSHER WILL BE USED.
KEEP THE AREA WELL VENTILATED.DO NOT LET
FLUSHING SOLVENT COME IN CONTACT WITH
YOUR EYES OR SKIN: IF EYE CONTAMINATION
OCCURS, FLUSH EYES WITH WATER FOR 15 TO 20
SECONDS. REMOVE CONTAMINATED CLOTHING
AND WASH AFFECTED SKIN WITH SOAP AND
WATER. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION.
(1) Remove cover plate filler plug on Tool 6906-B.
Fill reservoir 1/2 to 3/4 full of fresh flushing solution.
Flushing solvents are petroleum based solutions gen-
erally used to clean automatic transmission compo-
nents.DO NOTuse solvents containing acids, water,
gasoline, or any other corrosive liquids.(2) Reinstall filler plug on Tool 6906-B.
(3) Verify pump power switch is turned OFF. Con-
nect red alligator clip to positive (+) battery post.
Connect black (-) alligator clip to a good ground.
(4) Disconnect the cooler lines at the transmission.
NOTE: When flushing transmission cooler and
lines, ALWAYS reverse flush.
NOTE: The converter drainback valve must be
removed and an appropriate replacement hose
installed to bridge the space between the transmis-
sion cooler line and the cooler fitting. Failure to
remove the drainback valve will prevent reverse
flushing the system. A suitable replacement hose
can be found in the adapter kit supplied with the
flushing tool.
(5) Connect the BLUE pressure line to the OUT-
LET (From) cooler line.
(6) Connect the CLEAR return line to the INLET
(To) cooler line
(7) Turn pump ON for two to three minutes to
flush cooler(s) and lines.
(8) Turn pump OFF.
(9) Disconnect CLEAR suction line from reservoir
at cover plate. Disconnect CLEAR return line at
cover plate, and place it in a drain pan.
(10) Turn pump ON for 30 seconds to purge flush-
ing solution from cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(11) Place CLEAR suction line into a one quart
container of MopartATF +4, type 9602, Automatic
Transmission Fluid.
(12) Turn pump ON until all transmission fluid is
removed from the one quart container and lines. This
purges any residual cleaning solvent from the trans-
mission cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(13) Disconnect alligator clips from battery. Recon-
nect flusher lines to cover plate, and remove flushing
adapters from cooler lines.
7s - 30 TRANSMISSIONKJ
Page 287 of 1803

OPERATION
There are two common strategies that can be used
to suppress Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and
ElectroMagnetic Interference (EMI) radio noise. The
first suppression strategy involves preventing the
production of RFI and EMI electromagnetic signals
at their sources. The second suppression strategy
involves preventing the reception of RFI and EMI
electromagnetic signals by the audio system compo-
nents.
The use of braided ground straps in key locations
is part of the RFI and EMI prevention strategy.
These ground straps ensure adequate ground paths,
particularly for high current components such as
many of those found in the starting, charging, igni-
tion, engine control and transmission control sys-
tems. An insufficient ground path for any of these
high current components may result in radio noise
caused by induced voltages created as the high cur-
rent seeks alternative ground paths through compo-
nents or circuits intended for use by, or in close
proximity to the audio system components or circuits.
Preventing the reception of RFI and EMI is accom-
plished by ensuring that the audio system compo-
nents are correctly installed in the vehicle. Loose,
corroded or improperly soldered wire harness connec-
tions, improperly routed wiring and inadequate audio
system component grounding can all contribute to
the reception of RFI and EMI. A properly grounded
antenna body and radio chassis, as well as a shielded
antenna coaxial cable with clean and tight connec-
tions will each help reduce the potential for reception
of RFI and EMI.
REMOVAL
2.4L ENGINE
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the retaining bolt from the engine cyl-
inder head (Fig. 9).
(3) Remove the retaining nut from the plenum
(Fig. 10).
Fig. 9 GROUND STRAP TO ENGINE - 2.4L
1 - GROUND STRAP
2 - BOLT
Fig. 10 GROUND STRAP TO PLENUM - 2.4L
1 - PLENUM
2 - RETAINING NUT
3 - GROUND STRAP
8A - 10 AUDIOKJ
RADIO NOISE SUPPRESSION GROUND STRAP (Continued)
Page 298 of 1803

ever occurs first. The overspeed warning feature is
only enabled on a BCM that has been programmed
with a Middle East Gulf Coast Country (GCC) coun-
try code.
²No Airbag Indicator Message Warning- The
EMIC chime tone generator will generate one, short,
ªbong-likeº chime tone and turn on the ªAirbagº indi-
cator when the ignition switch is in the On position,
and a PCI data bus ªAirbagº indicator on or off mes-
sage is not received from the ACM for six consecutive
seconds.
²No Antilock Brake Indicator Message Warn-
ing- The EMIC chime tone generator will generate
one, short, ªbong-likeº chime tone and turn on the
ªABSº indicator when the ignition switch is in the On
position, and a PCI data bus ªABSº indicator on or
off message is not received from the CAB for six con-
secutive seconds.
²No Fuel Level Message Warning- The EMIC
chime tone generator will generate one, short, ªbong-
likeº chime tone and turn on the ªLow Fuelº indica-
tor when the ignition switch is in the On position,
and a PCI data bus fuel level message is not received
from the PCM for twelve consecutive seconds.
²Remote Keyless Entry Transmitter Pro-
gramming- On vehicles so equipped, the EMIC
chime tone generator will generate a single ªbong-
likeº chime tone when an electronic message is
received over the PCI data bus from the BCM indi-
cating that a Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmit-
ter has been successfully programmed by the
customer into the RKE module memory.
²Sentry Key Immobilizer System Transpon-
der Programming- On vehicles so equipped, the
EMIC chime tone generator will generate a single
ªbong-likeº chime tone when an electronic message is
received over PCI data bus message from the Sentry
Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) indicating that the
Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) has been
placed in the ªCustomer Learnº programming mode,
and again each time a new SKIS transponder has
been successfully programmed by the customer.
²Turn Signal Cancel Warning- The EMIC
chime tone generator will generate repetitive ªbong-
likeº chime tones at a slow rate when the vehicle is
driven for a distance of about 3.2 kilometers (about
two miles) with a turn signal indicator flashing. The
EMIC uses an electronic message received over the
PCI data bus from the PCM, and a hard wired input
from the turn signal switch circuitry of the multi-
function switch to determine when to sound the turn
signal cancel warning. The PCM uses internal pro-
gramming and distance pulse information received
over a hard wired vehicle speed pulse input from the
BCM to determine the proper vehicle speed messages
to send to the EMIC. The BCM uses an internallyprogrammed electronic pinion factor and a hard
wired input from the rear wheel speed sensor to cal-
culate the proper distance pulse information to send
to the PCM. The electronic pinion factor represents
the proper tire size and axle ratio information for the
vehicle. These chimes will continue to sound until
the turn signal is turned Off, until the hazard warn-
ing system is turned On, or until the ignition switch
is turned to the Off position, whichever occurs first.
²Water-In-Fuel Warning- On vehicles equipped
with a diesel engine, each time the ignition switch is
turned to the On position, the EMIC chime tone gen-
erator will generate a single ªbong-likeº chime tone
the first time an electronic message is received over
the PCI data bus from the PCM requesting ªWater-
in-Fuelº indicator illumination. The PCM uses inter-
nal programming and a hard wired input from the
water-in-fuel sensor to determine the proper water-
in-fuel messages to send to the EMIC. This warning
will only occur once during an ignition cycle.
The EMIC provides chime service for all available
features in the chime warning system. The EMIC
relies upon its internal programming and hard wired
inputs from the turn signal (multi-function) switch,
the washer fluid level switch, and the engine coolant
level sensor (diesel engine only) to provide chime ser-
vice for the turn signal cancel warning, the low
washer fluid warning, and the low coolant warning
respectively. The EMIC relies upon electronic mes-
sage inputs received from other electronic modules
over the PCI data bus network to provide chime ser-
vice for all of the remaining chime warning system
features. Upon receiving the proper inputs, the EMIC
activates the integral chime tone generator to pro-
vide the audible chime warning to the vehicle opera-
tor. The internal programming of the EMIC
determines the priority of each chime request input
that is received, as well as the rate and duration of
each chime tone that is to be generated. See the own-
er's manual in the vehicle glove box for more infor-
mation on the features provided by the chime
warning system.
The hard wired chime warning system inputs to
the EMIC, as well as other hard wired circuits for
this system may be diagnosed and tested using con-
ventional diagnostic tools and procedures. However,
conventional diagnostic methods may not prove con-
clusive in the diagnosis of the EMIC, the PCI data
bus network, or the electronic message inputs used
by the EMIC to provide chime warning system ser-
vice. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means
to diagnose the EMIC, the PCI data bus network,
and the electronic message inputs for the chime
warning system requires the use of a DRBIIItscan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
KJCHIME/BUZZER 8B - 5
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 299 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHIME WARNING
SYSTEM
The hard wired chime warning system inputs to
the EMIC, as well as other hard wired circuits for
this system may be diagnosed and tested using con-
ventional diagnostic tools and procedures. However,
conventional diagnostic methods may not prove con-
clusive in the diagnosis of the EMIC, the PCI data
bus network, or the electronic message inputs used
by the EMIC to provide chime warning system ser-
vice. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means
to diagnose the EMIC, the PCI data bus network,
and the electronic message inputs for the chime
warning system requires the use of a DRBIIItscan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
The hard wired chime warning system inputs to
the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC),
as well as other hard wired circuits for this system
may be diagnosed and tested using conventional
diagnostic tools and procedures. However, conven-
tional diagnostic methods may not prove conclusive
in the diagnosis of the EMIC, the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus network, or
the electronic message inputs used by the EMIC to
provide chime warning system service. The most reli-able, efficient, and accurate means to diagnose the
EMIC, the PCI data bus network, and the electronic
message inputs for the chime warning system
requires the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
8B - 6 CHIME/BUZZERKJ
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 306 of 1803

²Vacuum Fluorescent Display Synchroniza-
tion (CMTC, EMIC, Radio)
²Vehicle Theft Security System Status (PCM,
ITM) - premium only
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information for
additional details.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BODY CONTROL
MODULE
The hard wired inputs to and outputs from the
Body Control Module (BCM), as well as other hard
wired circuits for this module may be diagnosed and
tested using conventional diagnostic tools and proce-
dures. However, conventional diagnostic methods
may not prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the
BCM, the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus network, or the electronic messages
received and transmitted by the BCM over the PCI
data bus. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate
means to diagnose the BCM and the PCI data bus
network inputs to and outputs from this module
requires the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
NOTE: Before replacing a Body Control Module
(BCM), use a DRBIIITscan tool to retrieve the cur-
rent settings for the BCM programmable features
and the axle ratio/tire size (electronic pinion factor).
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
These settings should be duplicated in the replace-
ment BCM using the DRBIIITscan tool before
returning the vehicle to service.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the Junction Block Module (JBM) from
the instrument panel end bracket on the driver side
of the vehicle. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
DISTRIBUTION/JUNCTION BLOCK - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the four screws that secure the BCM
to the Junction Block (JB) (Fig. 3).
(4) Remove the BCM from the JB.
(5) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional
Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) system, remove the
RKE module from the receptacle on the BCM. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/REMOTE KEY-
LESS ENTRY MODULE - REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
KJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 7
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 313 of 1803

²Fuel injectors
²Ignition coil(s)
²Certain relays/solenoids
²Certain sensors
DESCRIPTION - SENSOR RETURN
The Sensor Return circuits are internal to the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM).
Sensor Return provides a low±noise ground refer-
ence for all engine control system sensors. Refer to
Power Grounds for more information.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM
The PCM operates the fuel system. The PCM is a
pre-programmed, triple microprocessor digital com-
puter. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain
transmission features, speed control, air conditioning
compressor clutch engagement and idle speed. The
PCM can adapt its programming to meet changing
operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operations
through different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to as Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) Outputs. The sensors and switches that pro-
vide inputs to the PCM are considered Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) Inputs.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based upon
inputs it receives from sensors that react to: engine
rpm, manifold absolute pressure, engine coolant tem-
perature, throttle position, transmission gear selec-
tion (automatic transmission), vehicle speed, power
steering pump pressure, and the brake switch.
The PCM adjusts idle speed based on inputs it
receives from sensors that react to: throttle position,
vehicle speed, transmission gear selection, engine
coolant temperature and from inputs it receives from
the air conditioning clutch switch and brake switch.
Based on inputs that it receives, the PCM adjusts
ignition coil dwell. The PCM also adjusts the gener-
ator charge rate through control of the generator
field and provides speed control operation.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²A/C request (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C select (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C pressure transducer
²Auto shutdown (ASD) sense
²Battery temperature
²Battery voltage
²Brake switch²J1850 bus (+) circuits
²J1850 bus (-) circuits
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Fuel level (through J1850 circuitry)
²Generator (battery voltage) output
²Ignition circuit sense (ignition switch in on/off/
crank/run position)
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Knock sensors (2 on 3.7L engine)
²Leak detection pump (switch) sense (if equipped)
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Oil pressure
²Oxygen sensors
²Park/neutral switch (auto. trans. only)
²Power ground
²Power steering pressure switch
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Speed control multiplexed single wire input
²Throttle position sensor
²Transfer case switch (4WD range position)
²Vehicle speed sensor
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²A/C clutch relay
²Auto shutdown (ASD) relay
²J1850 bus (+/-) circuits for: speedometer, voltme-
ter, fuel gauge, oil pressure gauge/lamp, engine temp.
gauge and speed control warn. lamp
²Clutch pedal position switch override relay
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²EGR valve control solenoid (if equipped)
²EVAP canister purge solenoid
²Five volt sensor supply (primary)
²Five volt sensor supply (secondary)
²Fuel injectors
²Fuel pump relay
²Generator field driver (-)
²Generator field driver (+)
²Idle air control (IAC) motor
²Ignition coil(s)
²Leak detection pump (if equipped)
²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp).
Driven through J1850 circuits.
²Oxygen sensor heater relays
²Oxygen sensors (pulse width modulated)
²Radiator cooling fan relay (pulse width modu-
lated)
²Speed control vacuum solenoid
²Speed control vent solenoid
²Tachometer (if equipped). Driven through J1850
circuits.
8E - 14 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESKJ
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 315 of 1803

lock cylinder housing and is concealed beneath the
steering column shrouds. The molded black plastic
housing for the SKIM has an integral molded plastic
halo-like antenna ring that extends from one end.
When the SKIM is properly installed on the steering
column, the antenna ring is oriented around the cir-
cumference of the ignition lock cylinder housing. A
single integral connector receptacle containing six
terminal pins is located on the opposite end of the
SKIM housing from the antenna ring. A stamped
metal mounting bracket secured to the SKIM hous-
ing has a U-shaped clip formation that is used to
secure the unit to the right lower flange of the steer-
ing column jacket.
The SKIM cannot be adjusted or repaired. If faulty
or damaged, the entire SKIM unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) con-
tains a Radio Frequency (RF) transceiver and a
microprocessor. The SKIM transmits RF signals to,
and receives RF signals from the Sentry Key tran-
sponder through a tuned antenna enclosed within the
molded plastic antenna ring integral to the SKIM
housing. If this antenna ring is not mounted properly
around the ignition lock cylinder housing, communi-
cation problems between the SKIM and the transpon-
der may arise. These communication problems will
result in Sentry Key transponder-related faults. The
SKIM also communicates over the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus with the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM), the ElectroMe-
chanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) and/or the
DRBIIItscan tool.The SKIM retains in memory the ID numbers of
any Sentry Key transponder that is programmed into
it. A maximum of eight Sentry Key transponders can
be programmed into the SKIM. For added system
security, each SKIM is programmed with a unique
Secret Key code. This code is stored in memory, sent
over the PCI data bus to the PCM, and is encoded to
the transponder of every Sentry Key that is pro-
grammed into the SKIM. Therefore, the Secret Key
code is a common element that is found in every com-
ponent of the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS).
Another security code, called a PIN, is used to gain
access to the SKIM Secured Access Mode. The
Secured Access Mode is required during service to
perform the SKIS initialization and Sentry Key tran-
sponder programming procedures. The SKIM also
stores the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) in its
memory, which it learns through a PCI data bus
message from the PCM during SKIS initialization.
In the event that a SKIM replacement is required,
the Secret Key code can be transferred to the new
SKIM from the PCM using the DRBIIItscan tool
and the SKIS initialization procedure. Proper com-
pletion of the SKIS initialization will allow the exist-
ing Sentry Keys to be programmed into the new
SKIM so that new keys will not be required. In the
event that the original Secret Key code cannot be
recovered, SKIM replacement will also require new
Sentry Keys. The DRBIIItscan tool will alert the
technician during the SKIS initialization procedure if
new Sentry Keys are required.
When the ignition switch is turned to the On posi-
tion, the SKIM transmits an RF signal to the tran-
sponder in the ignition key. The SKIM then waits for
an RF signal response from the transponder. If the
response received identifies the key as valid, the
SKIM sends a valid key message to the PCM over
the PCI data bus. If the response received identifies
the key as invalid, or if no response is received from
the key transponder, the SKIM sends an invalid key
message to the PCM. The PCM will enable or disable
engine operation based upon the status of the SKIM
messages. It is important to note that the default
condition in the PCM is an invalid key; therefore, if
no message is received from the SKIM by the PCM,
the engine will be disabled and the vehicle immobi-
lized after two seconds of running.
The SKIM also sends SKIS indicator status mes-
sages to the EMIC over the PCI data bus to tell the
EMIC how to operate the SKIS indicator. This indi-
cator status message tells the EMIC to turn the indi-
cator on for about three seconds each time the
ignition switch is turned to the On position as a bulb
test. After completion of the bulb test, the SKIM
sends indicator status messages to the EMIC to turn
the indicator off, turn the indicator on, or to flash the
Fig. 10 Sentry Key Immobilizer Module
1 - SKIM
2 - BRACKET
3 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
4 - ANTENNA RING
8E - 16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESKJ
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE (Continued)
Page 319 of 1803
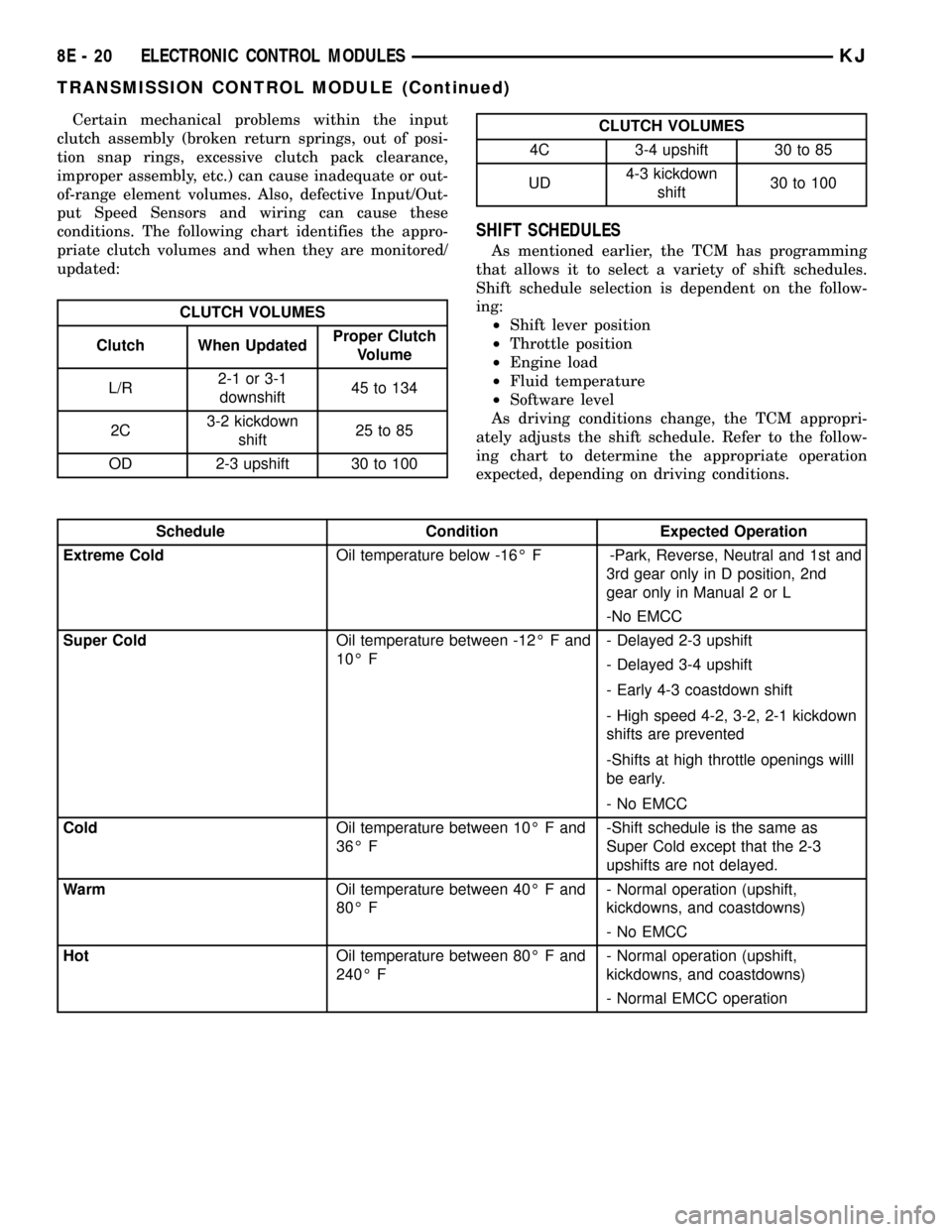
Certain mechanical problems within the input
clutch assembly (broken return springs, out of posi-
tion snap rings, excessive clutch pack clearance,
improper assembly, etc.) can cause inadequate or out-
of-range element volumes. Also, defective Input/Out-
put Speed Sensors and wiring can cause these
conditions. The following chart identifies the appro-
priate clutch volumes and when they are monitored/
updated:
CLUTCH VOLUMES
Clutch When UpdatedProper Clutch
Volume
L/R2-1 or 3-1
downshift45 to 134
2C3-2 kickdown
shift25 to 85
OD 2-3 upshift 30 to 100
CLUTCH VOLUMES
4C 3-4 upshift 30 to 85
UD4-3 kickdown
shift30 to 100
SHIFT SCHEDULES
As mentioned earlier, the TCM has programming
that allows it to select a variety of shift schedules.
Shift schedule selection is dependent on the follow-
ing:
²Shift lever position
²Throttle position
²Engine load
²Fluid temperature
²Software level
As driving conditions change, the TCM appropri-
ately adjusts the shift schedule. Refer to the follow-
ing chart to determine the appropriate operation
expected, depending on driving conditions.
Schedule Condition Expected Operation
Extreme ColdOil temperature below -16É F -Park, Reverse, Neutral and 1st and
3rd gear only in D position, 2nd
gear only in Manual 2 or L
-No EMCC
Super ColdOil temperature between -12É F and
10É F- Delayed 2-3 upshift
- Delayed 3-4 upshift
- Early 4-3 coastdown shift
- High speed 4-2, 3-2, 2-1 kickdown
shifts are prevented
-Shifts at high throttle openings willl
be early.
- No EMCC
ColdOil temperature between 10É F and
36É F-Shift schedule is the same as
Super Cold except that the 2-3
upshifts are not delayed.
WarmOil temperature between 40É F and
80É F- Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
- No EMCC
HotOil temperature between 80É F and
240É F- Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
- Normal EMCC operation
8E - 20 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESKJ
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)