ABS LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996Pages: 455, PDF Size: 6.44 MB
Page 24 of 455

04GENERAL SPECIFICATION DATA
6
INFORMATION SHOCK ABSORBERS
Type Telescopic, double-acting non-adjustable.................................................................................
Bore diameter 35.47mm...................................................................
BRAKES
Front service brake
Caliper AP Lockheed, four opposed pistons..............................................................................
Operation Hydraulic, self adjusting.........................................................................
Disc 90 - Solid, outboard, 110/130 - Ventilated, outboard..................................................................................
Disc diameter 298 mm (11.73 in)...................................................................
Disc thickness 90 - 14,1 mm (0.56in), 110/130 - 24mm (0.95 in)..................................................................
Wear limit 1 mm (0.04in) per side of disc.........................................................................
Disc run-out maximum 0,15mm (0.006 in).....................................................
Pad area 58 cm
2(9.0 in2) ..........................................................................
Total swept area 801,3 cm2(124.2 in2) ...............................................................
Pad material Ferodo 3440 non asbestos.....................................................................
Pad minimum thickness 3 mm (0.12in)...................................................
Rear service brake
Caliper AP Lockheed opposed piston..............................................................................
Operation Hydraulic, self adjusting.........................................................................
Disc Solid, outboard..................................................................................
Disc diameter 90 - 290 mm (11.42 in), 110/130 - 298 mm (11.73)...................................................................
Disc thickness 90 - 12,5 mm (0.49 in), 110/130 - 14,1 mm (0.56 in)..................................................................
Wear limit 90 - 0,38 mm (0.015 in), 110/130 - 1,0 mm (0.04 in).........................................................................
per side of disc
Disc run-out maximum 0,15 mm (0.006 in).....................................................
Pad area 90 - 30,5 cm
2(4.37 in2), 110/130 - 36,2 cm2(5.61 in2) ..........................................................................
Total swept area 90 - 694 cm2(106.98 in2) ...............................................................
Pad material Ferodo 3440 non asbestos.....................................................................
Pad minimum thickness 3 mm (0.12 in)...................................................
Parking brake
Type Mechanical, cable operated drum brake on the rear of.................................................................................
the transfer gearbox output shaft
Drum internal diameter 254 mm (10.0 in).....................................................
Width 70 mm (2.75 in)................................................................................
Pad material Ferodo 3611 non asbestos.....................................................................
Servo/master cylinder
Manufacturer Lucas....................................................................
Servo type LSC 80........................................................................
Master cylinder type 25,4 mm (1.0 in) diameter, tandem.........................................................
Pressure reducing valve, failure conscious Cut-in pressure, 90 - 24 bar (360 Ibf/in
2) ratio 4.0:1, ......................
110 - 43 bar (645 Ibf/in2) ratio 2.9:1*
NOTE: * Pressure reducing valves are not fitted to all 110 specifications.
Page 34 of 455

07GENERAL FITTING REMINDERS
2
INFORMATION PREPARATION
1.Clean components and surrounding area prior to
removal.
2.Blank off any openings exposed by component
removal using greaseproof paper and masking
tape.
3.Immediately seal fuel, oil or hydraulic lines when
separated, using plastic caps or plugs, to
prevent loss of fluid and entry of dirt.
4.Close open ends of oilways, exposed by
component removal, with tapered hardwood
plugs or readily visible plastic plugs.
5.Immediately a component is removed, place it in
a suitable container; use a separate container for
each component and its associated parts.
6.Before dismantling a component, clean it
thoroughly with a recommended cleaning agent;
check that agent is suitable for all materials of
component.
7.Clean bench and provide marking materials,
labels, containers and locking wire before
dismantling a component.
DISMANTLING
1.Observe scrupulous cleanliness when
dismantling components, particularly when
brake, fuel or hydraulic system parts are being
worked on. A particle of dirt or a cloth fragment
could cause a dangerous malfunction if trapped
in these systems.
2.Blow out all tapped holes, crevices, oilways and
fluid passages with an air line. Ensure that any
O-rings used for sealing are correctly replaced or
renewed, if disturbed.
3.Use marking ink to identify mating parts, to
ensure correct reassembly. If a centre punch or
scriber is used they may initiate cracks or
distortion of components.
4.Wire together mating parts where necessary to
prevent accidental interchange (e.g. roller
bearing components).
5.Wire labels on to all parts which are to be
renewed, and to parts requiring further
inspection before being passed for reassembly;
place these parts in separate containers from
those containing parts for rebuild.
6.Do not discard a part due for renewal until it has
been compared with the new part, to ensure that
its correct replacement has been obtained.INSPECTION-GENERAL
1.Never inspect a component for wear or
dimensional check unless it is absolutely clean;
a slight smear of grease can conceal an incipient
failure.
2.When a component is to be checked
dimensionally against figures quoted for it, use
correct equipment (surface plates, micrometers,
dial gauges, etc.) in serviceable condition.
Makeshift checking equipment can be
dangerous.
3.Reject a component if its dimensions are outside
limits quoted, or if damage is apparent. A part
may, however, be refitted if its critical dimension
is exactly limit size, and is otherwise satisfactory.
4.Use 'Plastigauge' 12 Type PG-1 for checking
bearing surface clearances. Directions for its
use, and a scale giving bearing clearances in
0,0025 mm steps are provided with it.
Page 35 of 455
GENERAL FITTING REMINDERS
3
INFORMATION BALL AND ROLLER BEARINGS
CAUTION: Never refit a ball or roller
bearing without first ensuring that it is in a
fully serviceable condition.
1.Remove all traces of lubricant from bearing
under inspection by washing in a suitable
degreaser; maintain absolute cleanliness
throughout operations.
2.Inspect visually for markings of any form on
rolling elements, raceways, outer surface of
outer rings or inner surface of inner rings. Reject
any bearings found to be marked, since any
marking in these areas indicates onset of wear.
3.Holding inner race between finger and thumb of
one hand, spin outer race and check that it
revolves absolutely smoothly. Repeat, holding
outer race and spinning inner race.
4.Rotate outer ring gently with a reciprocating
motion, while holding inner ring; feel for any
check or obstruction to rotation, and reject
bearing if action is not perfectly smooth.
5.Lubricate bearing generously with lubricant
appropriate to installation.
6.Inspect shaft and bearing housing for
discolouration or other marking suggesting that
movement has taken place between bearing and
seatings. (This is particularly to be expected if
related markings were found in operation 2).
7.Ensure that shaft and housing are clean and free
from burrs before fitting bearing.8.If one bearing assembly of a pair shows an
imperfection it is generally advisable to replace
both with new bearings; an exception could be
made if the faulty bearing had covered a low
mileage, and it could be established that
damage was confined to it only.
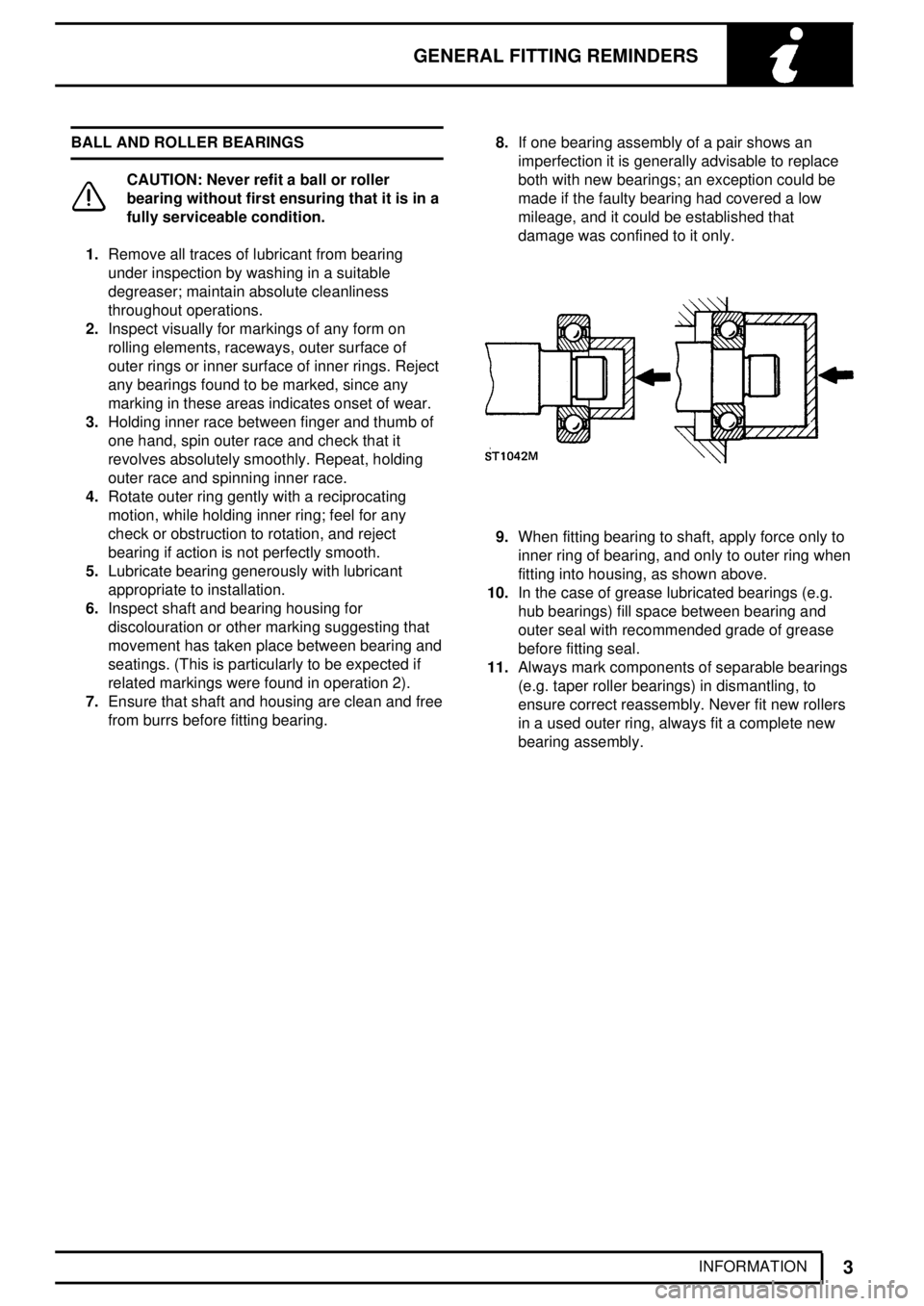
9.When fitting bearing to shaft, apply force only to
inner ring of bearing, and only to outer ring when
fitting into housing, as shown above.
10.In the case of grease lubricated bearings (e.g.
hub bearings) fill space between bearing and
outer seal with recommended grade of grease
before fitting seal.
11.Always mark components of separable bearings
(e.g. taper roller bearings) in dismantling, to
ensure correct reassembly. Never fit new rollers
in a used outer ring, always fit a complete new
bearing assembly.
Page 37 of 455

GENERAL FITTING REMINDERS
5
INFORMATION JOINTS AND JOINT FACES
1.Always use correct gaskets where they are
specified.
2.Use jointing compound only when
recommended. Otherwise fit joints dry.
3.When jointing compound is used, apply in a thin
uniform film to metal surfaces; take great care to
prevent it from entering oilways, pipes or blind
tapped holes.
4.Remove all traces of old jointing materials prior
to reassembly. Do not use a tool which could
damage joint faces.
5.Inspect joint faces for scratches or burrs and
remove with a fine file or oil stone; do not allow
removed material or dirt to enter tapped holes or
enclosed parts.
6.Blow out any pipes, channels or crevices with
compressed air, fit new 'O' rings or seals
displaced by air blast.FLEXIBLE HYDRAULIC PIPES, HOSES
1.Before removing any brake or power steering
hose, clean end fittings and area surrounding
them as thoroughly as possible.
2.Obtain appropriate plugs or caps before
detaching hose end fittings, so that ports can be
immediately covered to exclude dirt.
3.Clean hose externally and blow through with
airline. Examine carefully for cracks, separation
of plies, security of end fittings and external
damage. Reject any hose found faulty.
4.When refitting hose, ensure that no unnecessary
bends are introduced, and that hose is not
twisted before or during tightening of union nuts.
5.Containers for hydraulic fluid must be kept
absolutely clean.
6.Do not store brake fluid in an unsealed
container. It will absorb water, and fluid in this
condition would be dangerous to use due to a
lowering of its boiling point.
7.Do not allow brake fluid to be contaminated with
mineral oil, or use a container which has
previously contained mineral oil.
8.Do not re-use brake fluid bled from system.
9.Always use clean brake fluid to clean hydraulic
components.
10.Fit a cap to seal a hydraulic union and a plug to
its socket after removal to prevent ingress of dirt.
11.Absolute cleanliness must be observed with
hydraulic components at all times.
12.After any work on hydraulic systems, inspect
carefully for leaks underneath the vehicle while a
second operator applies maximum pressure to
the brakes (engine running) and operates the
steering.
Page 56 of 455

MAINTENANCE
13
MAINTENANCE REV: 05/992.When pure diesel is emitted, retighten drain
plug.
3.Disconnect fuel inlet pipe at sedimenter. Raise
and support pipe above level of fuel tank to
prevent fuel draining from tank.
4.Support sedimenter bowl, unscrew bolt and
remove bowl.
5.Remove sedimenter element.
6.Clean all components in kerosene.
7.Fit new seals.
8.Fit element into sedimenter bowl.
9.Secure bowl to sedimenter head.
10.Fit fuel inlet pipe to sedimenter.
11.Slacken drain plug and when pure diesel is
emitted, retighten plug.
12.If necessary, prime the system.
See FUEL SYSTEM, Adjustment, Priming
the fuel system
CHECK CONDITION OF ENGINE MOUNTING
RUBBERS
CHECK SECURITY OF TOWING BRACKET
FITTINGSCARRY OUT ROAD OR ROLLER TEST
WARNING: Two wheel roller tests MUST
NOT be carried out.
For details of dynamometer testing.
See
INTRODUCTION, Information, Dynamometer
testing
Check the following components:
1.Engine for excessive noise.
2.Clutch for slip, judder or spin/drag.
3.Gear selection/noise - high/low range.
4.Steering for abnormal noise/effort.
5.Steering for free play.
6.All instruments, gauges and warning indicators.
7.Heater and air conditioning systems.
8.Heated rear screen.
9.Shock absorbers - ride irregularities.
10.Foot brake, on emergency stop, pulling to one
side, binding and pedal effort.
11.Handbrake operation.
12.Seat reclining and latching.
13.Fully extend seat belt, check operation of
retraction and latching. Inertia belts lock when
snatched or vehicle on slope.
14.Road wheel balance.
15.Transmissions for vibrations.
16.Body noises, squeaks and rattles.
17.Excessive exhaust smoke.
18.Engine idle speed.
19.Endorse service record.
20.Report any unusual features of vehicle condition
and additional work required.
ENDORSE SERVICE RECORD
Page 60 of 455

ENGINE
1
REPAIR CYLINDER COMPRESSION TEST
Service repair no - 12.25.01
1.Start and run engine to normal operating
temperature.
2.Switch off engine.
3.Disconnect spill return hose and fuel pipe from
No.1 injector.
4.Remove retaining nut, release clamp and
withdraw injector from cylinder head.
See FUEL
SYSTEM, Repair, injectors
5.Disconnect electrical lead from fuel cut-off
solenoid at injection pump to prevent delivery of
fuel to injectors. On vehicles fitted with a digital
diesel shut-off valve (DDS) immobilisation
system, disconnect DDS multi-plug.
6.Ensure injector port is clean, If necessary, crank
the engine a few revolutions to remove any
loose carbon.
7.Fit dummy injector, from diesel compression
tester kitLRT-19-007, into the cylinder head and
clamp securely in position.
8.Connect flexible hose and gauge to dummy
injector as shown above.
9.Crank engine for 10-20 seconds and note
reading on gauge. The gauge will indicate the
compression of the cylinder and maintain the
reading until the pressure release valve on the
gauge is depressed.
Expected readings of a crank test, with vehicle
battery fully charged, compression ratio 19.5:1
should be 24 bar (348 lbf/in
2).10.Repeat test procedure for remaining clinders in
turn.
NOTE: A variation in compression
readings between cylinders is often a
better indication of an engine problem
than the absolute values of compression.
11.If compression is appreciably less than correct
reading, or varies by more than 10%, piston
rings or valves may be worn or damaged.
Low pressures in adjoining cylinders may
indicate a faulty cylinder head gasket.
Page 158 of 455
MANUAL GEARBOX
1
REPAIR REV: 05/99 R380 GEARBOX
Service repair no - 37.20.51
Remove
The R380 gearbox should be removed from
underneath the vehicle, using a hydraulic hoist and
support plateLRT-99-007.
WARNING: Where the use of a
transmission hoist is necessary, it is
absolutely essential to follow the
manufacturer's instructions to ensure safe and
effective use of equipment.
NOTE: A chassis undertray may be fitted
on some vehicle derivatives to conform to
legal requirements. When under chassis
remove and refit procedures are required, it may
be necessary to remove the undertray
See
CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair, Front undertray
or
See CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair, Rear undertray
.
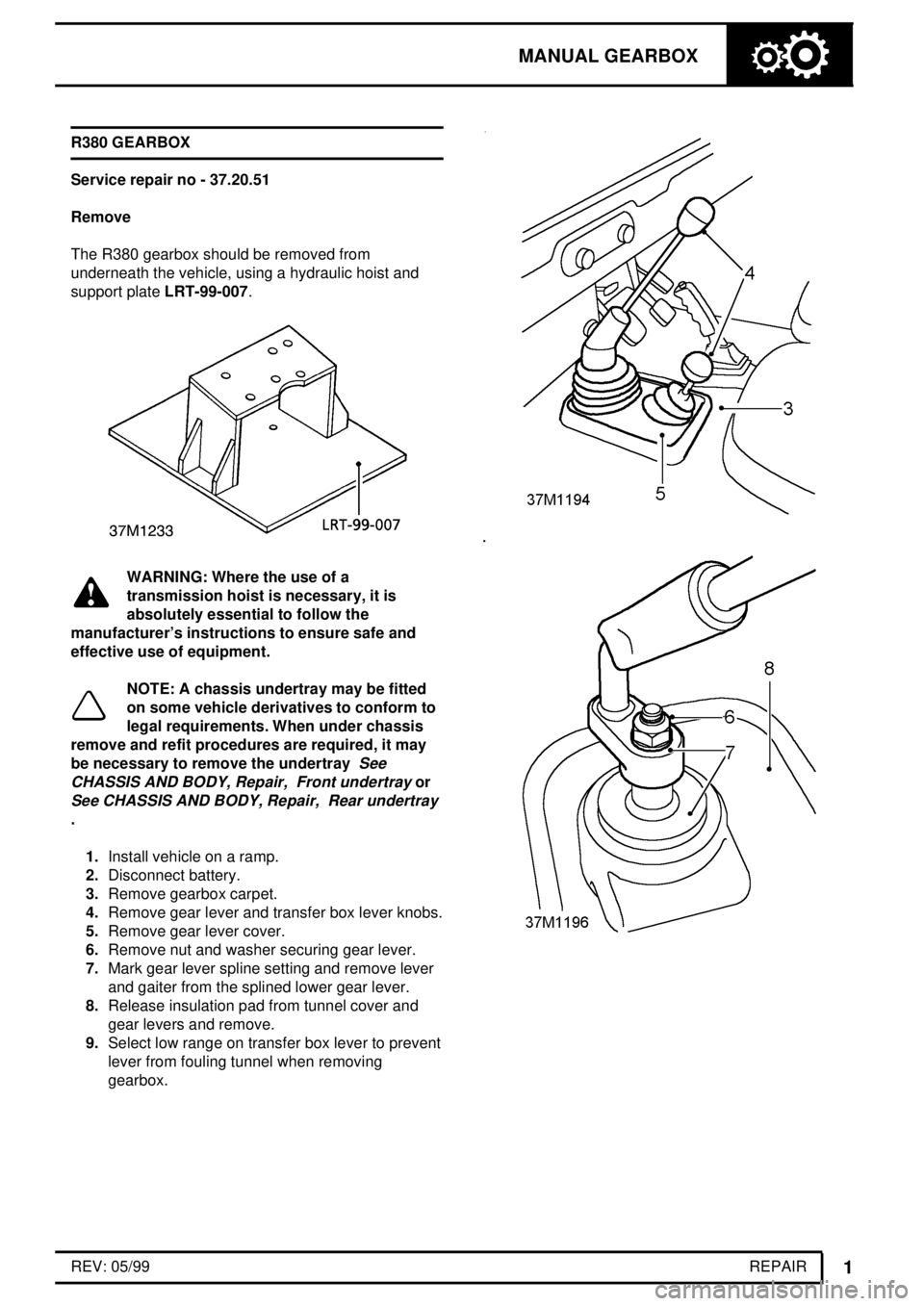
1.Install vehicle on a ramp.
2.Disconnect battery.
3.Remove gearbox carpet.
4.Remove gear lever and transfer box lever knobs.
5.Remove gear lever cover.
6.Remove nut and washer securing gear lever.
7.Mark gear lever spline setting and remove lever
and gaiter from the splined lower gear lever.
8.Release insulation pad from tunnel cover and
gear levers and remove.
9.Select low range on transfer box lever to prevent
lever from fouling tunnel when removing
gearbox.
Page 168 of 455

TRANSFER GEARBOX
1
REPAIR TRANSFER GEARBOX
Service repair no - 41.20.25
Remove
The transfer gearbox should be removed from
underneath the vehicle, using a hydraulic hoist and
adaptor plateLRT-99-010.
WARNING: Where use of a transmission
hoist is necessary, it is absolutely
essential to follow the manufacturers'
instructions to ensure safe and effective use of
the equipment.
NOTE: A chassis undertray may be fitted
on some vehicle derivatives to conform to
legal requirements. When under chassis
remove and refit procedures are required, it may
be necessary to remove the undertray
See
CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair, Front undertray
or
See CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair, Rear undertray
.
1.Position vehicle on a ramp.
2.Select LOW range gear and leave vehicle in
neutral.
3.Disconnect battery.
4.Remove front, centre, seat cushion, or cubby
box
See CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair,
Cubby box
.
5.If fitted, disconnect multi-plug from EGR control
unit located on base of seat cushion or cubby
box.
6.Remove 4 screws securing centre access panel
to seat or cubby box base.
7.Release EGR and alarm system diagnostic
connector mounting bracket.
8.Lift up access panel, complete with diagnostic
connector harness, and place aside.
9.Remove breather pipe union from transfer
gearbox high/low cross-shaft housing.
10.Remove retaining clip and disconnect high/low
lever from operating rod.
Page 183 of 455

REAR AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
1
REPAIR REAR AXLE
Service repair no - 51.25.01
Remove
WARNING: Remove and refit of axle
requires a further two persons to steady
the axle when lowering or repositioning
axle.
1.Drain brake system.
2.Support chassis rear.
3.Remove road wheels.
4.Support axle weight with hydraulic jack.
5.Disconnect shock absorbers.
6.Disconnect flexible brake hose at RH chassis
side member and breather hose at banjo
connection on axle casing.
7.Disconnect lower links at axle.8.Mark differential and propeller shaft flanges with
identification marks for assembly.
9.Remove 4 nuts and bolts, lower propeller shaft
and tie to one side.
10.Disconnect pivot bracket ball joint at axle
bracket.
11.Release bolts and remove coil spring retaining
plates.
12.Lower axle and remove road springs.
13.If applicable, remove anti-roll bar links at axle
See REAR SUSPENSION, Repair, anti-roll
bar
.
14.Remove axle assembly.
Page 184 of 455

51REAR AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
2
REPAIRREV: 05/99 Refit
15.Position axle and fit lower links. Tighten fixings
to
176 Nm (130 lbf/ft).
16.If applicable, fit anti-roll bar links to axleSee
REAR SUSPENSION, Repair, Anti-roll bar
links
.
17.Raise axle and locate road springs.
18.Fit coil spring retaining plates and secure with
fixing bolts.
19.Secure pivot bracket ball joint to axle bracket.
Tighten fixing to
176 Nm (130 lbf/ft).
20.Align propeller shaft to differential drive flange
and tighten fixings to
47 Nm (35 lbf/ft).
21.Reconnect flexible brake hose and axle breather
hose.
22.Refit shock absorbers.
23.Fit road wheels and tighten to correct torque:
Alloy wheels -
130 Nm (96 lbf/ft)
Steel wheels -100 Nm (80 lbf/ft)
Heavy Duty wheels -170 Nm (125 lbf/ft)
24.Remove rear chassis support.
25.Bleed brake system
See BRAKES, Repair,
brake system bleed
.