wheel KIA CARNIVAL 2007 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: KIA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: CARNIVAL, Model: KIA CARNIVAL 2007Pages: 1575, PDF Size: 44.86 MB
Page 292 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
INSPECTION
FUNCTION AND OPERATION PRICIPLE
Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS) detects the crankshaft position and is one of the most important sensors of the
engine control system. If there is no CKPS signal input, fuel is not supplied and the main relay does not operate. That
is, vehicle can't run without CKPS signal. This sensor is installed on transaxle housing and generates alternating
current by magnetic flux field which is made by the sensor and the target wheel when engine runs. The target wheel
consists of 58 slots and 2 missing slots on 360 CA (Crank Angle).
WAVEFORM
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Page 295 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
INSPECTION
FUNCTION AND OPERATION PRICIPLE
Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS) is a hall sensor and detects the camshaft position by using a hall element. It is
related with Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS) and detects the piston position of each cylinder which the CKPS can't
detect. The two CMPS are installed on engine head cover of bank 1 and 2 and uses a target wheel installed on the
camshaft. This sensor has a hall - effect IC which output voltage changes when magnetic field is made on the IC with
current flow.
Page 367 of 1575
6c.
Driving at constant
speed of 30 km/h in 2nd
gear
d. Driving at 50 km/h in 3rd
gear with accelerator
fully closed
e. Driving at constant
speed of 50 km/h in 4th
gear (1) 100%, (2) 0%, (3)
100%
Second solenoid valve
(2) 100%, (3) 100%,
(4) 0% Overdrive solenoid valve
(1) 0km/h
(4) 50km/h Vehicle speed sensor
(4) 1,800 ~ 2,100rpm Input shaft speed sensor
(4) 1,800 ~ 2,100rpm Output shaft speed sensor
7 Selector lever position
: D (Carry out on a
flat and straight road)
a.
Accelerate to 4th gear at
a throttle position sensor
output of 1.5V
(accelerator opening
angle of 30 %).
b. Gently decelerate to a
standstill.
c. Accelerate to 4th gear at
a throttle position sensor
output of 2.5 V
(accelerator opening
angle of 50%).
d. While driving at 60 km/h
in 4th gear, shift down
to 3rd gear.
e. While driving at 40 km/h
in 3rd gear, shift down
to 2nd gear.
f. While driving at 20 km/h
in 2nd gear, shift down
to 1st gear. For (1), (2) and (3),
the reading should be
the same as the
specified output shaft
torque, and no
abnormal shocks
should occur.
For (4), (5) and (6),
downshifting should
occur immediately
after the shifting
operation is made.
Malfunction when shifting
Displaced shift points
Does not shift
Does not shift from 1 to 2 or
2 to 1
Does not shift from 2 to 3 or
3 to 2
Does not shift from 3 to 4 or
4 to 3
8 Selector lever position
: N (Carry out on a
flat and straight road)
Move selector lever to R
range drive at constant
speed of 10km/h The ratio between
input and output shaft
speed sensor data
should be the same
as the gear ratio
when reversing.Does not shift
TORQUE CONVERTER STALL TEST
This test measures the maximum engine speed when the selector lever is in the D or R position. The torque converter
stalls to test the operation of the torque converter, starter motor, one- way clutch operation, the holding performance of
the clutches, and brakes in the transaxle.
Do not let anybody stand in front of or behind the vehicle while this test is being carried out
1. Check the automatic transmission fluid level and temperature, and the engine coolant temperature.
a. Fluid level : At the HOT mark on the oil level gauge
b. Fluid temperature : 80~100°C (176~212°F)
c. Engine coolant temperature : 80~100°C(176~212°F)
2. Prevent all the wheels from moving during the test.
3. Pull the parking brake lever up, with the brake pedal fully depressed.
4. Start the engine.
Page 368 of 1575
5.Move the selector lever to the "D" position, fully depress the accelerator pedal and take a reading of the maximum
engine speed at this time.
Stall speed : 2,100~2,900rpm
a.The throttle should not be left fully open for any more than five seconds.
b. If carrying out the stall test two or more times, move the selector lever to the "N" position and run the
engine at 1,000 r/min to let the automatic transaxle fluid cool down before carrying out subsequent tests.
6. Move the selector lever to the "R" position and carry out the same test again.
TORQUE CONVERTER STALL TEST CONCLUSION
1.Stall speed is too high in both "D" and "R" ranges
a. Low line pressure
b. Low & reverse brake(B) slippage
2. Stall speed is to high in "D" range only
a. Underdrive clutch(C) slippage
3. Stall speed is too high in "R" range only
a. Reverse clutch(A) slippage
4. Stall speed too low in both "D" and "R" ranges
a. Malfunction of torque converter(D)
b. Insufficient engine output
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TEST
1.Warm up the engine until the automatic transaxle fluid temperature is 80- 100°C.
2. Lift up the vehicle so that the wheels are free to turn.
3. Connect the special tool (oil pressure gauge) to each pressure discharge port.
4. Measure the hydraulic pressure at each port under the conditions given in the standard hydraulic pressure table,
and check that the measured values are within the standard value ranges.
5. If a value is outside the standard range, correct the problem while referring to the hydraulic pressure test diagnosis
table.
Page 383 of 1575

13.Remove the starter motor by disconnecting the connector. (see EE group)
14. Using the SST(09200- 38001), hold the engine and transaxle assembly safely.
15.Remove the transaxle insulator mounting (B) bolts (A).
16.Remove the front wheels. (see SS group)
17. Lift up the vehicle.
18. Remove the power steering column joint bolt and the VRS connector (A). (see ST group)
Page 386 of 1575

8.Install the under cover (A).
9.Install the steering column joint bolt and the VRS connector (A). (see ST group)
10. Connect the return tube(A) with a clamp. (see ST group)
11.Install the front wheels and tires.
12. Tighten the transaxle insulator mounting (B) bolt (A).
TORQUE:
90~110 Nm(9~11 kgf.m, 65.1~79.5 lb - ft)
Page 429 of 1575
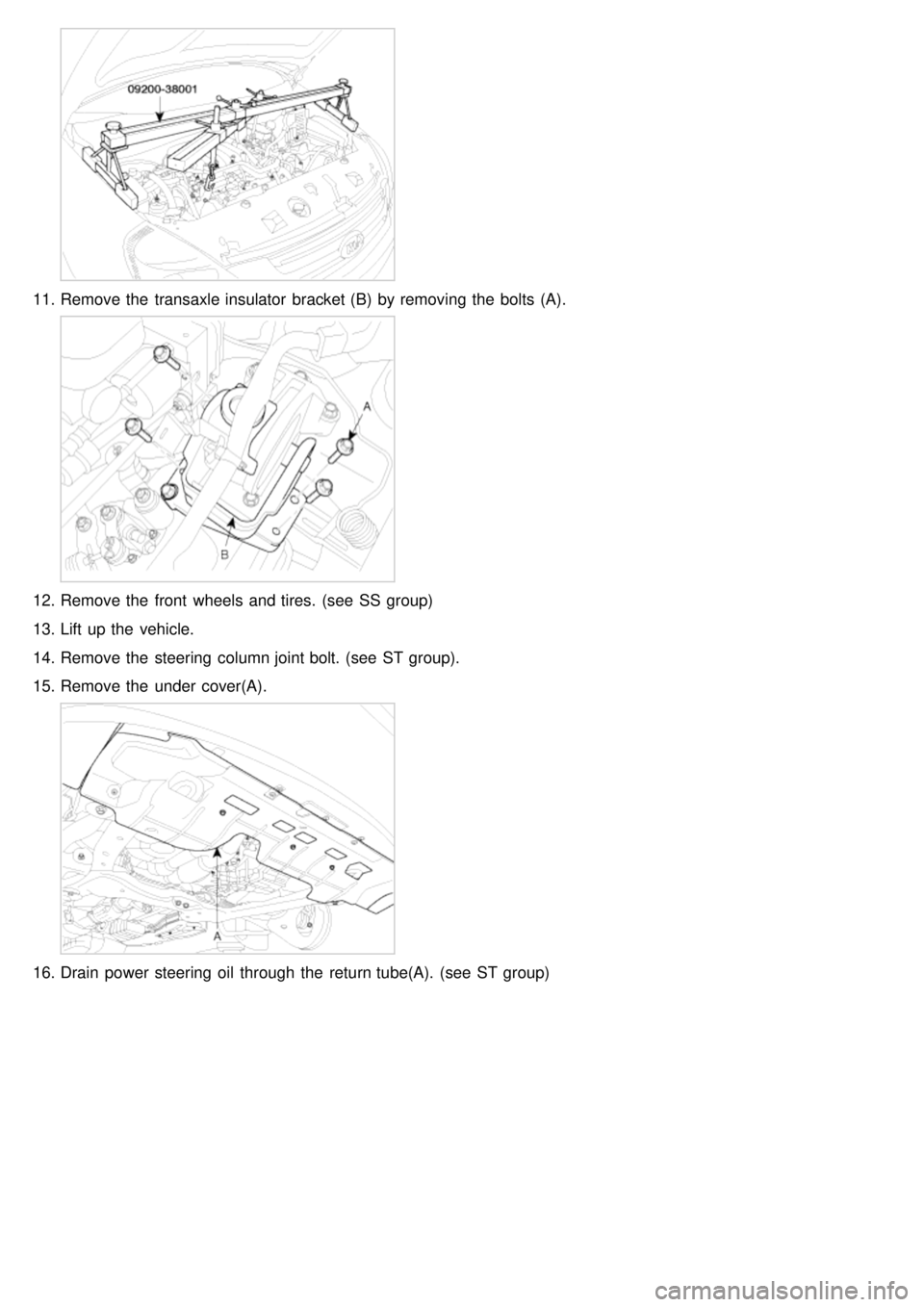
11.Remove the transaxle insulator bracket (B) by removing the bolts (A).
12.Remove the front wheels and tires. (see SS group)
13. Lift up the vehicle.
14. Remove the steering column joint bolt. (see ST group).
15. Remove the under cover(A).
16.Drain power steering oil through the return tube(A). (see ST group)
Page 438 of 1575

19.Install the under cover(A).
20.Install the steering column joint bolt.(See ST group).
21. Install the front wheels and tires. (see SS group)
22. Install the transaxle insulator and mounting bracket (B) by tightening the bolts (A).
TORQUE:
60~80 Nm (6~8 kgf.m, 43.6~58.2 lb - ft)
23.remove the SST (09200- 38001) holding the engine and transaxle assembly.
TORQUE:
65~85 Nm (6.5~8.5kgf.m, 47.0~61.5 lb - ft)
Page 444 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool(Number and name) IllustrationUse
Tie rod end puller
09568 - 4A000
Separation of a lower arm and a tie
rod end ball joint
Front hub remover and installer
09517 - 21500
Removal of a front hub from a
knuckle.
(use with 09517 - 21600)
Main shaft bearing puller
09432 - 11000
Removla of a tone wheel from a
driveshaft
09495 - 3K000
Band installer
Installation of ear type boot band
09495 - 39100
Band installer
Installation of hook type boot band
Page 445 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Possible cause Remedy
Vehicle pulls to one side Scoring of driveshaft ball joint
Wear, rattle or scoring of wheel bearing
Defective front suspension and steering Replace
Replace
Adjust or replace
Vibration Wear, damage or bending of driveshaft
Driveshaft rattle and worn hub splines
Wear, rattle or scratching of wheel bearing Replace
Replace
Replace
Shimmy Improper wheel balance
Bent wheel
Defective front suspension and steering Adjust or replace
Replace
Adjust or replace
Excessive noise Wear, damage or bending of driveshaft
Driveshaft rattle and worn hub splines
Driveshaft rattle and worn side gear splines
Wear, rattle or galling of wheel bearing
Loose hub nut
Defective front suspension and steering Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Adjust or replace
Adjust or replace
Bent cage Cage damaged by improper handling or tool usage Replace bearing
Galling Metal smears on roller end due to overheating,
incorrect lubricant or overloading Replace bearing
Check seals, check for
proper lubrication
Cracked inner race Race cracked due to improper fit, cocking or poor bearing
seats Replace bearing
Etching Bearing surfaces appear gray or grayish black
in color accompanied by material etched
away usually at roller spacing Replace bearing
Check seals, check for
proper lubrication
Brinelling Surface indentations on race surface caused by rollers
being under impact loading or vibration while the bearing
is not rotating Replace bearing
Heat discoloration Heat discoloration is dark blue resulting
from overload or no lubricant (Yellow or brown color is
normal) Replace bearing
Check seals and other parts
Fatigue spalling Flaking of surface metal resulting from fatigue Replace bearing
Clean all related parts