relay LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 378 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-41
Following the test, the system returns to normal purge operation after the canister vent solenoid opens. Possible
reasons for an EVAP system leak test failure are listed below:
lFuel filler not tightened or cap missing.
lSensor or actuator open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply or ground.
lEither purge or CVS valve stuck open.
lEither purge or CVS valve stuck shut or blocked pipe.
lPiping broken or not connected.
lLoose or leaking connection.
If the piping is broken forward of the purge valve or is not connected, the engine may run rough and fuelling adaptions
will drift. The fault will not be detected by the leak detection diagnostic, but it will be determined by the engine
management ECM through the fuelling adaption diagnostics.
The evaluation of leakage is dependent on the differential pressure between the fuel tank and ambient atmospheric
pressure, the diagnostic is disabled above altitudes of 9500 ft. (2800 m) to avoid false detection of fuel leaks due to
the change in atmospheric pressure at altitude.
Fuel leak detection system (positive pressure leak detection type) – NAS only
The EVAP system with positive pressure leak detection capability used on NAS vehicles is similar to the standard
system, but also includes a fuel evaporation leak detection pump with integral solenoid valve. It is capable of detecting
holes in the EVAP system down to 0.5 mm (0.02 in.). The test is carried out at the end of a drive cycle, when the
vehicle is stationary and the ignition switch has been turned off. The ECM maintains an earth supply to the Main relay
to hold it on, so that power can be supplied to the leak detection pump.
First a reference measurement is established by passing the pressurised air through a by-pass circuit containing a
fixed sized restriction. The restriction assimilates a 0.5 mm (0.02 in) hole and the current drawn by the pump motor
during this procedure is recorded for comparison against the value to be obtained in the system test. The purge valve
is held closed, and the reversing valve in the leak detection pump module is not energised while the leak detection
pump is switched on. The pressurised air from the leak detection pump is forced through an orifice while the current
drawn by the pump motor is monitored.
Next the EVAP system diagnostic is performed; the solenoid valve is energised so that it closes off the EVAP system's
vent line to atmosphere, and opens a path for the pressurised air from the leak detection pump to be applied to the
closed EVAP system.
The current drawn by the leak detection pump is monitored and checked against that obtained during the reference
measurement. If the current is less than the reference value, this infers there is a hole in the EVAP system greater
than 0.5 mm (0.02 in) which is allowing the positive air pressure to leak out. If the current drawn by the pump motor
is greater than the value obtained during the reference check, the system is sealed and free from leaks. If an EVAP
system leak is detected, the ECM stores the fault in diagnostic memory and the MIL light on the instrument pack is
illuminated.
On NAS vehicles, the ECM works on a 2 trip cycle before illuminating the MIL. On EU-3 vehicles, the ECM works on
a 3 trip cycle before illuminating the MIL.
Following the test, the solenoid valve is opened to normalise the EVAP system pressure and the system returns to
normal purge operation at the start of the next drive cycle. Possible reasons for an EVAP system leak test failure are
listed below:
lFuel filler not tightened or cap missing.
lSensor or actuator open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply or ground.
lEither purge or solenoid valve stuck open.
lEither purge or solenoid valve stuck shut.
lBlocked pipe or air filter.
lPiping broken or not connected.
lLoose or leaking connection.
If the piping is broken forward of the purge valve or is not connected, the engine may run rough and fuelling adaptions
will drift. The fault will not be detected by the leak detection test, but will be determined by the engine management
ECM through the fuelling adaption diagnostics. This test can be run from TestBook.
Page 379 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-42 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Secondary air injection system
When the engine is started, the engine control module checks the engine coolant temperature and if it is below 55°
C, the ECM grounds the electrical connection to the coil of the secondary air injection (SAI) pump relay.
A 12V battery supply is fed to the inertia switch via fuse 13 in the engine compartment fusebox. When the inertia
switch contacts are closed, the feed passes through the switch and is connected to the coil of the Main relay. An earth
connection from the Main relay coil is connected to the ECM. When the ECM completes the earth path, the coil
energises and closes the contacts of the Main relay.
The Main and Secondary Air Injection (SAI) pump relays are located in the engine compartment fusebox. When the
contacts of the Main relay are closed, a 12V battery supply is fed to the coil of the SAI pump relay. An earth connection
from the coil of the SAI pump relay is connected to the ECM. When the ECM completes the earth path, the coil
energises and closes the contacts of the SAI pump relay to supply 12V to the SAI pump via fusible link 2 in the engine
compartment fusebox. The SAI pump starts to operate, and will continue to do so until the ECM switches off the earth
connection to the coil of the SAI pump relay.
The SAI pump remains operational for a period determined by the ECM and depends on the starting temperature of
the engine, or for a maximum operation period determined by the ECM if the target engine coolant temperature has
not been reached in the usual time.
When the contacts of the main relay are closed, a 12V battery supply is fed to the SAI solenoid valve via Fuse 2 in
the engine compartment fusebox.
The ECM grounds the electrical connection to the SAI vacuum solenoid valve at the same time as it switches on the
SAI pump motor. When the SAI vacuum solenoid valve is energised, a vacuum is provided to the operation control
ports on both of the vacuum operated SAI control valves at the exhaust manifolds. The control vacuum is sourced
from the intake manifold depression and routed to the SAI control valves via a vacuum reservoir and the SAI vacuum
solenoid valve.
The vacuum reservoir is included in the vacuum supply circuit to prevent vacuum fluctuations caused by changes in
the intake manifold depression affecting the operation of the SAI control valves.
When a vacuum is applied to the control ports of the SAI control valves, the valves open to allow pressurised air from
the SAI pump to pass through to the exhaust ports in the cylinder heads for combustion.
When the ECM has determined that the SAI pump has operated for the desired duration, it switches off the earth paths
to the SAI pump relay and the SAI vacuum solenoid valve. With the SAI vacuum solenoid valve de-energised, the
valve closes, cutting off the vacuum supply to the SAI control valves. The SAI control valves close immediately and
completely to prevent any further pressurised air from the SAI pump entering the exhaust manifolds.
The engine coolant temperature sensor incurs a time lag in respect of detecting a change in temperature and the SAI
pump automatically enters a 'soak period' between operations to prevent the SAI pump overheating. The ECM also
compares the switch off and start up temperatures, to determine whether it is necessary to operate the SAI pump.
This prevents the pump running repeatedly and overheating on repeat starts.
Other factors which may prevent or stop SAI pump operation include the prevailing engine speed / load conditions.
Page 396 of 1672
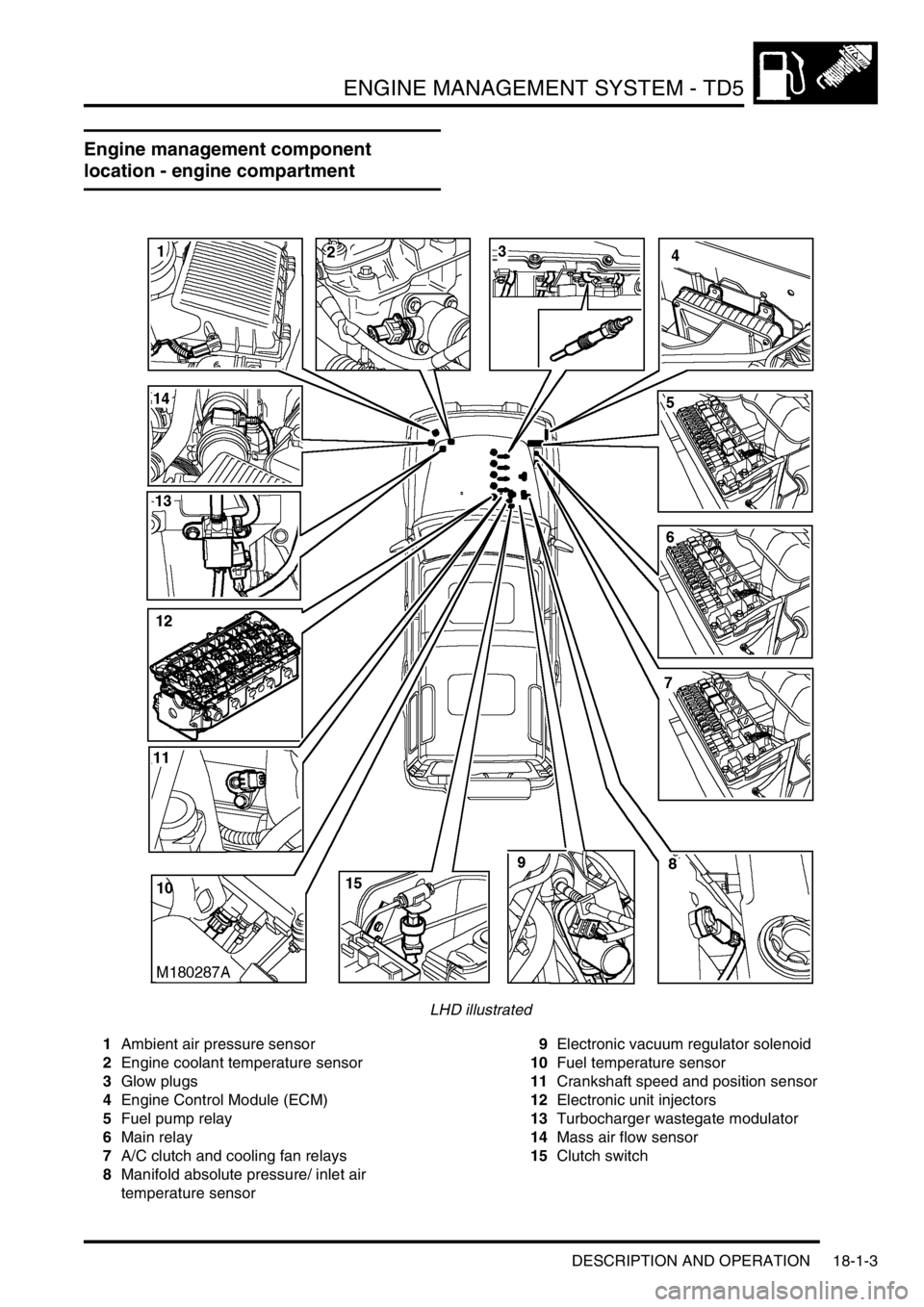
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-3
Engine management component
location - engine compartment
LHD illustrated
1Ambient air pressure sensor
2Engine coolant temperature sensor
3Glow plugs
4Engine Control Module (ECM)
5Fuel pump relay
6Main relay
7A/C clutch and cooling fan relays
8Manifold absolute pressure/ inlet air
temperature sensor9Electronic vacuum regulator solenoid
10Fuel temperature sensor
11Crankshaft speed and position sensor
12Electronic unit injectors
13Turbocharger wastegate modulator
14Mass air flow sensor
15Clutch switch
Page 398 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-5
1Mass air flow sensor
2Ambient air pressure sensor
3Manifold absolute pressure/ inlet air
temperature sensor
4Engine coolant temperature sensor
5Crankshaft speed and position sensor
6Throttle position sensor
7Fuel temperature sensor
8Brake pedal switch
9Clutch switch
10High/ Low ratio switch
11Main relay
12Malfunction indicator lamp
13Fuel pump relay
14Glow plug warning lamp
15Glow plugs16Electronic unit injectors
17Turbocharger wastegate modulator
18EGR modulator
19Diagnostic connector
20Engine control module
21Cruise control master switch
22Cruise control SET+ switch
23Cruise control RES switch
24Air conditioning clutch relay
25Air conditioning cooling fan relay
26Electronic automatic transmission ECU
27Self levelling and anti-lock brakes ECU
28Instrument cluster
29Body control unit
Page 399 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
An engine control module (ECM) controls the five-cylinder direct injection diesel engine, and works on the drive by
wire principle. This means there is no throttle cable, the ECM controls the drivers needs via a signal from the Throttle
Position (TP) sensor on the throttle pedal.
The ECM is a full authoritative diesel specific microprocessor that also incorporates features for cruise control and air
conditioning control. In addition, the ECM supplies output control for the exhaust gas recirculation and turbocharger
boost pressure. The ECM has a self-diagnostic function, which is able to provide backup strategies for most sensor
failures.
The ECM processes information from the following input sources:
lMass air flow sensor.
lAmbient air pressure sensor.
lManifold absolute pressure/inlet air temperature sensor.
lEngine coolant temperature sensor.
lCrankshaft speed and position sensor.
lThrottle position sensor.
lFuel temperature sensor.
lAir conditioning request.
lAir conditioning fan request.
lBrake pedal switch.
lClutch switch.
lCruise control master switch.
lCruise control SET+ switch.
lCruise control RES switch.
lHigh/low ratio switch.
The input from the sensors constantly updates the ECM with the current operating condition of the engine. Once the
ECM has compared current information with stored information within its memory, it can make any adjustment it
requires to the operation of the engine via the following:
lAir conditioning clutch relay.
lAir conditioning cooling fan relay.
lElectronic vacuum regulator solenoid.
lMalfunction indicator lamp.
lFuel pump relay.
lGlow plug warning lamp.
lGlow plugs.
lFuel injectors.
lMain relay.
lTurbocharger wastegate modulator.
lTemperature gauge.
The ECM interfaces with the following:
lElectronic Automatic Transmission (EAT).
lSelf Levelling and Anti-lock Brakes System (SLABS).
lSerial communication link.
lInstrument cluster.
lBody Control Unit (BCU).
Page 401 of 1672
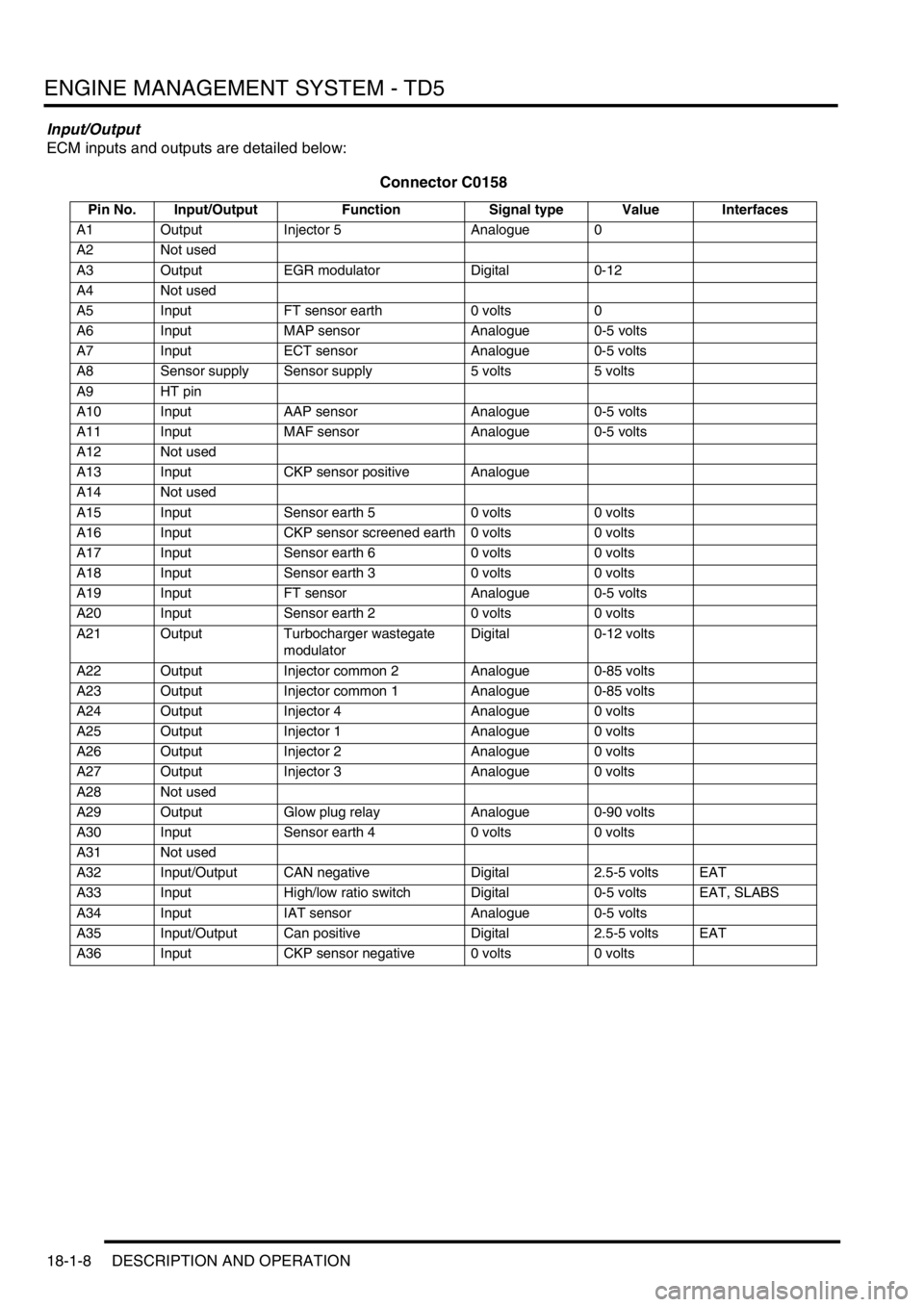
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Input/Output
ECM inputs and outputs are detailed below:
Connector C0158
Pin No. Input/Output Function Signal type Value Interfaces
A1 Output Injector 5 Analogue 0
A2 Not used
A3 Output EGR modulator Digital 0-12
A4 Not used
A5 Input FT sensor earth 0 volts 0
A6 Input MAP sensor Analogue 0-5 volts
A7 Input ECT sensor Analogue 0-5 volts
A8 Sensor supply Sensor supply 5 volts 5 volts
A9 HT pin
A10 Input AAP sensor Analogue 0-5 volts
A11 Input MAF sensor Analogue 0-5 volts
A12 Not used
A13 Input CKP sensor positive Analogue
A14 Not used
A15 Input Sensor earth 5 0 volts 0 volts
A16 Input CKP sensor screened earth 0 volts 0 volts
A17 Input Sensor earth 6 0 volts 0 volts
A18 Input Sensor earth 3 0 volts 0 volts
A19 Input FT sensor Analogue 0-5 volts
A20 Input Sensor earth 2 0 volts 0 volts
A21 Output Turbocharger wastegate
modulatorDigital 0-12 volts
A22 Output Injector common 2 Analogue 0-85 volts
A23 Output Injector common 1 Analogue 0-85 volts
A24 Output Injector 4 Analogue 0 volts
A25 Output Injector 1 Analogue 0 volts
A26 Output Injector 2 Analogue 0 volts
A27 Output Injector 3 Analogue 0 volts
A28 Not used
A29 Output Glow plug relay Analogue 0-90 volts
A30 Input Sensor earth 4 0 volts 0 volts
A31 Not used
A32 Input/Output CAN negative Digital 2.5-5 volts EAT
A33 Input High/low ratio switch Digital 0-5 volts EAT, SLABS
A34 Input IAT sensor Analogue 0-5 volts
A35 Input/Output Can positive Digital 2.5-5 volts EAT
A36 Input CKP sensor negative 0 volts 0 volts
Page 402 of 1672
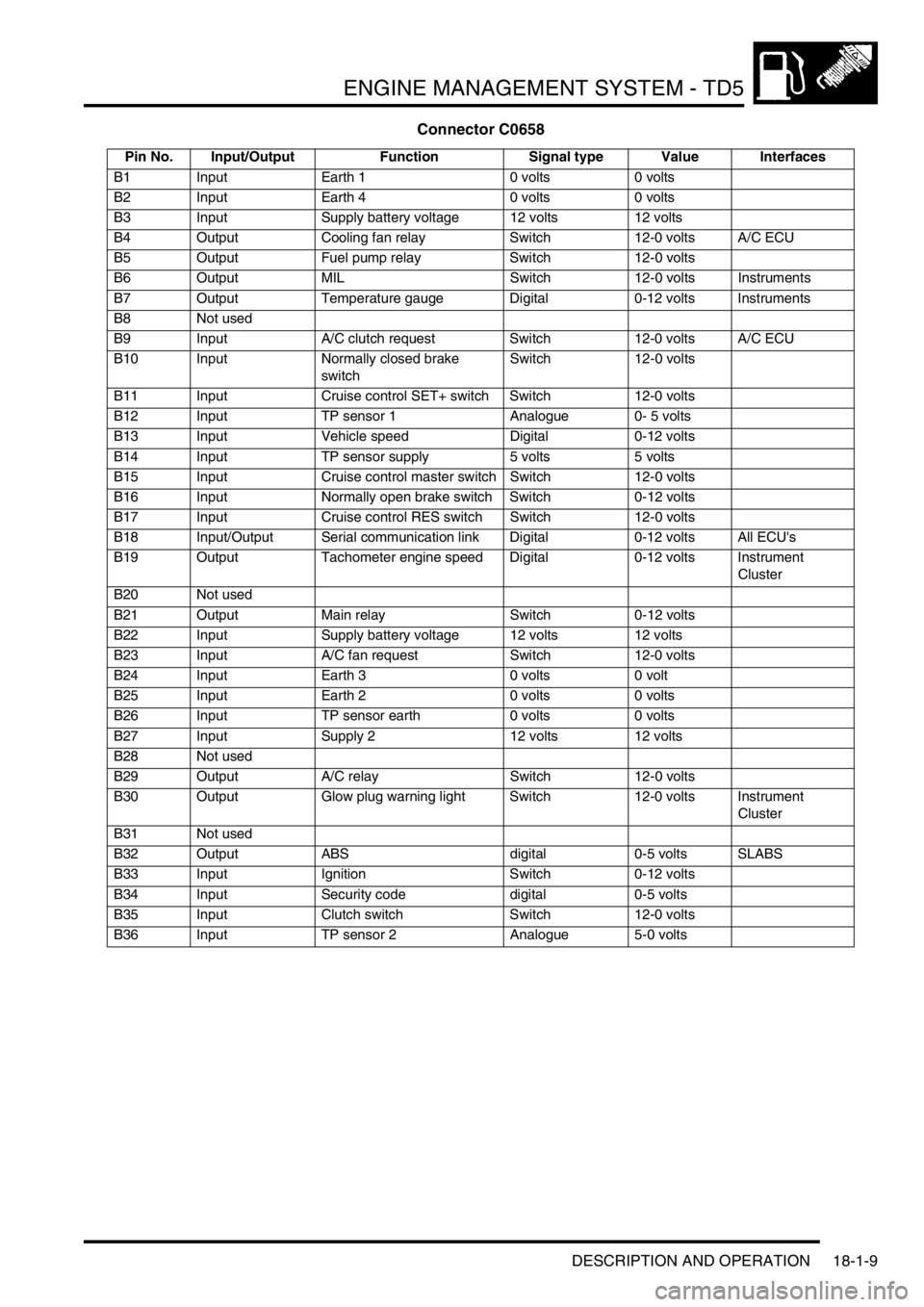
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-9
Connector C0658
Pin No. Input/Output Function Signal type Value Interfaces
B1 Input Earth 1 0 volts 0 volts
B2 Input Earth 4 0 volts 0 volts
B3 Input Supply battery voltage 12 volts 12 volts
B4 Output Cooling fan relay Switch 12-0 volts A/C ECU
B5 Output Fuel pump relay Switch 12-0 volts
B6 Output MIL Switch 12-0 volts Instruments
B7 Output Temperature gauge Digital 0-12 volts Instruments
B8 Not used
B9 Input A/C clutch request Switch 12-0 volts A/C ECU
B10 Input Normally closed brake
switchSwitch 12-0 volts
B11 Input Cruise control SET+ switch Switch 12-0 volts
B12 Input TP sensor 1 Analogue 0- 5 volts
B13 Input Vehicle speed Digital 0-12 volts
B14 Input TP sensor supply 5 volts 5 volts
B15 Input Cruise control master switch Switch 12-0 volts
B16 Input Normally open brake switch Switch 0-12 volts
B17 Input Cruise control RES switch Switch 12-0 volts
B18 Input/Output Serial communication link Digital 0-12 volts All ECU's
B19 Output Tachometer engine speed Digital 0-12 volts Instrument
Cluster
B20 Not used
B21 Output Main relay Switch 0-12 volts
B22 Input Supply battery voltage 12 volts 12 volts
B23 Input A/C fan request Switch 12-0 volts
B24 Input Earth 3 0 volts 0 volt
B25 Input Earth 2 0 volts 0 volts
B26 Input TP sensor earth 0 volts 0 volts
B27 Input Supply 2 12 volts 12 volts
B28 Not used
B29 Output A/C relay Switch 12-0 volts
B30 Output Glow plug warning light Switch 12-0 volts Instrument
Cluster
B31 Not used
B32 Output ABS digital 0-5 volts SLABS
B33 Input Ignition Switch 0-12 volts
B34 Input Security code digital 0-5 volts
B35 Input Clutch switch Switch 12-0 volts
B36 Input TP sensor 2 Analogue 5-0 volts
Page 403 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor
The MAF sensor is located in the intake system between the air filter housing and the turbocharger. The ECM uses
the information generated by the MAF to control exhaust gas recirculation (EGR).
The MAF sensor works on the hot film principal. The MAF sensor has 2 sensing elements contained within a film. One
element is controlled at ambient temperature e.g. 25
°C (77 °F) while the other is heated to 200 °C (392 °F) above
this temperature e.g. 225
°C (437 °F). As air passes through the MAF sensor the hot film will be cooled. The current
required to keep the constant 200
°C (392 °F) difference provides a precise although non-linear signal of the air drawn
into the engine. The MAF sensor sends a voltage between 0 and 5 volts to the ECM proportional to the mass of the
incoming air. This calculation allows the ECM to set the EGR ratio for varying operating conditions.
Input/Output
The MAF sensor receives battery voltage from the main relay in the engine compartment fuse box. Signal output from
the MAF sensor to the ECM is a variable voltage proportional to air drawn into the engine.
Input to the MAF sensor is via pin 5 of connector C0570 at the engine compartment fuse box. This 12 volt supply is
provided by the main relay via fuse 2 in the engine compartment fuse box. The MAF sensor receives the input voltage
at pin 3 of the sensor connector.
Output from the MAF sensor is measured at pin 11 of the ECM connector C0158. The earth path is via pin 20 of the
ECM connector C0158.
The MAF sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lContaminated sensor element.
lDamaged sensor element.
lDamaged in wiring harness.
lMAF supplies incorrect signal (due to air leak or air inlet restriction).
In the event of a MAF sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDuring driving engine speed may dip, before recovering.
lDifficult starting.
lEngine stalls after starting.
lDelayed throttle response.
lEGR inoperative.
lReduced engine performance.
lMAF signal out of parameters.
The MIL will not illuminate in a MAF sensor failure, and the ECM will use a fixed default value from its memory.
Page 417 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-24 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Fuel pump relay
The fuel pump relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It switches on the fuel pump to draw fuel from
the fuel tank to the electronic unit injectors (EUI).
Input/Output
The fuel pump relay is a 4 pin normally open relay. Voltage input to the fuel pump relay comes from the main relay
switching contacts. When the main relay is energised the switching contacts close and the fuel pump relay windings
are supplied a voltage. The ECM provides the earth for the relay windings to close the relay contacts and operate the
fuel lift pump. The fuel pump relay switching contacts are supplied voltage via fuse 10 located in the engine
compartment fuse box. Output from these switching contacts is supplied directly to the fuel pump. When the ECM
interrupts the earth the return spring in the relay pulls the contacts apart and the fuel lift pump stops operating. The
earth path is via pin 5 of ECM connector C0658.
The fuel pump relay can fail in the following ways:
lRelay open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBroken return spring.
In the event of a fuel pump relay failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine will crank but not start.
lIf the engine is running it will stop.
The MIL will not illuminate in a fuel pump relay failure.
Page 418 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-25
Main relay
The main relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box and supplies battery voltage to the following:
lECM.
lMAF.
lFuel pump relay.
lCruise control master switch.
lCruise control RES switch.
lCruise control SET+ switch.
It is a 4 pin normally open relay and must be energised to provide voltage to the ECM.
Input/Output
The earth path for the main relay is via a transistor within the ECM. When the earth path is completed, the main relay
energises to supply battery voltage to the ECM. Interrupting this earth path de-energises the main relay, preventing
battery voltage reaching the ECM.
Input to the main relay is via pin 1 of connector C0632, located at the engine compartment fuse box. Output from the
main relay is via fuse 1 to the ECM connector C0658 pins 3, 22 and 27. The earth path is via pin 21 of ECM connector
C0658.
The main relay can fail in the following ways:
lRelay open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBroken return spring.
In the event of a main relay failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine will crank but not start.
lIf the engine is running it will stop.
For the ECM start up to take place the ignition 'on' (position II) voltage must be greater than 6.0 volts.