engine LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999Pages: 667, PDF Size: 8.76 MB
Page 331 of 667

33CLUTCH
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION The dual mass flywheel is bolted on the rear of the crankshaft with eight bolts. A dowel on the crankshaft flange
ensures that the flywheel is correctly located. A ring gear is fitted on the outer diameter of the flywheel. The ring
gear is not serviceable. Thirty blind holes are drilled in the outer diameter of the flywheel adjacent to the ring gear.
The holes are positioned at 10°intervals with four 20°spaces. The holes are used by the crankshaft position
sensor for engine management.
The dual mass flywheel is used to insulate the gearbox from torsional and transient vibrations produced by the
engine. The flywheel comprises primary and secondary flywheels with the drive between the two transferred by a
torsional damper which comprises four coil springs. The springs are located in the inside diameter of the primary
flywheel. Two of the springs are of smaller diameter and fit inside the larger diameter springs.
The primary flywheel locates the ring gear and is attached to the crankshaft flange with eight bolts. The two pairs
of coil springs are located in a recess in the flywheel between two riveted retainers. A roller bearing is pressed
onto the central boss of the primary flywheel and retained with a riveted plate. The bearing provides the mounting
for the secondary flywheel.
The secondary flywheel comprises two parts; an outer flywheel which provides the friction surface for the clutch
drive plate and an inner drive plate which transfers the drive from the primary flywheel, via the coil springs, to the
outer flywheel. The two components of the secondary flywheel are secured to each other with rivets. The inner
drive plate is located between the two pairs of coil springs and can rotate on the ball bearing in either direction
against the combined compression force of the four coil springs. Under high torque loading conditions the
secondary flywheel can rotate in either direction up to 70°in relation to the primary flywheel.
The operating face of the secondary flywheel is machined to provide a smooth surface for the drive plate to
engage on. Three dowels and six studs and nuts provide for the location and attachment of the pressure plate.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 335 of 667

33CLUTCH
12
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OPERATION
Hydraulic operation
When the clutch pedal is depressed, the master cylinder piston is pushed into the master cylinder. The movement
of the piston pressurises the fluid in the master cylinder, forcing the pressurised fluid into the hydraulic feed pipe to
the slave cylinder. The hydraulic pressure is felt at the slave cylinder piston which moves under the hydraulic force
applied, pushing the clutch release lever via the piston rod.
When the clutch pedal is released, the force applied to the release lever by the fingers of the diaphragm, moves
the release lever, which pushes the slave cylinder piston into the cylinder. The displaced hydraulic fluid is pushed
up the hydraulic feed pipe and returns to the master cylinder.
Mechanism operation
When the clutch pedal is depressed, hydraulic pressure extends the piston and rod in the slave cylinder. The
extension of the piston pushes the rod against the outer end of the release lever which pivots around the ball
spigot.
The inner end of the release lever pivots towards the engine applying pressure to the release bearing. The release
bearing slides along the release bearing sleeve and pushes on the fingers of the diaphragm. The diaphragm
pivots around the chamfered rivets in the cover. As the diaphragm is deflected, it removes pressure from the
pressure plate. The pressure plate moves away from the drive plate assisted by the three leaf springs.
The removal of force from the pressure plate on the drive plate reduces the friction between the dual mass
flywheel, drive plate and pressure plate. The drive plate slips between the flywheel and the pressure plate
preventing rotary movement being transferred from the flywheel and pressure plate to the primary driveshaft.
When the clutch pedal is released, hydraulic force is removed from the piston in the slave cylinder. This allows the
fingers of the diaphragm to push the release bearing along the release bearing sleeve. The movement of the
release bearing moves the release lever which pivots on the ball spigot, pushing the piston and rod back into the
slave cylinder.
The removal of pressure from the release bearing on the diaphragm, causes the diaphragm to pivot around the
chamfered rivets in the cover. The force applied to the pressure plate from the diaphragm overcomes the force of
the leaf springs and the pressure plate moves towards the drive plate and flywheel.
The pressure plate applies pressure to the drive plate which is pushed against the flywheel. As the clutch pedal is
progressively released, the friction between the drive plate, flywheel and pressure plate increases. The increase in
friction transfers the rotary movement of the flywheel and pressure plate to the drive plate, which in turn starts to
rotate the primary drive shaft. When the clutch pedal is released fully, the force applied by the diaphragm to the
pressure plate forces the drive plate onto the flywheel with no slippage.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 353 of 667
37MANUAL GEARBOX
8
REPAIR
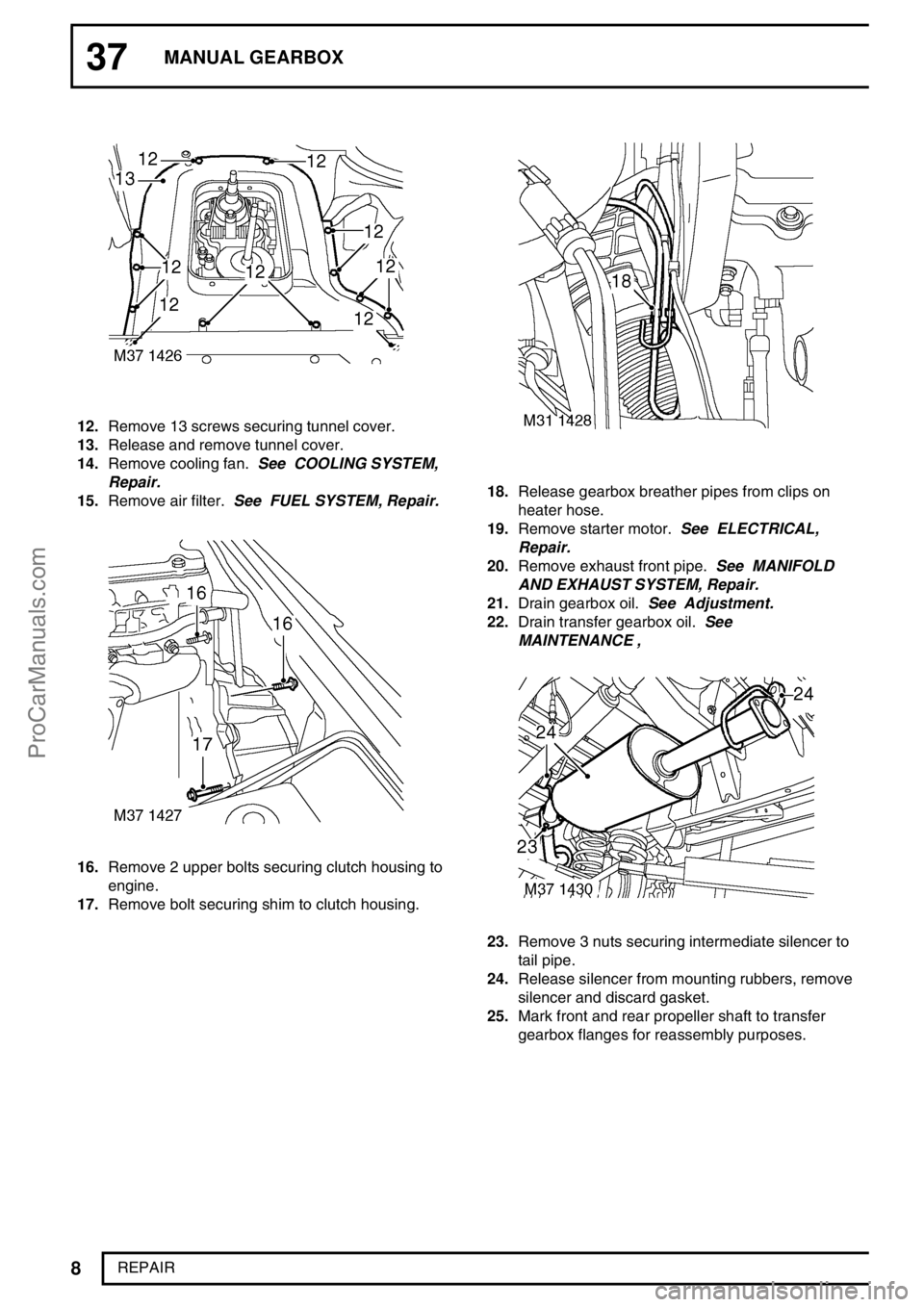
12.Remove 13 screws securing tunnel cover.
13.Release and remove tunnel cover.
14.Remove cooling fan.See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair.
15.Remove air filter.See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair.
16.Remove 2 upper bolts securing clutch housing to
engine.
17.Remove bolt securing shim to clutch housing.
18.Release gearbox breather pipes from clips on
heater hose.
19.Remove starter motor.See ELECTRICAL,
Repair.
20.Remove exhaust front pipe.See MANIFOLD
AND EXHAUST SYSTEM, Repair.
21.Drain gearbox oil.See Adjustment.
22.Drain transfer gearbox oil.See
MAINTENANCE ,
23.Remove 3 nuts securing intermediate silencer to
tail pipe.
24.Release silencer from mounting rubbers, remove
silencer and discard gasket.
25.Mark front and rear propeller shaft to transfer
gearbox flanges for reassembly purposes.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 355 of 667
37MANUAL GEARBOX
10
REPAIR
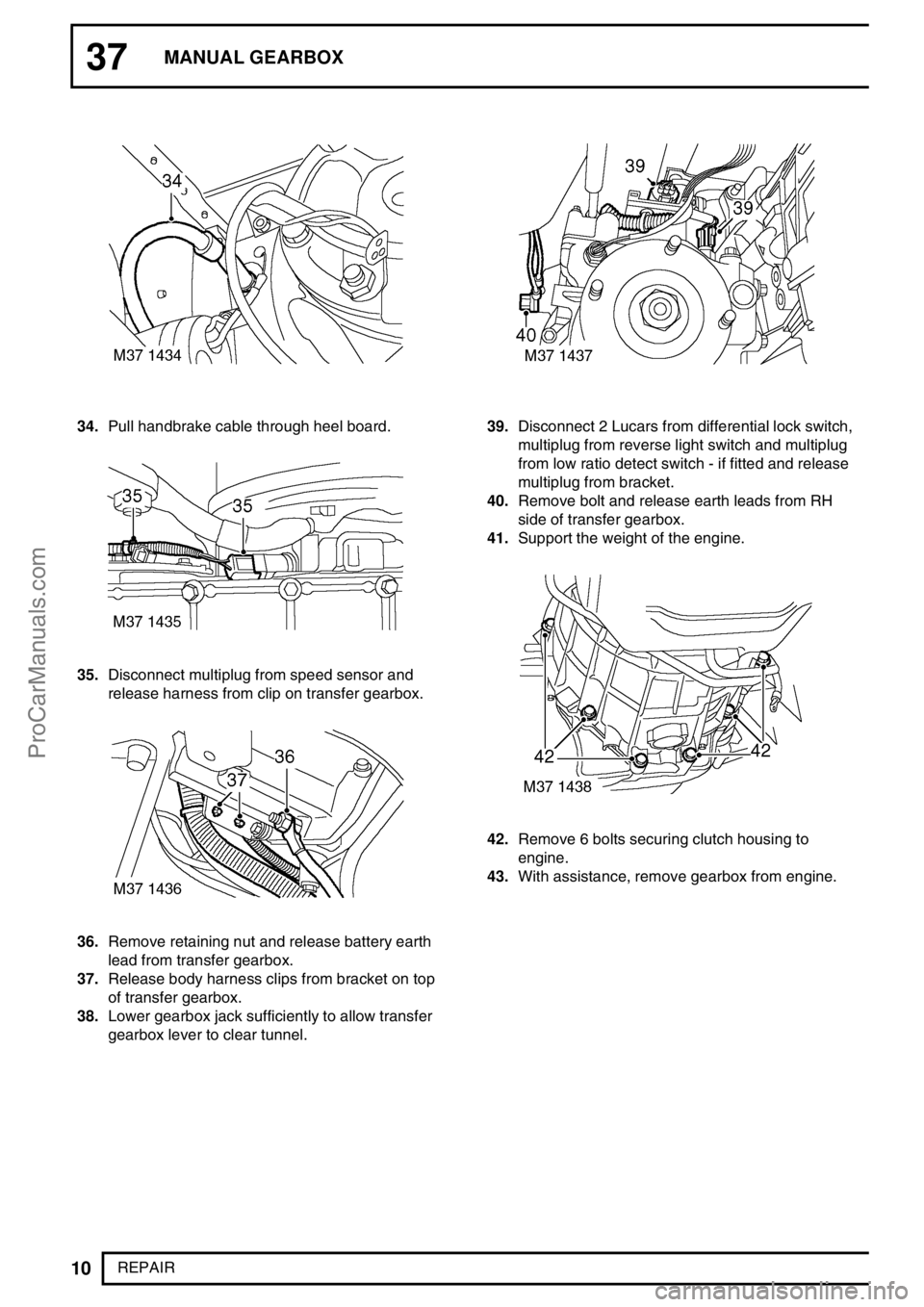
34.Pull handbrake cable through heel board.
35.Disconnect multiplug from speed sensor and
release harness from clip on transfer gearbox.
36.Remove retaining nut and release battery earth
lead from transfer gearbox.
37.Release body harness clips from bracket on top
of transfer gearbox.
38.Lower gearbox jack sufficiently to allow transfer
gearbox lever to clear tunnel.
39.Disconnect 2 Lucars from differential lock switch,
multiplug from reverse light switch and multiplug
from low ratio detect switch - if fitted and release
multiplug from bracket.
40.Remove bolt and release earth leads from RH
side of transfer gearbox.
41.Support the weight of the engine.
42.Remove 6 bolts securing clutch housing to
engine.
43.With assistance, remove gearbox from engine.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 356 of 667

MANUAL GEARBOX
11
REPAIR Refit
44.Clean gearbox to engine mating faces, dowels
and dowel holes.
45.With assistance raise gearbox on jack and align
to clutch and engine.
46.Fit lower bolts securing clutch housing to engine
and tighten to50 Nm (37 lbf.ft).
NOTE: Do not fit upper bolts at this stage.
47.Fit earth leads and secure with bolt.
48.Connect Lucars to differential lock switch,
multiplug to reverse light switch, position
multiplug to bracket and connect low ratio detect
multiplug - if fitted.
49.Raise gearbox jack and guide transfer gearbox
lever through tunnel.
50.Secure body harness clips to bracket on top of
transfer gearbox.
51.Position battery earth lead to transfer gearbox
and tighten retaining nut.
52.Connect multiplug to speed sensor and secure
harness in clip on transfer gearbox.
53.Position mounting brackets and rubber
mountings, positioning heat shield to LH
mounting and tighten bracket bolts to85 Nm (63
lbf.ft).
54.Position nuts to mountings and tighten to48 Nm
(35 lbf.ft).
55.Remove 3 bolts securing support plate
LRT-99-007to gearbox.
56.Position handbrake cable through heel board.
57.Position clutch slave cylinder, fit bolts and
tighten to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
58.Clean propeller shafts and mating faces.
59.Position propeller shafts, align to marks and
tighten nuts to48 Nm (35 lbf.ft).
60.Clean intermediate silencer and tail pipe mating
faces.
61.Position silencer and secure on mountings,
using a new gasket align to tail pipe, fit nuts and
tighten to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
62.Refill gearbox with oil.See Adjustment.
63.Refill transfer gearbox with oil.See
MAINTENANCE ,
64.Fit exhaust front pipe.See MANIFOLD AND
EXHAUST SYSTEM, Repair.
65.Refit starter motor.See ELECTRICAL, Repair.
66.Fit bolt securing shim plate to clutch housing and
tighten10 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
67.Position heater pipe to gearbox housing, fit
upper bolts securing clutch housing to engine
and tighten to50 Nm (37 lbf.ft).
68.Position gearbox breather pipes to clips on
heater hose.69.Fit air cleaner.See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair.
70.Fit cooling fan.See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair.
71.Fit and align tunnel cover, fit and tighten screws.
72.Position relay panel, fit spacers and tighten
screws.
73.Position hand-brake lever and tighten bolts to25
Nm (18 lbf.ft).
74.Connect handbrake cable to lever, fit clevis pin,
washer and new split pin.
75.Connect Lucar to hand-brake switch.
76.Position gaiter to handbrake lever and secure
with trim stud.
77.Locate insulation pad over gear levers and fit to
tunnel cover.
78.Align spline marks, fit gear lever to lower lever,
fit washer and secure with retaining nut.
79.Position gear lever cover.
80.Position gearbox tunnel carpet.
81.Fit gear lever and transfer gear lever knobs.
82.Reconnect battery negative lead.
83.Fit battery cover.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 365 of 667
41TRANSFER GEARBOX
4
REPAIR
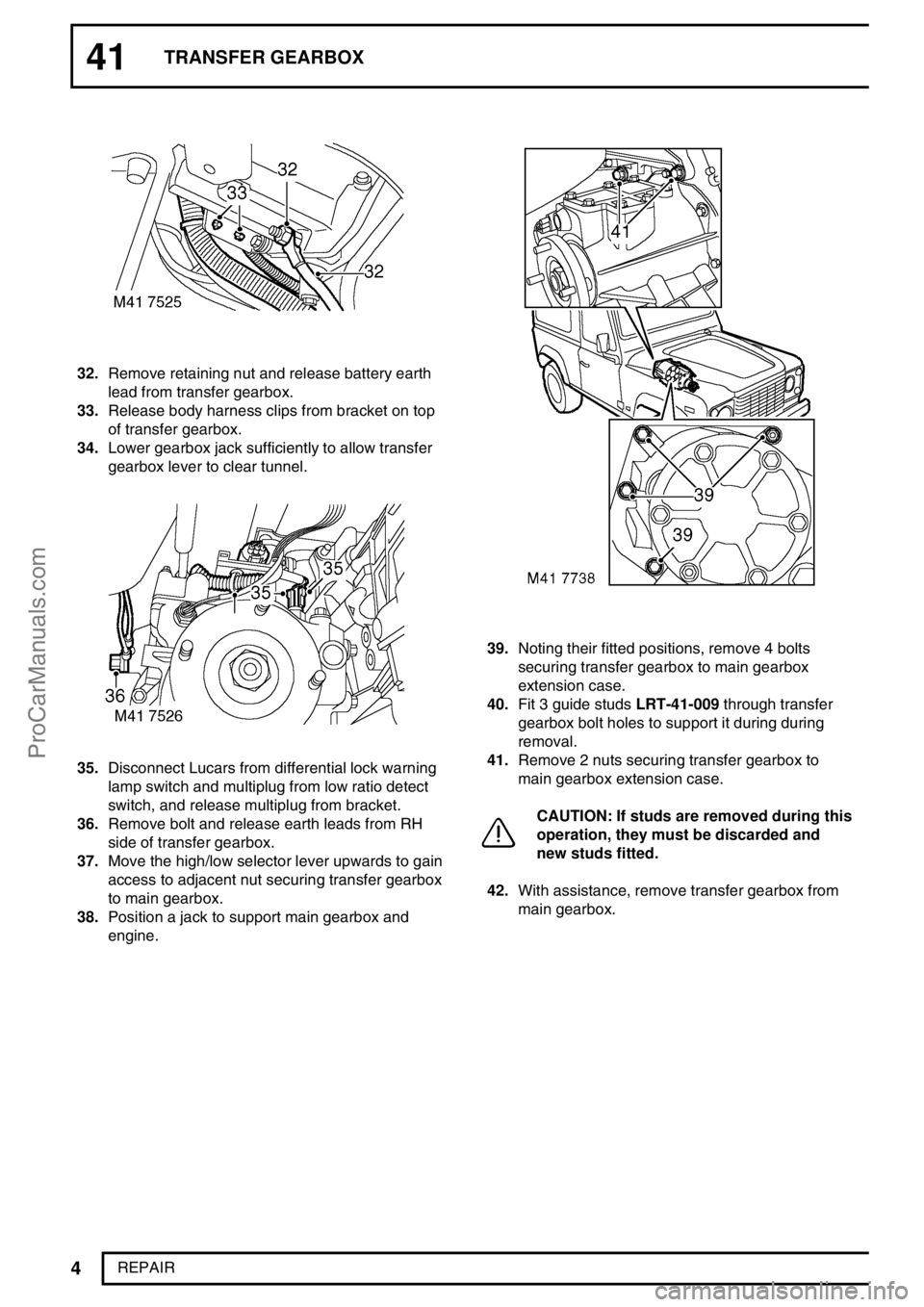
32.Remove retaining nut and release battery earth
lead from transfer gearbox.
33.Release body harness clips from bracket on top
of transfer gearbox.
34.Lower gearbox jack sufficiently to allow transfer
gearbox lever to clear tunnel.
35.Disconnect Lucars from differential lock warning
lamp switch and multiplug from low ratio detect
switch, and release multiplug from bracket.
36.Remove bolt and release earth leads from RH
side of transfer gearbox.
37.Move the high/low selector lever upwards to gain
access to adjacent nut securing transfer gearbox
to main gearbox.
38.Position a jack to support main gearbox and
engine.
39.Noting their fitted positions, remove 4 bolts
securing transfer gearbox to main gearbox
extension case.
40.Fit 3 guide studsLRT-41-009through transfer
gearbox bolt holes to support it during during
removal.
41.Remove 2 nuts securing transfer gearbox to
main gearbox extension case.
CAUTION: If studs are removed during this
operation, they must be discarded and
new studs fitted.
42.With assistance, remove transfer gearbox from
main gearbox.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 450 of 667
BRAKES
1
REPAIR ECU - ABS
Service repair no - 70.65.01
Remove
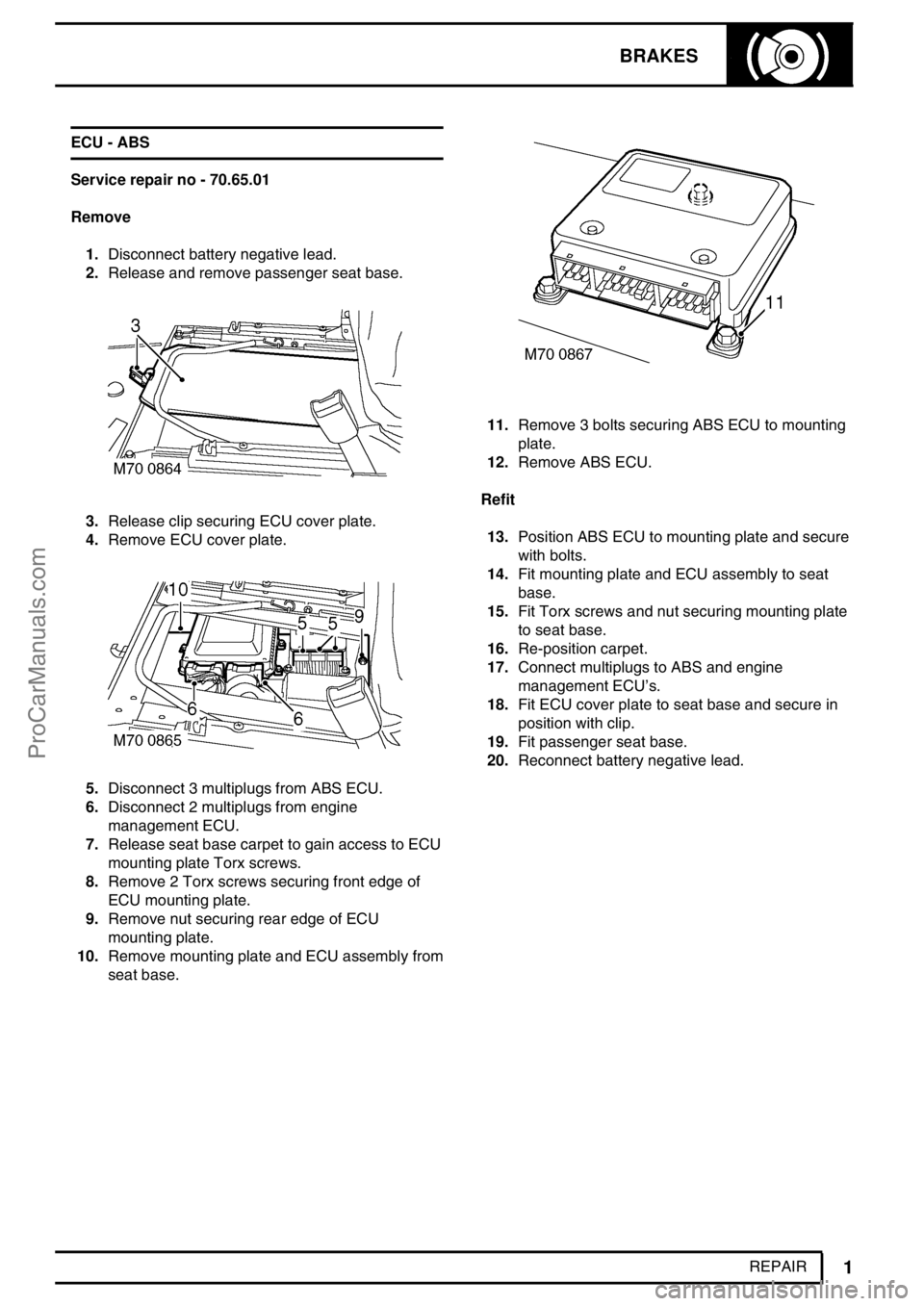
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Release and remove passenger seat base.
3.Release clip securing ECU cover plate.
4.Remove ECU cover plate.
5.Disconnect 3 multiplugs from ABS ECU.
6.Disconnect 2 multiplugs from engine
management ECU.
7.Release seat base carpet to gain access to ECU
mounting plate Torx screws.
8.Remove 2 Torx screws securing front edge of
ECU mounting plate.
9.Remove nut securing rear edge of ECU
mounting plate.
10.Remove mounting plate and ECU assembly from
seat base.
11.Remove 3 bolts securing ABS ECU to mounting
plate.
12.Remove ABS ECU.
Refit
13.Position ABS ECU to mounting plate and secure
with bolts.
14.Fit mounting plate and ECU assembly to seat
base.
15.Fit Torx screws and nut securing mounting plate
to seat base.
16.Re-position carpet.
17.Connect multiplugs to ABS and engine
management ECU’s.
18.Fit ECU cover plate to seat base and secure in
position with clip.
19.Fit passenger seat base.
20.Reconnect battery negative lead.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 510 of 667

PANEL REPAIRS
1
INFORMATION BODY REPAIRS
Body shells are of riveted, bolted and welded
construction and are bolted to the chassis frame.
It is essential that design dimensions and strength are
restored in accident rectification. It is important that
neither structural weakness nor excessive local
stiffness are introduced into the vehicle during body or
chassis repair.
Repairs usually involve a combination of operations
ranging from straightening procedures to renewal of
either individual panels or panel assemblies. The
repairer will determine the repair method and this
decision will take into account a balance of economics
between labour and material costs and the availability
of repair facilities in both equipment and skills. It may
also involve considerations of vehicles down-time,
replacement vehicle availability and repair turn-around
time.
It is expected that a repairer will select the best and
most economic repair method possible, making use of
the facilities available. The instructions given are
intended to assist a skilled body repairer by expanding
approved procedures for panel replacement with the
objective of restoring the vehicle to a safe running
condition and effecting a repair which is visually
acceptable and which, even to the experienced eye,
does not advertise the fact that it has been damaged.
This does not necessarily mean that the repaired
vehicle will be identical in all respects with original
factory build. Repair facilities cannot always duplicate
methods of construction used during production.
The panel repairs shown in this section are all based
on a 110 Station Wagon. Therefore all illustrations
and text relate only to this model. Although certain
areas of the vehicle, such as the front end, are
relevant to all models.
Operations covered in this Manual do not include
reference to testing the vehicle after repair. It is
essential that work is inspected and suspension
geometry checked after completion and if necessary a
road test of the vehicle is carried out, particularly
where safety related items are concerned.Where major units have been disconnected or
removed, it is necessary to ensure that fluid levels are
checked and topped up when necessary. It is also
necessary to ensure that the repaired vehicle is in a
roadworthy condition in respect of tyre pressures,
lights, washer fluid etc.
Body repairs often involve the removal of mechanical
and electrical units as well as associated wiring.
Where this is necessary use the relevant section in
this manual.
Taking into consideration the differences in body
styles, steering and suspension systems as well as
engine and suspension layouts, the location of the
following components as applicable to a particular
vehicle is critical:
Front suspension upper damper
mountings.
Front suspension or sub frame mountings.
Engine mountings on RH and LH chassis
longitudinals.
Rear suspension upper damper mountings.
Rear suspension mountings or lower
pivots.
Steering rack mountings.
Additional points which can be used to check
alignment and assembly are:
Inner holes in crossmember - side - main
floor.
Holes in valance front assembly.
Body to chassis mounting holes.
Holes in rear floor.
Holes in rear lower panels or extension
rear floor.
Fuel tank mountings.
Apertures for windscreen, backlight, bonnet and doors
can be checked by offering up an undamaged
component as a gauge and also by measuring known
dimensions.See BODY DIMENSIONS section.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 517 of 667
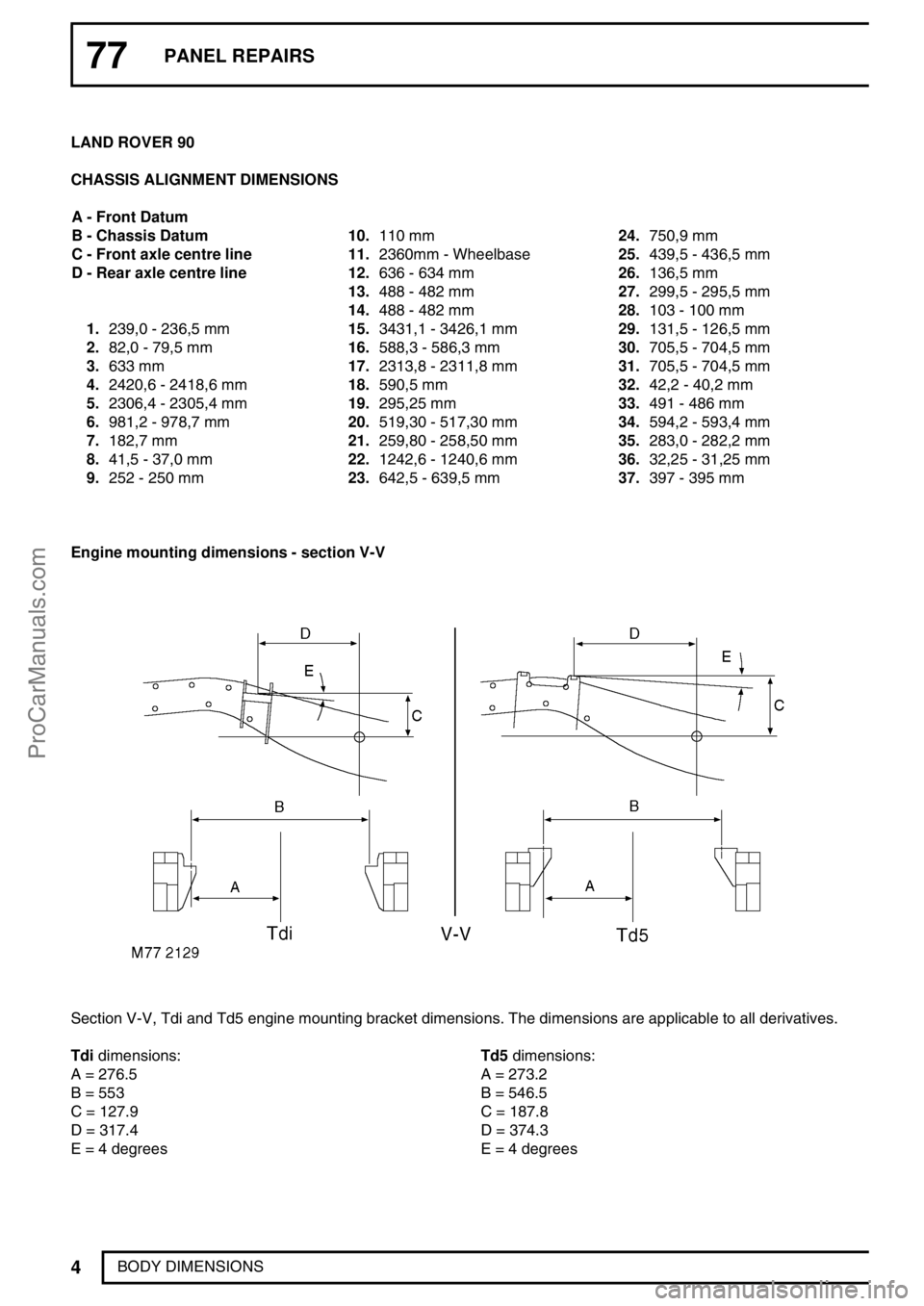
77PANEL REPAIRS
4
BODY DIMENSIONS LAND ROVER 90
CHASSIS ALIGNMENT DIMENSIONS
A - Front Datum
B - Chassis Datum
C - Front axle centre line
D - Rear axle centre line
1.239,0 - 236,5 mm
2.82,0 - 79,5 mm
3.633 mm
4.2420,6 - 2418,6 mm
5.2306,4 - 2305,4 mm
6.981,2 - 978,7 mm
7.182,7 mm
8.41,5 - 37,0 mm
9.252 - 250 mm10.110 mm
11.2360mm - Wheelbase
12.636 - 634 mm
13.488 - 482 mm
14.488 - 482 mm
15.3431,1 - 3426,1 mm
16.588,3 - 586,3 mm
17.2313,8 - 2311,8 mm
18.590,5 mm
19.295,25 mm
20.519,30 - 517,30 mm
21.259,80 - 258,50 mm
22.1242,6 - 1240,6 mm
23.642,5 - 639,5 mm24.750,9 mm
25.439,5 - 436,5 mm
26.136,5 mm
27.299,5 - 295,5 mm
28.103 - 100 mm
29.131,5 - 126,5 mm
30.705,5 - 704,5 mm
31.705,5 - 704,5 mm
32.42,2 - 40,2 mm
33.491 - 486 mm
34.594,2 - 593,4 mm
35.283,0 - 282,2 mm
36.32,25 - 31,25 mm
37.397 - 395 mm
Engine mounting dimensions - section V-V
Section V-V, Tdi and Td5 engine mounting bracket dimensions. The dimensions are applicable to all derivatives.
Tdidimensions:
A = 276.5
B = 553
C = 127.9
D = 317.4
E = 4 degreesTd5dimensions:
A = 273.2
B = 546.5
C = 187.8
D = 374.3
E = 4 degrees
ProCarManuals.com
Page 519 of 667

77PANEL REPAIRS
6
BODY DIMENSIONS LAND ROVER 110
CHASSIS ALIGNMENT DIMENSIONS
A - Front Datum
B - Chassis Datum
C - Front axle centre line
D - Rear axle centre line
1.4148 - 4143 mm
2.4009,5 - 4005 mm
3.978,7 - 981,2 mm
4.22 - 20 mm
5.252 - 250 mm
6.239 - 236,5 mm
7.3023,3 - 3022,3 mm
8.3030,7 - 3028,7 mm
9.155 - 153 mm
10.871,2 - 869,2 mm
11.2794 mm - Wheelbase
12.488 - 482 mm13.488 - 482 mm
14.82 - 79,5 mm
15.750,9 mm
16.750,9 mm
17.440,5 - 435,5 mm
18.440,5 - 435,5 mm
19.299,5 - 295,5 mm
20.500 - 495 mm
21.500 - 495 mm
22.594,2 - 593,4 mm
23.594,2 - 593,4 mm
24.283 - 282,2 mm
25.283 - 282,2 mm
26.1970 - 1968 mm
27.642,9 - 639,5 mm
28.750,9 mm29.290,5 mm
30.295,5 mm
31.299,5 - 295,5 mm
32.103 - 100 mm
33.1177,5 - 1175,5 mm
34.1692,5 - 1689,5 mm
35.2610 - 2606 mm
36.2040,5 - 2037,5 mm
37.1912,5 - 1909,5 mm
38.1359 - 1357 mm
39.1573 - 1571 mm
40.270 - 268 mm
41.665,5 - 663,5 mm
42.440 - 438 mm
43.32,25 - 31,25 mm
Section V-V is through the engine mountings. Dimensional information for the mountings can be found in Land
Rover’90’engine mounting dimensions.
ProCarManuals.com