cable JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 12 of 1803

VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER DECODING CHART
POSITION INTERPRETATION CODE = DESCRIPTION
1 Country of Origin 1 = United States
2 Make J = Jeep
3 Vehicle Type 4 = MPV W/O Side Airbags.
8 = MPV With Side Airbags.
4 Gross Vehicle Weight Rating F = 4001 - 5000 lbs.
G = 5001 - 6000 lbs.
5 Vehicle Line K = Liberty 4X2 (LHD)
L = Liberty 4X4 (LHD)
M = Cherokee 4X4 (RHD)
6 Series 3 = Liberty Renegade
4 = Liberty Sport/Cherokee Sport
5 = Liberty Limited/Cherokee Limited
7 Body Style 8 = Sport Utility - 4 Door
8 Engine K = 3.7L 6 cyl MPI Gasoline
1 = 2.4L 4 cyl MPI Gasoline
7 = 2.5L 4 cyl Diesel
9 Check Digit 0 through 9 or X
10 Model Year 2=2002
11 Assembly Plant W = Toledo North Assembly Plant
12 thru 17 Vehicle Build Sequence
VEHICLE SAFETY
CERTIFICATION LABEL
DESCRIPTION
A vehicle safety certification label (Fig. 6) is
attached to every DaimlerChrysler Corporation vehi-
cle. The label certifies that the vehicle conforms to all
applicable Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
The label also lists:
²Month and year of vehicle manufacture.
²Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR). The gross
front and rear axle weight ratings (GAWR's) arebased on a minimum rim size and maximum cold tire
inflation pressure.
²Vehicle Identification Number (VIN).
²Type of vehicle.
²Bar code.
²Month, Day and Hour (MDH) of final assembly.
²Paint and Trim codes.
²Country of origin.
The label is located above the door hinge on the
driver-side A-pillar.
Fig. 6 Vehicle Safety Certification LabelÐTypical
KJINTRODUCTION 9
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (Continued)
Page 17 of 1803
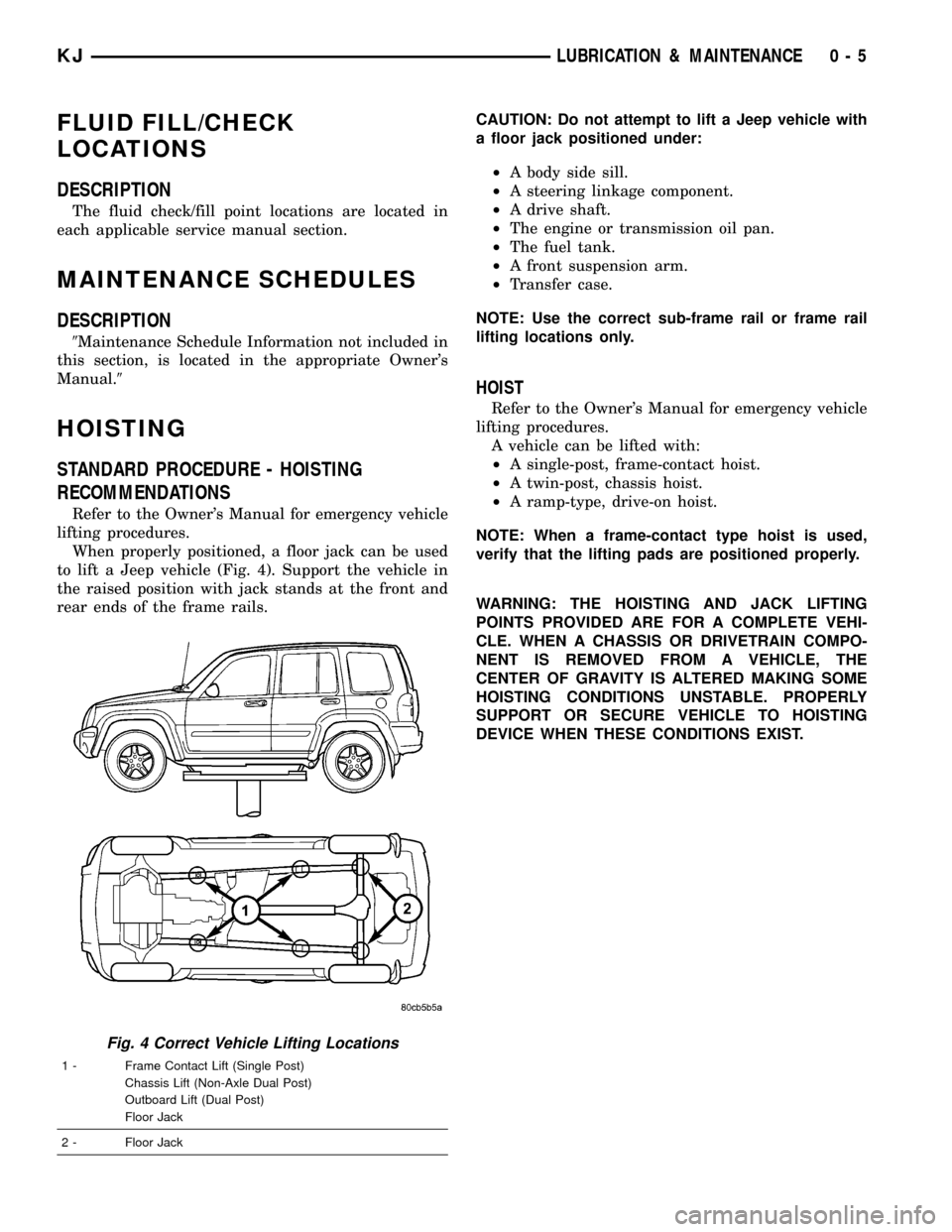
FLUID FILL/CHECK
LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION
The fluid check/fill point locations are located in
each applicable service manual section.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
DESCRIPTION
9Maintenance Schedule Information not included in
this section, is located in the appropriate Owner's
Manual.9
HOISTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HOISTING
RECOMMENDATIONS
Refer to the Owner's Manual for emergency vehicle
lifting procedures.
When properly positioned, a floor jack can be used
to lift a Jeep vehicle (Fig. 4). Support the vehicle in
the raised position with jack stands at the front and
rear ends of the frame rails.CAUTION: Do not attempt to lift a Jeep vehicle with
a floor jack positioned under:
²A body side sill.
²A steering linkage component.
²A drive shaft.
²The engine or transmission oil pan.
²The fuel tank.
²A front suspension arm.
²Transfer case.
NOTE: Use the correct sub-frame rail or frame rail
lifting locations only.
HOIST
Refer to the Owner's Manual for emergency vehicle
lifting procedures.
A vehicle can be lifted with:
²A single-post, frame-contact hoist.
²A twin-post, chassis hoist.
²A ramp-type, drive-on hoist.
NOTE: When a frame-contact type hoist is used,
verify that the lifting pads are positioned properly.
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN A CHASSIS OR DRIVETRAIN COMPO-
NENT IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE
CENTER OF GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME
HOISTING CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY
SUPPORT OR SECURE VEHICLE TO HOISTING
DEVICE WHEN THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.
Fig. 4 Correct Vehicle Lifting Locations
1 - Frame Contact Lift (Single Post)
Chassis Lift (Non-Axle Dual Post)
Outboard Lift (Dual Post)
Floor Jack
2 - Floor Jack
KJLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 5
Page 18 of 1803

JUMP STARTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - JUMP STARTING
PROCEDURE
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN GROUP 8A, BATTERY/START-
ING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS.
²DO NOT JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY,
PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT JUMP START WHEN BATTERY INDI-
CATOR DOT IS YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR. BAT-
TERY CAN EXPLODE.
²DO NOT ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO
TOUCH EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A
BOOSTER SOURCE.
²DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BATTERY.
²REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON
HANDS OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCI-
DENTAL ARCHING OF BATTERY CURRENT.
²WHEN USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING
DEVICE, DO NOT ALLOW DISABLED VEHICLE'S
BATTERY TO EXCEED 16 VOLTS. PERSONAL
INJURY OR DAMAGE TO ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually
inspect engine compartment for:
²Generator drive belt condition and tension.
²Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
²Frozen battery.
²Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
²Low battery fluid level.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, turn off all accessories, place gear selector in
park or neutral, set park brake or equivalent and
operate engine at 1200 rpm.
(3) On disabled vehicle, place gear selector in park
or neutral and set park brake or equivalent. Turn
OFF all accessories.
(4) Connect jumper cables to booster battery. RED
clamp to positive terminal (+). BLACK clamp to neg-
ative terminal (-). DO NOT allow clamps at opposite
end of cables to touch, electrical arc will result (Fig.
5). Review all warnings in this procedure.(5) On disabled vehicle, connect RED jumper cable
clamp to battery positive (+) terminal. Connect
BLACK jumper cable clamp to the engine as close to
the ground cable connection as possible (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not crank starter motor on disabled
vehicle for more than 15 seconds, starter will over-
heat and could fail.
(6) Allow battery in disabled vehicle to charge to
at least 12.4 volts (75% charge) before attempting to
start engine. If engine does not start within 15 sec-
onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 min.), before cranking again.
DISCONNECT CABLE CLAMPS AS FOLLOWS:
²Disconnect BLACK cable clamp from engine
ground on disabled vehicle.
²When using a Booster vehicle, disconnect
BLACK cable clamp from battery negative terminal.
Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery positive
terminal.
²Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery posi-
tive terminal on disabled vehicle.
TOWING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TOWING
A vehicle equipped with SAE approved wheel lift-
type towing equipment can be used to tow Jeep vehi-
cles. When towing a 4WD vehicle using a wheel-lift
Fig. 5 Jumper Cable Clamp Connections
1 - BOOSTER BATTERY
2 - NEGATIVE JUMPER CABLE
3 - ENGINE GROUND
4 - DO NOT ALLOW VEHICLES TO TOUCH
5 - BATTERY NEGATIVE CABLE
6 - DISCHARGED BATTERY
7 - POSITIVE JUMPER CABLE
0 - 6 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEKJ
Page 32 of 1803

(11) Remove the clevis bracket at the shock. (Fig.
5)
(12) Remove the shock assembly from the vehicle.
(Fig. 5)
(13) Remove the spring from the shock (if needed).
(Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/SPRING -
REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LEFT SIDE
(1) Install the spring to the shock (if removed).
(2) Install the shock assembly to the vehicle.
(3) Install the four upper shock mounting nuts.
Tighten the nuts to 108 N´m (80 ft.lbs.).
(4) Install the clevis bracket at the shock. (Refer to
2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/CLEVIS BRACKET -
INSTALLATION). Tighten the bolt to 88 N´m (65
ft.lbs.).
(5) Raise the lower control into place and recon-
nect the lower ball joint nut. Tighten the nut to 81
N´m (60 ft.lbs.).
(6) Install the clevis bracket at the lower control
arm. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/CLEVIS
BRACKET - INSTALLATION). Tighten the bolt to
150 N´m (110 ft.lbs.).(7) Install the lower stabilizer link at the lower
control arm. Tighten the bolt to 136 N´m (100 ft.lbs.)
(Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/STABILIZER
LINK - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the left tire and wheel assembly. (Refer
to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(9) Lower the vehicle.
(10) Reconnect the battery temperature sensor.
(11) Install the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - INSTALLA-
TION).
(12) Install the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - INSTALLA-
TION).
(13) Reconnect the battery cables.
INSTALLATION - RIGHT SIDE
(1) Install the spring to the shock (if removed).
(Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/SPRING -
INSTALLATION).
(2) Install the shock assembly to the vehicle.
(3) Install the four upper shock mounting nuts.
Tighten the nuts to 108 N´m (80 ft.lbs.).
(4) Install the clevis bracket at the shock. (Refer to
2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/CLEVIS BRACKET -
INSTALLATION). Tighten the bolt to 88 N´m (65
ft.lbs.).
(5) Raise the lower control into place and recon-
nect the lower ball joint nut. Tighten the nut to 81
N´m (60 ft.lbs.).
(6) Install the clevis bracket at the lower control
arm. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/CLEVIS
BRACKET - INSTALLATION). Tighten the bolt to
150 N´m (110 ft.lbs.).
(7) Install the lower stabilizer link at the lower
control arm. Tighten the bolt to 136 N´m (100 ft.lbs.)
(Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/STABILIZER
LINK - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the right tire and wheel assembly.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(9) Lower the vehicle.
(10) Install the cruise control servo mounting nuts.
(11) Install the airbox (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 5 SHOCK & CLEVIS ASSEMBLY
1 - FRONT CRADLE
2 - SPRING & SHOCK ASSEMBLY
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - CLEVIS BRACKET
5 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
2 - 12 FRONTKJ
SHOCK (Continued)
Page 103 of 1803

REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lift/jack under the axle and secure
axle to device.
(3) Remove wheels and tires.
(4) Mark propeller shaft and pinion yoke for
installation reference.
(5) Remove propeller shaft and suspend under the
vehicle.
(6) Remove brake drums, parking brake cables and
speed sensor from the axle.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the body junction
block.
(8) Remove brakes and backing plates.
(9) Remove vent hose from the axle shaft tube.
(10) Remove the stabilizer bar (Fig. 5).
(11) Remove upper control arm ball joint pinch
bolt from bracket (Fig. 6).
(12) Remove shock absorbers from axle brackets
(Fig. 7).
(13) Loosen all lower control arms mounting bolts
(Fig. 8).
(14) Lower axle enough to remove coil springs and
spring insulators.
(15) Remove lower control arm bolts from the axle
brackets.
(16) Lower and remove the axle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The weight of the vehicle must be sup-
ported by the springs before the lower control arms
are tightened. This must be done to maintain vehi-
cle ride height and prevent premature bushing fail-
ure.(1) Raise the axle under the vehicle.
(2) Install lower control arms onto the axle brack-
ets and loosely install the mounting bolts.
(3) Install coil spring isolators and spring.
(4) Raise axle up until springs are seated.
(5) Install upper control arm ball joint into axle
bracket and tighten pinch bolt to torque specification.
(6) Install shock absorbers and tighten nuts to
torque specification.
(7) Install stabilizer bar and tighten nuts to torque
specification.
(8) Install brake backing plates, parking brake
cables, brake drums and speed sensor.
(9) Install brake hose to the body junction block
and bleed the brakes.
Fig. 5 STABILIZER BAR MOUNTS
1 - STABILIZER BAR MOUNTING BOLTS
2 - LOWER SUSPENSION ARM
Fig. 6 BALL JOINT PINCH BOLT
1 - UPPER BALL JOINT
2 - PINCH BOLT
Fig. 7 SHOCK ABSORBER
1 - UPPER MOUNTING BOLT
2 - LOWER MOUNTING BOLT
3 - 54 REAR AXLE - 198RBIKJ
REAR AXLE - 198RBI (Continued)
Page 140 of 1803

REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lift/jack under the axle and secure
axle to device.
(3) Remove wheels and tires.
(4) Mark propeller shaft and pinion yoke for
installation reference.
(5) Remove propeller shaft and suspend under the
vehicle.
(6) Remove brake drums, parking brake cables and
speed sensor from the axle.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the body junction
block.
(8) Remove brakes and backing plates.
(9) Remove vent hose from the axle shaft tube.
(10) Remove the stabilizer bar (Fig. 4).
(11) Remove upper control arm ball joint pinch
bolt from bracket (Fig. 5).
(12) Remove shock absorbers from axle brackets
(Fig. 6).
(13) Loosen all lower control arms mounting bolts
(Fig. 7).
(14) Lower axle enough to remove coil springs and
spring insulators.
(15) Remove lower control arm bolts from the axle
brackets.
(16) Lower and remove the axle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The weight of the vehicle must be sup-
ported by the springs before the lower control arms
are tightened. This must be done to maintain vehi-
cle ride height and prevent premature bushing fail-
ure.(1) Raise the axle under the vehicle.
(2) Install lower control arms onto the axle brack-
ets and loosely install the mounting bolts.
(3) Install coil spring isolators and spring.
(4) Raise axle up until springs are seated.
(5) Install upper control arm ball joint into axle
bracket and tighten pinch bolt to torque specification.
(6) Install shock absorbers and tighten nuts to
torque specification.
(7) Install stabilizer bar and tighten nuts to torque
specification.
(8) Install brake backing plates, parking brake
cables, brake drums and speed sensor.
(9) Install brake hose to the body junction block
and bleed the brakes.
Fig. 4 STABILIZER BAR MOUNTS
1 - STABILIZER BAR MOUNTING BOLTS
2 - LOWER SUSPENSION ARM
Fig. 5 BALL JOINT PINCH BOLT
1 - UPPER BALL JOINT
2 - PINCH BOLT
Fig. 6 SHOCK ABSORBER
1 - UPPER MOUNTING BOLT
2 - LOWER MOUNTING BOLT
KJREAR AXLE - 8 1/4 3 - 91
REAR AXLE - 8 1/4 (Continued)
Page 166 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MASTER
CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER...........21
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MASTER
CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER...........24
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER
CYLINDER BLEEDING..................24
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
FLUID RESERVOIR
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
FLUID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE FLUID
CONTAMINATION.....................26
STANDARD PROCEDURES - MASTER
CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL................26
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID........................27
DRUM
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE DRUM . . . 27
STANDARD PROCEDURES - BRAKE DRUM
MACHINING..........................27SUPPORT PLATE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 198 RBI AXLE..............27
REMOVAL - 8 1/4 AXLE.................27
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 198 RBI AXLE...........28
INSTALLATION - 8 1/4 AXLE.............28
WHEEL CYLINDERS
REMOVAL.............................28
DISASSEMBLY.........................28
CLEANING............................28
INSPECTION..........................29
ASSEMBLY............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
PARKING BRAKE
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - LOCK OUT.............30
CABLES
REMOVAL.............................30
INSTALLATION.........................30
LEVER
REMOVAL.............................31
INSTALLATION.........................31
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION
Power assist front disc and rear drum brakes are
standard equipment. Disc brake components consist
of single piston calipers and ventilated rotors. Rear
drum brakes are dual shoe units with cast brake
drums.
The parking brake mechanism is lever and cable
operated. The cables are attached to levers on the
rear drum brake secondary shoes. The parking
brakes are operated by a hand lever.
A dual diaphragm vacuum power brake booster is
used for all applications. All models have an alumi-
num master cylinder with plastic reservoir.
All models are equipped with a combination valve.
The valve contains a pressure differential valve and
switch and a fixed rate rear proportioning valve.
Factory brake lining on all models consists of an
organic base material combined with metallic parti-
cles. The original equipment linings do not contain
asbestos.
WARNING
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ACCUMULATING ON
BRAKE PARTS DURING NORMAL USE MAY CON-
TAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM AFTERMARKET
LININGS. BREATHING EXCESSIVE CONCENTRA-
TIONS OF ASBESTOS FIBERS CAN CAUSE SERI-
OUS BODILY HARM. EXERCISE CARE WHEN
SERVICING BRAKE PARTS. DO NOT CLEAN
BRAKE PARTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY
DRY BRUSHING. USE A VACUUM CLEANER SPE-
CIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE REMOVAL OF
ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM BRAKE COMPONENTS.
IF A SUITABLE VACUUM CLEANER IS NOT AVAIL-
ABLE, CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE WITH A
WATER DAMPENED CLOTH. DO NOT SAND, OR
GRIND BRAKE LINING UNLESS EQUIPMENT USED
IS DESIGNED TO CONTAIN THE DUST RESIDUE.
DISPOSE OF ALL RESIDUE CONTAINING ASBES-
TOS FIBERS IN SEALED BAGS OR CONTAINERS
TO MINIMIZE EXPOSURE TO YOURSELF AND OTH-
ERS. FOLLOW PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY THE
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINIS-
TRATION AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
AGENCY FOR THE HANDLING, PROCESSING, AND
DISPOSITION OF DUST OR DEBRIS THAT MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS.
5 - 2 BRAKES - BASEKJ
Page 167 of 1803

CAUTION: Never use gasoline, kerosene, alcohol,
motor oil, transmission fluid, or any fluid containing
mineral oil to clean the system components. These
fluids damage rubber cups and seals. Use only
fresh brake fluid or Mopar brake cleaner to clean or
flush brake system components. These are the only
cleaning materials recommended. If system contam-
ination is suspected, check the fluid for dirt, discol-
oration, or separation into distinct layers. Also
check the reservoir cap seal for distortion. Drain
and flush the system with new brake fluid if con-
tamination is suspected.
CAUTION: Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent
quality fluid meeting SAE/DOT standards J1703 and
DOT 3. Brake fluid must be clean and free of con-
taminants. Use fresh fluid from sealed containers
only to ensure proper antilock component opera-
tion.
CAUTION: Use Mopar multi-mileage or high temper-
ature grease to lubricate caliper slide surfaces,
drum brake pivot pins, and shoe contact points on
the backing plates. Use multi-mileage grease or GE
661 or Dow 111 silicone grease on caliper slide pins
to ensure proper operation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM
Base brake components consist of the brake shoes,
calipers, wheel cylinders, brake drums, rotors, brake
lines, master cylinder, booster, and parking brake
components.
Brake diagnosis involves determining if the prob-
lem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic, or vacuum
operated component.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary check.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) Check condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, vibration, and a condition
similar to grab.
(2) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(3) Inspect brake fluid level and condition. Note
that the brake reservoir fluid level will decrease in
proportion to normal lining wear.Also note that
brake fluid tends to darken over time. This is
normal and should not be mistaken for contam-
ination.(a) If fluid level is abnormally low, look for evi-
dence of leaks at calipers, wheel cylinders, brake
lines, and master cylinder.
(b) If fluid appears contaminated, drain out a
sample to examine. System will have to be flushed
if fluid is separated into layers, or contains a sub-
stance other than brake fluid. The system seals
and cups will also have to be replaced after flush-
ing. Use clean brake fluid to flush the system.
(4) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and pedal. Also
note if vehicle was being operated with parking
brake partially applied.
(5) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does not bind and has adequate free play. If pedal
lacks free play, check pedal and power booster for
being loose or for bind condition. Do not road test
until condition is corrected.
(6) Check booster vacuum check valve and hose.
(7) If components checked appear OK, road test
the vehicle.
ROAD TESTING
(1) If complaint involved low brake pedal, pump
pedal and note if it comes back up to normal height.
(2) Check brake pedal response with transmission
in Neutral and engine running. Pedal should remain
firm under constant foot pressure.
(3) During road test, make normal and firm brake
stops in 25-40 mph range. Note faulty brake opera-
tion such as low pedal, hard pedal, fade, pedal pulsa-
tion, pull, grab, drag, noise, etc.
(4) Attempt to stop the vehicle with the parking
brake only and note grab, drag, noise, etc.
PEDAL FALLS AWAY
A brake pedal that falls away under steady foot
pressure is generally the result of a system leak. The
leak point could be at a brake line, fitting, hose, or
caliper/wheel cylinder. If leakage is severe, fluid will
be evident at or around the leaking component.
Internal leakage (seal by-pass) in the master cylin-
der caused by worn or damaged piston cups, may
also be the problem cause.
An internal leak in the ABS or RWAL system may
also be the problem with no physical evidence.
LOW PEDAL
If a low pedal is experienced, pump the pedal sev-
eral times. If the pedal comes back up worn linings,
rotors, drums, or rear brakes out of adjustment are
the most likely causes. The proper course of action is
to inspect and replace all worn component and make
the proper adjustments.
KJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 3
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 168 of 1803

SPONGY PEDAL
A spongy pedal is most often caused by air in the
system. However, thin brake drums or substandard
brake lines and hoses can also cause a spongy pedal.
The proper course of action is to bleed the system,
and replace thin drums and substandard quality
brake hoses if suspected.
HARD PEDAL OR HIGH PEDAL EFFORT
A hard pedal or high pedal effort may be due to
lining that is water soaked, contaminated, glazed, or
badly worn. The power booster or check valve could
also be faulty.
PEDAL PULSATION
Pedal pulsation is caused by components that are
loose, or beyond tolerance limits.
The primary cause of pulsation are disc brake
rotors with excessive lateral runout or thickness vari-
ation, or out of round brake drums. Other causes are
loose wheel bearings or calipers and worn, damaged
tires.
NOTE: Some pedal pulsation may be felt during
ABS activation.
BRAKE DRAG
Brake drag occurs when the lining is in constant
contact with the rotor or drum. Drag can occur at one
wheel, all wheels, fronts only, or rears only.
Drag is a product of incomplete brake shoe release.
Drag can be minor or severe enough to overheat the
linings, rotors and drums.
Minor drag will usually cause slight surface char-
ring of the lining. It can also generate hard spots in
rotors and drums from the overheat-cool down pro-
cess. In most cases, the rotors, drums, wheels and
tires are quite warm to the touch after the vehicle is
stopped.
Severe drag can char the brake lining all the way
through. It can also distort and score rotors and
drums to the point of replacement. The wheels, tires
and brake components will be extremely hot. In
severe cases, the lining may generate smoke as it
chars from overheating.
Common causes of brake drag are:
²Seized or improperly adjusted parking brake
cables.
²Loose/worn wheel bearing.
²Seized caliper or wheel cylinder piston.
²Caliper binding on corroded bushings or rusted
slide surfaces.
²Loose caliper mounting.
²Drum brake shoes binding on worn/damaged
support plates.
²Mis-assembled components.²Long booster output rod.
If brake drag occurs at all wheels, the problem
may be related to a blocked master cylinder return
port, or faulty power booster (binds-does not release).
BRAKE FADE
Brake fade is usually a product of overheating
caused by brake drag. However, brake overheating
and resulting fade can also be caused by riding the
brake pedal, making repeated high deceleration stops
in a short time span, or constant braking on steep
mountain roads. Refer to the Brake Drag information
in this section for causes.
BRAKE PULL
Front brake pull condition could result from:
²Contaminated lining in one caliper
²Seized caliper piston
²Binding caliper
²Loose caliper
²Rusty caliper slide surfaces
²Improper brake shoes
²Damaged rotor
A worn, damaged wheel bearing or suspension
component are further causes of pull. A damaged
front tire (bruised, ply separation) can also cause
pull.
A common and frequently misdiagnosed pull condi-
tion is where direction of pull changes after a few
stops. The cause is a combination of brake drag fol-
lowed by fade at one of the brake units.
As the dragging brake overheats, efficiency is so
reduced that fade occurs. Since the opposite brake
unit is still functioning normally, its braking effect is
magnified. This causes pull to switch direction in
favor of the normally functioning brake unit.
An additional point when diagnosing a change in
pull condition concerns brake cool down. Remember
that pull will return to the original direction, if the
dragging brake unit is allowed to cool down (and is
not seriously damaged).
REAR BRAKE GRAB OR PULL
Rear grab or pull is usually caused by improperly
adjusted or seized parking brake cables, contami-
nated lining, bent or binding shoes and support
plates, or improperly assembled components. This is
particularly true when only one rear wheel is
involved. However, when both rear wheels are
affected, the master cylinder or proportioning valve
could be at fault.
5 - 4 BRAKES - BASEKJ
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 175 of 1803

OPERATION - REAR DRUM BRAKE
When the brake pedal is depressed hydraulic pres-
sure pushes the rear brake wheel cylinder pistons
outward. The wheel cylinder push rods then push the
brake shoes outward against the brake drum. When
the brake pedal is released return springs attached
to the brake shoes pull the shoes back to there orig-
inal position (Fig. 9).
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT BRAKE PADS
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Drain a small amount of fluid from the master
cylinder brake reservoir with acleansuction gun.(4) Bottom the caliper pistons into the caliper by
prying the caliper over.
(5) Remove the caliper mounting bolts.
(6) Remove the disc brake caliper from the mount.
CAUTION: Never allow the disc brake caliper to
hang from the brake hose. Damage to the brake
hose will result. Provide a suitable support to hang
the caliper securely.
(7) Remove the inboard and outboard pads.
REMOVAL - DRUM BRAKE SHOES
(1) Raise the vehicle and remove the rear wheels.
(2) Remove and discard the spring nuts securing
drums to wheel studs.
(3) Remove the brake drums. If drums prove diffi-
cult to remove, retract brake shoes. Remove the
access hole plug at the rear of backing plate and
back off adjuster screw with brake tool and screw-
driver.
(4) Clean the individual brake components, includ-
ing the support plate and wheel cylinder exterior,
with a find mist of water. Then wipe the brake com-
ponents clean with a dampened cloth.
(5) Remove the primary and secondary return
springs from anchor pin with the brake spring pliers.
(6) Remove the U-clip and washer securing
adjuster cable to the parking brake lever.
(7) Remove the hold-down springs, retainers and
pins with standard retaining spring tool.
(8) Remove the parking brake strut and cable
guide.
(9) Remove the adjuster lever, adjuster screw and
spring.
(10) Remove the adjuster cable.
(11) Remove the brake shoes.
(12) Disconnect the cable from the parking brake
lever and remove the lever ( if needed).
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT BRAKE PADS
(1) Install the inboard and outboard pads.
(2) Install the caliper (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC BRAKE CALIPERS
- INSTALLATION).
(3) Install the tire and wheel assembly. (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
INSTALLATION - DRUM BRAKE SHOES
Bonded linings should be replaced when worn to a
thickness of 1.6 mm (1/16 in.).
Fig. 9 BRAKE COMPONENTS
1 - SECONDARY SHOE
2 - SHOE GUIDE PLATE
3 - PRIMARY SHOE
4 - HORSE SHOE RETAINING CLIP
5 - PRIMARY RETURN SPRING
6 - PARK BRAKE STRUT
7 - HOLD DOWN SPRING AND RETAINERS
8 - SHOE RETURN SPRING
9 - ADJUSTER SCREW ASSEMBLY
10 - ADJUSTER LEVER
11 - ADJUSTER CABLE
12 - SECONDARY RETURN SPRING
13 - CABLE GUIDE
14 - WHEEL CYLINDER
15 - PARK BRAKE STRUT AND SPRING
16 - SUPPORT PLATE
KJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 11
BRAKE PADS / SHOES (Continued)