ECO mode LINCOLN MARK LT 2006 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LINCOLN, Model Year: 2006, Model line: MARK LT, Model: LINCOLN MARK LT 2006Pages: 256, PDF Size: 2.81 MB
Page 72 of 256

Power door unlock/lock procedure
You must complete Steps 1–5 within
30 seconds, or the procedure will
have to be repeated. If the
procedure needs to be repeated,
you must wait a minimum of 30
seconds to begin again.
1. Turn the ignition to the 3 (ON)
position, then press the
control three times.
2. Turn the ignition to the 1 (OFF/LOCK) position, then press the
control three times.
3. Turn the ignition to the 3 (ON) position; the horn will chirp to
indicate the driver configuration mode has been activated.
4. Within five seconds, press
then thecontrol.Note:One horn
chirp should be heard, indicating the system has been disabled.
Conversely, a horn chirp followed by a honk will indicate the system is
enabled. Pressing the
control then thecontrol will turn the
feature ON if it was previously OFF, or OFF if it was previously ON. The
horn will chirp once if autolock was deactivated or twice (one short
chirp and one long honk) if autolock was activated.
5. Turn the ignition to the 1 (OFF/LOCK) position to exit programming.
Note:After exiting the driver configuration mode, the horn will chirp
once to indicate a feature has been activated/deactivated.
Keyless entry key pad procedure
1. Turn the ignition to the 1 (OFF/LOCK) position.
2. Close all the doors.
3. Enter 5–digit entry code
4. Press and hold the 7•8. While holding the 7•8pressthe3•4.
5. Release the 3•4.
6. Release the 7•8.
The user should receive ahorn chirpto indicate the system has
been disabled or a chirp followed by a honk to indicate the system
has been enabled.
Message center procedure
For information regarding the activation and deactivation of the autolocks
feature, refer toMessage center (SETUP button)in theDriver Controls
chapter.
2006 Mark LT(mlt)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA(fus)
Locks and Security
72
Page 109 of 256

•Place seat back in upright position.
•Put the safety belt in the automatic locking mode. Refer toAutomatic
locking modepassenger side front and rear seating positions (if
equipped).
•LATCH lower anchors are recommended for use by children up to 48
lb (22 kg) in a child restraint. Top tether anchors can be used for
children up to 60 lb (27 kg) in a child restraint, and to provide upper
torso restraint for children up to 80 lb (36 kg) using an upper torso
harness and a belt-positioning booster.
Ford recommends the use of a child safety seat having a top tether
strap. Install the child safety seat in a seating position with LATCH and
tether anchors. For more information on top tether straps and anchors,
refer toAttaching safety seats with tether strapsin this chapter. For
more information of LATCH anchors refer toAttaching safety seats with
LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) attachmentsin this
chapter.
Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions included
with the safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install
and use the safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden
stop or collision.
Installing child safety seats with combination lap and shoulder
belts
Airbags can kill or injure a child in a child seat.NEVERplace a
rear-facing child seat in front of an active airbag. If you must use
a forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move the seat all the way
back.
Children 12 and under should be properly restrained in the rear
seat whenever possible.
2006 Mark LT(mlt)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
109
Page 118 of 256
Power is supplied to all four wheels
through a transfer case or power
transfer unit. 4WD vehicles allow
you to select different drive modes
as necessary. Information on
transfer case operation and shifting
procedures can be found in the
Drivingchapter. Information on
transfer case maintenance can be found in theMaintenance and
Specificationchapter. You should become thoroughly familiar with this
information before you operate your vehicle.
On some 4WD models, the initial shift from two-wheel drive to 4WD
while the vehicle is moving can cause a momentary clunk and ratcheting
sound. These sounds are normal as the front drivetrain comes up to
speed and is not cause for concern.
Do not become overconfident in the ability of 4WD and AWD
vehicles. Although a 4WD or AWD vehicle may accelerate better
than two-wheel drive vehicle in low traction situations, it won’t stop
any faster than two-wheel drive vehicles. Always drive at a safe speed.
How your vehicle differs from other vehicles
SUV and trucks can differ from
some other vehicles in a few
noticeable ways. Your vehicle may
be:
•Higher – to allow higher load
carrying capacity and to allow it
to travel over rough terrain
without getting hung up or
damaging underbody components.
•Shorter – to give it the capability
to approach inclines and drive
over the crest of a hill without
getting hung up or damaging
underbody components. All other
things held equal, a shorter
wheelbase may make your vehicle quicker to respond to steering
inputs than a vehicle with a longer wheelbase.
2006 Mark LT(mlt)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA(fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
118
Page 125 of 256

•hold the steering wheel firmly.
•slowly move to a safe place on the side of the road.
The use of tire sealants may damage your tires.
Temporary Emergency Spare Tire Information
Your vehicle may be equipped with a temporary emergency spare tire.
This tire may be a T-type/mini-spare tire which will have the words
“Temporary Use Only” molded into the tire sidewall or it may be a full
size dissimilar spare tire/wheel that is different in brand, size or
appearance from the road tire, which will be identified with a “Caution”
label on the wheel. Both of these spare tires are considered “temporary”.
Replace these temporary emergency spare tires on the vehicle with a tire
of the same size, speed rating and load carrying capacity as the other
road tires as soon as possible.
It is not recommended that the vehicle be operated in 4WD modes with a
temporary emergency spare tire. If 4WD operation is necessary, do not
operate above speeds of 10 mph (16 km/h) or for distances above 50 miles
(80 km).
When driving with the temporary emergency spare tiredo not:
•Exceed 50 mph (80 km/h)
•Exceed 2000 miles (3200 km)
•Load the vehicle beyond maximum vehicle load rating listed on the
Safety Compliance Label
•Tow a trailer
•Use snow chains
•Use more than one temporary emergency spare tire
•Use commercial car washing equipment
•Try to repair the temporary emergency spare tire
Use of a temporary emergency spare tire at any one wheel location can
lead to impairment of the following:
•Handling, stability and braking performance
•Comfort and noise
•Ground clearance and parking at curbs
•Winter weather driving capability
•Wet weather driving capability
2006 Mark LT(mlt)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA(fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
125
Page 169 of 256

4WD Systems
4WD (when you select a 4WD mode) uses all four wheels to power the
vehicle. This increases traction, enabling you to drive over terrain and
road conditions that a conventional two-wheel drive vehicle cannot.
Power is supplied to all four wheels
through a transfer case. On 4WD
vehicles, the transfer case allows
you to select 4WD when necessary.
Information on transfer case
operation and shifting procedures
can be found in theFour-Wheel
Drive (4WD) Operationsection
earlier in this chapter. Information on transfer case maintenance can be
found in theMaintenance and Specificationschapter. You should
become thoroughly familiar with this information before you operate
your vehicle.
Normal characteristics
On some 4WD models, the initial shift from two-wheel drive to 4x4 while
the vehicle is moving can cause some momentary clunk and ratcheting
sounds. This is the front drivetrain coming up to speed and the
automatic locking hubs engaging and is not cause for concern.
Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four wheels on the most solid
area of the trail. Avoid reducing the tire pressures but shift to a lower
gear and drive steadily through the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly
and avoid spinning the wheels.
Avoid excessive speed because vehicle momentum can work against you
and cause the vehicle to become stuck to the point that assistance may
be required from another vehicle. Remember, you may be able to back
out the way you came if you proceed with caution.
2006 Mark LT(mlt)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA(fus)
Driving
169
Page 185 of 256
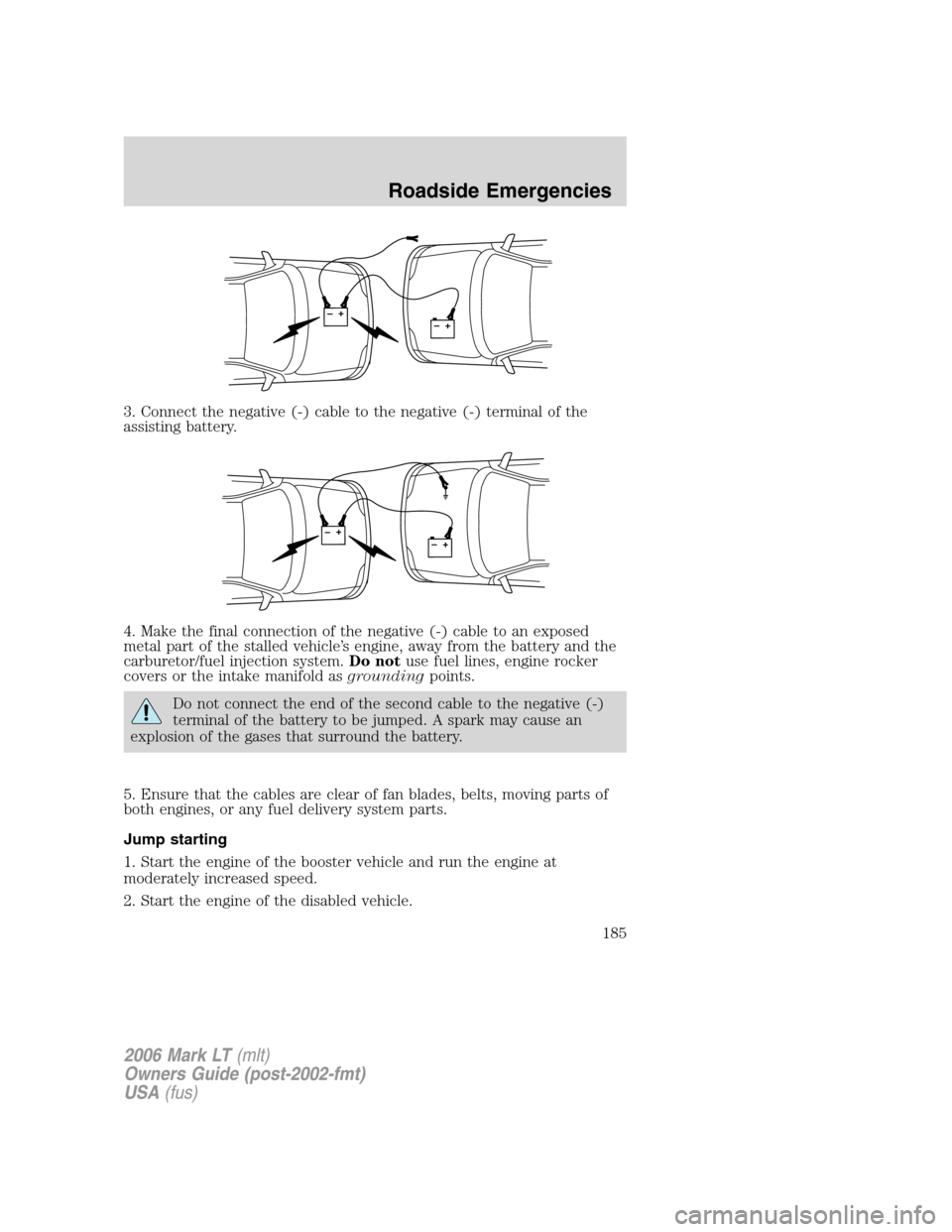
3. Connect the negative (-) cable to the negative (-) terminal of the
assisting battery.
4. Make the final connection of the negative (-) cable to an exposed
metal part of the stalled vehicle’s engine, away from the battery and the
carburetor/fuel injection system.Do notuse fuel lines, engine rocker
covers or the intake manifold asgroundingpoints.
Do not connect the end of the second cable to the negative (-)
terminal of the battery to be jumped. A spark may cause an
explosion of the gases that surround the battery.
5. Ensure that the cables are clear of fan blades, belts, moving parts of
both engines, or any fuel delivery system parts.
Jump starting
1. Start the engine of the booster vehicle and run the engine at
moderately increased speed.
2. Start the engine of the disabled vehicle.
+–+–
+–+–
2006 Mark LT(mlt)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
185
Page 193 of 256

Board membership
The Board consists of:
•Three consumer representatives
•A Ford or Lincoln Mercury dealership representative
Consumer candidates for Board membership are recruited and trained by
an independent consulting firm. The dealership Board member is chosen
from Ford and Lincoln Mercury dealership management, recognized for
their business leadership qualities.
What the Board needs
To have your case reviewed you must complete the application in the
DSB brochure and mail it to the address provided on the application
form. Some states will require you to use certified mail, with return
receipt requested.
Your application is reviewed and, if it is determined to be eligible, you
will receive an acknowledgment indicating:
•The file number assigned to your application.
•The toll-free phone number of the DSB’s independent administrator.
Your dealership and a Ford Motor Company representative will then be
asked to submit statements.
To properly review your case, the Board needs the following information:
•Legible copies of all documents and maintenance or repair orders
relevant to the case.
•The year, make, model, and Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) listed
on your vehicle ownership license.
•The date of repair(s) and mileage at the time of occurrence(s).
•The current mileage.
•The name of the dealer(s) who sold or serviced the vehicle.
•A brief description of your unresolved concern.
•A brief summary of the action taken by the dealer(s) and Ford Motor
Company.
•The names (if known) of all the people you contacted at the
dealership(s).
•A description of the action you expect to resolve your concern.
You will receive a letter of explanation if your application does not
qualify for Board review.
2006 Mark LT(mlt)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA(fus)
Customer Assistance
193
Page 224 of 256

•Have the vehicle loading and distribution the same every time.
Your results will be most accurate if your filling method is consistent.
Calculating fuel economy
1. Fill the fuel tank completely and record the initial odometer reading
(in miles or kilometers).
2. Each time you fill the tank, record the amount of fuel added (in
gallons or liters).
3. After at least three to five tank fill-ups, fill the fuel tank and record
the current odometer reading.
4. Subtract your initial odometer reading from the current odometer
reading.
5. Follow one of the simple calculations in order to determine fuel
economy:
Calculation 1:Divide total miles traveled by total gallons used.
Calculation 2:Multiply liters used by 100, then divide by total
kilometers traveled.
Keep a record for at least one month and record the type of driving (city
or highway). This will provide an accurate estimate of the vehicle’s fuel
economy under current driving conditions. Additionally, keeping records
during summer and winter will show how temperature impacts fuel
economy. In general, lower temperatures give lower fuel economy.
Driving style — good driving and fuel economy habits
Give consideration to the lists that follow and you may be able to change
a number of variables and improve your fuel economy.
Habits
•Smooth, moderate operation can yield up to 10% savings in fuel.
•Steady speeds without stopping will usually give the best fuel
economy.
•Idling for long periods of time (greater than one minute) may waste
fuel.
•Anticipate stopping; slowing down may eliminate the need to stop.
•Sudden or hard accelerations may reduce fuel economy.
•Slow down gradually.
•Driving at reasonable speeds (traveling at 55 mph [88 km/h] uses 15%
less fuel than traveling at 65 mph [105 km/h]).
2006 Mark LT(mlt)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA(fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
224