ABS LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 1279 of 1672

PANEL REPAIRS
77-2-30 REPAIRS
Valance upper assembly (front section) -
LH
In this procedure, the front wing, the valance outer
reinforcement (front section) and the bonnet alarm
switch mounting bracket are replaced in conjunction
with the LH valance upper assembly (front section).
Remove
1.Disconnect both battery leads, negative lead
first.
2.Disconnect leads/multiplug from alternator.
3.Remove front wing.
+ EXTERIOR FITTINGS, REPAIRS,
Wing - front - up to 03MY.
4.Remove air filter assembly.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
Td5, REPAIRS, Air filter assembly.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, REPAIRS, Air cleaner assembly.
5.Remove PAS/ACE reservoir.
6.Remove ABS modulator.
+ BRAKES, REPAIRS, Modulator unit
- ABS.
7.Release harness from valance and position
aside.
8. Models with A/C: Depressurise A/C system
and remove pipes from valance.
+ AIR CONDITIONING, REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY, RECYCLING AND
RECHARGING, Refrigerant recovery,
recycling and recharging.Repair
1.Remove existing panel(s), prepare panel joint
faces and install new panel(s) in accordance
with Panel Replacement Procedure. Punch or
drill holes in new panel for plug welding as
shown.
Refit
1. Models with A/C: Fit A/C pipes and recharge
A/C system.
+ AIR CONDITIONING, REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY, RECYCLING AND
RECHARGING, Refrigerant recovery,
recycling and recharging.
2.Fit harness to valance.
3.Fit ABS modulator.
+ BRAKES, REPAIRS, Modulator unit
- ABS.
4.Fit PAS/ACE reservoir and refill fluids to correct
levels.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION,
ADJUSTMENTS, ACE hydraulic system
bleeding.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS AND
LUBRICANTS, Fluids.
M77 1744
M77 1689A
Page 1282 of 1672

PANEL REPAIRS
REPAIRS 77-2-33
6. RHD models: Fit brake servo.
7. Diesel models: Fit EGR modulator mounting
bracket.
8. Petrol models: Fit cruise control actuator
mounting bracket.
9.Fit radiator expansion tank.
10.Fit fusebox and secure wiring.
11.Fit front bulkhead assembly.
+ PANEL REPAIRS, REPAIRS, Front
bulkhead assembly.
12.Connect battery leads, negative lead last.
Front valance assembly - LH
Remove
1.Disconnect both battery leads, negative lead
first.
2.Disconnect leads/multiplug from alternator.
3.Remove front bulkhead assembly.
+ PANEL REPAIRS, REPAIRS, Front
bulkhead assembly.
4.Remove ABS modulator unit.
+ BRAKES, REPAIRS, Modulator unit
- ABS.
5. LHD models: Remove brake servo.
+ BRAKES, REPAIRS, Servo - brake.
6.Remove brake pipes from valance assembly.
7.Remove PAS/ACE reservoir.
8. Models with A/C: Remove A/C pipes from
valance assembly.
9.Remove wiring harness from valance
assembly.
10.Remove LH front road wheel.
11.Remove LH front mud flap.
12.Remove insulation pad from engine bulkhead.
13.Remove windscreen side finisher.
+ EXTERIOR FITTINGS, REPAIRS,
Side finisher - windscreen.
Repair
1.Remove existing panel(s), prepare panel joint
faces and install new panel(s) in accordance
with Panel Replacement Procedure. Punch or
drill holes in new panel for plug welding as
shown.
M77 1742
Page 1283 of 1672

PANEL REPAIRS
77-2-34 REPAIRS
Refit
1.Fit windscreen side finisher.
+ EXTERIOR FITTINGS, REPAIRS,
Side finisher - windscreen.
2.Fit insulation pad to engine bulkhead.
3.Fit front mud flap.
4.Fit road wheel and tighten nuts to 140 Nm (103
lbf.ft).
5.Fit wiring harness to valance assembly.
6. Models with A/C: Fit A/C pipes to valance
assembly.
7.Fit PAS/ACE reservoir.
8.Fit brake pipes to valance assembly.
9. LHD models: Fit brake servo.
+ BRAKES, REPAIRS, Servo - brake.
10.Fit ABS modulator unit.
+ BRAKES, REPAIRS, Modulator unit
- ABS.
11.Fit front bulkhead assembly.
+ PANEL REPAIRS, REPAIRS, Front
bulkhead assembly.
12.Connect leads/multiplug to alternator.
13.Connect battery leads, negative lead last.
'A' post assembly
In this procedure, the front wing and the valance
outer reinforcement (rear section) are replaced in
conjunction with the 'A' post assembly. The dash side
assembly can also be replaced in this procedure if
required.
Remove
1.Disconnect both battery leads, negative lead
first.
2.Disconnect leads/multiplug from alternator.
3.Remove bonnet.
4.Remove front wing.
+ EXTERIOR FITTINGS, REPAIRS,
Wing - front - up to 03MY.
5.Remove RH or LH front door.
+ DOORS, REPAIRS, Door - front.
6.Remove RH or LH sill finisher.
7.Remove windscreen.
+ SCREENS, REPAIRS, Windscreen.
8. Diesel models: Remove ECM.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
Td5, REPAIRS, Engine control module
(ECM).
9.Remove RH or LH 'A' post inner finishers and
disconnect speaker multiplug (if fitted).
10.Release sunroof drain tube and position aside.
11.Remove RH or LH front seat.
+ SEATS, REPAIRS, Seat - front.
12. RH side: Remove CD autochanger.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT,
REPAIRS, CD autochanger.
13.Remove fascia.
+ INTERIOR TRIM COMPONENTS,
REPAIRS, Fascia.
14. Driver's side: Remove steering column
support bracket.
15.Remove relevant wiring from 'A' post.
16.Remove tread plate from front door aperture.
17.Release front carpet and position aside.
18.Remove front door aperture seal.
19.Remove engine bulkhead insulation.
Page 1339 of 1672

CORROSION PREVENTION AND SEALING
77-4-24 SEALING
Water leaks
Where water leakage is involved, always adopt a logical approach to the problem using a combination of skill,
experience and intuition. Do not reach a conclusion based only on visual evidence, such as assuming that a wet
footwell is caused by a leak emanating from the windscreen. It will often be found that the source of the leak is
elsewhere. Use of the correct procedure will increase the chance of locating a leak, however obscure it may seem.
Tools and equipment
The following tools and equipment are recommended for the purpose of detection and rectification of water leaks:
1Garden sprayer (hand-operated)
2Wet/dry vacuum cleaner
3Dry, absorbent cloths
4Battery torch
5Small mirror
6Weatherstrip locating tool
7Trim panel remover
8Small wooden or plastic wedges
9Dry compressed air supply
10Hot air blower
11Sealer applicators
12Ultrasonic leak detector
During leak detection, the vehicle should be considered in three basic sections:
lThe front interior space;
lThe rear passenger space;
lThe loadspace or boot.
Testing
From the information supplied by the customer it should be possible for the bodyshop operator to locate the starting
point from which the leak may be detected. After the area of the leak has been identified, find the actual point of entry
into the vehicle.
A simple and effective means in the first instance is an ordinary garden spray with provision for pressure and jet
adjustment, which will allow water to be directed in a jet or turned into a fine spray. Use a mirror and a battery-powered
torch (NOT a mains voltage inspection lamp) to see into dark corners.
The sequence of testing is particularly important. Start at the lowest point and work slowly upwards, to avoid testing
in one area while masking the leak in another. For example, if testing started at the level of the windscreen, any water
cascading into the plenum chamber could leak through a bulkhead grommet and into the footwells. Even at this point
it could still be wrongly assumed that the windscreen seal was at fault.
Another important part of identifying a water leak is by visual examination of door aperture seals, grommets and
weatherstrips for damage, deterioration or misalignment, together with the fit of the door itself against the seals.
Sealing
When the point of the leak has been detected, it will then be necessary to rectify it using the following procedure:
1Renew all door aperture seals and weatherstrips which have suffered damage, misalignment or deterioration
2Check all body seals to ensure that they are correctly located on their mounting flanges/faces using a lipping
tool if necessary
3Dry out body seams to be treated using compressed air and/or a hot air blower as necessary
4Apply sealant on the outside of the joint wherever possible to ensure the exclusion of water
5When rectifying leaks between a screen glass and it's weatherstrip (or in the case of direct glazing, between the
glass and bodywork), avoid removing the glass if possible. Apply the approved material at the appropriate
location (i.e. glass to weatherstrip or glass to body)
Page 1378 of 1672

AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 82-5
To accomplish the transfer of heat, the refrigerant is circulated around the system, where it passes through two
pressure/temperature regimes. In each of the pressure/temperature regimes, the refrigerant changes state, during
which process maximum heat absorption or release occurs. The low pressure/temperature regime is from the
thermostatic expansion valve, through the evaporator to the compressor; the refrigerant decreases in pressure and
temperature at the thermostatic expansion valve, then changes state from liquid to vapour in the evaporator, to absorb
heat. The high pressure/temperature regime is from the compressor, through the condenser and receiver drier to the
thermostatic expansion valve; the refrigerant increases in pressure and temperature as it passes through the
compressor, then releases heat and changes state from vapour to liquid in the condenser.
Compressor
1Pulley
2Inlet connection
3Outlet connection
4Pressure relief valve
5Clutch connector
The compressor circulates the refrigerant around the system by compressing low pressure, low temperature vapour
from the evaporator and discharging the resultant high pressure, high temperature vapour to the condenser.
The compressor is attached to a mounting bracket on the engine, and is a ten cylinder swash plate unit with a fixed
displacement of 177 ml/rev (0.19 US qt/rev). The auxiliary drive belt drives the compressor via a pulley and an
electrically actuated clutch. Operation of the clutch is controlled by the Engine Control Module (ECM).
To protect the refrigerant system from unacceptably high pressure, a pressure relief valve is installed in the outlet side
of the compressor. The pressure relief valve is set to operate at 34.3 to 41.4 bars (497 to 600 lbf.in
2) and vents excess
pressure into the engine compartment.
Page 1379 of 1672

AIR CONDITIONING
82-6DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Condenser
1Condenser matrix
2Outlet connection
3Inlet connection
The condenser transfers heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding air.
The condenser is installed immediately in front of the oil coolers. Rubber mounting bushes are used to mount the
condenser to the chassis sidemembers and brackets on the headlamp panels.
Ambient air, passing through the condenser matrix due to ram effect and/or the cooling fan, absorbs heat from the
refrigerant, which changes state from a vapour to a liquid.
Page 1380 of 1672
AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 82-7
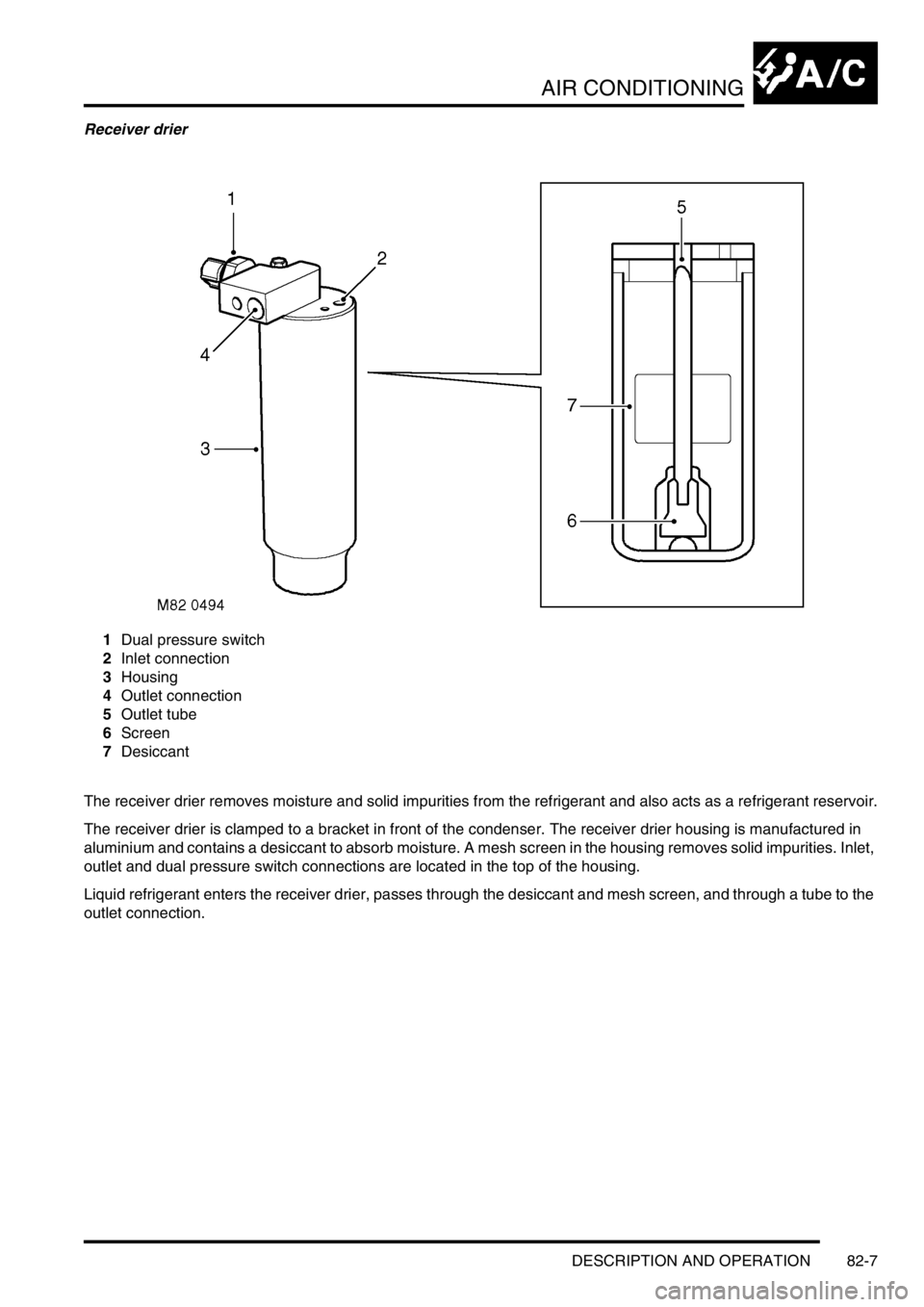
Receiver drier
1Dual pressure switch
2Inlet connection
3Housing
4Outlet connection
5Outlet tube
6Screen
7Desiccant
The receiver drier removes moisture and solid impurities from the refrigerant and also acts as a refrigerant reservoir.
The receiver drier is clamped to a bracket in front of the condenser. The receiver drier housing is manufactured in
aluminium and contains a desiccant to absorb moisture. A mesh screen in the housing removes solid impurities. Inlet,
outlet and dual pressure switch connections are located in the top of the housing.
Liquid refrigerant enters the receiver drier, passes through the desiccant and mesh screen, and through a tube to the
outlet connection.
Page 1382 of 1672

AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 82-9
Evaporator
The evaporator is installed in the air inlet of the heater assembly and absorbs heat from the exterior or recirculated
inlet air. Low pressure, low temperature refrigerant changes from liquid to vapour in the evaporator, absorbing large
quantities of heat as it changes state.
Refrigerant lines
To maintain similar flow velocities around the system, the diameter of the refrigerant lines varies to suit the two
pressure/temperature regimes. The larger diameters are installed in the low pressure/temperature regime and the
smaller diameters are installed in the high pressure/temperature regime. Low and high pressure charging connections
are incorporated into the refrigerant lines for system servicing. Where rear AC is installed, connections for the rear
refrigerant lines are incorporated next to the charging connections.
Page 1399 of 1672

AIR CONDITIONING
82-26DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The rear evaporator/blower assembly cools and dehumidifies air from the cabin and supplies it to the rear distribution
system. The unit is installed on the left side of the loadspace, behind the quarter trim. A grille in the quarter trim allows
air to flow from the loadspace into the evaporator/blower. Refrigerant lines for the evaporator and a condensate drain
tube are attached to the rear floor.
The evaporator and blower are installed in a common housing, which also incorporates the resistor pack for the
blower. A thermostatic expansion valve is integrated into the inlet refrigerant line. A rear blower relay is attached to
the top of the housing.
Evaporator
The evaporator absorbs heat from the recirculated air being supplied to the distribution ducts.
Thermostatic expansion valve
The thermostatic expansion valve meters the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator to match the heat load of the air
passing through the evaporator matrix. A capillary tube, attached to the outlet pipe of the evaporator and connected
to the thermostatic expansion valve, automatically adjusts the valve opening in relation to the refrigerant temperature
at the evaporator outlet.
Blower
The blower controls the volume of air being supplied to the distribution outlets. The blower is an open hub, centrifugal
fan powered by an electric motor. A dust filter is installed over the fan inlet. The blower switch on the control panel
and the resistor pack control the operation of the blower, which can be selected to run at one of four speeds.
Resistor pack
The resistor pack supplies reduced voltages to the blower motor for blower speeds 1, 2 and 3. For blower speed 4,
the resistor pack is bypassed and battery voltage drives the motor at full speed. The pack is installed in the air outlet
from the blower fan, so that any heat generated is dissipated by the air flow.
Distribution system
Air ducts
Ducts connected to the rear evaporator/blower motor assembly distribute air to five vent assemblies in the roof.
Vent assemblies
The vent assemblies allow occupants to control the flow and direction of air. Each vent assembly incorporates a
thumbwheel to regulate flow and moveable vanes to control direction.
Rear control system
The control system operates the blower to control the operation of the rear A/C. The control system consists of two
control switches and a rear blower relay.
Control switches
A rear A/C switch and a blower speed switch are installed on a control panel in the roof lining. The A/C switch is a
latching pushswitch with an amber indicator lamp which illuminates when rear A/C is selected on. The blower speed
switch is a slide switch with a positive detent at each of four speed positions (there is no off position).
Rear blower relay
The rear blower relay controls the electrical supply to the blower.
Page 1400 of 1672

AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 82-27
Operation
The rear A/C only operates if the front A/C is on to pump refrigerant through the rear evaporator/blower assembly.
When the rear A/C switch is selected on, the indicator lamp in the switch illuminates and the rear blower relay is
energised. The rear blower relay switches battery power to the blower motor, which runs at the speed selected on the
blower speed switch.
The air from the blower passes through the evaporator matrix, which absorbs heat from the air. The cooled air is then
supplied to the roof vents through the distribution ducts. The heat absorbed by the refrigerant in the evaporator is
sensed by the thermostatic expansion valve. The thermostatic expansion valve then opens and regulates the flow of
refrigerant through the evaporator in proportion to the amount of heat being absorbed from the air.
When the rear A/C switch is selected off, the blower stops. The thermostatic expansion valve senses the subsequent
decrease in temperature of the refrigerant in the evaporator. The thermostatic expansion valve then closes and stops
the flow of refrigerant, except for a minimal bleed flow.