relay LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 424 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-31
The purpose of the glow plugs is:
lAssist cold engine start.
lReduce exhaust emissions at low engine load/speed.
The main part of the glow plug is a tubular heating element that protrudes into the combustion chamber of the engine.
The heating element contains a spiral filament that is encased in magnesium oxide powder. At the tip of the tubular
heating element is the heater coil. Behind the heater coil and connected in series is a control coil. The control coil
regulates the heater coil to ensure that it does not overheat and cause a possible failure. The glow plug circuit has its
own control relay located in the engine compartment fuse box.
Pre-heat is the length of time the glow plugs operate prior to engine cranking. The ECM controls the pre-heat time of
the glow plugs based on battery voltage and coolant temperature information via the glow plug relay.
Post-heat is the length of time the glow plugs operate after the engine starts. The ECM controls the post-heat time
based on ECT information. If the ECT fails the ECM will operate pre/post-heat time strategies with default values from
its memory. The engine will be difficult to start.
Input/Output
The glow plugs receive voltage from the glow plug relay that is controlled by the ECM. The ECM provides the earth
path for the relay coil closing the relay contacts and supplying the glow plugs with battery voltage. The supply voltage
heats the coils to approximately 1000
°C (1832 °F). The glow plug circuit is wired in parallel, the body of each glow
plug is screwed directly into the engine block which provides each glow plug with an earth path.
The glow plugs can fail in the following ways:
lHeater coil open circuit.
lControl coil open circuit.
lPoor earth quality.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
lRelay windings open circuit.
lIncorrect relay fitted.
In the event of a glow plug failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDifficult starting.
lExcessive smoke emissions after engine start.
Page 427 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-34 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
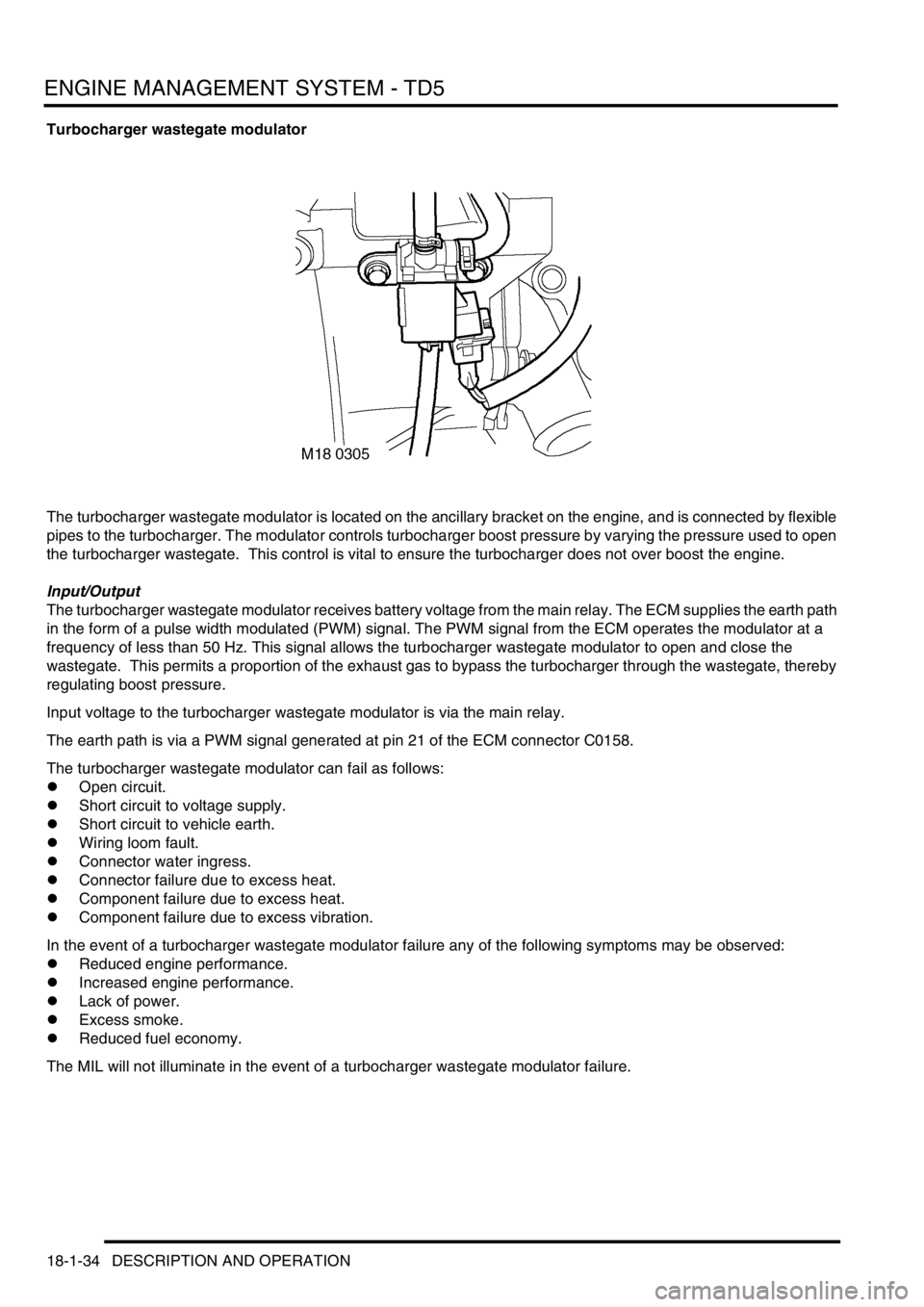
Turbocharger wastegate modulator
The turbocharger wastegate modulator is located on the ancillary bracket on the engine, and is connected by flexible
pipes to the turbocharger. The modulator controls turbocharger boost pressure by varying the pressure used to open
the turbocharger wastegate. This control is vital to ensure the turbocharger does not over boost the engine.
Input/Output
The turbocharger wastegate modulator receives battery voltage from the main relay. The ECM supplies the earth path
in the form of a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal. The PWM signal from the ECM operates the modulator at a
frequency of less than 50 Hz. This signal allows the turbocharger wastegate modulator to open and close the
wastegate. This permits a proportion of the exhaust gas to bypass the turbocharger through the wastegate, thereby
regulating boost pressure.
Input voltage to the turbocharger wastegate modulator is via the main relay.
The earth path is via a PWM signal generated at pin 21 of the ECM connector C0158.
The turbocharger wastegate modulator can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
lConnector water ingress.
lConnector failure due to excess heat.
lComponent failure due to excess heat.
lComponent failure due to excess vibration.
In the event of a turbocharger wastegate modulator failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lReduced engine performance.
lIncreased engine performance.
lLack of power.
lExcess smoke.
lReduced fuel economy.
The MIL will not illuminate in the event of a turbocharger wastegate modulator failure.
Page 428 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-35
Cruise control master switch
The cruise control master switch is located on the dashboard. When the driver activates the switch it requests the
cruise control system to be active. The switch acts as a latching switch, on the first operation of the switch the cruise
control system is activated, when the switch is pressed again the cruise control system is de-activated. The cruise
control warning lamp is part of the switch and illuminates when the switch is activated.
Input/Output
Input to the cruise control master switch is 12 volts via the main relay. When the switch is pressed the circuit is
completed by the ECM providing an earth path for the relay via pin 15 of connector C0658 of the ECM.
The cruise control master switch can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
In the event of a cruise control master switch failure cruise control does not operate.
Page 429 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-36 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Cruise control set/accelerate (SET+) switch
The cruise control SET+ switch is located on the vehicle steering wheel. The switch is a momentary switch and when
pressed by the driver reacts as follows:
lRequests the cruise control to become active and set at the current road speed if not already set.
lIf the cruise control is already set, pressing the switch increases the road speed at 1 mph (1.6 km/h) intervals.
The cruise control SET+ switch will only become active and operate under the following conditions:
lThe vehicle speed must be above 22 mph (35 km/h).
lThe cruise control master switch must be 'on'.
lThe brake pedal must not be pressed.
lThe automatic transmission must be in 'drive'.
lThe clutch pedal must not be pressed.
lThe suspend switch has not been operated.
Input/Output
Input to the cruise control SET+ switch is 12 volts via the main relay. When the switch is pressed the circuit is
completed by the ECM providing an earth path for the relay via pin 11 of connector C0658 of the ECM.
The cruise control SET+ switch can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault In the event of a cruise control SET+ switch failure cruise control does not operate.
Cruise control resume/suspend (RES) switch
The cruise control RES switch is located on the vehicle steering wheel. The switch is a momentary switch and when
pressed by the driver reacts as follows:
lRequests the cruise control to be suspended if it has already been set.
lRequests that cruise control is resumed at the previously set road speed.
The cruise control RES switch will only become active and operate under the following conditions:
lThe vehicle speed must be above 22 mph (35 km/h).
lThe cruise control master switch must be 'on'.
lThe brake pedal must not be pressed.
lThe automatic transmission must be in 'drive'.
lThe clutch pedal must not be pressed.
Page 430 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-37
Input/Output
Input to the cruise control RES switch is 12 volts via the main relay. When the switch is pressed the circuit is completed
by the ECM providing an earth path for the relay via pin 17 of connector C0658 of the ECM.
The cruise control RES switch can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
In the event of a cruise control RES switch failure cruise control resume/ suspend operation does not operate.
Page 432 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-39
With the ECM in a 'Secure' state, it will not function unless an alarm system is fitted to the vehicle. A 'Secure' ECM
cannot be configured into a 'No Code' ECM.
With the ECM in a 'No Code' state, it does not require an alarm system to be fitted to allow the engine to operate. If
the ECM senses that an alarm system is fitted it will not start. A 'No Code' ECM can be configured to a 'Secure' ECM
using TestBook. A 'Secure' ECM can not be configured to a 'No Code' state.
Setting up of the ECM immobilisation configurations can only be performed using TestBook.
If a vehicle stalls immediately after starting it is possible that it has been immobilised. This means either:
lThe ECM was configured as 'No Code' but the ECM is receiving a code at its alarm input pin.
lThe ECM received an incorrect code.
lThe ECM was expecting a security code but did not receive one at its alarm input pin.
Fuel delivery/injection control
The fuel delivery/injection control delivers a precise amount of finely atomised fuel to mix with the air in the
combustion chamber to create a controlled explosion.
To precisely control fuel delivery and control fuel injection, the following input conditions must be met:
lCKP information.
lInjection timing map information.
lFT information.
lECT information.
The ECM monitors the conditions required for optimum combustion of fuel in the cylinder from the various sensors
around the engine and then compares it against stored information. From this calculation the ECM can adjust the
quantity and timing of the fuel being delivered to the cylinder.
The ECM uses CKP information as follows:
lTo calculate engine speed.
lTo determine engine crankshaft position.
Engine speed and crankshaft position allows the ECM to determine fuel injection timing.
The ECM also uses ECT information and FT sensor information to allow optimum fuel delivery and injection control
for all engine coolant and fuel temperatures.
Turbocharger control
Turbocharger control is vital to ensure the turbocharger does not over boost the engine. Within the turbocharger is a
wastegate, which when operated by the turbocharger wastegate modulator will open and close a bypass valve
regulating boost pressure.
The turbocharger wastegate modulator, via the ECM, controls boost pressure under the following conditions:
lAcceleration.
lWide open throttle.
lIdle.
lOverrun.
The turbocharger wastegate modulator receives a battery voltage supply from the main relay. The ECM supplies the
earth path in the form of a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal. This signal allows the turbocharger wastegate
modulator to open and close the wastegate. A proportion of the exhaust gas can bypass the turbocharger through
the wastegate, regulating boost pressure.
Page 436 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-43
Air Conditioning (A/C)
The ECM controls operation of the A/C compressor and the engine's electric cooling fan in response to requests from
the Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) ECU.
A/C request
When the ATC ECU supplies the ECM with an A/C request, the ECM energises the compressor clutch relay. The
compressor clutch relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It is a four pin normally open relay. This means
that the relay must be energised to drive the compressor clutch. During periods of high driver demand such as hard
acceleration or maximum rev/min the ECM will disable the compressor clutch for a short time. This is to reduce the
load on the engine.
The operation of the A/C request is via a switch being connected to earth. Voltage is supplied via pin 9 of connector
C0658 of the ECM, at the point at which the switch is pressed the connection to the earth path is made and the
compressor clutch is engaged.
The ECM provides the earth for the relay windings to allow the compressor clutch relay contacts to close and the
compressor clutch drive to receive battery voltage. The ECM uses a transistor as a switch to generate an open circuit
in the earth path of the relay windings. When the ECM closes down the earth path, the return spring in the relay will
pull the contacts apart to shut down the compressor clutch drive. Fuse 6, located in the engine compartment fuse box,
provides voltage to the compressor clutch relay switching contacts. The relay windings are supplied with battery
voltage from the main relay, also located in the engine compartment fuse box. The earth path for the relay windings
is via pin 29 of the ECM connector C0658. When the relay is energised the output from the switching contacts is
directly to the compressor clutch.
Cooling fan request
The A/C fan request is an input to the ECM from the ATC ECU to request that the engine's electric cooling fan is
activated to provide additional cooling for the A/C condenser.
The cooling fan relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box and is also controlled by the ECM. It is a four pin
normally open relay. This means that the relay must be energised to drive the cooling fan. The cooling fan is used
especially when the engine is operating at excessively high temperatures. It is also used as a part of the ECM backup
strategy if the ECT sensor fails.
The operation of the cooling fan request is via a switch being connected to earth. Voltage is supplied via pin 23 of
connector C0658 of the ECM, at the point at when the switch is pressed the connection to the earth path is made and
the cooling fan is engaged.
The ECM provides the earth for the cooling fan relay windings to allow the relay contacts to close and the cooling fan
motor to receive battery voltage. The ECM uses a transistor as a switch to generate an open circuit in the earth path
of the relay windings. When the ECM closes down the earth path, the return spring in the relay will pull the contacts
apart to shut down the cooling fan motor drive. Input to the A/C cooling fan relay switching contacts is via fuse 4
located in the engine compartment fuse box. The relay windings are supplied with battery voltage from the main relay,
also located in the engine compartment fuse box. The earth path for the relay windings is via pin 4 of the ECM
connector C0658. When the relay is energised the output from the switching contacts is directly to the cooling fan
motor.
Page 460 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-3
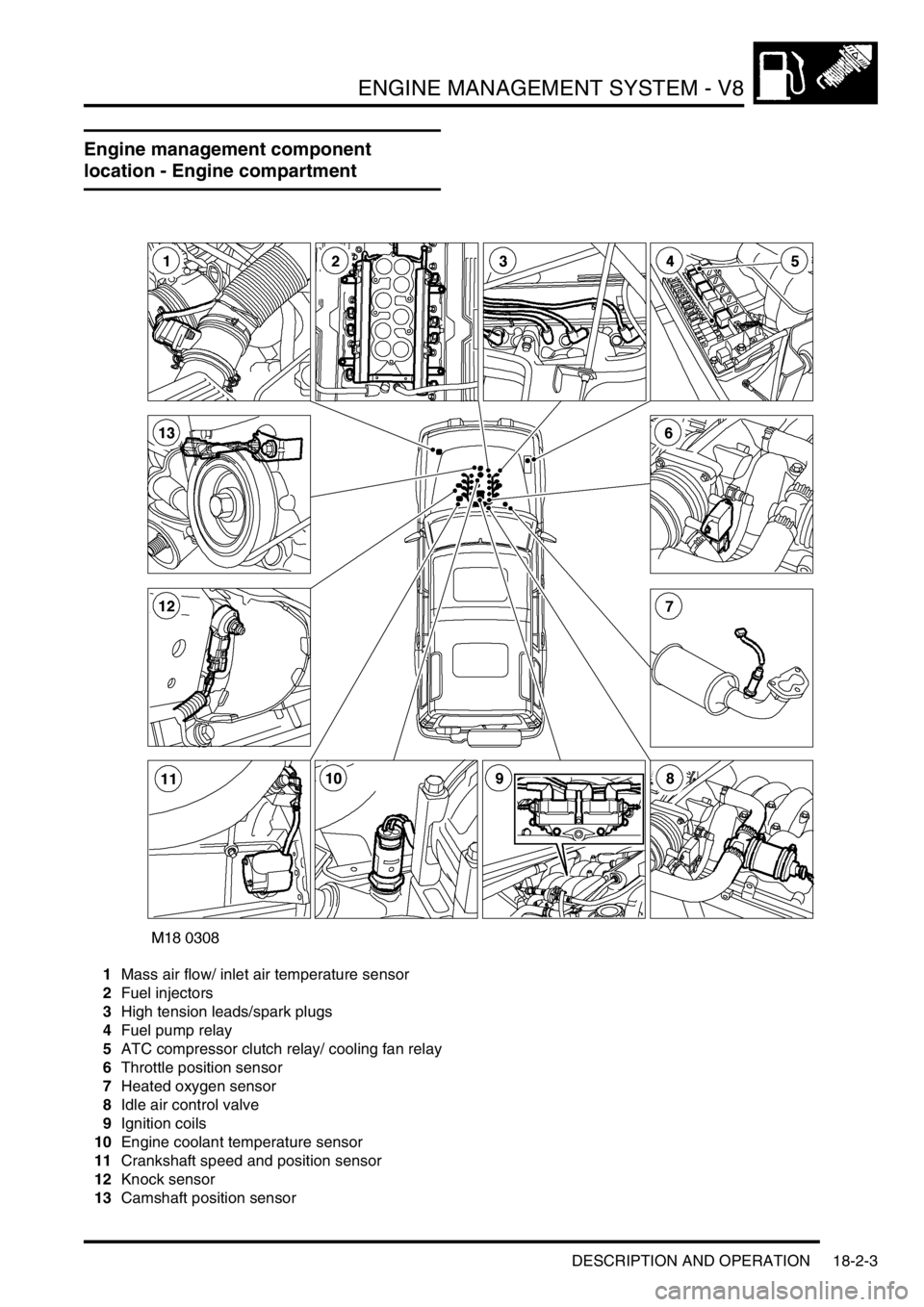
Engine management component
location - Engine compartment
1Mass air flow/ inlet air temperature sensor
2Fuel injectors
3High tension leads/spark plugs
4Fuel pump relay
5ATC compressor clutch relay/ cooling fan relay
6Throttle position sensor
7Heated oxygen sensor
8Idle air control valve
9Ignition coils
10Engine coolant temperature sensor
11Crankshaft speed and position sensor
12Knock sensor
13Camshaft position sensor
Page 462 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-5
1Engine control module
2Crankshaft speed and position sensor
3Camshaft position sensor
4Engine coolant temperature sensor
5Mass air flow/ inlet air temperature sensor
6Throttle position sensor
7Heated oxygen sensors
8Fuel injectors
9Idle air control valve
10Fuel pump relay
11EVAP canister
12EVAP canister vent valve
13EVAP canister purge valve
14Fuel tank pressure sensor
15Ignition coils
16Knock sensor
17Spark plugs
18High/ Low ratio switch
19Malfunction indication lamp
20Diagnostic connector
21Air temperature control clutch relay
22Air temperature control cooling fan relay
23ATC ECU
24CAN link to EAT
25SLABS ECU
26BCU
27Instrument cluster
28Thermostat monitoring sensor (where fitted)
Page 464 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-7
The ECM controls the following outputs:
lFuel injectors (1 per cylinder).
lIgnition coils/ high tension leads/ spark plugs.
lFuel pump relay.
lIdle air control valve.
lHeated oxygen sensors.
lEVAP canister purge valve.
lEVAP canister vent solenoid (CVS) valve (where fitted).
lMalfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)/ service engine soon lamp (where fitted).
lHill descent control (via SLABS interface).
lEVAP system fuel leak detection pump (where fitted)
lSecondary air injection pump (where fitted)
The ECM also interfaces with the following:
lDiagnostics via diagnostic connector with TestBook.
lController Area Network (CAN) link to EAT ECU.
lAir conditioning system.
lSelf Levelling & Anti-lock Braking System (SLABS) ECU.
lImmobilisation system via the body control unit (BCU).
lInstrument cluster.
lCruise control ECU
lActive Cornering Enhancement (ACE) ECU
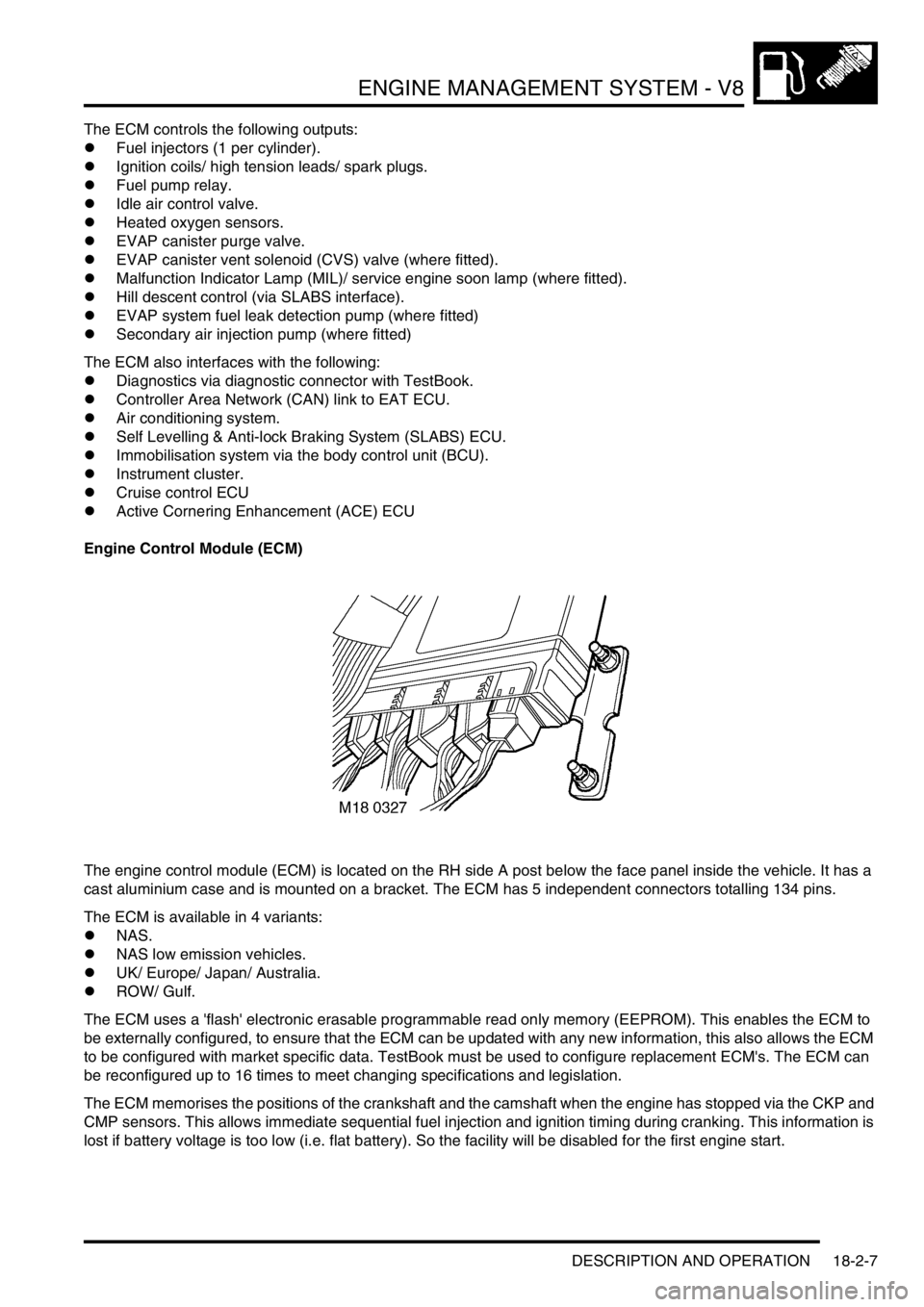
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located on the RH side A post below the face panel inside the vehicle. It has a
cast aluminium case and is mounted on a bracket. The ECM has 5 independent connectors totalling 134 pins.
The ECM is available in 4 variants:
lNAS.
lNAS low emission vehicles.
lUK/ Europe/ Japan/ Australia.
lROW/ Gulf.
The ECM uses a 'flash' electronic erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM). This enables the ECM to
be externally configured, to ensure that the ECM can be updated with any new information, this also allows the ECM
to be configured with market specific data. TestBook must be used to configure replacement ECM's. The ECM can
be reconfigured up to 16 times to meet changing specifications and legislation.
The ECM memorises the positions of the crankshaft and the camshaft when the engine has stopped via the CKP and
CMP sensors. This allows immediate sequential fuel injection and ignition timing during cranking. This information is
lost if battery voltage is too low (i.e. flat battery). So the facility will be disabled for the first engine start.