LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1995, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995Pages: 873, PDF Size: 12.89 MB
Page 111 of 873

V8i
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
1. Cylinder heads (2)
2. Rocker covers (2)
3. PCV filter
4. Rocker shafts (2)
5. Hydraulic tappets (8)
6. Pushrods (8)
7. Rocker brackets (8)
8. Rocker arms (4) left and (4) right
9. Rocker shaft springs (6)
10. Inlet manifold
11. Plenum chamber lower
12. Ram pipes (8)13. Plenum chamber upper
14. PCV air intake filter
15. Oil filler
16. Thermostat
17. Thermostat cover
18. Inlet valve seal, spring, cap and collets (8)
19. Exhaust valve seal, spring, cap and collets (8)
20. Inlet valve and seat (8)
21. Exhaust valve and seat (8)
22. Inlet manifold gasket and seals
23. Cylinder head gaskets (2)
24. Valve guides (16)
Page 112 of 873
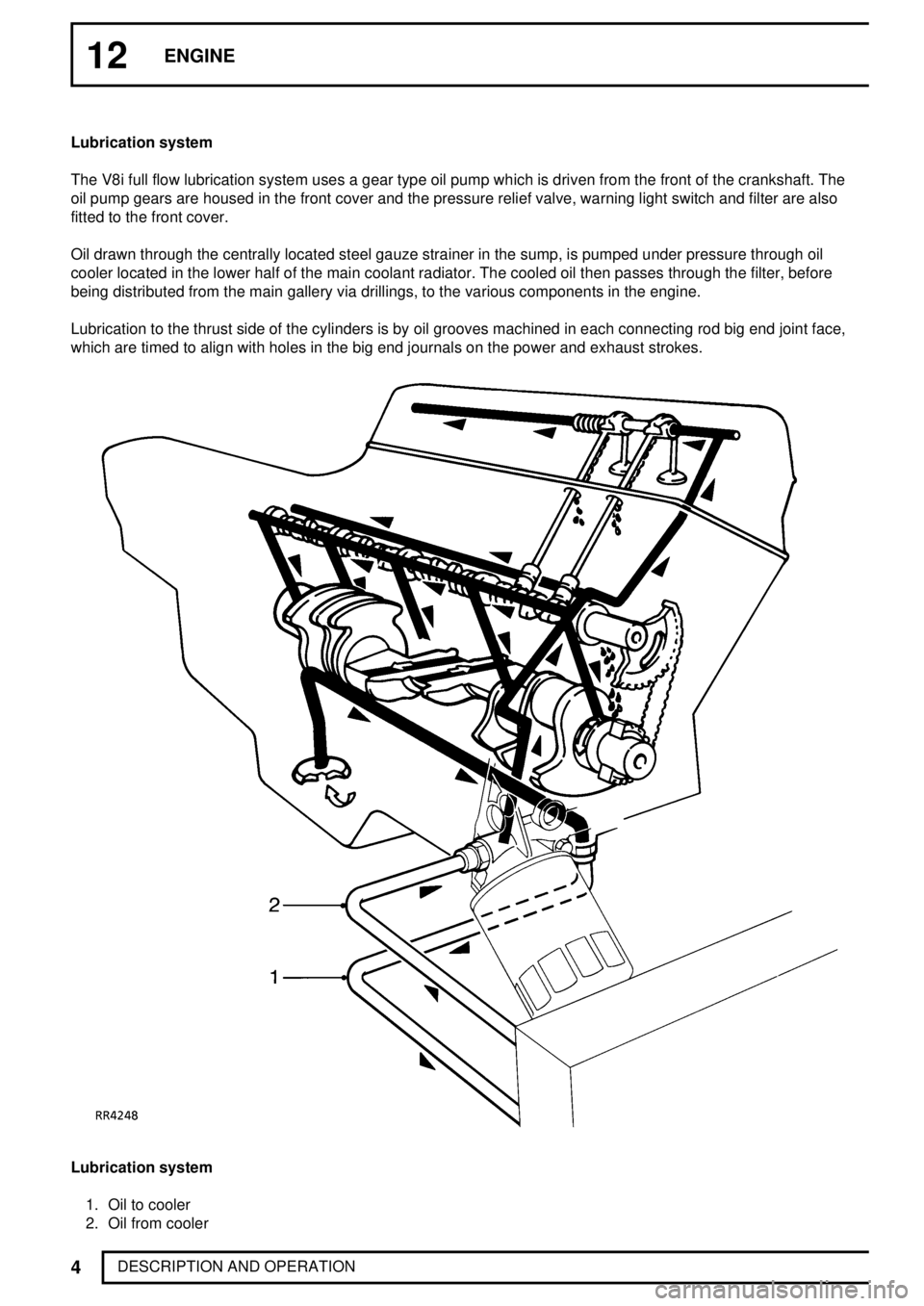
12ENGINE
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Lubrication system
The V8i full flow lubrication system uses a gear type oil pump which is driven from the front of the crankshaft. The
oil pump gears are housed in the front cover and the pressure relief valve, warning light switch and filter are also
fitted to the front cover.
Oil drawn through the centrally located steel gauze strainer in the sump, is pumped under pressure through oil
cooler located in the lower half of the main coolant radiator. The cooled oil then passes through the filter, before
being distributed from the main gallery via drillings, to the various components in the engine.
Lubrication to the thrust side of the cylinders is by oil grooves machined in each connecting rod big end joint face,
which are timed to align with holes in the big end journals on the power and exhaust strokes.
Lubrication system
1. Oil to cooler
2. Oil from cooler
Page 113 of 873
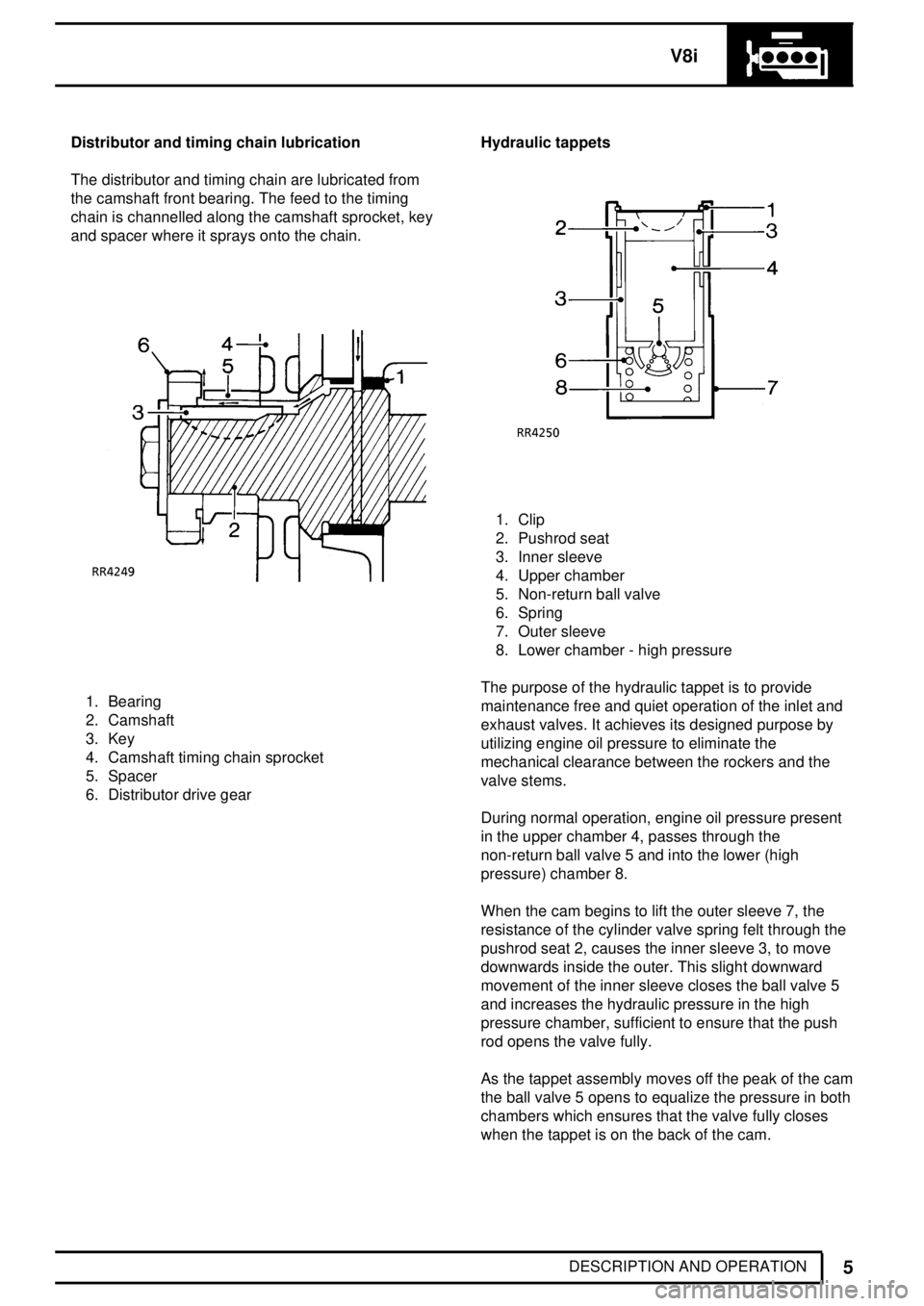
V8i
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Distributor and timing chain lubrication
The distributor and timing chain are lubricated from
the camshaft front bearing. The feed to the timing
chain is channelled along the camshaft sprocket, key
and spacer where it sprays onto the chain.
1. Bearing
2. Camshaft
3. Key
4. Camshaft timing chain sprocket
5. Spacer
6. Distributor drive gearHydraulic tappets
1. Clip
2. Pushrod seat
3. Inner sleeve
4. Upper chamber
5. Non-return ball valve
6. Spring
7. Outer sleeve
8. Lower chamber - high pressure
The purpose of the hydraulic tappet is to provide
maintenance free and quiet operation of the inlet and
exhaust valves. It achieves its designed purpose by
utilizing engine oil pressure to eliminate the
mechanical clearance between the rockers and the
valve stems.
During normal operation, engine oil pressure present
in the upper chamber 4, passes through the
non-return ball valve 5 and into the lower (high
pressure) chamber 8.
When the cam begins to lift the outer sleeve 7, the
resistance of the cylinder valve spring felt through the
pushrod seat 2, causes the inner sleeve 3, to move
downwards inside the outer. This slight downward
movement of the inner sleeve closes the ball valve 5
and increases the hydraulic pressure in the high
pressure chamber, sufficient to ensure that the push
rod opens the valve fully.
As the tappet assembly moves off the peak of the cam
the ball valve 5 opens to equalize the pressure in both
chambers which ensures that the valve fully closes
when the tappet is on the back of the cam.
Page 114 of 873
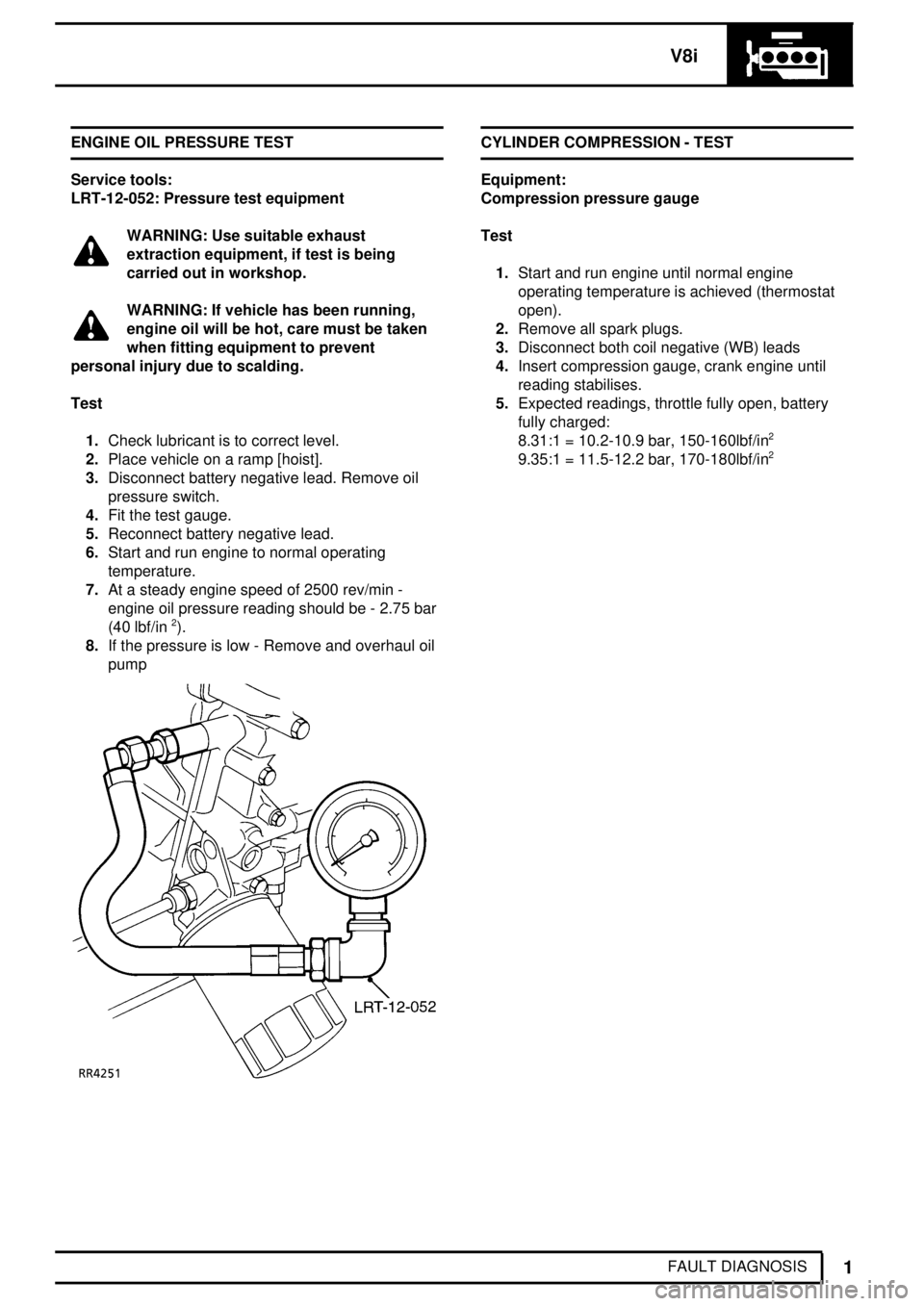
V8i
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS ENGINE OIL PRESSURE TEST
Service tools:
LRT-12-052: Pressure test equipment
WARNING: Use suitable exhaust
extraction equipment, if test is being
carried out in workshop.
WARNING: If vehicle has been running,
engine oil will be hot, care must be taken
when fitting equipment to prevent
personal injury due to scalding.
Test
1.Check lubricant is to correct level.
2.Place vehicle on a ramp [hoist].
3.Disconnect battery negative lead. Remove oil
pressure switch.
4.Fit the test gauge.
5.Reconnect battery negative lead.
6.Start and run engine to normal operating
temperature.
7.At a steady engine speed of 2500 rev/min -
engine oil pressure reading should be - 2.75 bar
(40 lbf/in
2).
8.If the pressure is low - Remove and overhaul oil
pump
CYLINDER COMPRESSION - TEST
Equipment:
Compression pressure gauge
Test
1.Start and run engine until normal engine
operating temperature is achieved (thermostat
open).
2.Remove all spark plugs.
3.Disconnect both coil negative (WB) leads
4.Insert compression gauge, crank engine until
reading stabilises.
5.Expected readings, throttle fully open, battery
fully charged:
8.31:1 = 10.2-10.9 bar, 150-160lbf/in
2
9.35:1 = 11.5-12.2 bar, 170-180lbf/in2
Page 115 of 873

12ENGINE
2
FAULT DIAGNOSIS ENGINE NOISES
Excessive or obtrusive noise from the engine
compartment originates from three main sources:
A. The exhaust system, which makes an
unmistakable and easy to diagnose noise.
B. External components emit the greatest variety of
noises, but are also easy to diagnose by simply
removing the drive belt.
C. Engine internal mechanical noises which can
vary in volume and pitch and may be a
combination of, tapping - knocking or rumbling,
are the most difficult to diagnose. The following
is therefore a guide to diagnosis of engine
internal mechanical noises only.
Engine internal mechanical noises.
Single or multiple, light tapping noise, particularly
when engine is cold.
See Description and
operation, Description
1.Is engine oil level correct?
NO - Top up to correct level.
See
LUBRICANTS, FLUIDS AND
CAPACITIES, Information,
Recommended Lubricants and Fluids
YES - Continue.
2.Is the lubricating pressure correct?
NO -
See Engine Oil Pressure Test
YES - Suspect valve operating mechanism.
3.To confirm diagnosis, remove the rocker covers
and with the engine idling, insert a feeler gauge
of 0,015mm between each rocker and valve
stem. A faulty valve operating mechanism will
emit a different noise when the feeler gauge is
inserted.
See Repair, Rocker Shaft Renew
Heavy knocking noise (particularly on load and
when engine is hot).
See Description and
operation, Description
1.Is engine oil level correct?
NO - Top up to correct level.
See
LUBRICANTS, FLUIDS AND
CAPACITIES, Information,
Recommended Lubricants and Fluids
YES - Continue.
2.Is the lubricating pressure correct?
NO -
See Engine Oil Pressure Test
YES - Drain engine oil and filter, and examine
for metallic contamination.
3.Is the oil contaminated with metal particles?
YES - Suspect faulty big end bearings. To
confirm diagnosis, short out the ignition to
each spark plug in turn. The noise will
disappear or be reduced when the
cylinder with the faulty big end is shorted
out.
4.If noise is not conclusively diagnosed, check the
security of the flywheel and crankshaft front
pulley. Temporarily release the drive belt to
reduce general noise level and use a
stethoscope to locate source of noise.
Heavy rumbling noise (particularly during hard
acceleration).
See Description and operation,
Description
1.Is engine oil level correct?
NO - Top up to correct level.
See
LUBRICANTS, FLUIDS AND
CAPACITIES, Information,
Recommended Lubricants and Fluids
YES - Continue.
2.Is the lubricating pressure correct?
NO -
See Engine Oil Pressure Test
YES - Drain engine oil and filter, and examine
for metallic contamination.
3.Is the oil contaminated with metal particles?
YES - Suspect faulty main bearings. If noise is
not conclusively diagnosed, check the
security of the flywheel and crankshaft
front pulley. Temporarily release the drive
belt to reduce general noise level and use
a stethoscope to locate source of noise.
Page 116 of 873

V8i
3
FAULT DIAGNOSIS ENGINE STARTING PROBLEMS
Engine fails to crank in park or neutral (Automatic
Transmission)
1.Is battery in good state of charge?
NO -
See INTRODUCTION, Information,
Jump Starting
YES - Continue.
2.Is automatic transmission inhibitor switch faulty
or gear selection linkage incorrectly adjusted?
YES -
See AUTOMATIC GEARBOX, Repair,
Inhibitor Switch
,
NO -
See Electrical Trouble Shooting
Manual.
If problem is not diagnosed repeat tests, starting
at 1.
Engine fails to crank (Manual Transmission)
1.Is battery in good state of charge?
NO -
See INTRODUCTION, Information,
Jump Starting
YES -See Electrical Trouble Shooting
Manual.
If problem is not diagnosed repeat tests, starting
at 1.
Engine cranks but fails to start
1.Is the cranking speed fast enough (120 rpm)?
NO -
See INTRODUCTION, Information,
Jump Starting
If necessary also.See Electrical Trouble
Shooting Manual.
YES - Continue.
2.Is there combustion in any cylinder?
NO -
See ELECTRICAL, Fault diagnosis,
Lucas Constant Energy Ignition
System - V8i See Electrical Trouble
Shooting Manual.
YES - Continue.
3.Are the fuel supply, tank, pump, ventilation and
emission control systems in correct working
order or the fuel contaminated?
NO -
See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair, Fuel
Filter See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Tank See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel pump and Sender Unit See
EMISSION CONTROL, Description and
operation, Emission control
If problem is not diagnosed repeat tests, starting
at 2.ENGINE RUNNING PROBLEMS
Engine runs at high speed but will not idle (stops)
Engine idle speed erratic Engine starts but stops
immediately
Engine stalls Engine misfires/hesitation
1.Multiport fuel injection.
See Electrical Trouble
Shooting Manual. See ELECTRICAL, Fault
diagnosis, Lucas Constant Energy Ignition
System - V8i
Check brake vacuum connections.See
BRAKES, Description and operation, Brake
Servo Unit
Check heater/ventilation unit vacuum
connections.
See HEATING AND
VENTILATION, Description and operation,
Heating and Ventilation Unit
If problem is not diagnosed continue.
2.Are HT leads correctly routed and clipped?
NO -
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Distributor
- V8i
YES - Continue.
3.Is fuel supply, tank, pump, ventilation and
emission control systems in correct working
order or the fuel contaminated?
NO -
See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair, Fuel
Filter See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Tank See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Pump and Sender Unit See
EMISSION CONTROL, Description and
operation, Emission Control
If problem is not diagnosed repeat tests, starting
at 1.
Engine lacks power/poor performance
1.Is throttle travel restricted or cable incorrectly
adjusted?
YES - Check thickness of carpets.
See FUEL
SYSTEM, Repair, Throttle Cable See
FUEL SYSTEM, Repair, Accelerator
Pedal
NO - Continue.
2.Are the Ignition and Multiport Fuel Injection
systems in order?
NO -
See Electrical Trouble Shooting
Manual.A1 See ELECTRICAL, Fault
diagnosis, Lucas Constant Energy
Ignition System - V8i See
ELECTRICAL, Repair, Distributor - V8i
YES - Continue.
Page 117 of 873

12ENGINE
4
FAULT DIAGNOSIS 3.Are fuel supply, tank, pump, ventilation and
emission control systems in correct working
order or the fuel contaminated?
NO -
See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair, Fuel
Filter See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Tank See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Pump and Sender Unit
YES - Suspect valves held open by hydraulic
tappets due to high oil pressure.
See
Engine Oil Pressure Test
4.Is oil pressure high?
YES - Remove oil filter and cooler adaptor and
check pressure relief valve strainer gauze
for blockage and that the relief valve is
not stuck closed.
See Description and
operation, Description
NO - Carry out cylinder compression tests to
determine condition of head gaskets and
valves.
See Cylinder Compression -
Test
5.Are cylinder compressions satisfactory?
NO -
See Repair, Cylinder Heads - Renew
YES - Check brake vacuum connections.See
BRAKES, Description and operation,
Brake Servo Unit
Check heater/ventilation unit vacuum connections.
See HEATING AND VENTILATION, Description and
operation, Heating and Ventilation Unit
If problem is not diagnosed: Continue.
6.Are the brakes binding?
YES - Investigate cause of binding.
NO - Continue.
7.Automatic Transmission only. Is the Torque
Converter and Transmission operating correctly?
Carry out Road test, Static tests and Stall tests
to determine condition of Automatic
transmission.
If problem is not diagnosed: repeat tests starting at 1.Engine backfires into exhaust system
1.Are there any leaking joints/connections or holes
in the exhaust system?
YES -
See MANIFOLD AND EXHAUST
SYSTEM, Repair, Exhaust System
Complete
NO - Continue.
2.Is distributor fitted correctly, HT leads in correct
firing order and routed correctly?
NO -
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Distributor
- V8i
YES - Continue.
3.Is air fuel ratio correct?
NO - Check multiport fuel injection.
See
Electrical Trouble Shooting Manual.
Check brake vacuum connections.See
BRAKES, Description and operation, Brake
Servo Unit
Check heater/ventilation unit vacuum
connections.
See HEATING AND
VENTILATION, Description and operation,
Heating and Ventilation Unit
Check the crank case and fuel tank ventilation
system.
See EMISSION CONTROL,
Description and operation, Emission Control
YES - Continue.
4.Are cylinder compressions satisfactory?
NO - Carry out compression test to check for
leaking gaskets valves etc.
See
Cylinder Compression - Test
See Repair, Cylinder Heads - Renew
If problem is not diagnosed: repeat tests starting
at 1.
Page 118 of 873

V8i
5
FAULT DIAGNOSIS Engine backfires into inlet system
1.Is the Distributor, HT connections and routing
correct?
NO -
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Distributor
- V8i
YES - Continue.
2.Is air fuel ratio correct?
NO - Check multiport fuel injection.
See
Electrical Trouble Shooting Manual.
Check brake vacuum connections.See
BRAKES, Description and operation, Brake
Servo Unit
Check heater/ventilation unit vacuum
connections.
See HEATING AND
VENTILATION, Description and operation,
Heating and Ventilation Unit
Check the crank case and fuel tank ventilation
system.
See EMISSION CONTROL,
Description and operation, Emission Control
YES - Continue.
3.Are cylinder compressions satisfactory?
NO - Carry out compression test to check for
leaking gaskets valves etc.
See
Cylinder Compression - Test
For repairSee Repair, Cylinder Heads -
Renew
If problem is not diagnosed: repeat tests starting
at 1.
Page 119 of 873
V8i
1
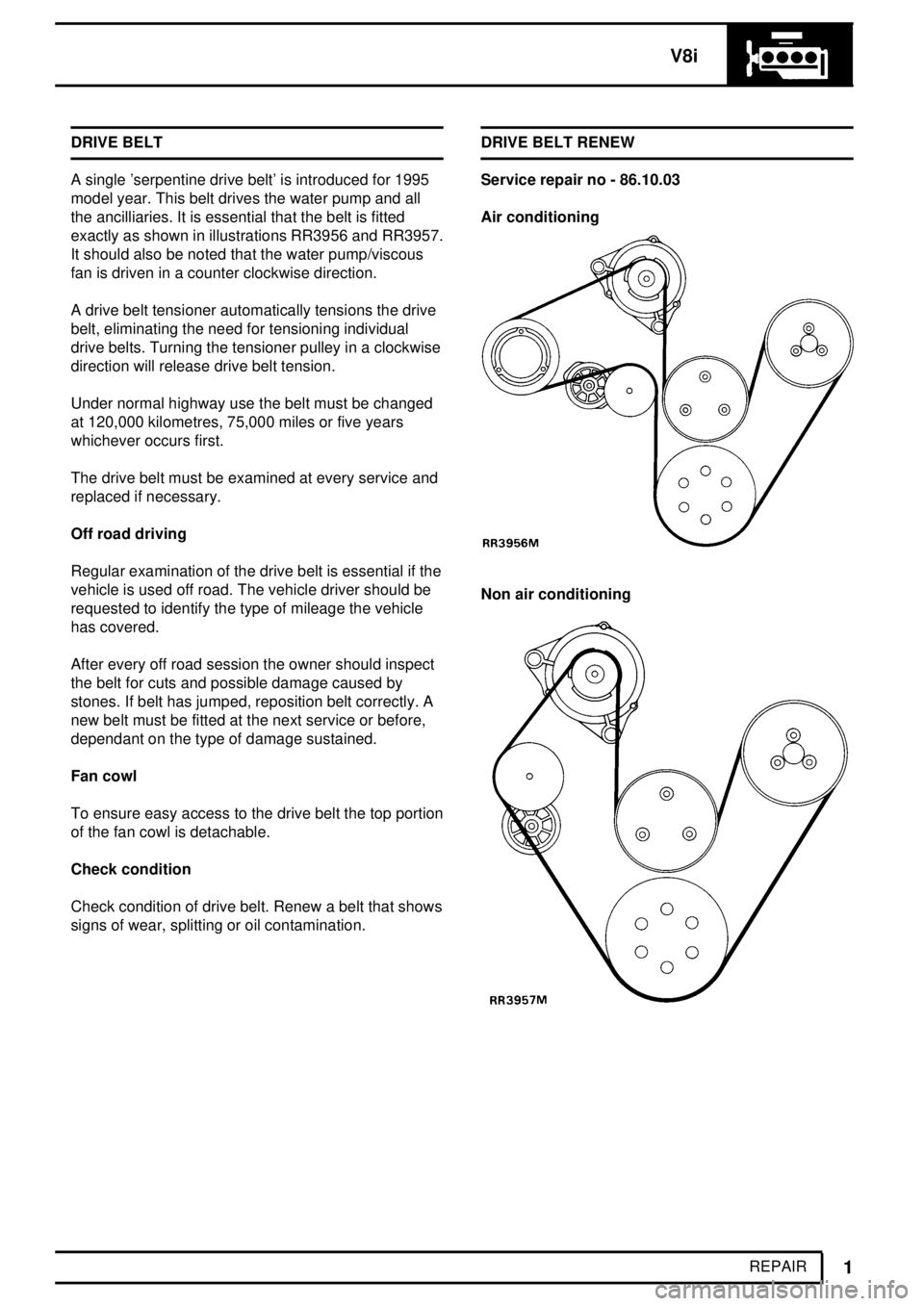
REPAIR DRIVE BELT
A single 'serpentine drive belt' is introduced for 1995
model year. This belt drives the water pump and all
the ancilliaries. It is essential that the belt is fitted
exactly as shown in illustrations RR3956 and RR3957.
It should also be noted that the water pump/viscous
fan is driven in a counter clockwise direction.
A drive belt tensioner automatically tensions the drive
belt, eliminating the need for tensioning individual
drive belts. Turning the tensioner pulley in a clockwise
direction will release drive belt tension.
Under normal highway use the belt must be changed
at 120,000 kilometres, 75,000 miles or five years
whichever occurs first.
The drive belt must be examined at every service and
replaced if necessary.
Off road driving
Regular examination of the drive belt is essential if the
vehicle is used off road. The vehicle driver should be
requested to identify the type of mileage the vehicle
has covered.
After every off road session the owner should inspect
the belt for cuts and possible damage caused by
stones. If belt has jumped, reposition belt correctly. A
new belt must be fitted at the next service or before,
dependant on the type of damage sustained.
Fan cowl
To ensure easy access to the drive belt the top portion
of the fan cowl is detachable.
Check condition
Check condition of drive belt. Renew a belt that shows
signs of wear, splitting or oil contamination.DRIVE BELT RENEW
Service repair no - 86.10.03
Air conditioning
Non air conditioning
Page 120 of 873

12ENGINE
2
REPAIR Remove
1.Remove fan cowl upper.
2.Release drive belt tension by turning tensioner
clockwise.
3.With tension released, remove belt from
generator pulley.
4.Release tensioner pulley.
5.Remove drive belt. Mark direction of rotation on
belt if refitting
Refit
6.Clean drive belt pulley grooves and ensure
grooves are not damaged.
7.Position belt correctly around all pulleys except
generator. Illustrations RR3956 and RR3957
show correct drive belt run.
8.Turn drive belt tensioner clockwise.
9.Locate drive belt on generator pulley.
10.Ensure drive belt is squarely located on pulleys
with all grooves engaged.
11.Release tensioner to tension drive belt.
12.Fit upper fan cowl section.DRIVE BELT - CHECK TENSION
As the drive belt is automatically tensioned, no tension
check or adjustment should be necessary. If the drive
belt is believed to be slack carry out the following
checks:
1.Visually check drive belt tension.
2.Watch movement of tensioner with engine
running, 5 mm 'bounce' is normal. If tensioner
movement is 12 mm or more, fit a new tensioner.
See Drive Belt Tensioner
3.Inspect tensioner. Is the tensioner arm and
spring case in contact? If so fit a new tensioner.
4.Using a recognised drive belt tensioning gauge,
check belt tension several times, running engine
between checks. The checks should be made at
the same point on the belt, away from the
tensioner.
Drive belt tension, with used tensioner and used drive
belt should be more than:-
270N. Non air conditioning or
295N with air conditioning.