Turn signals JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 196 of 1803

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................32
OPERATION...........................32
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKING SYSTEM....................33
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ABS BRAKE
BLEEDING...........................33
SPECIFICATIONS.......................33
ELECTRICAL
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
REMOVAL.............................36
INSTALLATION.........................36
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
ANTILOCK BRAKING SYSTEM
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching 20 to 30 percent of
actual vehicle speed during braking. Periods of high
wheel slip occur when brake stops involve high pedal
pressure and rate of vehicle deceleration.
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB ignition ter-
minal when the ignition switch is turned to Run posi-
tion. The CAB performs a system initialization
procedure at this point. Initialization consists of a
static and dynamic self check of system electrical
components.
The static check occurs after the ignition switch is
turned to Run position. The dynamic check occurs
when vehicle road speed reaches approximately 30
kph (18 mph). During the dynamic check, the CAB
briefly cycles the pump and solenoids to verify oper-
ation.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ELECTRONIC BRAKE DISTRIBUTION
The electronic brake distribution (EBD) functions
like a rear proportioning valve. The EBD system usesthe ABS system to control the slip of the rear wheels
in partial braking range. The braking force of the
rear wheels is controlled electronically by using the
inlet and outlet valves located in the HCU.
OPERATION
ANTILOCK BRAKING SYSTEM
During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
During antilock braking fluid pressure is modu-
lated according to wheel speed, degree of slip and
rate of deceleration. A sensor at each wheel converts
wheel speed into electrical signals. These signals are
transmitted to the CAB for processing and determi-
nation of wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a high slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program. Two solenoid valves are used
in each antilock control channel. The valves are all
located within the HCU valve body and work in pairs
to either increase, hold, or decrease apply pressure as
needed in the individual control channels. The sole-
noid valves are not static during antilock braking.
They are cycled continuously to modulate pressure.
Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be mea-
sured in milliseconds.
ELECTRONIC BRAKE DISTRIBUTION
Upon entry into EBD the inlet valve for the rear
brake circuit is switched on so that the fluid supply
from the master cylinder is shut off. In order to
decrease the rear brake pressure the outlet valve for
5 - 32 BRAKES - ABSKJ
Page 199 of 1803

REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Disconnect the sensor wire harness.
(3) Remove mounting stud from the sensor (Fig. 2).
(4) Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect harness to sensor.Be sure seal is
securely in place between sensor and wiring
connector.
(2) Install O-ring on sensor (if removed).
(3) Insert sensor in differential housing.
(4) Install the sensor mounting stud and tighten to
9 N´m (80 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the sensor electical connector.
(6) Lower vehicle.
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL
UNIT)
DESCRIPTION
The HCU consists of a valve body, pump motor,
and wire harness.
OPERATION
Accumulators in the valve body store extra fluid
released to the system for ABS mode operation. The
pump provides the fluid volume needed and is oper-
ated by a DC type motor. The motor is controlled by
the CAB.The valves modulate brake pressure during
antilock braking and are controlled by the CAB.
The HCU provides three channel pressure control
to the front and rear brakes. One channel controls
the rear wheel brakes in tandem. The two remaining
channels control the front wheel brakes individually.
During antilock braking, the solenoid valves are
opened and closed as needed. The valves are not
static. They are cycled rapidly and continuously to
modulate pressure and control wheel slip and decel-
eration.
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
During antilock braking, solenoid valve pressure
modulation occurs in three stages, pressure increase,
pressure hold, and pressure decrease. The valves are
all contained in the valve body portion of the HCU.
PRESSURE DECREASE
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle.
A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the CAB closes the inlet
then opens the outlet valve, which also opens the
return circuit to the accumulators. Fluid pressure is
allowed to bleed off (decrease) as needed to prevent
wheel lock.
Once the period of high wheel slip has ended, the
CAB closes the outlet valve and begins a pressure
increase or hold cycle as needed.
PRESSURE HOLD
Both solenoid valves are closed in the pressure
hold cycle. Fluid apply pressure in the control chan-
nel is maintained at a constant rate. The CAB main-
tains the hold cycle until sensor inputs indicate a
pressure change is necessary.
PRESSURE INCREASE
The inlet valve is open and the outlet valve is
closed during the pressure increase cycle. The pres-
sure increase cycle is used to counteract unequal
wheel speeds. This cycle controls re-application of
fluid apply pressure due to changing road surfaces or
wheel speed.
Fig. 2 REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - MOUNTING BOLT
3 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
KJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 35
Page 307 of 1803

NOTE: Before replacing a Body Control Module
(BCM), use a DRBIIITscan tool to retrieve the cur-
rent settings for the BCM programmable features
and the axle ratio/tire size (electronic pinion factor).
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
These settings should be duplicated in the replace-
ment BCM using the DRBIIITscan tool before
returning the vehicle to service.
(1) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional
Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) system, reinstall the
RKE module into the receptacle on the BCM. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/REMOTE KEY-
LESS ENTRY MODULE - INSTALLATION).
(2) Position the BCM onto the Junction Block (JB)
(Fig. 3).
(3) Install and tighten the four screws that secure
the BCM to the JB. Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (18
in. lbs.).
(4) Reinstall the Junction Block Module (JBM)
onto the instrument panel end bracket on the driver
side of the vehicle. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
POWER DISTRIBUTION/JUNCTION BLOCK -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
COMMUNICATION
DESCRIPTION
The DaimlerChrysler Programmable Communica-
tion Interface (PCI) data bus system is a single wire
multiplex system used for vehicle communications on
many DaimlerChrysler Corporation vehicles. Multi-
plexing is a system that enables the transmission of
several messages over a single channel or circuit. All
DaimlerChrysler vehicles use this principle for com-
munication between various microprocessor-based
electronic control modules. The PCI data bus exceeds
the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) J1850
Standard for Class B Multiplexing.
Many of the electronic control modules in a vehicle
require information from the same sensing device. In
the past, if information from one sensing device was
required by several controllers, a wire from each con-
troller needed to be connected in parallel to that sen-
sor. In addition, each controller utilizing analog
sensors required an Analog/Digital (A/D) converter in
order to9read9these sensor inputs. Multiplexing
reduces wire harness complexity, sensor current
loads and controller hardware because each sensing
device is connected to only one controller, which
reads and distributes the sensor information to the
other controllers over the data bus. Also, because
each controller on the data bus can access the con-
troller sensor inputs to every other controller on the
data bus, more function and feature capabilities are
possible.
In addition to reducing wire harness complexity,
component sensor current loads and controller hard-
ware, multiplexing offers a diagnostic advantage. A
multiplex system allows the information flowing
between controllers to be monitored using a diagnos-
tic scan tool. The DaimlerChrysler system allows an
electronic control module to broadcast message data
out onto the bus where all other electronic control
modules can9hear9the messages that are being sent.
When a module hears a message on the data bus
that it requires, it relays that message to its micro-
processor. Each module ignores the messages on the
data bus that are being sent to other electronic con-
trol modules.
OPERATION
Data exchange between modules is achieved by
serial transmission of encoded data over a single wire
broadcast network. The wire colors used for the PCI
data bus circuits are yellow with a violet tracer, or
violet with a yellow tracer, depending upon the appli-
cation. The PCI data bus messages are carried over
the bus in the form of Variable Pulse Width Modu-
lated (VPWM) signals. The PCI data bus speed is an
average 10.4 Kilo-bits per second (Kbps). By compar-
Fig. 3 Body Control Module Remove/Install
1 - SCREW (4)
2 - RKE MODULE
3 - BODY CONTROL MODULE
4 - JUNCTION BLOCK
8E - 8 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESKJ
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 313 of 1803

²Fuel injectors
²Ignition coil(s)
²Certain relays/solenoids
²Certain sensors
DESCRIPTION - SENSOR RETURN
The Sensor Return circuits are internal to the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM).
Sensor Return provides a low±noise ground refer-
ence for all engine control system sensors. Refer to
Power Grounds for more information.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM
The PCM operates the fuel system. The PCM is a
pre-programmed, triple microprocessor digital com-
puter. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain
transmission features, speed control, air conditioning
compressor clutch engagement and idle speed. The
PCM can adapt its programming to meet changing
operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operations
through different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to as Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) Outputs. The sensors and switches that pro-
vide inputs to the PCM are considered Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) Inputs.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based upon
inputs it receives from sensors that react to: engine
rpm, manifold absolute pressure, engine coolant tem-
perature, throttle position, transmission gear selec-
tion (automatic transmission), vehicle speed, power
steering pump pressure, and the brake switch.
The PCM adjusts idle speed based on inputs it
receives from sensors that react to: throttle position,
vehicle speed, transmission gear selection, engine
coolant temperature and from inputs it receives from
the air conditioning clutch switch and brake switch.
Based on inputs that it receives, the PCM adjusts
ignition coil dwell. The PCM also adjusts the gener-
ator charge rate through control of the generator
field and provides speed control operation.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²A/C request (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C select (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C pressure transducer
²Auto shutdown (ASD) sense
²Battery temperature
²Battery voltage
²Brake switch²J1850 bus (+) circuits
²J1850 bus (-) circuits
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Fuel level (through J1850 circuitry)
²Generator (battery voltage) output
²Ignition circuit sense (ignition switch in on/off/
crank/run position)
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Knock sensors (2 on 3.7L engine)
²Leak detection pump (switch) sense (if equipped)
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Oil pressure
²Oxygen sensors
²Park/neutral switch (auto. trans. only)
²Power ground
²Power steering pressure switch
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Speed control multiplexed single wire input
²Throttle position sensor
²Transfer case switch (4WD range position)
²Vehicle speed sensor
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²A/C clutch relay
²Auto shutdown (ASD) relay
²J1850 bus (+/-) circuits for: speedometer, voltme-
ter, fuel gauge, oil pressure gauge/lamp, engine temp.
gauge and speed control warn. lamp
²Clutch pedal position switch override relay
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²EGR valve control solenoid (if equipped)
²EVAP canister purge solenoid
²Five volt sensor supply (primary)
²Five volt sensor supply (secondary)
²Fuel injectors
²Fuel pump relay
²Generator field driver (-)
²Generator field driver (+)
²Idle air control (IAC) motor
²Ignition coil(s)
²Leak detection pump (if equipped)
²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp).
Driven through J1850 circuits.
²Oxygen sensor heater relays
²Oxygen sensors (pulse width modulated)
²Radiator cooling fan relay (pulse width modu-
lated)
²Speed control vacuum solenoid
²Speed control vent solenoid
²Tachometer (if equipped). Driven through J1850
circuits.
8E - 14 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESKJ
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 315 of 1803

lock cylinder housing and is concealed beneath the
steering column shrouds. The molded black plastic
housing for the SKIM has an integral molded plastic
halo-like antenna ring that extends from one end.
When the SKIM is properly installed on the steering
column, the antenna ring is oriented around the cir-
cumference of the ignition lock cylinder housing. A
single integral connector receptacle containing six
terminal pins is located on the opposite end of the
SKIM housing from the antenna ring. A stamped
metal mounting bracket secured to the SKIM hous-
ing has a U-shaped clip formation that is used to
secure the unit to the right lower flange of the steer-
ing column jacket.
The SKIM cannot be adjusted or repaired. If faulty
or damaged, the entire SKIM unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) con-
tains a Radio Frequency (RF) transceiver and a
microprocessor. The SKIM transmits RF signals to,
and receives RF signals from the Sentry Key tran-
sponder through a tuned antenna enclosed within the
molded plastic antenna ring integral to the SKIM
housing. If this antenna ring is not mounted properly
around the ignition lock cylinder housing, communi-
cation problems between the SKIM and the transpon-
der may arise. These communication problems will
result in Sentry Key transponder-related faults. The
SKIM also communicates over the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus with the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM), the ElectroMe-
chanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) and/or the
DRBIIItscan tool.The SKIM retains in memory the ID numbers of
any Sentry Key transponder that is programmed into
it. A maximum of eight Sentry Key transponders can
be programmed into the SKIM. For added system
security, each SKIM is programmed with a unique
Secret Key code. This code is stored in memory, sent
over the PCI data bus to the PCM, and is encoded to
the transponder of every Sentry Key that is pro-
grammed into the SKIM. Therefore, the Secret Key
code is a common element that is found in every com-
ponent of the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS).
Another security code, called a PIN, is used to gain
access to the SKIM Secured Access Mode. The
Secured Access Mode is required during service to
perform the SKIS initialization and Sentry Key tran-
sponder programming procedures. The SKIM also
stores the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) in its
memory, which it learns through a PCI data bus
message from the PCM during SKIS initialization.
In the event that a SKIM replacement is required,
the Secret Key code can be transferred to the new
SKIM from the PCM using the DRBIIItscan tool
and the SKIS initialization procedure. Proper com-
pletion of the SKIS initialization will allow the exist-
ing Sentry Keys to be programmed into the new
SKIM so that new keys will not be required. In the
event that the original Secret Key code cannot be
recovered, SKIM replacement will also require new
Sentry Keys. The DRBIIItscan tool will alert the
technician during the SKIS initialization procedure if
new Sentry Keys are required.
When the ignition switch is turned to the On posi-
tion, the SKIM transmits an RF signal to the tran-
sponder in the ignition key. The SKIM then waits for
an RF signal response from the transponder. If the
response received identifies the key as valid, the
SKIM sends a valid key message to the PCM over
the PCI data bus. If the response received identifies
the key as invalid, or if no response is received from
the key transponder, the SKIM sends an invalid key
message to the PCM. The PCM will enable or disable
engine operation based upon the status of the SKIM
messages. It is important to note that the default
condition in the PCM is an invalid key; therefore, if
no message is received from the SKIM by the PCM,
the engine will be disabled and the vehicle immobi-
lized after two seconds of running.
The SKIM also sends SKIS indicator status mes-
sages to the EMIC over the PCI data bus to tell the
EMIC how to operate the SKIS indicator. This indi-
cator status message tells the EMIC to turn the indi-
cator on for about three seconds each time the
ignition switch is turned to the On position as a bulb
test. After completion of the bulb test, the SKIM
sends indicator status messages to the EMIC to turn
the indicator off, turn the indicator on, or to flash the
Fig. 10 Sentry Key Immobilizer Module
1 - SKIM
2 - BRACKET
3 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
4 - ANTENNA RING
8E - 16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESKJ
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE (Continued)
Page 451 of 1803
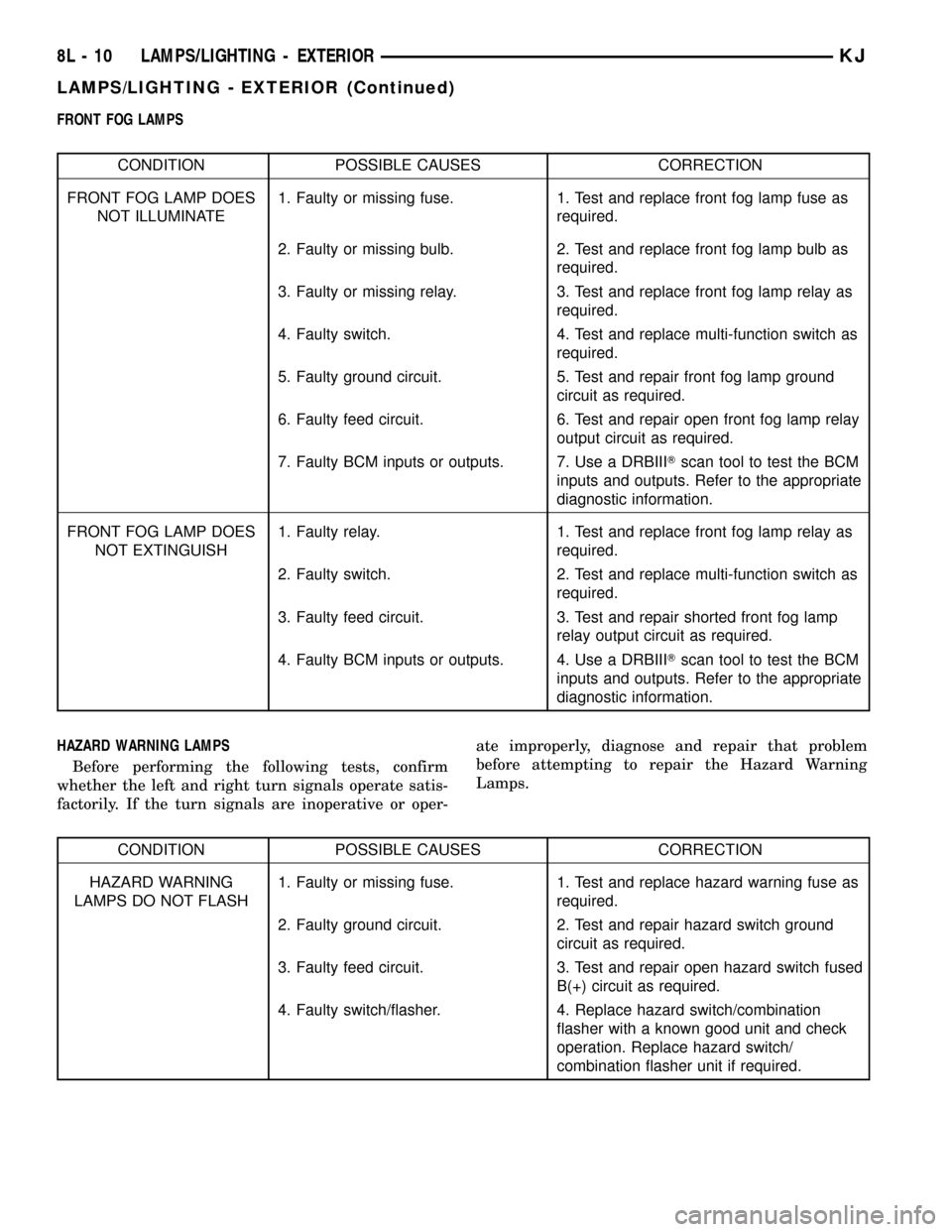
FRONT FOG LAMPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
FRONT FOG LAMP DOES
NOT ILLUMINATE1. Faulty or missing fuse. 1. Test and replace front fog lamp fuse as
required.
2. Faulty or missing bulb. 2. Test and replace front fog lamp bulb as
required.
3. Faulty or missing relay. 3. Test and replace front fog lamp relay as
required.
4. Faulty switch. 4. Test and replace multi-function switch as
required.
5. Faulty ground circuit. 5. Test and repair front fog lamp ground
circuit as required.
6. Faulty feed circuit. 6. Test and repair open front fog lamp relay
output circuit as required.
7. Faulty BCM inputs or outputs. 7. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to test the BCM
inputs and outputs. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
FRONT FOG LAMP DOES
NOT EXTINGUISH1. Faulty relay. 1. Test and replace front fog lamp relay as
required.
2. Faulty switch. 2. Test and replace multi-function switch as
required.
3. Faulty feed circuit. 3. Test and repair shorted front fog lamp
relay output circuit as required.
4. Faulty BCM inputs or outputs. 4. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to test the BCM
inputs and outputs. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
HAZARD WARNING LAMPS
Before performing the following tests, confirm
whether the left and right turn signals operate satis-
factorily. If the turn signals are inoperative or oper-ate improperly, diagnose and repair that problem
before attempting to repair the Hazard Warning
Lamps.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HAZARD WARNING
LAMPS DO NOT FLASH1. Faulty or missing fuse. 1. Test and replace hazard warning fuse as
required.
2. Faulty ground circuit. 2. Test and repair hazard switch ground
circuit as required.
3. Faulty feed circuit. 3. Test and repair open hazard switch fused
B(+) circuit as required.
4. Faulty switch/flasher. 4. Replace hazard switch/combination
flasher with a known good unit and check
operation. Replace hazard switch/
combination flasher unit if required.
8L - 10 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORKJ
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 455 of 1803
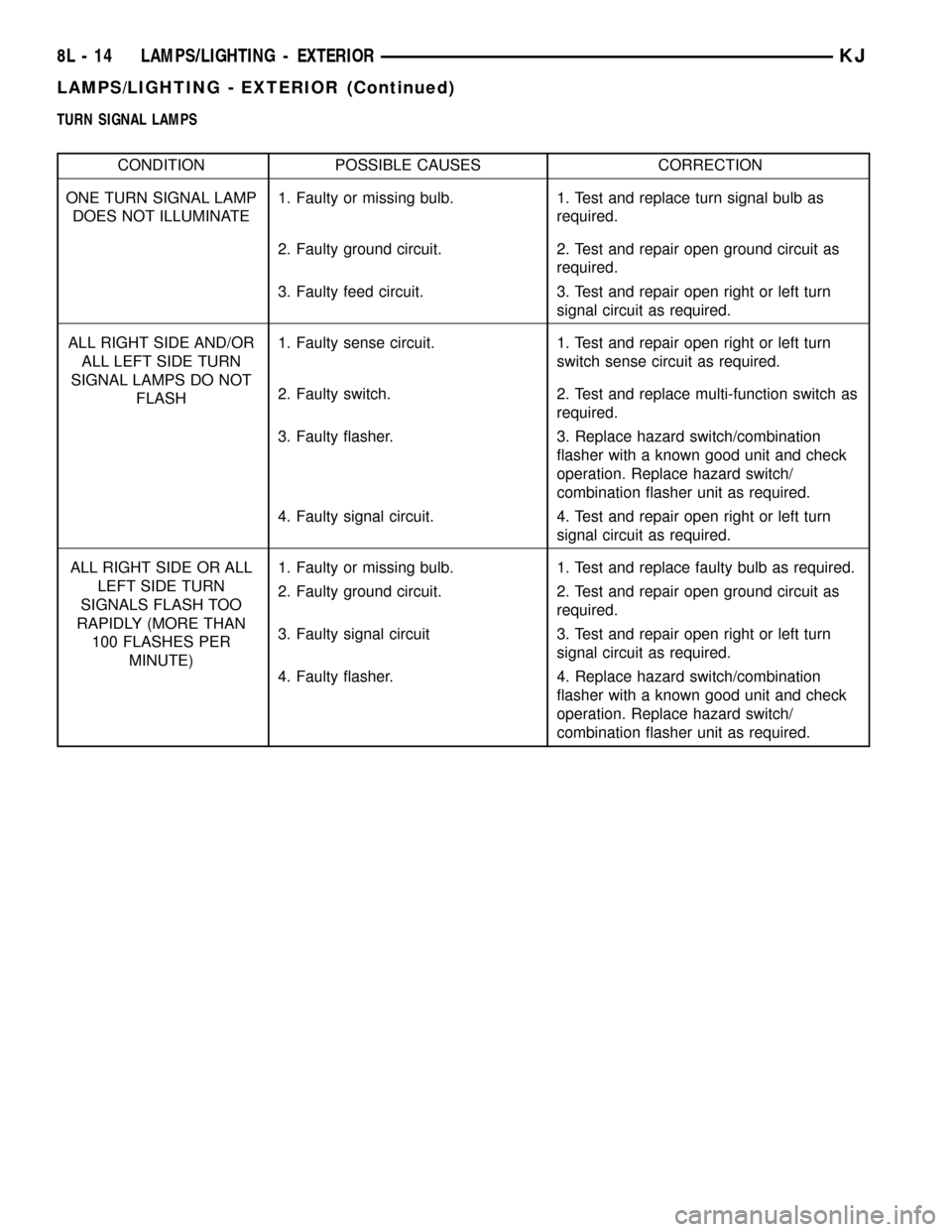
TURN SIGNAL LAMPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ONE TURN SIGNAL LAMP
DOES NOT ILLUMINATE1. Faulty or missing bulb. 1. Test and replace turn signal bulb as
required.
2. Faulty ground circuit. 2. Test and repair open ground circuit as
required.
3. Faulty feed circuit. 3. Test and repair open right or left turn
signal circuit as required.
ALL RIGHT SIDE AND/OR
ALL LEFT SIDE TURN
SIGNAL LAMPS DO NOT
FLASH1. Faulty sense circuit. 1. Test and repair open right or left turn
switch sense circuit as required.
2. Faulty switch. 2. Test and replace multi-function switch as
required.
3. Faulty flasher. 3. Replace hazard switch/combination
flasher with a known good unit and check
operation. Replace hazard switch/
combination flasher unit as required.
4. Faulty signal circuit. 4. Test and repair open right or left turn
signal circuit as required.
ALL RIGHT SIDE OR ALL
LEFT SIDE TURN
SIGNALS FLASH TOO
RAPIDLY (MORE THAN
100 FLASHES PER
MINUTE)1. Faulty or missing bulb. 1. Test and replace faulty bulb as required.
2. Faulty ground circuit. 2. Test and repair open ground circuit as
required.
3. Faulty signal circuit 3. Test and repair open right or left turn
signal circuit as required.
4. Faulty flasher. 4. Replace hazard switch/combination
flasher with a known good unit and check
operation. Replace hazard switch/
combination flasher unit as required.
8L - 14 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORKJ
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 461 of 1803

stant battery voltage is supplied to the flasher so that it
can perform the hazard warning function, and ignition
switched battery voltage is supplied for the turn signal
function. The Integrated Circuit (IC) within the combi-
nation flasher contains the logic that controls the
flasher operation and the flash rate. The IC receives
separate sense ground inputs from the multi-function
switch for the right and left turn signals, and from the
hazard switch contacts or the BCM for the hazard
warning signals. A special design feature of the combi-
nation flasher allows it to9sense9that a turn signal cir-
cuit or bulb is not operating, and provide the driver an
indication of the condition by flashing the remaining
bulbs in the affected circuit at a higher rate (120 flash-
es-per-minute or higher). Conventional flashers either
continue flashing at their typical rate (heavy-duty type),
or discontinue flashing the affected circuit entirely
(standard-duty type).
Because of the active electronic elements within
the combination flasher, it cannot be tested with con-
ventional automotive electrical test equipment. If the
combination flasher is believed to be faulty, test the
turn signal and hazard warning system. Then
replace the hazard switch with a known good unit to
confirm system operation.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMP
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The Daytime Running Lamp (DRL) relay (Fig. 8) is
a solid state relay that is used only on vehicles man-
ufactured for sale in Canada. The DRL relay features
a die cast aluminum housing with integral cooling
fins that act as a heat sink for the solid state DRL
circuitry. Four male spade terminals extend from the
base of the relay through a potting material that
encloses and protects the DRL circuitry. Although the
DRL relay has four terminals that are laid out in a
footprint that is similar to that of a conventional
International Standards Organization (ISO) relay, a
standard ISO relay should never be installed in place
of the DRL relay. The DRL relay is installed in the
Junction Block (JB) on the driver side outboard end
of the instrument panel. Vehicles equipped with this
relay do not have a headlamp high beam relay
installed in the JB.
The DRL relay cannot be adjusted or repaired and,
if faulty or damaged, the unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The Daytime Running Lamp (DRL) relay is a solid
state relay that controls the flow of battery current
to the high beam filaments of both headlamp bulbs
based upon a duty cycled control input received from
the Body Control Module (BCM) of vehicles equipped
with the DRL feature. By cycling the DRL relay out-
put, the BCM controls the illumination intensity of
the high beam filaments. The DRL relay terminals
are connected to the vehicle electrical system through
a connector receptacle in the Junction Block (JB).
The inputs and outputs of the DRL relay include:
²Battery Current Input- The DRL relay
receives battery current on a fused B(+) circuit from
a fuse in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
²Ground Input- The DRL relay receives a path
to ground through a splice block located in the
instrument panel wire harness with an eyelet termi-
nal connector that is secured by a nut to a ground
stud on the driver side instrument panel end bracket
near the Junction Block (JB).
²Control Input- The DRL relay control input is
received from the BCM and/or the momentary optical
horn (flash-to-pass) output of the multi-function
switch through a high beam relay control circuit.
²Control Output- The DRL relay supplies bat-
tery current output to the headlamp high beam fila-
ments through the high beam relay output circuit.
Because of active electronic elements within the
DRL relay, it cannot be tested with conventional
automotive electrical test equipment. If the DRL
relay is believed to be faulty, replace the relay with a
known good unit to confirm system operation.
Fig. 8 Daytime Running Lamp Relay
1 - DRL RELAY
2 - HEAT SINK
3 - POTTING MATERIAL
4 - TERMINAL (4)
8L - 20 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORKJ
COMBINATION FLASHER (Continued)
Page 470 of 1803

HAZARD SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The hazard switch is integral to the hazard switch
module, which is secured near the center of instrument
panel just above the radio (Fig. 21). Only the hazard
switch button is visible through a dedicated, round, bev-
eled opening on the outer surface of the instrument
panel between the two center panel outlets of the heater
and air conditioning system. A red, stencil-like Interna-
tional Control and Display Symbol icon for ªHazard
Warningº identifies the hazard switch button. On the
opposite end of the black, molded plastic hazard switch
module housing from the switch button is an integral
connector receptacle and a stamped steel mounting
bracket with two latch feature tabs that extend down-
ward, while a short dowel-like alignment pin is integral
to each side of the housing just below the switch button.
The switch module is connected to the vehicle electrical
system through a dedicated take out and connector of
the instrument panel wire harness. Within the hazard
switch module housing is the hazard switch circuitry
and an electronic circuit board with the integral combi-
nation flasher circuitry. The electronic combination
flasher circuitry performs both the hazard flasher and
turn signal flasher functions.
The hazard switch module cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the unit must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The hazard switch button is slightly recessed in the
instrument panel when the switch is in the Off position,
and latches at a position that is flush with the outer
surface of the instrument panel when in the On posi-tion. The hazard switch module produces an audible
clicking sound that emulates the sound of a conven-
tional flasher whenever the turn signals or the hazard
warning system are activated. The hazard switch mod-
ule receives battery current on a fused B(+) circuit from
a fuse in the Junction Block (JB) at all times for oper-
ation of the hazard warning, and on a fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit from another fuse in the JB
whenever the ignition switch is in the On position for
operation of the turn signals. The module receives a
path to ground through a splice block located in the
instrument panel wire harness with an eyelet terminal
connector that is secured by a nut to a ground stud on
the driver side instrument panel end bracket near the
JB. Inputs to and outputs from the hazard switch mod-
ule include:
²Panel Lamps Dimmer Input- A non-service-
able incandescent bulb soldered onto the hazard
switch module circuit board provides illumination of
the switch button when the exterior lighting is
turned On through an input received on the fused
panel lamps dimmer switch signal circuit. However,
this bulb flashes on and off at full intensity whenever
the hazard switch button is in the On position,
regardless of the status of the exterior lighting.
²Hazard Switch Input- The combination
flasher circuitry of the hazard switch module receives
an internal ground input from the hazard switch to
request hazard flasher operation.
²Multi-Function Switch Input- The combina-
tion flasher circuitry of the hazard switch module
receives separate ground inputs from the turn signal
switch circuitry of the multi-function switch on right
and left turn switch sense circuits to request right or
left turn signal flasher operation.
²Body Control Module Input- The Body Con-
trol Module (BCM) can request hazard flasher opera-
tion by providing a ground path to the combination
flasher circuitry of the hazard switch module through
a hazard lamp control circuit.
²Turn Signal Output- The combination flasher
circuitry within the hazard switch module responds
to the flasher request inputs by energizing and
de-energizing two miniature relays on the module
circuit board. These relays control the switch output
through the right and left turn signal circuits. One
relay controls the right lamps, while the other con-
trols the left.
Because of active electronic elements within the
hazard switch module, it cannot be tested with con-
ventional automotive electrical test equipment. If the
hazard switch module is believed to be faulty, replace
the switch with a known good unit to confirm system
operation.
Fig. 21 Hazard Switch
1 - HAZARD SWITCH BUTTON
2 - SCREW (1)
3 - MOUNTING BRACKET TABS
KJLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 29
Page 490 of 1803

towards the steering wheel to just before a detent, to
momentarily activate the headlamp optical horn fea-
ture. The high beams will remain illuminated until
the control stalk is released. The multi-function
switch provides a ground output on a high beam
relay control circuit to energize the headlamp high
beam relay (Daytime Running Lamp relay in Cana-
dian vehicles) in the Junction Block (JB) as required.
²Interior Lamps Defeat- The control ring on
the multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk
is rotated to a full rearward (clockwise) detent to
defeat the illumination of all interior courtesy lamps.
The multi-function switch provides a resistor multi-
plexed output to the Body Control Module (BCM) on
a panel lamps dimmer switch mux circuit, and the
BCM responds by de-energizing its internal courtesy
lamp driver circuit.
²Interior Lamps On- The control ring on the
multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk is
rotated to a full forward (counterclockwise) detent to
illuminate all interior courtesy lamps. The multi-
function switch provides a resistor multiplexed out-
put to the Body Control Module (BCM) on a panel
lamps dimmer switch mux circuit, and the BCM
responds by energizing its internal courtesy lamp
driver circuit.
²Panel Lamps Dimming- The control ring on
the multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk
is rotated to one of six minor intermediate detents to
simultaneously select the desired illumination inten-
sity of all adjustable instrument panel and instru-
ment cluster lighting. The control ring is rotated
rearward (clockwise) to dim, or forward (counter-
clockwise) to brighten. The multi-function switch pro-
vides a resistor multiplexed output to the Body
Control Module (BCM) on a panel lamps dimmer
switch mux circuit, and the BCM responds by send-
ing an electronic panel lamps dimming level message
to the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC)
over the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus. The EMIC electronic circuitry then
provides the proper PWM output to the cluster illu-
mination lamps and the VFD on the EMIC circuit
board, then provides a matching PWM output on the
hard wired fused panel lamps dimmer switch signal
circuit.
²Parade Mode- The control ring on the multi-
function switch left (lighting) control stalk is rotated
to an intermediate detent that is one detent rear-
ward (clockwise) from the full forward (counterclock-
wise) detent to select the Parade mode. The multi-
function switch provides a resistor multiplexed
output to the Body Control Module (BCM) on a panel
lamps dimmer switch mux circuit, and the BCM
responds by sending an electronic panel lamps dim-
ming level message to the ElectroMechanical Instru-ment Cluster (EMIC) over the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus. The EMIC
electronic circuitry then provides the proper PWM
output to the cluster illumination lamps and the
VFD on the EMIC circuit board, then provides a
matching PWM output on the hard wired fused panel
lamps dimmer switch signal circuit to illuminate all
lamps at full (daylight) intensity with the exterior
lamps turned On.
²Park Lamps- The control knob on the end of
the multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk
is rotated forward (counterclockwise) to its first
detent from the Off position to activate the park
lamps. The multi-function switch provides a resistor
multiplexed output to the Body Control Module
(BCM) on a headlamp switch sense circuit, and the
BCM responds by energizing or de-energizing the
park lamp relay in the Junction Block (JB) as
required.
²Rear Fog Lamps- For vehicles so equipped,
the control knob on the end of the multi-function
switch left (lighting) control stalk is rotated forward
(counterclockwise) to its third detent position to acti-
vate the rear fog lamps. The multi-function switch
provides a resistor multiplexed output to the Body
Control Module (BCM) on a headlamp switch sense
circuit, and the BCM responds by energizing or de-
energizing the rear fog lamp relay in the Junction
Block (JB) as required. Rear fog lamps are optional
only for vehicles manufactured for certain markets,
where they are required.
²Turn Signal Control- The left (lighting) con-
trol stalk of the multi-function switch is moved
upward to activate the right turn signal circuitry,
and, downward to activate the left turn signal cir-
cuitry. The turn signal switch has a detent position
in each direction that provides turn signals with
automatic cancellation, and an intermediate, momen-
tary position in each direction that provides turn sig-
nals only until the left multi-function switch control
stalk is released. When the control stalk is moved to
a turn signal switch detent position, the cancel
actuator extends toward the center of the steering
column. A turn signal cancel cam that is integral to
the clockspring rotates with the steering wheel and
the cam lobes contact the cancel actuator when it is
extended from the left multi-function switch. When
the steering wheel is rotated during a turning
maneuver, one of the two turn signal cancel cam
lobes will contact the turn signal cancel actuator. The
cancel actuator latches against the cancel cam rota-
tion in the direction opposite that which is signaled.
In other words, if the left turn signal detent is
selected, the lobes of the cancel cam will ratchet past
the cancel actuator when the steering wheel is
rotated to the left, but will unlatch the cancel actua-
KJLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 49
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH (Continued)