oil pressure LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996Pages: 455, PDF Size: 6.44 MB
Page 103 of 455
FUEL SYSTEM
1
REPAIR FUEL INJECTION PUMP
Service repair no - 19.30.07
Remove
1.Disconnect battery.
2.Disconnect and remove high pressure fuel
injection pipes, pump to injectors.
3.Viewing valve mechanism through oil filler cap
aperture, turn crankshaft clockwise until No. 1
cylinder is just before TDC.
4.Remove blanking plug from flywheel housing
and fit timing toolLRT-12-044, locating centre
pin on flywheel.
NOTE: A chassis undertray may be fitted
on some vehicle derivatives to conform to
legal requirements. When under chassis
adjustments or remove and refit procedures are
required, it may be necessary to remove the
undertray and/or integral access panels
See
CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair, Front undertray
or
See CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair, Rear undertray
5.Carefully rotate crankshaft clockwise until centre
pin engages with timing slot in flywheel.
6.Remove injection pump access plate, complete
with gasket, from front cover plate.
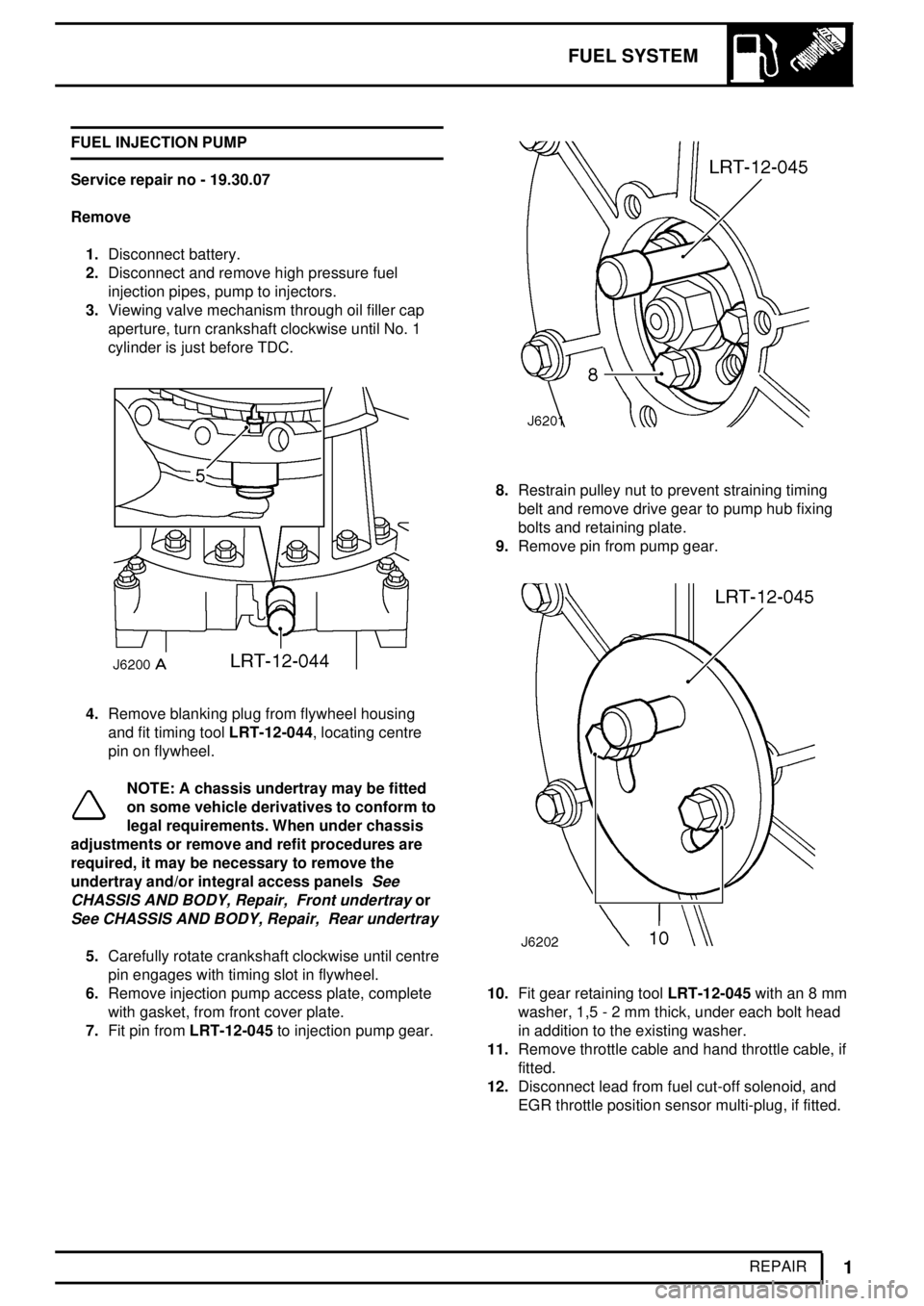
7.Fit pin fromLRT-12-045to injection pump gear.
8.Restrain pulley nut to prevent straining timing
belt and remove drive gear to pump hub fixing
bolts and retaining plate.
9.Remove pin from pump gear.
10.Fit gear retaining toolLRT-12-045with an 8 mm
washer, 1,5 - 2 mm thick, under each bolt head
in addition to the existing washer.
11.Remove throttle cable and hand throttle cable, if
fitted.
12.Disconnect lead from fuel cut-off solenoid, and
EGR throttle position sensor multi-plug, if fitted.
Page 105 of 455
FUEL SYSTEM
3
REPAIR FUEL INJECTORS
Service repair no - 19.60.10
Remove
NOTE: When a fuel injector is considered
to be the cause of irregular running and
loss of power it will be necessary to fit a
donor set of injectors to determine which injector
is at fault. DO NOT attempt to dismantle or carry
out spray tests on the fuel injectors. This work
can only carried out by authorised Bosch dealers.
1.Remove oil filler cap and release sound
insulation cover from top of engine.
2.Disconnect high pressure fuel supply pipes from
injectors and injection pump. Remove in pairs.
3.Disconnect spill return hose(s) from injectors.
4.Plug pipes and injector connections to prevent
the ingress of dirt and foriegn matter.5.Remove retaining nut and release each injector
clamp plate from cylinder head.
6.Remove injector and discard copper washer.
Refit
7.Ensure injectors and seating in cylinder head are
clean.
8.Lightly grease a new copper sealing washer and
position on each injector.
9.Fit injectors in cylinder head with spill return
outlets facing outward.
10.Secure injector with clamp plate and nut. Tighten
nut to
25 Nm (18 lbf/ft).
NOTE: The clamp plates are slightly
curved and should be fitted with the
convex side uppermost.
11.Fit the spill return pipe with a single copper
washer under the head of the banjo bolt and 2
copper washers fitted between the injector and
the banjo. Tighten banjo bolt to
10 Nm (7 lbf/ft).
12.Fit high pressure pipes to injectors and injection
pump. Tighten union nuts to
28 Nm (21 lbf/ft).
13.Fit sound insulation cover and oil filler cap.
Page 123 of 455
COOLING SYSTEM
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION COOLANT CIRCULATION
Operation
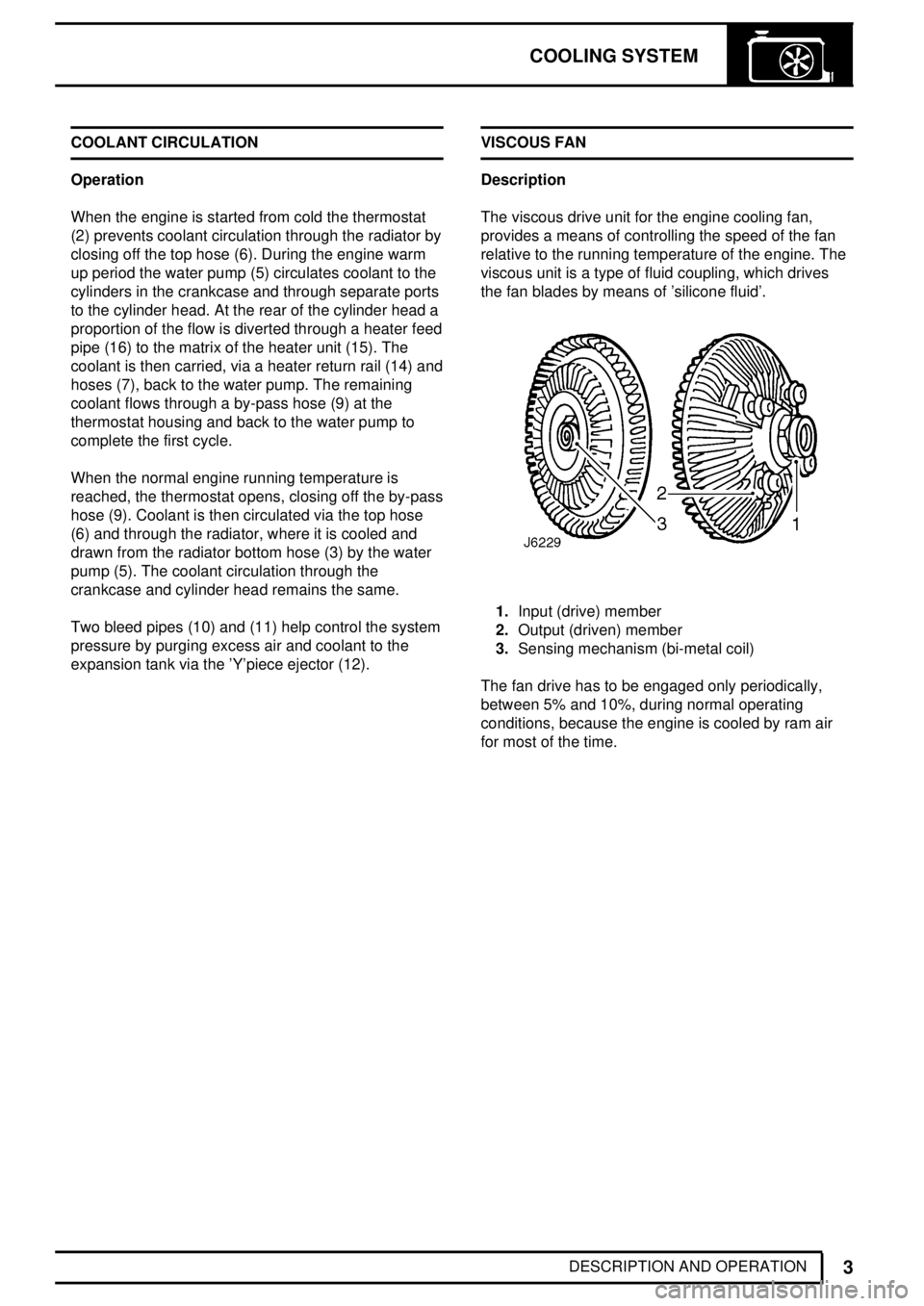
When the engine is started from cold the thermostat
(2) prevents coolant circulation through the radiator by
closing off the top hose (6). During the engine warm
up period the water pump (5) circulates coolant to the
cylinders in the crankcase and through separate ports
to the cylinder head. At the rear of the cylinder head a
proportion of the flow is diverted through a heater feed
pipe (16) to the matrix of the heater unit (15). The
coolant is then carried, via a heater return rail (14) and
hoses (7), back to the water pump. The remaining
coolant flows through a by-pass hose (9) at the
thermostat housing and back to the water pump to
complete the first cycle.
When the normal engine running temperature is
reached, the thermostat opens, closing off the by-pass
hose (9). Coolant is then circulated via the top hose
(6) and through the radiator, where it is cooled and
drawn from the radiator bottom hose (3) by the water
pump (5). The coolant circulation through the
crankcase and cylinder head remains the same.
Two bleed pipes (10) and (11) help control the system
pressure by purging excess air and coolant to the
expansion tank via the 'Y'piece ejector (12).VISCOUS FAN
Description
The viscous drive unit for the engine cooling fan,
provides a means of controlling the speed of the fan
relative to the running temperature of the engine. The
viscous unit is a type of fluid coupling, which drives
the fan blades by means of 'silicone fluid'.
1.Input (drive) member
2.Output (driven) member
3.Sensing mechanism (bi-metal coil)
The fan drive has to be engaged only periodically,
between 5% and 10%, during normal operating
conditions, because the engine is cooled by ram air
for most of the time.
Page 136 of 455

30MANIFOLD AND EXHAUST SYSTEM
2
REPAIR Refit
11.Fit new gasket over manifold studs.
12.Loosely fit induction manifold lower nuts to
studs.
13.Fit exhaust manifold and secure with central
upper and lower nuts.
14.Locate heater rail to its correct position and
secure with outer exhaust manifold nuts.
15.Tighten all exhaust manifold nuts to
45 Nm (33
lbf/ft).
16.Tighten exhaust front pipe to intermediate
silencer nuts to
50 Nm (37 lbf/ft).
17.Fit turbocharger outlet pipe.
18.Fit induction manifold
See Induction manifold
.EXHAUST MANIFOLD/TURBOCHARGER
ASSEMBLY
Service repair no - 30.15.10
Remove
1.Remove induction manifold
See Induction
manifold
.
2.Disconnect turbocharger inlet hose.
3.Disconnect boost pressure pipe at turbocharger.
4.Remove intercooler bottom hose.
5.Place suitable container under engine and
disconnect turbocharger oil feed and return
pipes at cylinder block.
6.Remove 3 nuts securing exhaust front pipe to
manifold flange.
7.Remove 7 nuts and lift exhaust manifold and
turbocharger assembly from cylinder head.
8.Discard manifold gasket.
Refit
9.Fit new manifold gasket.
10.Position exhaust manifold assembly onto
location studs and secure to cylinder head.
Tighten nuts to
45 Nm (33 lbf/ft).
11.Secure exhaust front pipe to manifold flange.
Tighten fixings to
50 Nm (37 lbf/ft).
12.Reconnect turbocharger oil feed and return
pipes at cylinder block.
13.Fit intercooler bottom hose.
14.Fit boost pressure pipe at turbocharger.
15.Fit turbocharger inlet hose.
16.Fit induction manifold
See Induction manifold
.
Page 142 of 455

CLUTCH
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS CLUTCH ASSEMBLY CONDITIONS
For the clutch to operate correctly it is important the
following conditions are satisfied:-
·The primary shaft (15) must be free in the
crankshaft spigot bush (17).
·The friction plate (2) must be able to slide easily on
the splines on the primary shaft (15), to a position
where it does not contact either the flywheel or the
pressure plate.
·The friction plate must not be distorted or the
linings contaminated with oil, which may cause it to
stick or continue to run in contact with the flywheel
or pressure plate.
A number of faults can develop in the operation of the
clutch for a variety of reasons and most faults are due
to normal wear at high mileage. Problems can also
occur if the unit has been renewed by an unskilled
operator.
Recognising and diagnosing a particular clutch fault is
therefore of paramount importance in ensuring that
the problem is rectified at the first attempt.
Problems which develop in the clutch are as follows:-
·Clutch spin/drag
·Clutch slip
·Clutch judder/fierceCLUTCH SPIN - DRAG
Symptoms
Clutch spin is that, with engine running and clutch
pedal depressed, the gears cannot be immediately
engaged without making a grinding noise. This
indicates the clutch is not making a clean break.
However, if the clutch pedal is held depressed for
several seconds the friction plate will eventually break
free from the engine and the gear will engage silently.
Clutch spin as it becomes more severe develops into
clutch drag, making the silent engagement of a gear
impossible, regardless of how long the pedal is held
depressed.
CLUTCH SLIP
Symptoms
Clutch slip is most evident climbing a hill or when the
vehicle is moving off from stationary with a heavy
load. As the clutch is released, slip occurs between
the engine and the transmission, allowing the engine
speed to increase without a corresponding increase in
vehicle speed.
Clutch slip can develop to the stage where no power
is transmitted through the clutch as the pedal is
released.
CLUTCH JUDDER - FIERCE
Symptoms
Clutch judder or fierce engagement, like slip, is most
likely to occur when the vehicle is moving off from
stationary. As the clutch pedal is released the vehicle
will move rapidly or in a series of jerks, which cannot
be controlled even by careful operation of the clutch
by the driver.
It should be noted that a vehicle may display all the
symptoms or any combination of the symptoms
described, depending on the driving conditions vehicle
load and operating temperatures.
Page 150 of 455
33CLUTCH
2
OVERHAUL
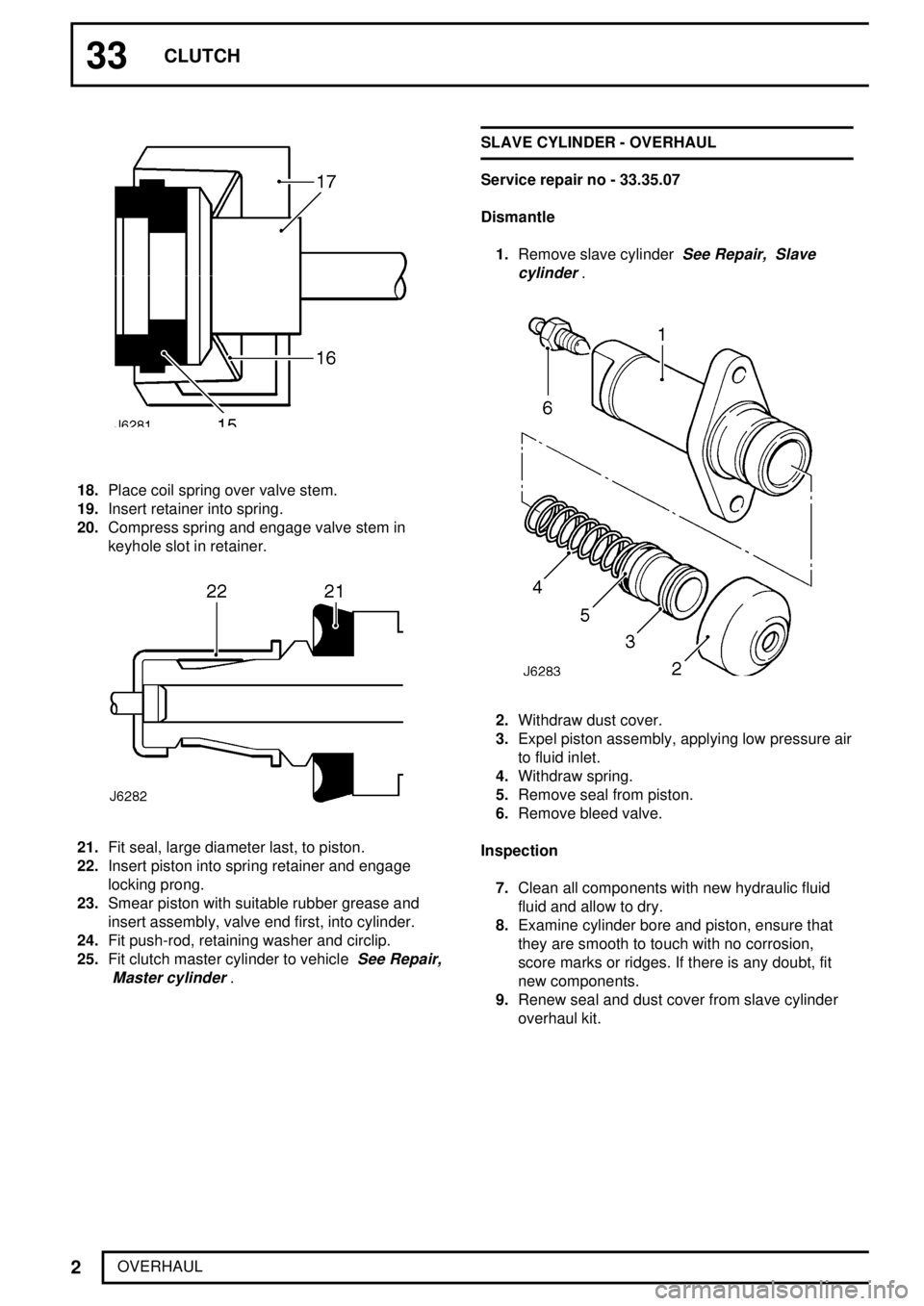
18.Place coil spring over valve stem.
19.Insert retainer into spring.
20.Compress spring and engage valve stem in
keyhole slot in retainer.
21.Fit seal, large diameter last, to piston.
22.Insert piston into spring retainer and engage
locking prong.
23.Smear piston with suitable rubber grease and
insert assembly, valve end first, into cylinder.
24.Fit push-rod, retaining washer and circlip.
25.Fit clutch master cylinder to vehicle
See Repair,
Master cylinder
.SLAVE CYLINDER - OVERHAUL
Service repair no - 33.35.07
Dismantle
1.Remove slave cylinder
See Repair, Slave
cylinder
.
2.Withdraw dust cover.
3.Expel piston assembly, applying low pressure air
to fluid inlet.
4.Withdraw spring.
5.Remove seal from piston.
6.Remove bleed valve.
Inspection
7.Clean all components with new hydraulic fluid
fluid and allow to dry.
8.Examine cylinder bore and piston, ensure that
they are smooth to touch with no corrosion,
score marks or ridges. If there is any doubt, fit
new components.
9.Renew seal and dust cover from slave cylinder
overhaul kit.
Page 152 of 455
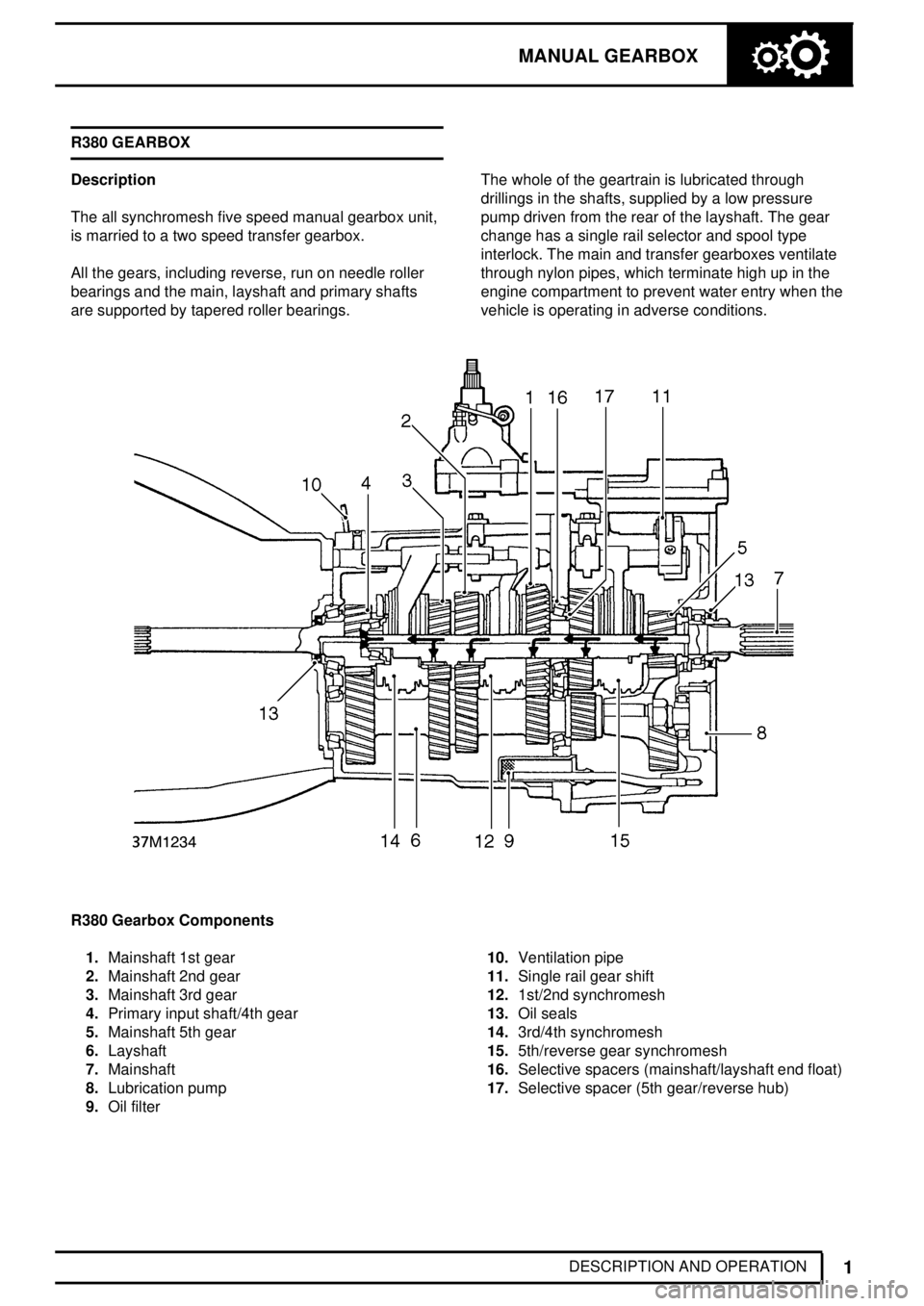
MANUAL GEARBOX
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION R380 GEARBOX
Description
The all synchromesh five speed manual gearbox unit,
is married to a two speed transfer gearbox.
All the gears, including reverse, run on needle roller
bearings and the main, layshaft and primary shafts
are supported by tapered roller bearings.The whole of the geartrain is lubricated through
drillings in the shafts, supplied by a low pressure
pump driven from the rear of the layshaft. The gear
change has a single rail selector and spool type
interlock. The main and transfer gearboxes ventilate
through nylon pipes, which terminate high up in the
engine compartment to prevent water entry when the
vehicle is operating in adverse conditions.
R380 Gearbox Components
1.Mainshaft 1st gear
2.Mainshaft 2nd gear
3.Mainshaft 3rd gear
4.Primary input shaft/4th gear
5.Mainshaft 5th gear
6.Layshaft
7.Mainshaft
8.Lubrication pump
9.Oil filter10.Ventilation pipe
11.Single rail gear shift
12.1st/2nd synchromesh
13.Oil seals
14.3rd/4th synchromesh
15.5th/reverse gear synchromesh
16.Selective spacers (mainshaft/layshaft end float)
17.Selective spacer (5th gear/reverse hub)
Page 182 of 455

REAR AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS FAULT DIAGNOSIS
Complaint - Oil leaks
An external leak of lubrication from the hub seals can
be caused by a faulty internal seal. For example, if the
seals which separate the differential from the hubs are
faulty and the vehicle is operating or parked on an
embankment, oil from the differential may flood one
hub resulting in a lack of lubrication in the differential.
When a seal is found to be leaking check the axle
ventilation system, as a blockage can cause internal
pressure to force oil past the seals.
See 'Description and Operation' for illustrations of oil
seal locations.
When investigating hub seal leaks check the grease
for dilution with oil. Also check the differential oil level,
for signs of metal particles in the oil and the condition
of internal seals.
If the vehicle is driven in deep water with defective oil
seals, water may contaminate the lubricants and raise
the differential oil level, giving a false impression that
the housing has been overfilled.
Do not assume that a high oil level in the
differential is due to over filling or, that a low level
is because of an external leak.
Page 208 of 455

FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS FAULT DIAGNOSIS
Complaint - Oil leaks
An external leak of lubrication can be caused by a
faulty internal seal. For example, if the seals which
separate the differential from the swivel housings are
faulty and the vehicle is operating or parked on an
embankment, oil may leak across the axle leaving one
swivel with a high level and the opposite swivel and
differential lacking lubrication.
See 'Description and Operation' for illustrations of oil
seal locations.
When investigating leaks or checking oil levels, it is
essential that all the lubrication is drained from any
housing with a high level and that the other levels are
checked.
Swivel oil should be checked for signs of grease
leaking from the hub bearings and oil contamination of
the hub grease.
Check that the axle ventilation system is clear, as a
blockage can cause internal pressure to force oil past
the seals.
If the vehicle is driven in deep water with defective oil
seals, water may contaminate the lubricants and when
checked, give a false impression that the housing has
been overfilled with oil.
Do not assume that a high oil level is due to over
filling or, that a low level is because of an external
leak.
Page 221 of 455

57STEERING
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Rotary valve misaligned
Demand for assistance (Valve misaligned)
When the steering wheel and input shaft is turned,
steering resistance transmitted to the worm causes
the torsion bar to be twisted and the valve ports to be
misaligned for a right or left turn. The misalignment of
the valve ports directs all fluid pressure A to one side
of the piston only and allows displaced fluid B on the
other side.
When demanding maximum assistance, any
excessive fluid output from the pump due to high
pump speed, will circulate through the regulator valve
located in the pump unit, causing the temperature of
the fluid and the pump to rise rapidly.CAUTION: To avoid excessive fluid
temperatures which could damage the oil
seals, the steering must not be held on full
lock for more than 30 seconds in one minute.
Only when the steering wheel, and the demand for
assistance, is released, will the torsion bar return the
valve to neutral, allowing the fluid to circulate through
the reservoir where it is cooled.
In the unlikely event of mechanical failure of the
torsion bar, a coarse splined connection (7) between
the input shaft and worm, ensures steering control is
maintained sufficient to allow the vehicle to be
recovered.