coolant temperature LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 348 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-49
Operation - engine management
Fuel quantity
The ECM controls engine fuel quantity by providing sequential injection to the cylinders. Sequential injection allows
each injector to deliver fuel to the cylinders in the required firing order.
To achieve optimum fuel quantity under all driving conditions, the ECM provides an adaptive fuel strategy.
Conditions
Adaptive fuel strategy must be maintained under all throttle positions except:
lCold starting.
lHot starting.
lWide open throttle.
lAcceleration.
All of the throttle positions mentioned above are deemed to be 'open loop'. Open loop fuelling does not rely on
information from the HO
2 sensors, but the air/ fuel ratio is set directly by the ECM. During cold start conditions the
ECM uses ECT information to allow more fuel to be injected into the cylinders to facilitate cold starting. This strategy
is maintained until the HO
2 sensors are at working temperature and can pass exhaust gas information to the ECM.
Because of the specific nature of the other functions e.g. hot starting, idle, wide open throttle, and acceleration they
also require an 'open loop' strategy. For NAS vehicles with secondary air injection for cold start conditions, refer to
the Emissions section.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Secondary Air Injection System.
Adaptive fuel strategy also allows for wear in the engine and components, as well as slight differences in component
signals, as no two components will give exactly the same readings.
Function
To be able to calculate the amount of fuel to be injected into each cylinder, the ECM needs to determine the amount
of air mass drawn into each cylinder. To perform this calculation, the ECM processes information from the following
sensors:
lMass air flow (MAF) sensor.
lCrank speed and position (CKP) sensor.
lEngine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
lThrottle position (TP) sensor.
During one engine revolution, 4 of the 8 cylinders draw in air. The ECM uses CKP sensor information to determine
that one engine revolution has taken place, and the MAF sensor information to determine how much air has been
drawn into engine. The amount of air drawn into each cylinder is therefore 1/4 of the total amount measured by the
ECM via the MAF sensor.
The ECM refers the measured air mass against a fuel quantity map in its memory and then supplies an earth path to
the relevant fuel injector for a period corresponding to the exact amount of fuel to be injected into the lower inlet
manifold. This fuel quantity is in direct relation to the air mass drawn into each cylinder to provide the optimum ratio.
During adaptive fuelling conditions, information from the heated oxygen sensors (HO
2S) is used by the ECM to correct
the fuel quantity to keep the air/ fuel ratio as close to the stoichiometric ideal as possible.
Closed loop fuelling
The ECM uses a closed loop fuelling system as part of its fuelling strategy. The operation of the three-way catalytic
converter relies on the ECM being able to optimise the air/ fuel mixture, switching between rich and lean either side
of lambda one. Closed loop fuelling is not standard for all markets, vehicles that are not fitted with HO
2S do not have
closed loop fuelling.
The ideal stoichiometric ratio is represented by λ =1. The ratio can be explained as 14.7 parts of air to every 1 part of
fuel.
Page 356 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-57
Low fuel level signal
When the fuel level in the fuel tank becomes low enough to illuminate the low fuel level warning lamp in the instrument
cluster, the instrument cluster generates a low fuel level signal. If the low fuel level signal is present during the ECM
misfire detection function the ECM can use it to check for a 'false misfire'.
Conditions
The fuel sender generates the low fuel level signal when the fuel sender resistance is greater than 158 ± 8 ohms.
Function
The illumination of the low fuel level warning lamp in the instrument cluster triggers the low fuel level signal to be sent
to the ECM. This signal is processed via pin 8 of connector C0637 of the ECM.
Should a misfire occur while the fuel level is low, the following fault code may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Coolant temperature gauge signal
The ECM controls the temperature gauge in the instrument cluster. The ECM sends a coolant temperature signal to
the temperature gauge in the instrument cluster in the form of a PWM square wave signal.
The frequency of the signal determines the level of the temperature gauge.
Conditions
The ECM operates the PWM signal under the following parameters:
l-40 °C (-40 °F) = a pulse width of 768 µs.
l140 °C (284 °F) = a pulse width of 4848 µs.
Function
The coolant temperature signal is an output from the ECM to the instrument cluster. The coolant temperature signal
is generated via pin 44 of connector C0636 of the ECM.
The coolant temperature signal can fail in the following ways:
lWiring short circuit to vehicle supply.
lWiring short circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring open circuit.
In the event of a coolant temperature signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lCoolant temperature gauge will read cold at all times.
lCoolant temperature warning lamp remains on at all times.
Controller Area Network (CAN) system
The controller area network (CAN) system is a high speed serial interface between the ECM and the Electronic
Automatic Transmission (EAT) ECU. The CAN system uses a 'data bus' to transmit information messages between
the ECM and the EAT ECU. Because there are only two components in this CAN system, one will transmit information
messages and the other will receive information messages, and vice-versa.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1319 Misfire detected at low fuel level Misfire detected with low fuel level
Page 357 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-58 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Conditions
The CAN system is used by the EAT ECU and the ECM for transmission of the following information:
lGearshift torque control information.
lEAT OBD information.
lMIL request.
lVehicle speed signal.
lEngine temperature.
lEngine torque and speed.
lGear selected.
lGear change information.
lAltitude adaptation factor
lAir intake temperature
lThrottle angle / pedal position
Function
The CAN system uses a twisted pair of wires to form the 'data bus' to minimise electrical interference. This method of
serial interface is very reliable and very fast. The information messages are structured so that each of the receivers
(ECM or EAT ECU) is able to interpret and react to the messages sent.
The CAN 'data bus' is directly connected between pin 36 of connector C0637 of the ECM and pin 16 of connector
C0193 at the EAT ECU, and pin 37 of connector C0637 of the ECM and pin 44 of connector C0193 at the EAT ECU.
The CAN system can fail in the following ways:
lCAN data bus wiring open circuit.
lCAN data bus wiring short circuit.
In the event of a CAN data bus failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lMIL illuminated after 2 drive cycles (NAS only).
lEAT defaults to 3rd gear only.
lHarsh gearshifts.
l'Sport' and 'manual' lights flash alternately.
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Drive cycles
The following are the TestBook drive cycles:
⇒ Drive cycle A:
1Switch on the ignition for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
⇒ Drive cycle B:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Allow engine to idle for 2 minutes.
8Connect TestBook and with the engine still running, check for fault codes.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0600 Serial communication link malfunction CAN time out
P1776 Transmission control system torque interface
malfunctionEAT torque interface error
Page 358 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-59
⇒ Drive cycle C:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Cruise at 60 mph (100 km/h) for 8 minutes.
8Cruise at 50 mph (80 km/h) for 3 minutes.
9Allow engine to idle for 3 minutes.
10Connect TestBook and with the engine still running, check for fault codes.
NOTE: The following areas have an associated readiness test which must be flagged as complete, before a problem
resolution can be verified:
lcatalytic converter fault;
lEvaporative loss system fault;
lHO
2 sensor fault;
lHO
2 sensor heater fault.
When carrying out a drive cycle C to determine a fault in any of the above areas, select the readiness test icon to
verify that the test has been flagged as complete.
⇒ Drive cycle D:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 35°C (95°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Cruise at 60 mph (100 km/h) for 5 minutes.
8Cruise at 50 mph (80 km/h) for 5 minutes.
9Cruise at 35 mph (60 km/h) for 5 minutes.
10Allow engine to idle for 2 minutes.
11Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
⇒ Drive cycle E:
1Ensure fuel tank is at least a quarter full.
2Carry out Drive Cycle A.
3Switch off ignition.
4Leave vehicle undisturbed for 20 minutes.
5Switch on ignition.
6Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
Page 381 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-82 REPAIRS
Sensor - engine coolant temperature
(ECT)
$% 18.30.10
Remove
1.Release turnbuckles and remove battery cover.
2.Disconnect battery earth lead.
3.Remove auxiliary drive belt.
+ CHARGING AND STARTING,
REPAIRS, Belt - auxiliary drive.
4.Remove 2 bolts securing alternator, release
alternator from support bracket and position
aside. 5.Disconnect multiplug from ECT sensor.
6.Remove sensor from inlet manifold and discard
sealing washer.
Refit
1.Clean sealant from threads in manifold.
2.Apply sealant, Part No. STC 50552 to sensor
threads.
3.Fit new sealing washer to ECT sensor and
tighten sensor to 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
4.Connect multiplug to ECT sensor.
5.Position alternator, fit bolts and tighten to 45
Nm (33 lbf.ft).
6.Fit auxiliary drive belt.
+ CHARGING AND STARTING,
REPAIRS, Belt - auxiliary drive.
7.Top up cooling system.
8.Connect battery earth lead.
9.Fit battery cover and secure with fixings.
Page 383 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-84 REPAIRS
Sensor - radiator temperature
$% 18.30.20
Remove
1.Disconnect battery earth lead.
2.Position container to collect coolant spillage.
3.Disconnect multiplug from sensor.
4.Remove sensor and discard sealing washer.
Refit
1.Fit new sealing washer to sensor.
2.Fit and tighten sensor.
3.Connect multiplug to sensor.
4.Refill cooling system.
5.Connect battery earth lead.
Sensor - camshaft position (CMP)
$% 18.30.24
Remove
1.Release fixings and remove battery cover.
2.Disconnect battery earth lead.
3.Raise front of vehicle.
WARNING: Do not work on or under a
vehicle supported only by a jack. Always
support the vehicle on safety stands.
4.Release fixings and remove underbelly panel.
5.Remove engine oil filter.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Filter - oil.
6.Disconnect engine harness from CMP sensor
and release CMP sensor multiplug from
bracket.
7.Remove bolt from clamp securing CMP sensor
to timing gear cover.
8.Remove clamp and CMP sensor. Discard 'O'
ring from CMP sensor.
Refit
1.Ensure CMP sensor is clean, fit new 'O' ring
and sensor to cover.
2.Fit clamp to CMP sensor and tighten bolt to 8
Nm (6 lbf.ft).
3.Fit sensor multiplug to bracket and connect
engine harness to multiplug.
4.Fit engine oil filter.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Filter - oil.
5.Fit underbelly panel and secure with fixings.
6.Lower vehicle and connect battery earth lead.
7.Fit battery cover and secure with fixings.
Page 421 of 1529

COOLING SYSTEM - V8
26-2-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The cooling system used on the V8 engine is a pressure relief by-pass type system which allows coolant to circulate
around the cylinder block and the heater circuit when the thermostat is closed. With coolant not passing through the
radiator, this promotes faster heater warm-up which in turn improves passenger comfort.
A coolant pump is located in a housing at the front of the engine and is driven by a drive belt. The pump is connected
into the coolant passages cast in the cylinder block and pumps coolant from the radiator through the cylinder block.
A viscous fan is attached by means of a nut to the coolant pump pulley drive spindle. The fan draws air through the
radiator to assist in cooling when the vehicle is stationary. The fan rotational speed is controlled relative to the running
temperature of the engine by a thermostatic valve regulated by a bi-metallic coil.
The cooling system uses a 50/50 mix of anti-freeze and water.
Thermostat housing
A plastic thermostat housing is located behind the radiator. The housing has three connections which locate the
radiator bottom hose, top hose and coolant pump feed hose. The housing contains a wax element and a spring loaded
by-pass flow valve.
Thermostat - Main valve
The thermostat is used to maintain the coolant at the optimum temperature for efficient combustion and to aid engine
warm-up. The thermostat is closed at temperatures below approximately 82°C (179°F). When the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 82°C the thermostat starts to open and is fully open at approximately 96°C
(204°F). In this condition the full flow of coolant is directed through the radiator.
The thermostat is exposed to 90% hot coolant from the engine on one side and 10% cold coolant returning from the
radiator bottom hose on the other side.
Hot coolant from the engine passes from the by-pass pipe through four sensing holes in the flow valve into a tube
surrounding 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the engine, cooled by the radiator,
conducts through 10% of the sensitive area.
In cold ambient temperatures, the engine temperature is raised by approximately 10°C (50°F) to compensate for the
heat loss of 10% exposure to the cold coolant returning from the bottom hose.
By-pass flow valve
The by-pass flow valve is held closed by a light spring. It operates to further aid heater warm-up. When the main valve
is closed and the engine speed is at idle, the coolant pump does not produce sufficient flow and pressure to open the
valve. In this condition the valve prevents coolant circulating through the by-pass circuit and forces the coolant through
the heater matrix only. This provides a higher flow of coolant through the heater matrix to improve passenger comfort
in cold conditions.
When the engine speed increases above idle the coolant pump produces a greater flow and pressure than the heater
circuit can take. The pressure acts on the flow valve and overcomes the valve spring pressure, opening the valve and
limiting the pressure in the heater circuit. The valve modulates to provide maximum coolant flow through the heater
matrix and yet allowing excess coolant to flow into the by-pass circuit to provide the engine's cooling needs at higher
engine rev/min.
Page 422 of 1529

COOLING SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 26-2-7
Inlet manifold - Cooling connections
Coolant leaves the cylinder block via an outlet pipe attached to the front of the air intake manifold. The pipe is
connected to the thermostat housing and the radiator by a branch hose off the radiator top hose.
Hot coolant from the engine is also directed from the inlet manifold via pipes and hoses into the heater matrix. Coolant
is circulated through the heater matrix at all times when the engine is running.
A further tapping from the inlet manifold supplies coolant to the throttle housing via a hose. The coolant circulates
through a plate attached to the bottom of the housing and is returned through a plastic bleed pipe to an expansion
tank. The hot coolant heats the air intake of the throttle housing preventing ice from forming.
An Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is fitted in the inlet manifold adjacent to the manifold outlet pipe. The
sensor monitors coolant temperature emerging from the engine and sends signals to the ECM for engine
management and temperature gauge operation.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
Expansion tank
The expansion tank is located in the engine compartment. The tank is made from moulded plastic and attached to
brackets on the right hand inner wing. A maximum coolant when cold level is moulded onto the tank.
Excess coolant created by heat expansion is returned to the expansion tank from the radiator bleed pipe at the top of
the radiator. An outlet pipe is connected into the pump feed hose and replaces the coolant displaced by heat
expansion into the system when the engine is cool.
The expansion tank is fitted with a sealed pressure cap. The cap contains a pressure relief valve which opens to allow
excessive pressure and coolant to vent through the overflow pipe. The relief valve opens at a pressure of 1.4 bar (20
lbf.in
2) and above.
Heater matrix
The heater matrix is fitted in the heater assembly inside the passenger compartment. Two pipes pass through the
bulkhead into the engine compartment and provide coolant flow to and from the matrix. The pipes from the bulkhead
are connected to the matrix, sealed with 'O' rings and clamped with circular rings.
The matrix is constructed from aluminium with two end tanks interconnected with tubes. Aluminium fins are located
between the tubes and conduct heat away from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes. Air from the heater
assembly is warmed as it passes through the matrix fins. The warm air is then distributed into the passenger
compartment as required.
+ HEATING AND VENTILATION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.When the engine is
running, coolant from the engine is constantly circulated through the heater matrix.
Radiator
The 45 row radiator is located at the front of the vehicle. The cross-flow type radiator is manufactured from aluminium
with moulded plastic end tanks interconnected with tubes. Aluminium fins are located between the tubes and conduct
heat from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes, reducing the cooling temperature as it flows through the radiator.
Air intake from the front of the vehicle when moving carries heat away from the fins. When the vehicle is stationary,
the viscous fan draws air through the radiator fins to prevent the engine from overheating.
Two connections at the top of the radiator provide for the attachment of the top hose and bleed pipe. A connection at
the bottom of the radiator allows for the attachment of the bottom hose to the thermostat housing.
Two smaller radiators are located in front of the cooling radiator. The lower radiator provides cooling of the gearbox
oil and the upper radiator provides cooling for the engine oil.
+ MANUAL GEARBOX - R380, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
+ AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22 - 24, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
+ ENGINE - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Pipes and hoses
The coolant circuit comprises flexible hoses and metal formed pipes which direct coolant into and out of the engine,
radiator and heater matrix. Plastic pipes are used for the bleed and overflow pipes to the expansion tank.
A bleed screw is installed in the radiator top hose and is used to bleed air during system filling. A drain plug is fitted
to each cylinder bank in the cylinder block. These are used to drain the block of coolant.
Page 424 of 1529
COOLING SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 26-2-9
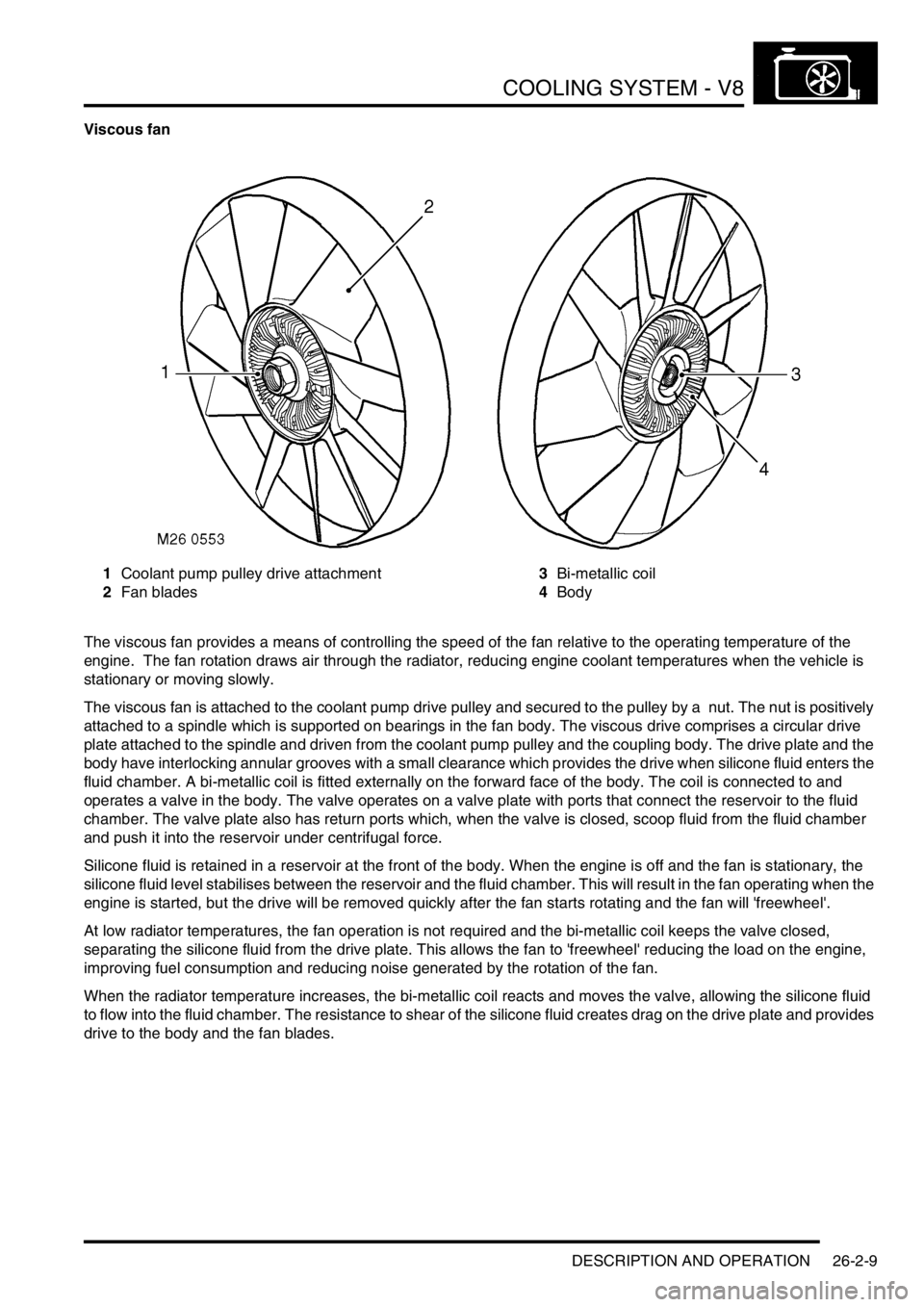
Viscous fan
1Coolant pump pulley drive attachment
2Fan blades3Bi-metallic coil
4Body
The viscous fan provides a means of controlling the speed of the fan relative to the operating temperature of the
engine. The fan rotation draws air through the radiator, reducing engine coolant temperatures when the vehicle is
stationary or moving slowly.
The viscous fan is attached to the coolant pump drive pulley and secured to the pulley by a nut. The nut is positively
attached to a spindle which is supported on bearings in the fan body. The viscous drive comprises a circular drive
plate attached to the spindle and driven from the coolant pump pulley and the coupling body. The drive plate and the
body have interlocking annular grooves with a small clearance which provides the drive when silicone fluid enters the
fluid chamber. A bi-metallic coil is fitted externally on the forward face of the body. The coil is connected to and
operates a valve in the body. The valve operates on a valve plate with ports that connect the reservoir to the fluid
chamber. The valve plate also has return ports which, when the valve is closed, scoop fluid from the fluid chamber
and push it into the reservoir under centrifugal force.
Silicone fluid is retained in a reservoir at the front of the body. When the engine is off and the fan is stationary, the
silicone fluid level stabilises between the reservoir and the fluid chamber. This will result in the fan operating when the
engine is started, but the drive will be removed quickly after the fan starts rotating and the fan will 'freewheel'.
At low radiator temperatures, the fan operation is not required and the bi-metallic coil keeps the valve closed,
separating the silicone fluid from the drive plate. This allows the fan to 'freewheel' reducing the load on the engine,
improving fuel consumption and reducing noise generated by the rotation of the fan.
When the radiator temperature increases, the bi-metallic coil reacts and moves the valve, allowing the silicone fluid
to flow into the fluid chamber. The resistance to shear of the silicone fluid creates drag on the drive plate and provides
drive to the body and the fan blades.
Page 425 of 1529

COOLING SYSTEM - V8
26-2-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Coolant flow - Engine warm up
Refer to illustration.
+ COOLING SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Cooling system coolant flow.
During warm-up the coolant pump moves fluid through the cylinder block and it emerges from the inlet manifold outlet
pipe. From the outlet pipe, the warm coolant flow is prevented from flowing through the radiator because the
thermostat is closed. The coolant is directed into the heater circuit.
Some coolant from the by-pass pipe can pass through small sensing holes in the flow valve. The warm coolant enters
a tube in the thermostat housing and surrounds 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the
radiator bottom hose conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area. In cold ambient temperatures the engine
temperature can be raised by up to 10°C (50°F) to compensate for the heat loss of the 10% exposure to the cold
coolant returning from the radiator bottom hose.
At engine idle speed, the by-pass valve is closed only allowing the small flow through the sensing holes. As the engine
speed increases above idle, the greater flow and pressure from the pump overcomes the light spring and opens the
by-pass flow valve. The flow valve opens to meet the engines cooling needs at higher engine speeds and prevents
excess pressure in the system. With the thermostat closed, maximum flow is directed through the heater circuit.
The heater matrix acts as a heat exchanger reducing coolant temperature as it passes through the matrix. Coolant
emerges from the matrix and flows into the coolant pump feed pipe and recirculated around the heater circuit. In this
condition the cooling system is operating at maximum heater performance.
Coolant flow - Engine hot
As the coolant temperature increases the thermostat opens. This allows some coolant from the outlet housing to flow
through the top hose and into the radiator to be cooled. The hot coolant flows from the left tank in the radiator, along
the tubes to the right tank. The air flowing through the fins between the tubes cools the coolant as it passes through
the radiator.
A controlled flow of the lower temperature coolant is drawn by the pump and blended with hot coolant from the by-
pass and the heater return pipes in the pump feed pipe. The pump then passes this coolant into the cylinder block to
cool the cylinders.