relay LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999Pages: 667, PDF Size: 8.76 MB
Page 17 of 667
01INTRODUCTION
10
INFORMATION CROSS REFERENCE OF EMISSION SYSTEM
TERMINOLOGY
NEW TERM (ACRONYM)
Accelerator pedal (AP).................................................
Air cleaner (ACL)..........................................................
Air conditioning (A/C)...................................................
Battery positive voltage (B+)........................................
Closed loop (CL)..........................................................
Closed throttle position (CTP)......................................
Canister purge valve (CANPV)....................................
Data link connector (DLC)...........................................
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC).....................................
Distributor ignition (DI).................................................
Engine control module (ECM)......................................
Engine coolant level (ECL)...........................................
Engine coolant temperature (ECT)..............................
Engine speed (RPM)....................................................
Evaporative emission system (EVAP)..........................
Engine fuel temperature sensor (EFTS)......................
4th gear, 3rd gear etc. (4GR, 3GR)..............................
Fuel pump (FP)............................................................
Fan control module (FCM)...........................................
Generator (GEN)..........................................................
Ground (GND)..............................................................
Heated oxygen sensor (H02S)....................................
Idle air control (IAC)......................................................
Idle air control valve (IACV).........................................
Ignition control module (ICM).......................................
Intake air temperature (IAT).........................................
Manifold vacuum zone (MVZ)......................................
Mass air flow sensor (MAF).........................................
Open loop (OL)............................................................
Relay module (RM)......................................................
Solid state relay module (SSRM).................................
Three way catalytic converter (TWC)..........................
Throttle body (TB)........................................................
Throttle position sensor (TP)........................................
Transmission range (TR)..............................................
Wide open throttle (WOT)............................................OLD TERM (ACRONYM)
Throttle pedal (-)..........................................................
Air cleaner (-)...............................................................
Air conditioning (AC)....................................................
Battery plus, bat +, bat feed (B+).................................
Closed loop (-).............................................................
Closed throttle, idle position (-)....................................
Charcoal canister purge valve (-).................................
Serial link (-)................................................................
Fault code (-)...............................................................
Electronic ignition (-)....................................................
Electronic control unit (ECU)........................................
Coolant level (-)...........................................................
Coolant temperature (temp).........................................
Coolant temperature thermistor (-)..............................
Engine speed (rev/min)................................................
Evaporative loss system (ELC)...................................
Fuel temperature thermistor (-)....................................
Fourth gear, 3rd gear (-)..............................................
Fuel pump (-)...............................................................
Condenser fan timer (-)................................................
Alternator (-)................................................................
Ground, earth (B-)........................................................
Lambda (02) sensor (-)................................................
Idle speed control (ISC)................................................
Stepper motor (-).........................................................
Ignition module (-)........................................................
Intake temperature/ambient temperature (-)................
Manifold depression, vacuum (-).................................
Air flow meter (-)..........................................................
Fault code display unit (-)............................................
Open loop (-)...............................................................
Relay (-).......................................................................
Control unit (-)..............................................................
Catalyst, catalytic converter (CAT)..............................
Throttle housing (-)......................................................
Transmission gear (-)...................................................
Full throttle, wide open throttle (WOT).........................
ProCarManuals.com
Page 222 of 667

18 - ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPONENT LOCATION 2...................................................................................
DESCRIPTION 5.....................................................................................................
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) 6.................................................................
SENSOR - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) 7....................................................................
SENSOR - AMBIENT AIR PRESSURE AND 8.......................................................
SENSOR - MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE 9................................................
SENSOR - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE 11.............................................
SENSOR - CRANKSHAFT SPEED AND 12...........................................................
SENSOR - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) 14............................................................
SENSOR - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) 15............................................................
ELECTRONIC UNIT INJECTOR (EUI) 18...............................................................
SENSOR - FUEL TEMPERATURE (FT) 20............................................................
RELAY - FUEL PUMP 21........................................................................................
RELAY - MAIN 21...................................................................................................
SWITCH - BRAKE PEDAL 22.................................................................................
SWITCH - CLUTCH PEDAL 22...............................................................................
MODULATOR - EXHAUST GAS REGULATOR (EGR) 23.....................................
WARNING LAMP - GLOW PLUG 23......................................................................
GLOW PLUGS 24...................................................................................................
TURBOCHARGER 26.............................................................................................
INTERCOOLER 27.................................................................................................
OPERATION 28......................................................................................................
REPAIR
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) 1.................................................................
SENSOR - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) 1....................................
SENSOR - CRANKSHAFT SPEED AND POSITION (CKP) 2................................
ProCarManuals.com
Page 226 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1.Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
2.Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
3.Glow plugs.
4.Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) / Inlet Air Temperature (IAT) sensor.
5.Fuel pump relay.
6.Engine Control Module (ECM).
7.Air Conditioning (A/C) and cooling fan relay.
8.Fuel Temperature (FT) sensor.
9.Crankshaft Speed and Position (CKP) sensor.
10.Electronic Unit Injectors (EUI).
11.Ambient Air Pressure (AAP) sensor.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 228 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
General
An engine control module (ECM) controls the five cylinder direct injection diesel engine, and works on the drive by
wire principal. This means there is no throttle cable, the ECM controls the drivers needs via a signal from the
Throttle Position (TP) sensor on the throttle pedal.
The ECM is a full authoritative diesel specific microprocessor that also incorporates features for air conditioning. In
addition, the ECM supplies output control for the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) and turbocharger boost
pressure. The ECM has a self diagnostic function, which is able to provide backup strategies for most sensor
failures.
The ECM processes information from the following input sources:
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
Ambient Air Pressure (AAP) sensor.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) / Inlet Air Temperature (IAT) sensor.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
Crankshaft Speed and Position (CKP) sensor.
Throttle Position (TP) sensor.
Fuel Temperature (FT) sensor.
Air conditioning request.
Air conditioning fan request.
Brake pedal switch.
Clutch pedal switch.
The input from the sensors constantly updates the ECM with the current operating condition of the engine. Once
the ECM has compared current information with stored information within its memory, it can make any adjustment
it requires to the operation of the engine via the following:
Air conditioning clutch relay.
Air conditioning cooling fan relay.
Electronic vacuum regulator solenoid.
Fuel pump relay.
Glow plug warning lamp.
Glow plugs.
Fuel injectors.
Main relay.
Turbocharger wastegate modulator.
Temperature gauge.
The ECM interfaces with the following:
Serial communication link.
Instrument pack.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 244 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
21
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION RELAY - FUEL PUMP
The fuel pump relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It switches on the fuel pump to draw fuel from
the tank to the electronic unit injectors (EUI).
Input / Output
The fuel pump relay is a 4 pin normally open relay. The fuel pump relay (C0730-4) is provided with a feed by the
main relay (C0063-78) via header 291 on a brown/orange wire. An earth path is provided for the fuel pump relay
(C0730-6) via the ECM (C658-5) on a blue/purple wire. This energises the fuel pump relay and allows a feed to be
provided to the fuel pump. When the ECM interrupts the earth, the relay is de-energised and the fuel pump stops
operating.
The fuel pump relay can fail in one or more of the following ways:
Relay open circuit.
Short circuit to vehicle supply.
Short circuit to vehicle earth.
Broken relay return spring.
In the event of a fuel pump relay failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
Engine will crank but not start.
If the engine is running, it will stop.
RELAY - MAIN
The main relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box and supplies battery voltage to the following:
The ECM.
The MAF sensor.
Fuel pump relay.
Input / Output
The main relay is a 4 pin normally open relay, which must be energised to provide a voltage to the ECM. The main
relay (C0063-86) is provided with an earth path via a transistor within the ECM (C0658-21) on a blue/red wire.
When the earth path is completed, the relay is energised and supplies the ECM (C0658-3, C0658-22 & C0658-27)
with a feed on brown/orange wires via header 291.
The main relay can fail in the following ways:
Relay open circuit.
Short circuit to vehicle supply.
Short circuit to vehicle earth.
Broken relay return spring.
In the event of a main relay failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
Engine will crank but not start.
If the engine is running, it will stop.
For the ECM start up to take place the ignition feed when the switch is in position’II’must be greater than 6.0
volts.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 246 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
23
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION MODULATOR - EXHAUST GAS REGULATOR (EGR)
The EGR modulator is located on the RH side inner front wing. It regulates the vacuum source to the EGR valve
allowing it to open or close. The ECM utilises the EGR modulator to control the amount of exhaust gas being
recirculated in order to reduce exhaust emissions and combustion noise. Optimum EGR is usually obtained when
the vehicle is operating at light throttle openings, and the vehicle is cruising at approximately 2000 to 3000
rev/min.
Input / Output
The EGR modulator (C0191-1) receives a feed from the main relay (C0063-87) on a brown/orange wire via header
294. The earth path for the modulator (C0191-2) is controlled by the ECM (C0158-3) on a blue wire. The length of
time the ECM supplies an earth is how long the exhaust gases are allowed to recirculate. The ECM decides how
long to supply the earth by looking at engine temperature and engine load.
The EGR modulator can fail in one or more of the following ways:
Solenoid open circuit.
Short circuit to vehicle supply.
Short circuit to earth.
In the event of an EGR modulator failure, the EGR system will become inoperative.
WARNING LAMP - GLOW PLUG
The glow plug warning lamp is located in the instrument pack. It illuminates to alert the driver that the glow plugs
are being heated prior to the engine being started. The length of time that the lamp illuminates and the glow plugs
are operating prior to cranking is the pre-heat period. The length of time of this period is determined by the ECT
sensor signal, controlled by the ECM.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 247 of 667
18ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
24
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION GLOW PLUGS
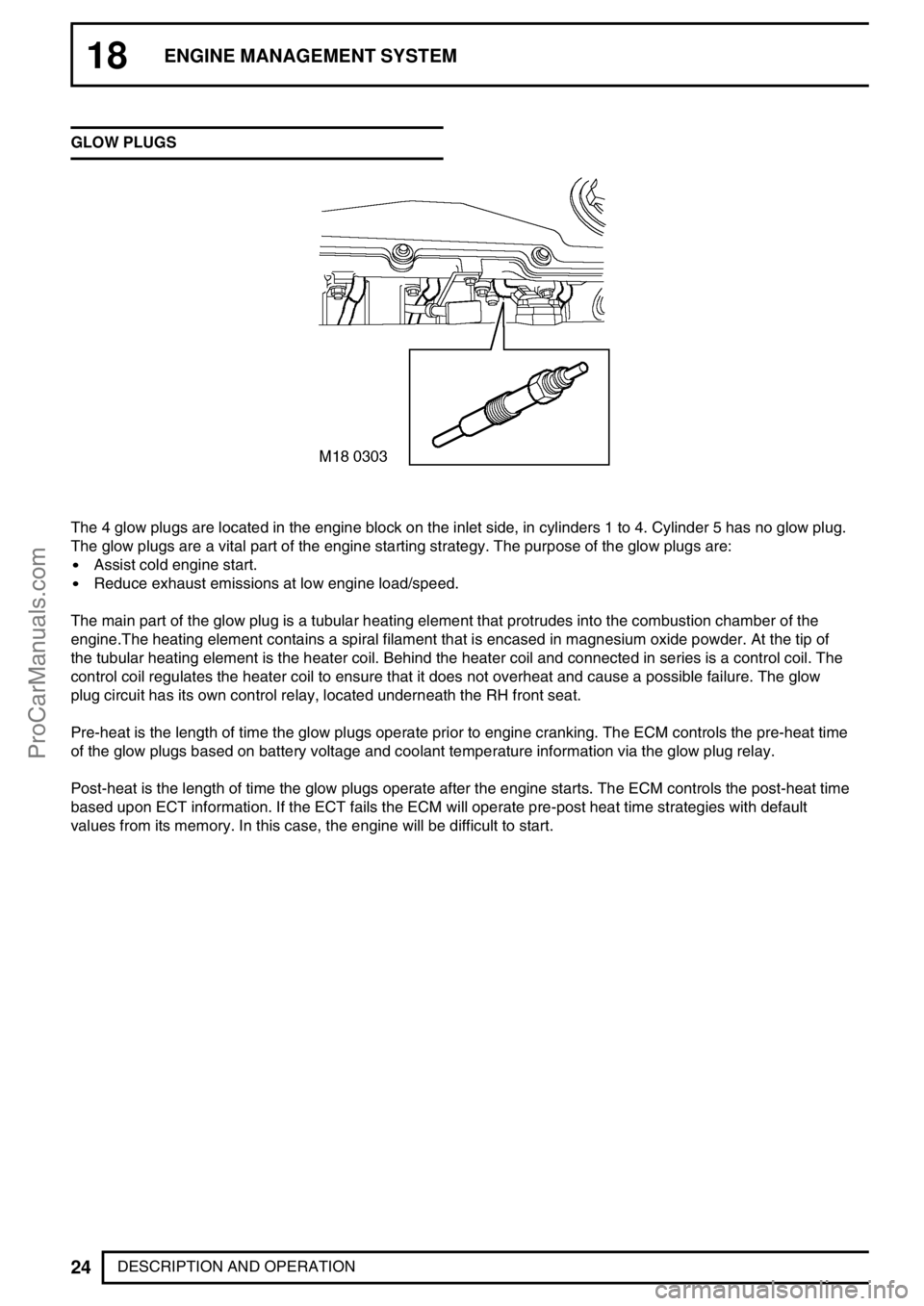
The 4 glow plugs are located in the engine block on the inlet side, in cylinders 1 to 4. Cylinder 5 has no glow plug.
The glow plugs are a vital part of the engine starting strategy. The purpose of the glow plugs are:
Assist cold engine start.
Reduce exhaust emissions at low engine load/speed.
The main part of the glow plug is a tubular heating element that protrudes into the combustion chamber of the
engine.The heating element contains a spiral filament that is encased in magnesium oxide powder. At the tip of
the tubular heating element is the heater coil. Behind the heater coil and connected in series is a control coil. The
control coil regulates the heater coil to ensure that it does not overheat and cause a possible failure. The glow
plug circuit has its own control relay, located underneath the RH front seat.
Pre-heat is the length of time the glow plugs operate prior to engine cranking. The ECM controls the pre-heat time
of the glow plugs based on battery voltage and coolant temperature information via the glow plug relay.
Post-heat is the length of time the glow plugs operate after the engine starts. The ECM controls the post-heat time
based upon ECT information. If the ECT fails the ECM will operate pre-post heat time strategies with default
values from its memory. In this case, the engine will be difficult to start.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 248 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
25
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Input / Output
The glow plugs receive a feed from the glow plug relay (C0215-3) on a yellow/black then individual black wires.
The ECM provides the earth path for the glow plug relay (C0151-6), working in tandem with the Alarm ECU. The
supply voltage heats the coils to approximately 1000°C (1832°F). The glow plug circuit is wired in parallel, the
body of each glow plug is screwed directly into the engine block which provides each glow plug with an earth path.
The glow plugs can fail in one or more of the following ways:
Heater coil open circuit.
Control coil open circuit.
Poor earth quality.
Short circuit to vehicle supply.
Short circuit to vehicle earth.
Harness fault.
Relay windings open circuit.
Incorrect relay fitted.
In the event of a glow plug failure, any of the following symptoms may be observed:
Difficult starting.
Excessive smoke emissions after engine start.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 257 of 667

19FUEL SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
General
The fuel delivery system comprises a fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, five injectors and a fuel filter.
The system is controlled by the ECM, which energises the fuel pump relay and controls the operation and timing
of each injector solenoid.
Unlike other Diesel engines, the Td5 has no injection pump. The diesel direct injection system receives fuel at
pressure from a two stage fuel pump located in the fuel tank. The system incorporates a fuel return to the fuel
pump, via a fuel cooler attached to the inlet manifold, and a fuel filter. A fuel pressure regulator is located in a
housing on the rear of the cylinder head. The regulator maintains the fuel delivered to the injectors at a constant
pressure and returns excess fuel back to the fuel filter and pump via the fuel cooler.
A fuel filter is positioned on the chassis longitudinal, below the RH rear wheel arch. The fuel feed and return to and
from the engine passes through the filter. The filter also incorporates a water sensor, which illuminates a warning
lamp in the instrument pack.
A moulded fuel tank is located at the rear underside of the vehicle between the chassis longitudinals. The tank
provides the attachment for the fuel pump and the fuel gauge sender unit, which is located inside the tank.
Fuel Tank and Breather
The fuel tank and breather system is a major part of the fuel delivery system. The fuel tank and breathers are
located at the rear of the vehicle between the chassis longitudinals.
Fuel Tank
The moulded fuel tank is made from High Molecular Weight (HMW) High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), and is
manufactured using a proportion of recycled plastic.
The tank is held in position by a metal cradle which is secured to the chassis cross members by four bolts, two
holding the front of the cradle in position, two holding the rear. The fuel tank has a useable capacity of 75 litres
(16.5 gallons).
An aperture in the top surface of the tank allows for the fitment of the fuel pump and fuel gauge sender unit, which
is retained with a locking ring. A reflective metallic covering is attached to the tank with three scrivets to shield the
tank from heat generated by the exhaust system.
Fuel Tank Breather System
The fuel tank filler tube incorporates a tank vent which allows air and fuel vapour displaced from the tank when
filling to vent to atmosphere via the filler neck.
A breather spout within the tank controls the tank’Full’height. When fuel covers the spout it prevents fuel vapour
and air from escaping from the tank. This causes the fuel to’back-up’in the filler tube and shuts off the filler gun.
The position of the spout ensures that when the filler gun shuts off, a vapour space of approximately 10% of the
tanks total capacity remains. The vapour space ensures that the Roll Over Value (ROV) is always above the fuel
level and vapour can escape and allow the tank to breathe.
The ROV is welded to the top surface of the tank. It is connected by a tube to the filler tube, which in turn is
connected to the atmospheric vent pipe. The ROV allows fuel vapour to pass through it during normal vehicle
operation. In the event of the vehicle being overturned the valve shuts off, sealing the tank and preventing fuel
from spilling from the atmospheric vent pipe.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 258 of 667
FUEL SYSTEM
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL PUMP AND FUEL GAUGE SENDER
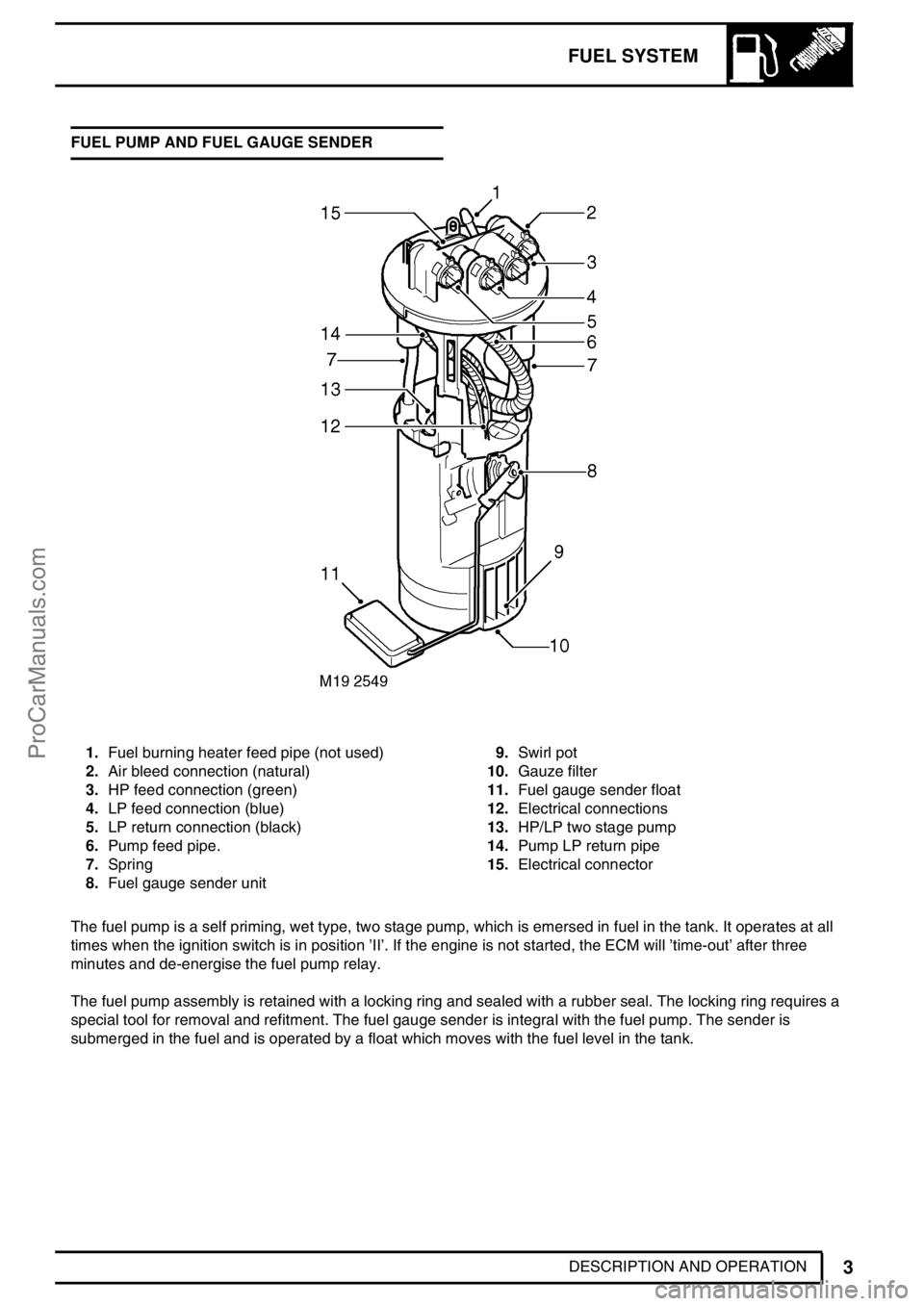
1.Fuel burning heater feed pipe (not used)
2.Air bleed connection (natural)
3.HP feed connection (green)
4.LP feed connection (blue)
5.LP return connection (black)
6.Pump feed pipe.
7.Spring
8.Fuel gauge sender unit9.Swirl pot
10.Gauze filter
11.Fuel gauge sender float
12.Electrical connections
13.HP/LP two stage pump
14.Pump LP return pipe
15.Electrical connector
The fuel pump is a self priming, wet type, two stage pump, which is emersed in fuel in the tank. It operates at all
times when the ignition switch is in position’II’. If the engine is not started, the ECM will’time-out’after three
minutes and de-energise the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump assembly is retained with a locking ring and sealed with a rubber seal. The locking ring requires a
special tool for removal and refitment. The fuel gauge sender is integral with the fuel pump. The sender is
submerged in the fuel and is operated by a float which moves with the fuel level in the tank.
ProCarManuals.com