oil pressure LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 365 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-28 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The SAI pump is attached to a bracket at the rear RH side of the engine compartment and is fixed to the bracket by
three studs and nuts. The pump is electrically powered from a 12V battery supply via a dedicated relay and supplies
approximately 35kg/hr of air when the vehicle is at idle in Neutral/Park on a start from 20
°C (68°F).
Air is drawn into the pump through vents in its front cover and is then passed through a foam filter to remove
particulates before air injection. The air is delivered to the exhaust manifold on each side of the engine through a
combination of plastic and metal pipes.
The air delivery pipe is a flexible plastic type, and is connected to the air pump outlet via a plastic quick-fit connector.
The other end of the flexible plastic pipe connects to the fixed metal pipework via a short rubber hose. The part of the
flexible plastic pipe which is most vulnerable to engine generated heat is protected by heat reflective sleeving. The
metal delivery pipe has a fabricated T-piece included where the pressurised air is split for delivery to each exhaust
manifold via the SAI control valves.
The pipes from the T-piece to each of the SAI control valves are approximately the same length, so that the pressure
and mass of the air delivered to each bank will be equal. The ends of the pipes are connected to the inlet port of each
SAI control valve through short rubber hose connections.
The T-piece is mounted at the rear of the engine (by the ignition coils) and features a welded mounting bracket which
is fixed to the engine by two studs and nuts.
The foam filter in the air intake of the SAI pump provides noise reduction and protects the pump from damage due to
particulate contamination. In addition, the pump is fitted on rubber mountings to help prevent noise which is generated
by pump operation from being transmitted through the vehicle body into the passenger compartment.
If the secondary air injection pump malfunctions, the following fault codes may be stored in the ECM diagnostic
memory, which can be retrieved using 'Testbook':
Secondary air injection (SAI) pump relay
The secondary air injection pump relay is located in the engine compartment fusebox. The engine control module
(ECM) is used to control the operation of the SAI pump via the SAI pump relay. Power to the coil of the relay is supplied
from the vehicle battery via the main relay and the ground connection to the coil is via the ECM.
Power to the SAI pump relay contacts is via fusible link FL2 which is located in the engine compartment fusebox.
P-code Description
P0418Secondary air injection pump powerstage fault (e.g. - SAI pump relay fault / SAI
pump or relay not connected / open circuit / harness damage).
Page 370 of 1672
EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-33
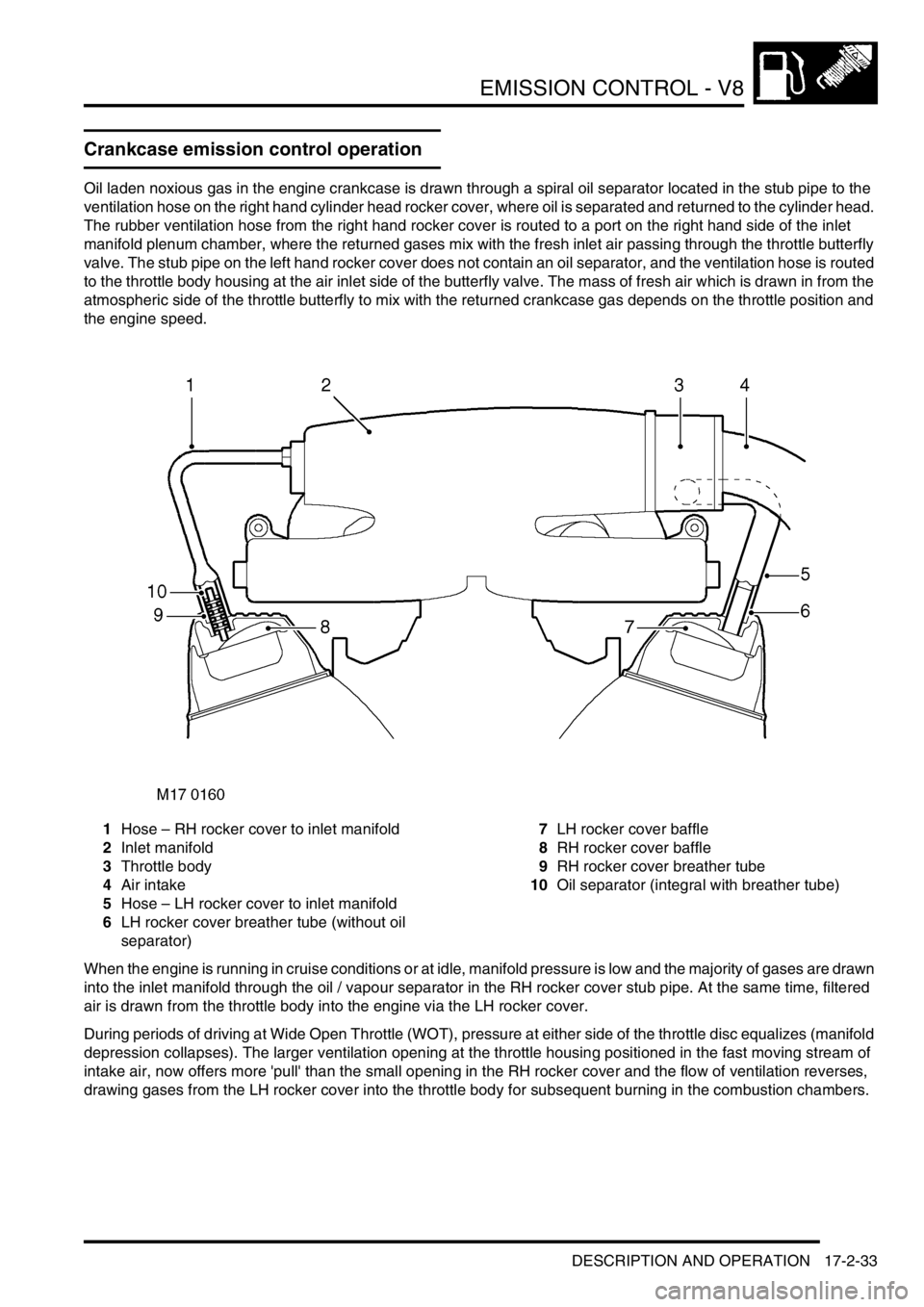
Crankcase emission control operation
Oil laden noxious gas in the engine crankcase is drawn through a spiral oil separator located in the stub pipe to the
ventilation hose on the right hand cylinder head rocker cover, where oil is separated and returned to the cylinder head.
The rubber ventilation hose from the right hand rocker cover is routed to a port on the right hand side of the inlet
manifold plenum chamber, where the returned gases mix with the fresh inlet air passing through the throttle butterfly
valve. The stub pipe on the left hand rocker cover does not contain an oil separator, and the ventilation hose is routed
to the throttle body housing at the air inlet side of the butterfly valve. The mass of fresh air which is drawn in from the
atmospheric side of the throttle butterfly to mix with the returned crankcase gas depends on the throttle position and
the engine speed.
1Hose – RH rocker cover to inlet manifold
2Inlet manifold
3Throttle body
4Air intake
5Hose – LH rocker cover to inlet manifold
6LH rocker cover breather tube (without oil
separator)7LH rocker cover baffle
8RH rocker cover baffle
9RH rocker cover breather tube
10Oil separator (integral with breather tube)
When the engine is running in cruise conditions or at idle, manifold pressure is low and the majority of gases are drawn
into the inlet manifold through the oil / vapour separator in the RH rocker cover stub pipe. At the same time, filtered
air is drawn from the throttle body into the engine via the LH rocker cover.
During periods of driving at Wide Open Throttle (WOT), pressure at either side of the throttle disc equalizes (manifold
depression collapses). The larger ventilation opening at the throttle housing positioned in the fast moving stream of
intake air, now offers more 'pull' than the small opening in the RH rocker cover and the flow of ventilation reverses,
drawing gases from the LH rocker cover into the throttle body for subsequent burning in the combustion chambers.
Page 426 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-33
The turbocharger is exposed to extremely high operating temperatures (up to 1,000 °C (1832 °F)) because of the hot
exhaust gases and the high speed revolution of the turbine (up to 150,000 rev/min). In order to resist wear of the
turbine bearings a flow of lubrication oil is supplied from the engine lubrication system to keep the bearings cool. Oil
is supplied from a tapping at the front of the full-flow filter adaptor housing via a metal pipe with banjo connections.
Oil is returned to the sump via a metal pipe which connects to the cylinder block at a port below the turbocharger
assembly.
A heatshield is attached to the left hand side of the engine to protect adjacent components from the heat generated
at the turbocharger. The heatshield is attached to the engine by two bolts an additional bolt attaches the heatshield
to the turbocharger casting.
The engine control module controls the amount of boost pressure the engine receives by way of the turbocharger.
When full boost is reached a control signal is sent to the wastegate modulator, and a vacuum is applied to the
wastegate valve. The wastegate valve opens, bypassing some of the exhaust gas away from the turbine to be output
to the exhaust system.
The engine should be allowed to idle for 15 seconds following engine start up and before the engine is switched off
to protect the turbocharger by maintaining oil supply to the turbine bearings.
Intercooler
The intercooler is an air-to-air heat exchanger which lowers the intake air temperature to obtain a higher air density
for better combustion efficiency. The intercooler receives compressed air from the turbocharger via a metal pipe; it
cools the intake air via the intercooler matrix and delivers it to the intake manifold by means of a rubber hose which
connects between the intercooler outlet and the intake manifold outlet. The rubber hose is connected to ports at each
end by metal band clips.
+ COOLING SYSTEM - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
The intercooler is located at the front of the engine bay, forward of the radiator.
Page 462 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-5
1Engine control module
2Crankshaft speed and position sensor
3Camshaft position sensor
4Engine coolant temperature sensor
5Mass air flow/ inlet air temperature sensor
6Throttle position sensor
7Heated oxygen sensors
8Fuel injectors
9Idle air control valve
10Fuel pump relay
11EVAP canister
12EVAP canister vent valve
13EVAP canister purge valve
14Fuel tank pressure sensor
15Ignition coils
16Knock sensor
17Spark plugs
18High/ Low ratio switch
19Malfunction indication lamp
20Diagnostic connector
21Air temperature control clutch relay
22Air temperature control cooling fan relay
23ATC ECU
24CAN link to EAT
25SLABS ECU
26BCU
27Instrument cluster
28Thermostat monitoring sensor (where fitted)
Page 490 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-33
In the event of an IACV signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEither low or high idle speed.
lEngine stalls.
lDifficult starting.
lIdle speed in default condition.
There are eight IACV diagnostic checks performed by the ECM:
lOutput short circuit to earth – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to battery supply – opening coil
lOutput open circuit – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to earth – closing coil
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage – closing coil
lOutput open circuit – closing coil
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error low (engine speed must be 100 rev/min less than the target speed, engine load
less than 2.5 and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h less than the expected air flow for a fault condition to
be flagged).
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error high (the engine speed must be more than 180 rev/min greater than the target
speed and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h greater than the expected air flow for a fault condition to be
flagged).
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Fuel pump relay
The fuel pump relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It is a 4 pin normally open relay. Input from the
ECM allows the fuel pump relay to control the electrical input to the fuel pump, regulating the fuel supply to the fuel
injectors. When the ignition is switched on and the engine is cranked, the fuel pump relay is activated by the ECM,
allowing the fuel system to be pressurised to 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in
2). The ECM then deactivates the relay until the engine
has started.
If the fuel pump runs, but the fuel pressure is out of limits, adaptive fuel faults will be stored.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1510 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - opening winding
P1513 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - opening winding
P1514 IACV opening coil malfunction Open circuit - opening winding
P1553 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - closing winding
P1552 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - closing winding
P1551 IACV closing coil malfunction Open circuit - closing winding
P0505 Idle control system malfunction Blocked IACV - high or low rev/min error
Page 503 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-46 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Idle speed control
The ECM regulates the engine speed at idling. The ECM uses the idle air control valve (IACV) to compensate for the
idle speed drop that occurs when the engine is placed under greater load than usual. When the throttle is in the rest
position i.e. it has not been pressed, the majority of intake air that the engine consumes comes from the idle air control
valve.
IACV control idle speed
Conditions in which the ECM operates the IACV control idle speed is as follows:
lIf any automatic transmission gears other than P or N are selected.
lIf air conditioning is switched on.
lIf cooling fans are switched on.
lAny electrical loads activated by the driver.
Function
The idle air control valve utilises two coils that use opposing pulse width modulated (PWM) signals to control the
position of a rotary valve. If one of the circuits that supplies the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining
signal preventing the idle air control valve from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the idle
air control valve assumes a default idle position at which the engine idle speed is raised to 1200 rev/min with no load
placed on the engine.
Evaporative emission control
Due to increasing legislation, all new vehicles must be able to limit evaporative emissions (fuel vapour) from the fuel
tank.
The ECM controls the emission control system using the following components:
lEVAP canister.
lPurge valve.
lCanister vent solenoid (CVS) valve – (NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability
only)
lFuel tank pressure sensor – (NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability only)
lFuel leak detection pump – (NAS vehicles with positive pressure type EVAP system leak detection capability
only)
lInterconnecting pipe work.
Refer to Emissions section for operating conditions of evaporative emission systems.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Evaporative emission control operation.
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) - North American Specification vehicles only
The ECM monitors performance of the engine for misfires, catalyst efficiency, exhaust leaks and evaporative control
loss. If a fault occurs, the ECM stores the relevant fault code and warns the driver of component failure by illuminating
the Malfunction Indicator Light in the instrument pack.
On vehicles fitted with automatic gearbox, the ECM combines with the Electronic Automatic Transmission (EAT) ECU
to provide the OBD strategy.
Conditions
If the OBD function of the ECM flags a fault during its operation, it falls into one of the following categories:
lmin = minimum value of the signal exceeded.
lmax = maximum value of the signal exceeded.
lsignal = signal not present.
lplaus = an implausible condition has been diagnosed.
Page 550 of 1672

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-1-5
The fuel pump is a 'self priming', wet type, two stage pump which is immersed in fuel in the tank and operates at all
times when the ignition switch is in position II. If the engine is not started, the ECU will 'time-out' after three minutes
and de-energise the fuel pump relay. The pump receives a feed from the battery via fuse 10 in the engine
compartment fusebox and the fuel pump relay. The relay is energised by the ECM when the ignition switch is moved
to position II.
The fuel pump assembly is retained with a locking ring and sealed with a rubber seal. The locking ring requires a
special tool for removal and refitment. An access panel for the fuel pump is located in the loadspace floor below the
carpet. The access panel is sealed to the floor with a rubber seal and retained by six self-tapping screws. A four pin
electrical connector is located on the top cover and provides power feed and earth for the fuel pump and also inputs
and outputs for the fuel gauge sender operation.
The fuel gauge sender is integral with the fuel pump. The sender is submerged in the fuel and is operated by a float
which moves with the fuel level in the tank.
Fuel pump
The fuel pump assembly comprises a top cover which locates the electrical connector, fuel burning heater connection
and four fuel pipe couplings. The top cover is attached to a plastic cup shaped housing and retained on three sliding
clips. Two coil springs are located between the cover and the housing and ensure that the fuel pump remains seated
positively at the bottom of the tank when installed.
The housing locates the two stage fuel pump and also the fuel gauge sender unit. The lower part of the housing is the
swirl pot which maintains a constant level of fuel at the fuel pick-up. A coarse filter is located in the base of the housing
and prevents the ingress of contaminants into the pump and the fuel system from the fuel being drawn into the pump.
A fine filter is located in the intake to the low pressure stage to protect the pump from contaminants. Flexible pipes
connect the couplings on the top cover to the pump.
A non-return valve is located in the base of the housing. When the fuel tank is full, fuel pressure keeps the valve lifted
from its seat allowing fuel to flow into the swirl pot. As the tank level reduces, the fuel pressure in the tank reduces
causing the valve to close. When the valve is closed fuel is retained in the swirl pot, ensuring that the swirl pot remains
full and maintains a constant supply to the fuel pump.
The two stage pump comprises a high and a low pressure stage. The low pressure stage draws fuel from the swirl
pot through the filter. The low pressure stage pumps fluid at a pressure of 0.75 bar (10.9 lbf.in
2) and a flow of 30 litres/
hour (8 US Gallons/hour) to the fuel filter. A proportion of the fuel from the low pressure stage also passes, via a
restrictor, through a jet pump which keeps fuel circulating in the swirl pot. The high pressure stage draws the low
pressure fuel from the fuel filter and pressurises it to a pressure of 4.0 bar (58 lbf.in
2). The pressurised fuel is then
passed from the pump to the injectors at a flow of 180 litres/hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour). A fuel pressure regulator is
located at the rear of the engine and ensures that the delivery pressure remains at 4.0 bar (58 lbf.in
2) by controlling
the amount of fuel returning to the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a maximum current draw of 15 Amps at 12.5 V and is protected by a 20 Amp fuse in the engine
compartment fusebox.
Page 586 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 26-1-3
1Pressure cap
2Overflow pipe
3Heater return hose
4Heater matrix
5Heater inlet hose
6Oil cooler return pipe — EU3 models
7Connecting hose
8Oil cooler housing assembly
9Heater inlet pipe
10Connecting hose
11Outlet housing
12Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
13Bleed screw
14Radiator top hose
15Radiator - upper
16Intercooler
17Gearbox oil cooler
18Radiator - lower
19Viscous fan
20Drain plug21Connecting hose
22Fuel cooler feed hose
23Radiator bottom hose
24Thermostat housing
25Connecting hose
26Coolant pump feed pipe
27Coolant by-pass pipe
28Radiator bleed pipe
29Connecting hose
30Coolant pump
31Fuel cooler
32Heater/expansion tank return hose
33Expansion tank
34EGR Cooler - EU3 models
35Connecting hose - EU3 models
36Connecting hose - EU3 models
37Hose - EGR Cooler to oil cooler return pipe -
EU3 models
38Radiator lower feed hose - Pre EU3 models
39Oil cooler return pipe - Pre EU3 models
Page 588 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 26-1-5
Description
General
The cooling system used on the Diesel engine is a pressure relief by-pass type system which allows coolant to
circulate around the engine block and heater circuit when the thermostat is closed. With coolant not passing through
the by-pass or the radiator promotes faster heater warm-up which in turn improves passenger comfort.
A coolant pump is mounted on a casting behind the PAS pump and is driven from the PAS pump at crankshaft speed
by the auxiliary drive belt. The pump mounting casting connects with passages in the cylinder block and pumps
coolant from the radiator through the cylinder block.
A viscous fan is attached to an idler pulley at the front of the engine. The fan is attached to a threaded spigot on the
pulley with a left hand threaded nut. The fan draws air through the radiator to assist in cooling when the vehicle is
stationary. The fan rotational speed is controlled relative to the running temperature of the engine by a thermostatic
valve regulated by a bi-metallic coil.
The cooling system uses a 50/50 mix of anti-freeze and water.
A Fuel Burning Heater (FBH) is available as an optional item for Diesel engine variants. The FBH is located on the
bulkhead and is connected in series in the coolant supply to the heater. The FBH is used to compensate for the
relatively low coolant temperatures inherent in the Diesel engine.
+ HEATING AND VENTILATION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Thermostat housing
A plastic thermostat housing is located behind the radiator. The housing has three connections which locate the
radiator bottom hose, top hose and coolant pump feed pipe. The housing contains a wax element thermostat and a
spring loaded by-pass flow valve.
Thermostat - Main valve
The thermostat is used to maintain the coolant at the optimum temperature for efficient combustion and to aid engine
warm-up. The thermostat is closed at temperatures below approximately 82
°C (179°F). When the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 82
°C the thermostat starts to open and is fully open at approximately 96°C
(204
°F). In this condition the full flow of coolant is directed through the radiator.
The thermostat is exposed to 90% hot coolant from the engine on one side and 10% cold coolant returning from the
radiator bottom hose on the other side.
Hot coolant from the engine passes from the by-pass pipe through four sensing holes in the flow valve into a tube
surrounding 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the radiator, cooled by the ambient air,
conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area.
In cold ambient temperatures, the engine temperature is raised approximately 10
°C (50°F) to compensate for the heat
loss of 10% exposure to the cold coolant returning from the radiator bottom hose.
By-pass flow valve
The by-pass flow valve is held closed by a light spring. It operates to further aid heater warm-up. When the main valve
is closed and the engine speed is below 1500 rev/min, the coolant pump does not produce sufficient flow and pressure
to open the valve. In this condition the valve prevents coolant circulating through the by-pass circuit and forces the
coolant through the heater matrix only. This provides a higher flow of warm coolant through the heater matrix to
improve passenger comfort in cold conditions.
When the engine speed increases above 1500 rev/min the coolant pump produces a greater flow and pressure than
the heater circuit can take. The pressure acts on the flow valve and overcomes the valve spring pressure, opening
the valve and limiting the pressure in the heater circuit. The valve modulates to provide maximum coolant flow through
the heater matrix and yet allowing excess coolant to flow into the by-pass circuit to provide the engines cooling needs
at higher engine rev/min.
Page 589 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - TD5
26-1-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Outlet housing
A cast aluminium outlet housing is attached to the cylinder head with three bolts and sealed with a gasket. Coolant
leaves the engine through the outlet housing and is directed through a hose to the heater matrix, the radiator or the
by-pass circuit.
An Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is installed in a threaded port on the side of the outlet housing. The
sensor monitors coolant temperature emerging from the engine and sends signals to the Engine Control Module
(ECM) for engine management and temperature gauge operation.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Expansion tank
The expansion tank is located in the engine compartment. The tank is made from moulded plastic and attached to
brackets on the right hand inner wing. A maximum coolant when cold level is moulded onto the tank.
Excess coolant created by heat expansion is returned to the expansion tank from the radiator bleed pipe at the top of
the radiator. An outlet pipe is connected into the coolant pump feed hose and replaces the coolant displaced by heat
expansion into the system when the engine is cool.
The expansion tank is fitted with a sealed pressure cap. The cap contains a pressure relief valve which opens to allow
excessive pressure and coolant to vent through the overflow pipe. The relief valve is open at a pressure of 1.4 bar (20
lbf.in
2) and above.
Heater matrix
The heater matrix is fitted in the heater assembly inside the passenger compartment. Two pipes pass through the
bulkhead into the engine compartment and provide coolant flow to and from the matrix. The pipes from the bulkhead
are connected to the matrix, sealed with 'O' rings and clamped with circular rings.
The matrix is constructed from aluminium with two end tanks interconnected with tubes. Aluminium fins are located
between the tubes and conduct heat from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes. Air from the heater assembly is
warmed as it passes through the matrix fins. The warm air is then distributed in to the passenger compartment as
required.
+ HEATING AND VENTILATION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
When the engine is running, coolant from the engine is constantly circulated through the heater matrix.
Radiator
The 44 row radiator is located at the front of the vehicle in the engine compartment. The cross flow type radiator is
manufactured from aluminium with moulded plastic end tanks interconnected with tubes. The bottom four rows are
separate from the upper radiator and form the lower radiator for the fuel cooler. Aluminium fins are located between
the tubes and conduct heat from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes, reducing the coolant temperature as it
flows through the radiator. Air intake from the front of the vehicle when moving carries the heat away from the fins.
When the vehicle is stationary, the viscous fan draws air through the radiator fins to prevent the engine from
overheating.
Two connections at the top of the radiator provide for the attachment of the top hose from the outlet housing and bleed
pipe to the expansion tank. Three connections at the bottom of the radiator allow for the attachment of the bottom
hose to the thermostat housing and the return hose from the oil cooler and the feed hose to the fuel cooler.
The bottom four rows of the lower radiator are dedicated to the fuel cooler. The upper of the two connections at the
bottom of the radiator receives coolant from the oil cooler. This is fed through the four rows of the lower radiator in a
dual pass and emerges at the lower connection. The dual pass lowers the coolant temperature by up to 24
°C before
being passed to the fuel cooler.
Two smaller radiators are located in front of the cooling radiator. The upper radiator is the intercooler for the air intake
system and the lower radiator provides cooling of the gearbox oil.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Emission Control Systems.
+ MANUAL GEARBOX - R380, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
+ AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22 - 24, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.