differential LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996Pages: 455, PDF Size: 6.44 MB
Page 10 of 455

INTRODUCTION
5
INFORMATION JACKING
The following instructions must be carried out before
raising the vehicle off the ground.
1.Use a solid level ground surface.
2.Apply parking brake.
3.Select 1st gear in main gearbox.
4.Select Low range in transfer gearbox.
CAUTION: To avoid damage occurring to
the under body components of the vehicle
the following jacking procedures must be
adhered to.
DO NOT POSITION JACKS OR AXLE STANDS
UNDER THE FOLLOWING COMPONENTS.
Body structure
Bumpers
Fuel lines
Brake lines
Front radius arms
Panhard rod
Steering linkage
Rear Trailing links
Fuel tank
Engine sump
Gearbox bell housing
Jack or support vehicle by axles only.
Vehicle jack
The jack provided with the vehicle is only intended to
be used in an emergency, for changing a tyre. Do
NOTuse the jack for any other purpose. Refer to
Owner's Manual for vehicle jack location points and
procedure. Never work under a vehicle supported by
the vehicle jack.
Hydraulic jack
A hydraulic jack with a minimum 1500 kg, 3,300 lbs
load capacity must be used, see J6083.
CAUTION: Do not commence work on the
underside of the vehicle until suitable axle
stands have been positioned under the
axle, see J6084.
Raise the front of the vehicle
1.Position cup of hydraulic arm under differential
casing.
NOTE: The differential casing is not
central to the axle. Care should be taken
when raising the front road wheels off the
ground as the rear axle has less sway stiffness.
2.Raise front road wheels to enable an axle stand
to be installed under left hand axle tube.
Page 11 of 455

01INTRODUCTION
6
INFORMATION 3.Position an axle stand under right hand axle
tube, carefully lower jack until axle sits securely
on both axle stands, remove trolley jack.
4.Before commencing work on underside of
vehicle re-check security of vehicle on stands.
5.Reverse procedure when removing vehicle from
stands.
Raise rear of vehicle
1.Position cup of hydraulic arm under differential
casing.
2.Raise vehicle to enable axle stands to be
installed under left and right hand axle tubes.
3.Lower jack until axle sits securely on axle
stands, remove trolley jack.
4.Before commencing work on underside of
vehicle re-check security of vehicle on stands.
5.Reverse procedure when removing vehicle from
stands.
HYDRAULIC VEHICLE RAMP (FOUR POST)
Use only a 'drive on' type ramp which supports vehicle
on its road wheels. If a 'wheel-free' condition is
required, use a 'drive on' ramp incorporating a
'wheel-free' system providing support beneath axle
casings. Alternatively, place vehicle on a firm, flat floor
and support on axle stands.
TWO POST VEHICLE RAMPS
The manufacturer of LAND ROVER VEHICLES
DOES NOT recommend using 'Two Post' ramps
that employ four adjustable support arms. These
are NOT considered safe for Land Rover vehicles.
If vehicle is installed on a Two Post ramp
responsibility for safety of vehicle and personnel
performing service operations is in the hands of
the Service Provider.DYNAMOMETER TESTING
The front and rear axles cannot be driven
independently.
WARNING: DO NOT attempt to drive
individual wheels with vehicle supported
on floor jacks or stands.
Four wheel dynamometers
Provided that front and rear dynamometer rollers are
rotating at identical speeds and that normal workshop
safety standards are applied, there is no speed
restriction during testing except any that may apply to
the tyres.
Two wheel dynamometers
IMPORTANT: Use a four wheel dynamometer for
brake testing if possible.
If brake testing on a single axle rig is necessary it
must be carried out with propeller shaft to rear axle
removed, AND neutral selected in BOTH main
gearbox and transfer gearbox. When checking brakes,
run engine at idle speed to maintain servo vacuum.
If checking engine performance, the transfer box must
be in high range and propeller shaft to stationary axle
must be removed.
Page 21 of 455

GENERAL SPECIFICATION DATA
3
INFORMATION FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel lift pump type Mechanical with hand primer............................................................
Fuel lift pump pressure 42 - 55 Kgf/cm
2(3 - 4 lbf/in2) at 1800 rpm .....................................................
Fuel filter Paper element in disposable canister..........................................................................
Air cleaner Paper element type........................................................................
COOLING SYSTEM
System type Pressurised, spill return, thermostatically controlled.....................................................................
water and anti freeze mixture. Pump assisted thermo
syphon. Coolant radiator combined with oil cooler and
turbo intercooler.
Cooling fan 11 blade axial flow 433 mm diameter, 1.29:1 drive.......................................................................
ratio, with viscous coupling.
Pump type Centrifugal, impellor, belt driven........................................................................
Thermostat opening 88°C .........................................................
Expansion tank cap pressure 1,06 Kgf/cm
2(15 Ibf/in2) (system pressure) ...........................................
CLUTCH
Type Valeo diaphragm spring.................................................................................
Centre plate diameter 235 mm.......................................................
Facing material Verto F202 grooved.................................................................
Release bearing Ball journal...............................................................
TRANSMISSION
Main gearbox
Type R380 Single helical constant mesh.......................................................................
Speeds 5 forward, 1 reverse, all synchromesh.............................................................................
Transfer box
Type LT230 Two speed reduction on main gearbox output. Front......................................................................
and rear drive permanently engaged via a lockable
differential
Rear axle
Type Spiral bevel, fully floating shafts.................................................................................
Ratio 3.54:1.................................................................................
Page 42 of 455

LUBRICANTS, FLUIDS AND CAPACITIES
3
INFORMATION REV: 05/99 CAPACITIES
The following capacity figures are approximate and are provided as a guide only.
Capacities (approx.)* Litres Pints
Engine sump oil 5,8................................................................ 10.20
Extra when refilling after fitting new filter 0,85.......................... 1.50
Manual gearbox 2,67............................................................... 4.70
Transfer gearbox oil 2,30......................................................... 4.00
Front differential 1,70............................................................... 3.00
Rear differential 1,70................................................................ 3.00
Power steering box and reservoir LHD 2,90............................ 5.00
Power steering box and reservoir RHD 3,40............................ 6.00
Swivel pin housing oil/grease (each) 0,35................................ 0.60
Fuel tank usable fuel 79,5........................................................ 17.5 gall
Cooling system 11,50................................................................ 20.20
Washer bottle 3,0................................................................... 5.28
NOTE: * All levels must be checked by dipstick or level plugs as applicable.
ANTI-FREEZE
PERCENTAGE CONCENTRATION - 50%
PROTECTION - LOWER TEMPERATURE LIMIT
Complete protection
Vehicle may be driven away immediately from cold,
-33°C (-36°F).
Safe limit protection
Coolant in semi-frozen state. Engine may be started
and driven away after warm-up period, -41°C (-42°
F).Lower protection
Prevents frost damage to cylinder head, block and
radiator. Thaw out before starting engine, -47°C (-53°
F).
CAUTION: Anti-freeze content must never
be allowed to fall below 25% (pre 99MY) or
50% (99MY on) otherwise damage to the
engine is liable to occur. Anti-freeze content
should not exceed 60% (all models) as this will
greatly reduce cooling efficiency.
Page 124 of 455

26COOLING SYSTEM
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Operation
To engage and disengage the fan drive the bi-metal
coil senses air temperature behind the radiator. When
a pre-determined temperature is reached, the coil
opens a valve (5) which allows fluid to enter the drive
area and, due to centrifugal force, circulates to the
annular drive area.
There are two sets of annular grooves (3), one in the
drive clutch and the other in the drive body, a specific
clearance being provided between the two sets of
grooves.
Viscous unit disengaged (engine at normal
running temperature)
1.Input (drive) member
2.Output (driven) member
3.Running clearance
4.Pump plate
5.Valve (closed)
6.Sensing mechanism (bi-metal coil)
7.Fluid seal
8.Bearing, input member
9.Fluid chamber
10.Fluid reservoirWhen this clearance is filled with viscous fluid, a
shearing action, caused by the speed differential
between the two drive components, transmits torque
to the fan. The fluid is thrown to the outside of the unit
by centrifugal force from where it is recirculated to the
reservoir (10) via the pump plate (4) adjacent to the
drive member.
If the engine speed is increased the amount of slip will
also increase to limit the maximum fan speed.
When the air temperature from the radiator drops
sufficiently, the bi-metal coil closes the valve and
prevents fluid entering the drive area. The fluid that is
in the drive area will gradually pump out into the
reservoir (10) and the fan will return to an idle
condition.
Viscous unit engaged (hot running temperature)
Bi-metal coil (6) expanded, valve (5) open.
Page 161 of 455
37MANUAL GEARBOX
4
REPAIR
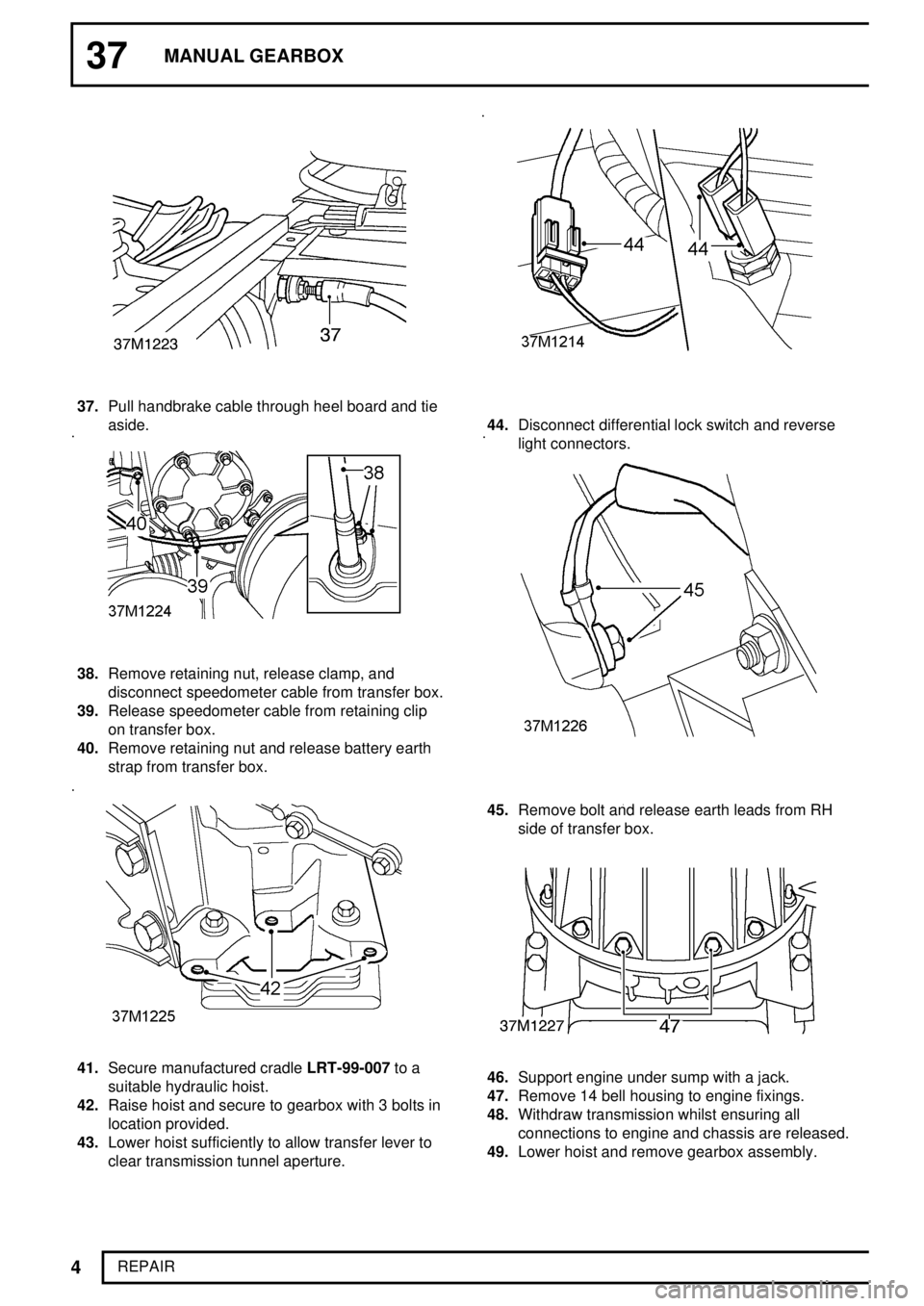
37.Pull handbrake cable through heel board and tie
aside.
38.Remove retaining nut, release clamp, and
disconnect speedometer cable from transfer box.
39.Release speedometer cable from retaining clip
on transfer box.
40.Remove retaining nut and release battery earth
strap from transfer box.
41.Secure manufactured cradleLRT-99-007to a
suitable hydraulic hoist.
42.Raise hoist and secure to gearbox with 3 bolts in
location provided.
43.Lower hoist sufficiently to allow transfer lever to
clear transmission tunnel aperture.
44.Disconnect differential lock switch and reverse
light connectors.
45.Remove bolt and release earth leads from RH
side of transfer box.
46.Support engine under sump with a jack.
47.Remove 14 bell housing to engine fixings.
48.Withdraw transmission whilst ensuring all
connections to engine and chassis are released.
49.Lower hoist and remove gearbox assembly.
Page 162 of 455
MANUAL GEARBOX
5
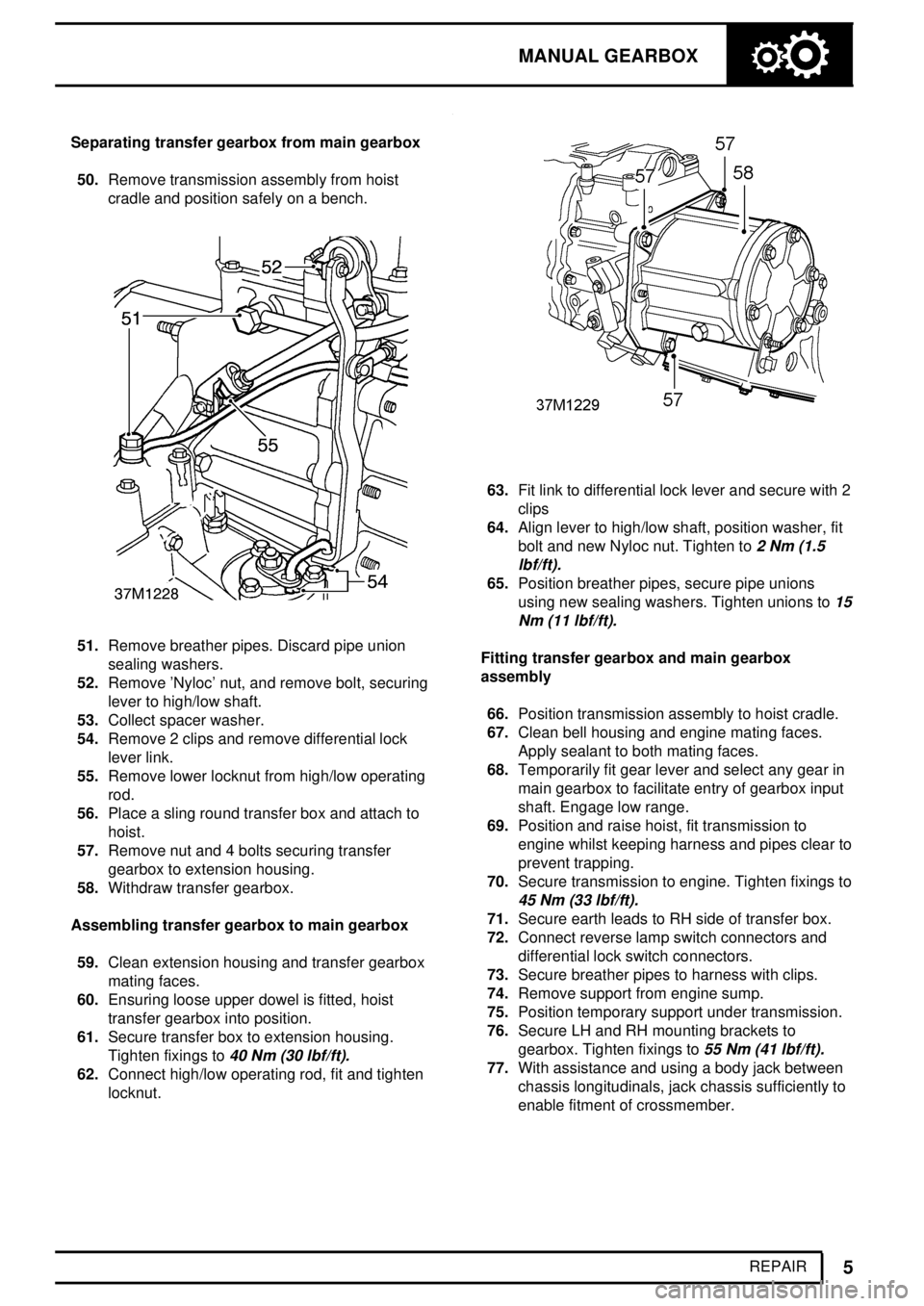
REPAIR Separating transfer gearbox from main gearbox
50.Remove transmission assembly from hoist
cradle and position safely on a bench.
51.Remove breather pipes. Discard pipe union
sealing washers.
52.Remove 'Nyloc' nut, and remove bolt, securing
lever to high/low shaft.
53.Collect spacer washer.
54.Remove 2 clips and remove differential lock
lever link.
55.Remove lower locknut from high/low operating
rod.
56.Place a sling round transfer box and attach to
hoist.
57.Remove nut and 4 bolts securing transfer
gearbox to extension housing.
58.Withdraw transfer gearbox.
Assembling transfer gearbox to main gearbox
59.Clean extension housing and transfer gearbox
mating faces.
60.Ensuring loose upper dowel is fitted, hoist
transfer gearbox into position.
61.Secure transfer box to extension housing.
Tighten fixings to
40 Nm (30 lbf/ft).
62.Connect high/low operating rod, fit and tighten
locknut.
63.Fit link to differential lock lever and secure with 2
clips
64.Align lever to high/low shaft, position washer, fit
bolt and new Nyloc nut. Tighten to
2 Nm (1.5
lbf/ft).
65.Position breather pipes, secure pipe unions
using new sealing washers. Tighten unions to
15
Nm (11 lbf/ft).
Fitting transfer gearbox and main gearbox
assembly
66.Position transmission assembly to hoist cradle.
67.Clean bell housing and engine mating faces.
Apply sealant to both mating faces.
68.Temporarily fit gear lever and select any gear in
main gearbox to facilitate entry of gearbox input
shaft. Engage low range.
69.Position and raise hoist, fit transmission to
engine whilst keeping harness and pipes clear to
prevent trapping.
70.Secure transmission to engine. Tighten fixings to
45 Nm (33 lbf/ft).
71.Secure earth leads to RH side of transfer box.
72.Connect reverse lamp switch connectors and
differential lock switch connectors.
73.Secure breather pipes to harness with clips.
74.Remove support from engine sump.
75.Position temporary support under transmission.
76.Secure LH and RH mounting brackets to
gearbox. Tighten fixings to
55 Nm (41 lbf/ft).
77.With assistance and using a body jack between
chassis longitudinals, jack chassis sufficiently to
enable fitment of crossmember.
Page 165 of 455

TRANSFER GEARBOX
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION TRANSFER GEARBOX
Description
The transfer gearbox is a permanent 4 wheel drive,
two speed ratio reducing gearbox, incorporating high
and low range outputs with mechanically lockable
centre differential (diff-lock). High/low range and
diff-lock selection are made via a single lever located
forward of the main gear lever.
The transfer gearbox is mounted at the rear of the
main gearbox, the mainshaft of which extends into the
transfer casing. A transfer gear, supported on taper
roller bearings and splined to the gearbox mainshaft,
passes the drive to an intermediate gear cluster
supported on a single shaft and rotating on taper roller
bearings.The intermediate gears pass the drive to high and low
speed gears on the rear output shaft. The rear output
shaft passes through the speedo drive housing, which
also forms the mounting for the transmission brake. A
worm gear fitted to the rear output shaft drives a
pinion fitted in the speedo housing.
Integral with the output shafts is a differential
assembly which compensates for speed differences
between the front and rear prop shafts. To prevent all
the power being transmitted to the axle offering the
least resistance, a diff-lock is provided. The differential
lock should only be engaged during severe off-road
conditions and should be disengaged as soon as
conditions permit. Selection of differential lock
engages, through mechanical linkage, a dog clutch
with the front output shaft, this action locks the centre
differential and provides a fixed drive, giving equal
power to the front and rear output shafts.
Page 169 of 455

41TRANSFER GEARBOX
2
REPAIR
11.Remove 3 trim studs and lift up handbrake
gaiter.
12.Remove split pin, clevis pin, washer and
disconnect cable from handbrake lever. Ensure
handbrake is off.
13.Release handbrake outer cable from heelboard.
14.Remove fan cowl
See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair, Fan cowl
.
15.Raise vehicle on ramp.
16.Drain transfer box oil
See SECTION 10,
Maintenance, Under vehicle maintenance
.
17.Remove intermediate silencer.
See MANIFOLD
AND EXHAUST SYSTEM, Repair,
Intermediate pipe - 90
orSee MANIFOLD
AND EXHAUST SYSTEM, Repair,
Intermediate pipe - 110/130
.
18.Mark rear propeller shaft drive flange and
transmission brake drum for reassembly.
19.Remove 4 nuts, disconnect propeller shaft from
brake drum, and tie aside.
20.Mark front propeller shaft drive flange and
transfer box output flange for reassembly.
21.Remove 4 nuts, disconnect propeller shaft from
transfer box, and tie aside.
22.Remove retaining clip at lower end of pivot arm
and disconnect differential lock control operating
rod.
Page 170 of 455

TRANSFER GEARBOX
3
REPAIR 23.Position 4, 30 mm (1.25 in), spacers between
top of hoist and adaptor plate,LRT-99-010,at
securing points and secure adaptor plate to
hoist.
24.Remove 4 central bolts from transfer box bottom
cover, move hoist into position and secure
adaptor plate to transfer box.
25.Adjust hoist to take weight of transfer box.
26.Remove nut securing transfer box LH mounting
rubber to chassis crossmember.
27.Remove 4 nuts and bolts securing chassis
crossmember to chassis longitudinal.
28.Remove nut securing transfer box RH mounting
rubber to chassis crossmember.
29.Remove 4 nuts and bolts securing chassis
crossmember to chassis longitudinal.
30.With assistance and using a body jack between
chassis longitudinals, jack chassis sufficiently to
enable removal of crossmember.
31.Remove chassis crossmember.
32.Remove 4 bolts from both sides and remove LH
and RH mounting brackets from transfer box.
33.Disconnect electrical leads from differential lock
switch.
34.Move the small cranked lever, for high/low
selector, upward to allow access to adjacent nut
securing transfer box to main gearbox.
35.Position a jack to support main gearbox.
CAUTION: Use a block of wood or hard
rubber pad to protect gearbox.