oil type LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999Pages: 667, PDF Size: 8.76 MB
Page 294 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Radiator
The 44 row radiator is located at the front of the vehicle in the engine compartment. The cross flow type radiator is
manufactured from aluminium with moulded plastic end tanks interconnected with tubes. The bottom four rows are
separate from the upper radiator and form the lower radiator for the fuel cooler. Aluminium fins are located
between the tubes and conduct heat from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes, reducing the coolant
temperature as it flows through the radiator. Air intake from the front of the vehicle when moving carries the heat
away from the fins. When the vehicle is stationary, the viscous fan draws air through the radiator fins to prevent
the engine from overheating.
Two connections at the top of the radiator provide for the attachment of the top hose from the outlet housing and
bleed pipe to the expansion tank. Three connections at the bottom of the radiator allow for the attachment of the
bottom hose to the thermostat housing and the return hose from the oil cooler and the feed hose to the fuel cooler.
The bottom four rows of the lower radiator are dedicated to the fuel cooler. The upper of the two connections at
the bottom of the radiator receives coolant from the oil cooler. This is fed through the four rows of the lower
radiator in a dual pass and emerges at the lower connection. The dual pass lowers the coolant temperature by up
to 24°C before being passed to the fuel cooler. Two smaller radiators are located in front of the cooling radiator.
The upper radiator is the intercooler for the air intake system and the lower radiator provides cooling of the
gearbox oil.
Pipes and Hoses
The coolant circuit comprises flexible hoses and metal formed pipes which direct the coolant into and out of the
engine, radiator and heater matrix. Plastic pipes are used for the bleed and overflow pipes to the expansion tank.
A bleed screw is installed in the radiator top hose and is used to bleed air during system filling. A drain plug to
drain the heater and cylinder block circuit of coolant is located on the underside of the coolant pump feed pipe.
Oil Cooler
The oil cooler is located on the left hand side of the engine block behind the oil centrifuge and oil filter. Oil from the
oil pump is passed through a heat exchanger which is surrounded by coolant in a housing on the side of the
engine.
Full water pump flow is directed along the cooler housing which also distributes the flow evenly along the block
into three core holes for cylinder cooling. This cools the engine oil before it is passed into the engine. A small
percentage of the coolant from the oil cooler passes into a metal pipe behind the engine. It then flows into the
lower radiator via a hose.
Fuel Cooler
The fuel cooler is located on the right hand side of the engine and is attached to the inlet manifold. The cooler is
cylindrical in design and has a coolant feed connection at its forward end. A’T’connection at the rear of the cooler
provides a connection for the coolant return from the heater matrix and coolant return from the fuel cooler.
The’T’connection houses a thermostat which opens at approximately 82°C. This prevents the cooler operating in
cold climates. Two quick release couplings on the cooler allow for the connection of the fuel feed from the
pressure regulator and return to the fuel tank. A counter flow system is used within the cooler.
Fuel flows around a coolant jacket within the cooler and flows from the back to the front of the cooler. As the hot
fuel cools travelling slowly forwards it meets progressively colder coolant travelling in the opposite direction
maintaining a differential cooling effect.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 329 of 667

33CLUTCH
6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
General
The clutch system is a diaphragm type clutch operated by a hydraulic cylinder. The drive plate is of the rigid centre
type with no integral damping springs. The flywheel is of the dual mass type with damping springs integral with the
flywheel. The clutch requires no adjustment to compensate for wear.
Hydraulic Clutch
The hydraulic clutch comprises a master cylinder, slave cylinder and a hydraulic reservoir. The master and slave
cylinders are connected to each other hydraulically by plastic and metal pipes. The plastic section of the pipe
allows ease of pipe routing and also absorbs engine movements and vibrations.
The master cylinder comprises a body with a central bore. Two ports in the body connect the bore to the hydraulic
feed pipe to the slave cylinder and the fluid reservoir. The bore is also connected to a damper which prevents
engine pulses being transferred hydraulically to the clutch pedal. A piston is fitted in the bore and has an external
rod which is attached to the clutch pedal with a pin. Two coil springs on the clutch pedal reduce the effort required
to depress the pedal.
The master cylinder is mounted on the bulkhead and secured with two bolts. The cylinder is connected to the
shared brake/clutch reservoir on the brake servo by a braided connecting hose.
The slave cylinder is located on the left hand side of the gearbox housing and secured with two bolts. A heat
shield is fitted to protect the underside of the slave cylinder from heat generated from the exhaust system. The
slave cylinder comprises a cylinder with a piston and a rod. A port in the cylinder body provides the attachment for
the hydraulic feed pipe from the master cylinder. A second port is fitted witha bleed nipple used for removing air
from the hydraulic system after servicing. The piston rod locates on a clutch release lever located in the gearbox
housing. The rod is positively retained on the release lever with a clip.
Clutch Mechanism
The clutch mechanism comprises a flywheel, drive plate, pressure plate, release lever and a release bearing. The
clutch mechanism is fully enclosed at the rear of the engine by the gearbox housing.
A clutch release bearing sleeve is attached in the gearbox housing with two bolts and located on two dowels. A
spigot with a ball end is formed on the release bearing sleeve and provides a mounting and pivot point for the
clutch release lever. A dished pivot washer is located on the ball of the spigot. When the release lever is located
on the ball, the pivot washer seats against the rear face of the release lever. A spring clip is located on the lever
and the pivot washer and secures the lever on the spigot. A small bolt retains the spring clip in position.
The release lever is forked at its inner end and locates on the clutch release bearing carrier. The outer end of the
release lever has a nylon seat which locates the slave cylinder piston rod. A second nylon seat, positioned
centrally on the release lever, locates on the ball spigot of the release bearing sleeve and allows the release lever
to pivot freely around the ball.
The clutch release bearing locates on the clutch release lever and release bearing sleeve. The bearing is retained
on a carrier which has two flats to prevent the carrier rotating on the release lever. A clip retains the release lever
on the carrier. The bearing and carrier are not serviceable individually.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 384 of 667

REAR AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
The welded steel rear axle casing houses a separate
spiral bevel type differential unit, which is off set to the
right of the vehicle centre line. The differential unit
drives the rear wheels via the axle shafts and fully
floating hubs which are mounted on tapered roller
bearings.
Lubrication
The differential is lubricated with oil and the hub
bearings with grease.The hub bearings are fitted with inner and outer seals.
The outer seals prevent the differential oil mixing with
the hub grease and the inner seals prevent dirt
ingress into the hub.
Ventilation
Ventilation of the hub bearings is through the outer oil
seals and the differential ventilation pipe, which
terminates at a high level.
Rear axle hub - 90
1.Axle casing
2.Ventilation pipe
3.Axle shaft
4.Wheel studs and hub
5.Wheel bearing stub axle6.Wheel bearings
7.Inner hub seal
8.Outer hub/axle shaft seal
9.Hub lock plate, thrust washer and nuts
10.Brake disc
ProCarManuals.com
Page 543 of 667

77PANEL REPAIRS
18
SEALING AND CORROSION PROTECTION Seam Sealers
A heat cured, PVC Plastisol sealer is applied to joint
areas during factory assembly. This material is not
suitable for service use.
Carry out seam sealing after the application of primer
and before the surfacer and final paint coats. Ensure
that surfaces are first cleaned of all grease and oil.
Apply the sealer material to the joint as a bead, either
by hand or using an applicator gun. Where necessary,
brush sealer well into the joint and wipe smooth using
a cloth soaked with solvent such as Shell SBP3. This
will ensure an acceptable cosmetic finish.
Apply sealer to ALL accessible joints following repair
work. Be aware that damage to a vehicle can often
result in deflection to those areas of the body which
are remote from the impact. The sealers in these
areas can therefore be disturbed by subsequent
straightening and repair operations. Check joints in
the vicinity of the area undergoing repair for evidence
of cracked sealer, clean them out as required and
re-treat them with fresh sealer using the following
procedure:
Clean the affected joint or seam and
re-treat any exposed metal areas with a
suitable etch phosphate primer.
Treat affected area with an acid-etch
primer.
Apply appropriate seam sealer as
necessary.
Apply appropriate colour coat (and
underbody sealer as applicable).
Where joints are inaccessible following the
reassembly or fitment of components, ensure that a
paste-type sealer is applied to such joints. Certain
seams also become inaccessible after the completion
of panel repairs. In such instances the paint process
should be carried out and sealers applied before final
assembly.Provided access is adequate, apply the sealer to both
sides of the repair joint. Where access is limited to
one side only (e.g. box sections), inject the affected
box member with cavity wax.
CAUTION: ALWAYS deploy an extractor
unit to remove toxic fumes when using
oxy-acetylene equipment to remove panels
treated with wax and sealers.
The following Illustrations show the treatment areas
for Seam Sealing.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 585 of 667

82AIR CONDITIONING
2
ADJUSTMENT Recharging
WARNING: Refrigerant must always be
recycled before re-use, to ensure that the
purity of the refrigerant is high enough for
safe use within the air conditioning system.
Recycling should always be carried out with
equipment which is design certified by
Underwriter Laboratory Inc. for compliance with
SAE-J1991. Other equipment may not re-cycle the
refrigerant to the required level of purity.
WARNING: A R134a Refrigerant Recovery
Recycling Recharging station must not be
used with any other type of refrigerant.
WARNING: R134a refrigerant from
domestic and commercial sources must
not be used in motor vehicle air
conditioning systems.
CAUTION: When a major repair has been
carried out, a leak test should be carried
out using inert gas.
1.Close valves on refrigerant station.
2.Close valve on oil charger.
3.Disconnect yellow hose from refrigerant station.
4.Remove lid from oil charger.
5.Pour correct quantity of refrigerant oil into oil
charger.
6.Fit lid to oil charger.
7.Connect yellow hose to refrigerant station.
8.Open valve on oil charger.
9.Move pointer on refrigerant gauge to mark
position of refrigerant drop.
10.Slowly open correct valve on refrigerant station
and allow vacuum to pull refrigerant into system.
11.Close valve on refrigerant station when correct
amount of refrigerant has been drawn into air
conditioning system.
12.If the full charge is not accepted by the system,
start the engine and run it at 1,500 rev/min for a
minimum of 2 minutes. Switch on the air
conditioning system, open the vehicle windows,
set the temperature control to cold and the
blower switch to maximum.
13.Consult Refrigerant station instruction manual for
correct procedure to complete the charge.
14.Turn Main switch to’OFF’.
15.Close valves on connectors.
16.Disconnect high and low pressure hoses from
connectors.
17.Fit dust caps to connectors.
18.Carry out performance test on air conditioning
system.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 616 of 667

ELECTRICAL
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Alarm Sounders
1.Battery Backed Up Sounder (BBUS)
2.Alarm sounder
Two types of alarm sounder are available, dependant on the vehicle market configuration.
A Battery Backed-Up Sounder (BBUS) is used in some markets and located in the LH front wing, behind the
headlamp. This is a tamper proof sounder with its own power supply which allows it to continue operating even if
disconnected from the vehicle power supply. The BBUS is connected to a permanent battery supply via fuse 7 in
the under seat fuse box. Two further connections are made to the anti-theft alarm ECU and a fourth connection is
to an earth header. If the BBUS is disconnected without first being disarmed by the anti-theft alarm ECU, it will
operate for 4.5 minutes.
To disarm the BBUS, when the battery is to be disconnected for instance, the ignition must be turned on to
position II and back to the off position , after which a 17 second delay is initiated to allow the battery or BBUS
connector to be disconnected. If the BBUS sounds, it can be disarmed by unlocking the vehicle with the remote
handset.
Where a BBUS is not specified, a standard vehicle horn is used for the alarm sounder and is located in the LH
front wing, behind the headlamp. The sounder is operated by an alarm relay which is controlled by the anti-theft
alarm ECU. The relay receives a permanent battery supply via fusible link 6 in the under seat fuse box. The relay
coil is connected to the anti-theft alarm ECU which provides an earth for the coil when horn operation is required.
This operates the relay contacts and supplies battery voltage to the sounder, causing it to operate.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 621 of 667
86ELECTRICAL
12
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION IMMOBILISATION SYSTEM - FROM 02MY
Engine immobilisation is available on all 2002MY engine derivatives, although it is not available in selected
markets. On Td5 models, the immobilisation system is controlled directly by the anti-theft alarm ECU. On 300Tdi
models, the immobilisation system is controlled by an engine immobilisation ECU in conjunction with the anti-theft
alarm ECU.
When immobilisation occurs on Td5 models, engine crank is disabled by the anti-theft alarm ECU breaking the
earth path for the starter relay coil and the ECM disables the fuel pump relay and the glow plug relay.
When immobilisation occurs on 300Tdi models, engine crank is disabled by the anti-theft alarm ECU breaking the
earth path for the starter relay coil and the engine immobilisation ECU disables the fuel cut-off solenoid, the starter
motor solenoid and the glow plug relay.
Two types of immobilisation are available; passive and active.
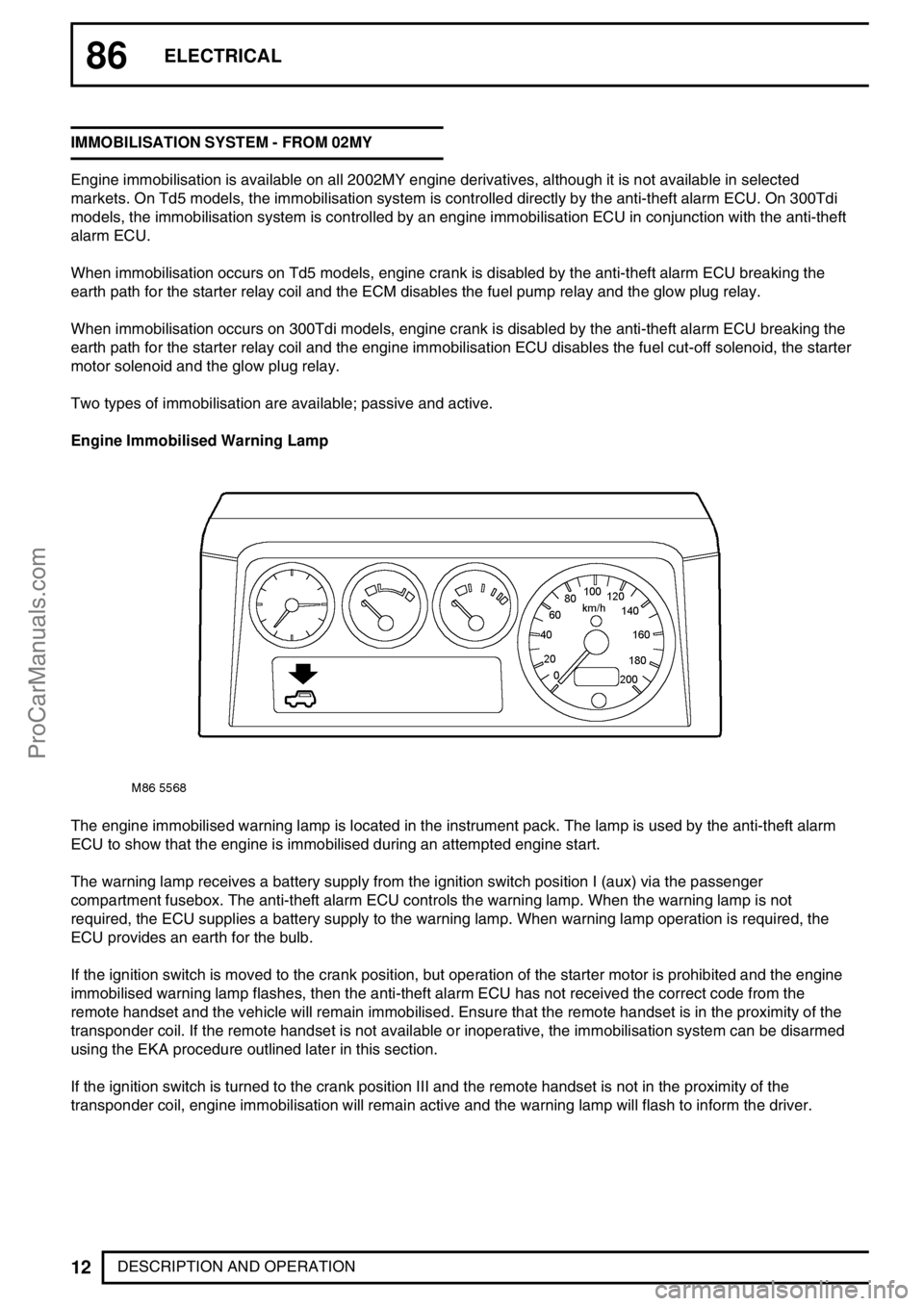
Engine Immobilised Warning Lamp
The engine immobilised warning lamp is located in the instrument pack. The lamp is used by the anti-theft alarm
ECU to show that the engine is immobilised during an attempted engine start.
The warning lamp receives a battery supply from the ignition switch position I (aux) via the passenger
compartment fusebox. The anti-theft alarm ECU controls the warning lamp. When the warning lamp is not
required, the ECU supplies a battery supply to the warning lamp. When warning lamp operation is required, the
ECU provides an earth for the bulb.
If the ignition switch is moved to the crank position, but operation of the starter motor is prohibited and the engine
immobilised warning lamp flashes, then the anti-theft alarm ECU has not received the correct code from the
remote handset and the vehicle will remain immobilised. Ensure that the remote handset is in the proximity of the
transponder coil. If the remote handset is not available or inoperative, the immobilisation system can be disarmed
using the EKA procedure outlined later in this section.
If the ignition switch is turned to the crank position III and the remote handset is not in the proximity of the
transponder coil, engine immobilisation will remain active and the warning lamp will flash to inform the driver.
ProCarManuals.com