service LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 247 of 1529
EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-14 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The heated oxygen sensor is screwed into threaded mountings welded into the top of the front exhaust pipes at
suitable locations. They are used to detect the level of residual oxygen in the exhaust gas to provide an instantaneous
indication of whether combustion is complete. By positioning sensors in the stream of exhaust gases from each
separate bank of the exhaust manifold, the engine management system is better able to control the fuelling
requirements on each bank independently of the other, so allowing much closer control of the air:fuel ratio and
optimising catalytic converter efficiency.
Two pre-catalytic converter heated oxygen sensors are mounted in the front pipes for monitoring the oxygen content
of the exhaust gas. NAS models also have two additional post-catalytic converter heated oxygen sensors in the
exhaust front pipe.
CAUTION: HO2 sensors are easily damaged by dropping, over torquing, excessive heat or contamination.
Care must be taken not to damage the sensor housing or tip.
The oxygen sensors consist of a ceramic body (Galvanic cell) which is a practically pure oxygen-ion conductor made
from a mixed oxide of zirconium and yttrium. The ceramic is then coated with gas-permeable platinum, which when
heated to a sufficiently high temperature (≥ 350° C) generates a voltage which is proportional to the oxygen content
in the exhaust gas stream.
The heated oxygen sensor is protected by an outer tube with a restricted flow opening to prevent the sensor's
ceramics from being cooled by low temperature exhaust gases at start up. The post-catalytic sensors have improved
signal quality, but a slower response rate.
The pre-catalytic and post-catalytic converter sensors are not interchangeable, and although it is possible to mount
them in transposed positions, their harness connections are of different gender and colour. It is important not to
confuse the sensor signal pins; the signal pins are gold plated, whilst the heater supply pins are tinned,
mixing them up will cause contamination and adversely affect system performance.
Each of the heated oxygen sensors have a four pin connector with the following wiring details:
lSensor signal ground (grey wire – connects to engine management ECM)
lSensor signal (black wire – connects to engine management ECM)
lHeater drive (white wire – connects to engine management ECM)
lHeater supply (white wire – connects to fuse 2, underbonnet fuse box)
The ECM connector pins for exhaust emission control are listed in the following table:
ECM Connector 2 (C635) pin-out details for exhaust emission control system
The heated oxygen sensors should be treated with extreme care, since the ceramic material within them can be easily
cracked if dropped, banged or over-torqued; the sensors should be torqued to the recommended values indicated in
the repair procedures. Apply anti-seize compound to the sensor's threads when refitting.
WARNING: Some types of anti-seize compound used in service are a health hazard. Avoid skin contact.
WARNING: To prevent personal injury from a hot exhaust system, do not attempt to disconnect any
components until the exhaust system has cooled down.
CAUTION: Do not allow anti-seize compound to come into contact with tip of sensor or enter exhaust system.
NOTE: A new HO2 sensor is supplied pre-treated with anti-seize compound.
Pin Number Function Signal Type Control
2-01 Post-cat sensor heater (RH) - NAS only Output, Drive PWM, 12 - 0V
2-07 Post-cat sensor heater (LH) - NAS only Output, Drive PWM, 12 - 0V
2-08 Post-cat sensor (RH) - NAS only Ground, Signal 0V
2-09 Pre-cat sensor (LH) Ground, Signal 0V
2-10 Pre-cat sensor (RH) Ground, Signal 0V
2-11 Post-cat sensor (LH) - NAS only Ground, Signal 0V
2-13 Pre-cat sensor heater (RH) Output, Drive PWM, 12 - 0V
2-14 Post-cat sensor (RH) - NAS only Input, Signal Analogue, 0 - 1V
2-15 Pre-cat sensor (LH) Input, Signal Analogue, 0 - 1V
2-16 Pre-cat sensor (RH) Input, Signal Analogue, 0 - 1V
2-17 Post-cat sensor (LH) - NAS only Input, Signal Analogue, 0 - 1V
2-19 Pre-cat sensor heater (LH) Output, Drive PWM, 12 - 0V
Page 253 of 1529
EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
For NAS vehicles with positive pressure, EVAP system leak detection capability, the atmosphere vent line from the
EVAP canister connects to a port on the fuel leak detection pump via a short, large bore hose which is secured to the
component ports by crimped metal clips at each end. A large bore plastic hose from the top of the leak detection pump
is routed to the RH side of the engine bay where it connects to an air filter canister. Under normal operating conditions
(when the fuel leak detection solenoid valve is not energised), the EVAP canister is able to take in clean air via the
air filter, through the pipework and past the open solenoid valve to allow normal purge operation to take place and
release any build up of EVAP system pressure to atmosphere.
The EVAP system pipes are clipped at various points along the pipe runs and tied together with tie straps at suitable
points along the runs.
The NAS and ROW EVAP canisters are of similar appearance, but use charcoal of different consistency. The ROW
vehicles use granular charcoal of 11 bwc (butane working capacity) and NAS vehicles use pelletised charcoal with a
higher absorption capacity of 15 bwc. All canisters are of rectangular shape and have capacities of 1.8 litres (3 1/8
imp. pts) with purge foam retention.
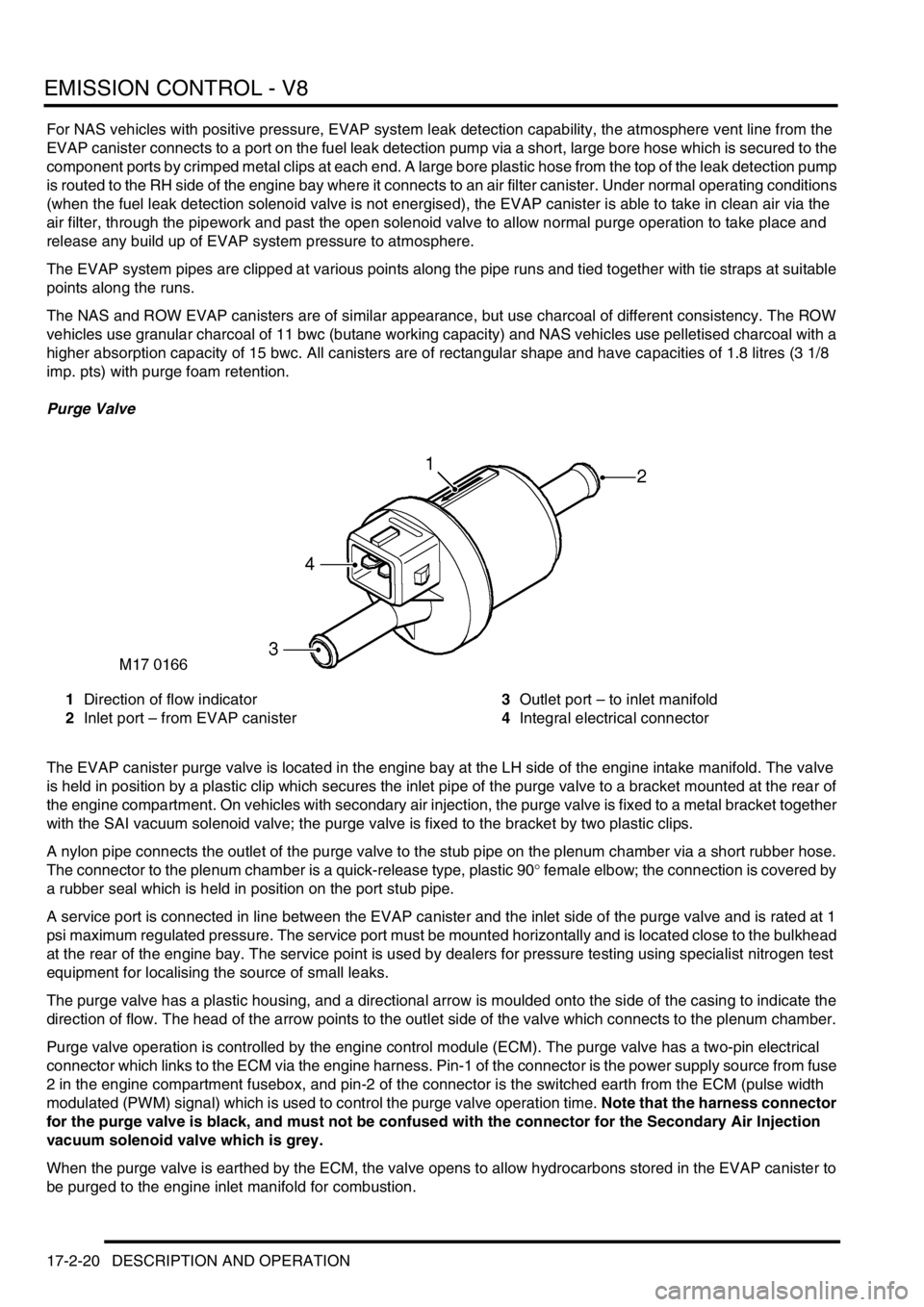
Purge Valve
1Direction of flow indicator
2Inlet port – from EVAP canister3Outlet port – to inlet manifold
4Integral electrical connector
The EVAP canister purge valve is located in the engine bay at the LH side of the engine intake manifold. The valve
is held in position by a plastic clip which secures the inlet pipe of the purge valve to a bracket mounted at the rear of
the engine compartment. On vehicles with secondary air injection, the purge valve is fixed to a metal bracket together
with the SAI vacuum solenoid valve; the purge valve is fixed to the bracket by two plastic clips.
A nylon pipe connects the outlet of the purge valve to the stub pipe on the plenum chamber via a short rubber hose.
The connector to the plenum chamber is a quick-release type, plastic 90° female elbow; the connection is covered by
a rubber seal which is held in position on the port stub pipe.
A service port is connected in line between the EVAP canister and the inlet side of the purge valve and is rated at 1
psi maximum regulated pressure. The service port must be mounted horizontally and is located close to the bulkhead
at the rear of the engine bay. The service point is used by dealers for pressure testing using specialist nitrogen test
equipment for localising the source of small leaks.
The purge valve has a plastic housing, and a directional arrow is moulded onto the side of the casing to indicate the
direction of flow. The head of the arrow points to the outlet side of the valve which connects to the plenum chamber.
Purge valve operation is controlled by the engine control module (ECM). The purge valve has a two-pin electrical
connector which links to the ECM via the engine harness. Pin-1 of the connector is the power supply source from fuse
2 in the engine compartment fusebox, and pin-2 of the connector is the switched earth from the ECM (pulse width
modulated (PWM) signal) which is used to control the purge valve operation time. Note that the harness connector
for the purge valve is black, and must not be confused with the connector for the Secondary Air Injection
vacuum solenoid valve which is grey.
When the purge valve is earthed by the ECM, the valve opens to allow hydrocarbons stored in the EVAP canister to
be purged to the engine inlet manifold for combustion.
Page 255 of 1529
EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-22 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The valve is normally open, allowing any build up of air pressure within the evaporation system to escape, whilst
retaining the environmentally harmful hydrocarbons in the EVAP canister. When the ECM is required to run a fuel
system test, the CVS valve is closed to seal the system. The ECM is then able to measure the pressure in the fuel
evaporative system using the fuel tank pressure sensor.
The ECM performs electrical integrity checks on the CVS valve to determine wiring or power supply faults. The ECM
can also detect a valve blockage if the signal from the fuel tank pressure sensor indicates a depressurising fuel tank
while the CVS valve should be open to atmosphere.
The following failure modes are possible:
lConnector or harness wiring fault (open or short circuit)
lValve stuck open or shut
lValve blocked
If the CVS valve malfunctions, the following fault codes may be stored in the ECM diagnostic memory, which can be
retrieved using TestBook/T4:
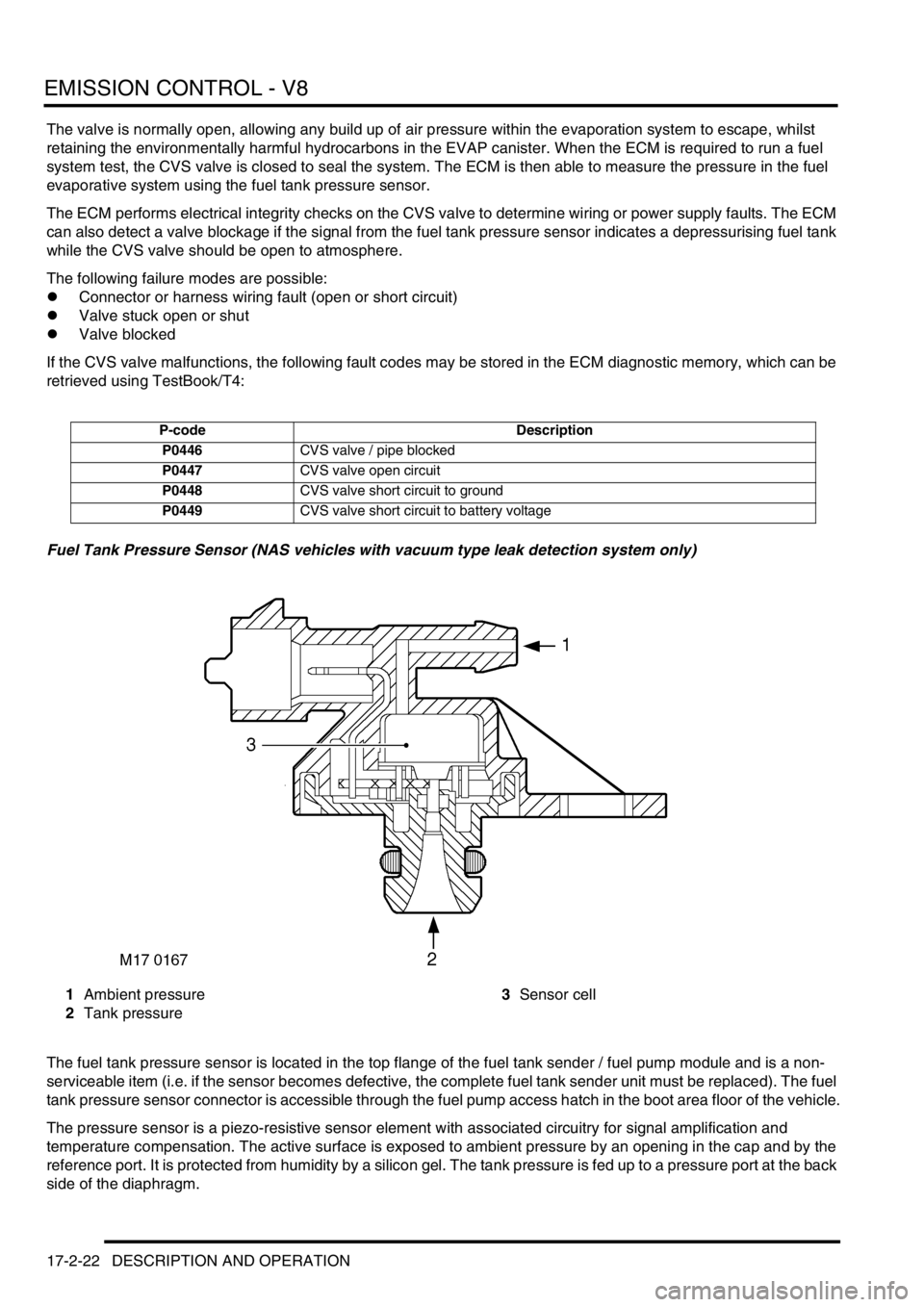
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (NAS vehicles with vacuum type leak detection system only)
1Ambient pressure
2Tank pressure3Sensor cell
The fuel tank pressure sensor is located in the top flange of the fuel tank sender / fuel pump module and is a non-
serviceable item (i.e. if the sensor becomes defective, the complete fuel tank sender unit must be replaced). The fuel
tank pressure sensor connector is accessible through the fuel pump access hatch in the boot area floor of the vehicle.
The pressure sensor is a piezo-resistive sensor element with associated circuitry for signal amplification and
temperature compensation. The active surface is exposed to ambient pressure by an opening in the cap and by the
reference port. It is protected from humidity by a silicon gel. The tank pressure is fed up to a pressure port at the back
side of the diaphragm.
P-code Description
P0446CVS valve / pipe blocked
P0447CVS valve open circuit
P0448CVS valve short circuit to ground
P0449CVS valve short circuit to battery voltage
Page 258 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-25
During the leakage test, the solenoid valve is energised, closing the atmosphere vent line between the EVAP canister
and atmosphere and opening a path to the pressurised air supplied from the leak detection pump motor. Air is pumped
into the EVAP system, while the current drawn by the pump motor is monitored. The current drawn during the leakage
test is compared against the value obtained during the reference check, to determine if an EVAP system leak is
present.
The fuel leak detection pump is powered from a 12V supply and operates at a working pressure of 3 kPa.
Air Filter – (NAS vehicles with positive pressure leak detection system only)
1Air vents through canister lid
2Air filter canister3To fuel leak detection pump
(EVAP canister atmosphere vent)
A paper element air filter (40 µm) is located in a plastic canister at the RH side of the engine compartment. The air
filter canister is fixed to the cruise control mounting bracket by a single nut and bolt. A large bore plastic pipe is
connected to a port at the base of the air filter canister and is secured to the port by a short nylon hose and two crimped
metal band clips.
The air filter is used to prevent particulate contaminants down to 40 µm from entering the fuel leak detection pump.
A press-fit lid on top of the canister contains slots to allow the passage of air into and out of the EVAP system.
The bottom end of the paper element is sealed to the canister and is non-serviceable (i.e fit for life). If necessary, the
canister and paper filter must be replaced as a single, complete assembly.
M17 0203
2
1
3
Page 289 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-56 REPAIRS
Sensor - heated oxygen (HO2S) - pre-
catalytic converter
$% 19.22.16
Remove
1.Raise vehicle on a ramp.
2.Release HO
2S multiplug from support bracket.
3.Release HO
2S harness from clip and
disconnect multiplug from HO
2S .
4.Using a 22 mm crow's-foot spanner, remove
HO
2S.
CAUTION: HO
2 sensors are easily damaged
by dropping, excessive heat or
contamination. Care must be taken not to
damage the sensor housing or tip.Refit
1.Clean sensor and exhaust pipe mating
surfaces.
2.If refitting existing sensor, apply anti-seize
compound to sensor threads.
WARNING: Some types of anti-seize
compound used in service are a health
hazard. Avoid skin contact.
NOTE: A new HO
2 sensor is supplied pre-
treated with anti-seize compound.
3.Fit a new sealing washer to HO
2S
4.Fit HO
2S and tighten to 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
5. Connect multiplug to HO
2S, and secure to
support bracket and harness clip.
6.Lower vehicle.
Page 290 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
REPAIRS 17-2-57
Sensor - heated oxygen (HO2S) - post-
catalytic converter
$% 19.22.17
Remove
1.Raise vehicle on ramp.
2.Release HO
2S multiplug from support bracket.
3.Disconnect HO
2S multiplug from harness.
4.Using a 22 mm crowsfoot spanner, remove
HO
2S.
CAUTION: HO2 sensors are easily damaged
by dropping, excessive heat or
contamination. Care must be taken not to
damage the sensor housing or tip.Refit
1.Clean sensor and exhaust pipe mating
surfaces.
2.If refitting existing sensor, apply anti-seize
compound to sensor threads.
WARNING: Some types of anti-seize
compound used in service are a health
hazard. Avoid skin contact.
NOTE: A new HO2 sensor is supplied pre-
treated with anti-seize compound.
3.Fit a new sealing washer to HO
2S
4.Fit HO
2S and tighten to 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
5. Connect HO
2S multiplug to harness and fit
harness to bracket.
6.Secure harness to clip.
7.Lower vehicle.
Page 306 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-7
The ECM controls the following outputs:
lFuel injectors (1 per cylinder).
lIgnition coils/ high tension leads/ spark plugs.
lFuel pump relay.
lIdle air control valve.
lHeated oxygen sensors.
lEVAP canister purge valve.
lEVAP canister vent solenoid (CVS) valve (where fitted).
lMalfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)/ service engine soon lamp (where fitted).
lHill descent control (via SLABS interface).
lEVAP system fuel leak detection pump (where fitted)
lSecondary air injection pump (where fitted)
The ECM also interfaces with the following:
lDiagnostics via diagnostic connector with TestBook.
lController Area Network (CAN) link to EAT ECU.
lAir conditioning system.
lSelf Levelling & Anti-lock Braking System (SLABS) ECU.
lImmobilisation system via the body control unit (BCU).
lInstrument cluster.
lCruise control ECU
lActive Cornering Enhancement (ACE) ECU
Page 335 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-36 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) (C0641)
The IACV is located on the side of the air inlet pipe on top of the engine. The IACV is used to maintain good quality
idle speed under all operating conditions.
When an engine is running at idle it is subject to a combination of internal and external loads that can affect idle speed.
These loads include engine friction, water pump, alternator operation, and air conditioning.
The IACV acts as an air bypass valve. The ECM uses the IACV to enable the closed loop idle speed calculation to be
made by the ECM. This calculation regulates the amount of air flow into the engine at idle, therefore compensating
for any internal or external loads that may affect idle speed.
The IACV utilises two coils that use opposing PWM signals to control the position of opening/closing of a rotary valve.
If one of the circuits that supply the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining signal preventing the IACV
from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the IACV automatically resumes a default idle
position. In this condition, the engine idle speed is raised and maintained at 1200 rev/min with no load placed on the
engine.
The idle speed in cold start condition is held at 1200 rev/min in neutral for 20 seconds and ignition timing is retarded
as a catalyst heating strategy. The cold start idle speed and the default idle position give the same engine speed 1200
rev/min, and although they are the same figure they must not be confused with each other as they are set separately
by the ECM.
Note that the rotary valve must not be forced to move by mechanical means. The actuator can not be
serviced; if defective, the entire IACV must be replaced.
Input/Output
The input to the IACV is a 12 volt signal from fuse 2 located in the engine compartment fuse box. The output earth
signal to open and close the actuator is controlled by the ECM as follows:
lIACV (open signal) - via pin 42 of connector C0636 of the ECM
lIACV (closed signal) - via pin 43 of connector C0636 of the ECM
The IACV can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lActuator faulty.
lRotary valve seized.
lWiring loom fault.
lConnector fault.
lIntake system air leak.
lBlocked actuator port or hoses.
lRestricted or crimped actuator port or hoses.
In the event of an IACV signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEither low or high idle speed.
lEngine stalls.
lDifficult starting.
lIdle speed in default condition.
Page 344 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-45
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)/ service engine soon warning lamp
The MIL/ service engine soon warning lamp is located in the instrument cluster. It illuminates to alert the driver to
system malfunctions. Service engine soon warning lamp is the name for this warning lamp in NAS only, it is called
MIL in all other markets.
During ignition a self-test function of the lamp is carried out. The lamp will illuminate for 3 seconds then it will
extinguish if no faults exist.
+ INSTRUMENTS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Input/Output
The MIL is supplied with battery voltage from the instrument cluster. When the ECM detects a fault, it provides an
earth path to illuminate the MIL. Output to the MIL is via pin 20 of connector C0637 of the ECM.
Air Temperature Control (ATC) request
The ATC request comes via the ATC switch located in the facia panel. When the driver operates the switch it acts as
a request from the ATC ECU to engage the ATC clutch to drive the system.
During periods of high driver demand such as hard acceleration or maximum rev/min the ATC clutch will be disabled
for a short time. This is to reduce the load on the engine.
+ AIR CONDITIONING, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Page 404 of 1529

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-2-7
Fuel pump
The fuel pump assembly comprises a top cover which locates the fuel pressure regulator, electrical connector and
fuel pipe coupling. The top cover is attached to a plastic cup shaped housing by two metal springs. The housing
locates the pump and the fuel gauge sender unit.
The lower part of the housing is the swirl pot, which maintains a constant fuel level at the fuel pick-up. A feed pipe
from the pump to the coupling connection and a return pipe from the regulator connect between the top cover and the
housing.
A coarse filter is attached to the base of the housing and prevents the ingress of large contaminants into the swirl pot.
A gauze filter prevents particles entering the fuel pump.
Surrounding the pump is a large fine paper filter element which further protects the fuel pressure regulator, engine
and injectors from particulate contamination. The paper filter is not a serviceable item and removes the requirement
for an external in-line filter.
A non-return valve is located in the base of the housing. When the fuel tank is full, fuel pressure keeps the valve lifted
from its seat allowing fuel to flow into the swirl pot. As the tank level reduces, the fuel pressure in the tank reduces
causing the valve to close. When the valve is closed fuel is retained in the swirl pot, ensuring that the swirl pot remains
full and maintains a constant supply to the fuel pump.
A four pin electrical connector is located on the top cover of the pump and provides power feed and return for fuel
pump and fuel gauge rotary potentiometer operation. A single quick release coupling connects the fuel feed pipe to
the outer top surface of the pump.
Two metal springs are attached to the top cover and the housing of the pump. When the pump is installed it seats on
the lower surface inside the tank. The springs exert a downward pressure on the pump and ensure that the pump is
located positively at the bottom of the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a maximum current draw of 6.5 A at 12.5 V.
On NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability only, the fuel pump top cover is fitted with
an On Board Diagnostics (OBD) pressure sensor. This sensor has a three pin electrical connector which provides a
connection between the sensor and the ECM. The sensor is sealed in the top cover with an 'O' ring and secured with
a clip. The sensor monitors tank pressure during OBD tests of the fuel evaporation system integrity. A hose is
connected to the sensor and is routed across the top of the fuel tank and terminates at the top of the fuel filler tube.
The pipe is open to atmosphere and provides atmospheric pressure for the sensor operation.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
Fuel pressure regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is located in the underside of the top cover. The regulator is sealed with two 'O' rings and
retained with a clip.
The regulator is connected to the fuel feed pipe at the top of the pump housing and maintains the fuel pump delivery
pressure to 3.5 bar (50 lbf.in
2). When the fuel delivery pressure exceeds 3.5 bar (50 lbf.in2), the regulator opens and
relieves excess pressure back to the swirl pot via a return pipe. The regulator ensures that the fuel rails and injectors
are supplied with a constant pressure.
The fuel pump delivery pressure and pressure regulator operating pressure can be checked using a Schraeder type
valve located at the rear of the engine on the fuel rail. The valve allows the pump delivery pressure to be measured
using a suitable gauge and an adaptor and hose which are special tools.