steering LINCOLN NAVIGATOR 2016 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LINCOLN, Model Year: 2016, Model line: NAVIGATOR, Model: LINCOLN NAVIGATOR 2016Pages: 419, PDF Size: 3.59 MB
Page 140 of 419

1. With the ignition on, move the memory
positions to the desired positions.
2. Press and hold the desired preset button
for about five seconds. A tone will sound
after about two seconds. Continue
holding until a second tone is heard.
3. Within three seconds, press the lock button on the remote control you are
linking.
To unlink a remote control, follow the same
procedure – except in step 3, press the
unlock button on the remote control.
Note: If more than one linked remote control
or intelligent access key is in range, the
memory function moves to the settings of
the first key to initiate a memory recall.
Easy Entry and Exit Feature (If Equipped)
This feature adjusts the position of the seat
and steering column to allow easier exit and
entry to the vehicle. The driver seat automatically moves 2 inches
(5 centimeters) rearward when the
transmission is in park (P) and you remove
the key from the ignition or you switch the
ignition off.
The driver seat returns to the previous
position when you put the key in the ignition
or switch the ignition on.
You can enable or disable this feature in the
information display.
See Information
Displays (page 105).
REAR SEATS
Folding Down the Second Row 40%
Seat WARNINGS
Use caution when folding the seatback
to the flat back position as the system
will move forward when you lift the release
handle. WARNINGS
Before returning the seatback to its
original position, make sure that cargo
or any objects are not trapped behind the
seatback. After returning the seatback to its
original position, pull on the seatback to
make sure that it has fully latched. An
unlatched seat may become dangerous in
the event of a sudden stop or crash. Make sure that the head restraint is in the
down position and no objects such as books,
purses or briefcases are on the floor in front
of the second row seats before folding them
down.
Move the front passenger seat forward so
that the second row seat head restraint
clears the front seat.
137
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Seats
Page 162 of 419

Automatic Engine Shutdown
For vehicles with a keyless ignition, this
feature automatically shuts down the engine
if it has been idling for an extended period.
The ignition also turns off to save battery
power. Before your vehicle shuts down, a
message appears in the information display
showing a timer counting down. If you do
not intervene within 30 seconds, your vehicle
shuts down. Another message appears in
the information display to inform you that
your vehicle has shut down to save fuel.
Start your vehicle as normal.
Automatic Engine Shutdown Override
Note:
You cannot permanently switch off
the automatic shutdown. When you switch
it off temporarily, it turns on at the next
ignition cycle. You can stop the shutdown, or reset the
timer, at any point before the 30-second
countdown has expired by doing any of the
following:
•
Interacting with your vehicle, for example
pressing the brake or accelerator pedal.
• You can temporarily switch off the
shutdown feature any time the ignition is
on using the information display. See
Information Displays (page 105). The
feature only remains off for the current
ignition cycle.
• During the 30-second countdown, the
system prompts you to press OK or
RESET to temporarily switch the feature
off for the current ignition cycle only.
Stopping the Engine When Your
Vehicle is Stationary
1. Shift into park (P).
2. Press the push button ignition switch.
3. Apply the parking brake.
Note: The ignition, all electrical circuits and
all warning lamps and indicators will be
turned off. Note:
If the engine is idling for 30 minutes,
the ignition and engine automatically shuts
down.
Stopping the Engine When Your
Vehicle is Moving WARNING
Switching off the engine when the
vehicle is still moving will result in a
loss of brake and steering assistance. The
steering will not lock, but higher effort will
be required. When the ignition is switched
off, some electrical circuits, including air
bags, warning lamps and indicators may also
be off. If the ignition was turned off
accidentally, you can shift into neutral (N) and
re-start the engine. 1. Shift into neutral and use the brakes to
bring your vehicle to a safe stop.
2. When your vehicle has stopped, shift into
park (P).
3. Press and hold the push button ignition switch, or press it three times within two
seconds.
159
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Starting and Stopping the Engine
Page 178 of 419
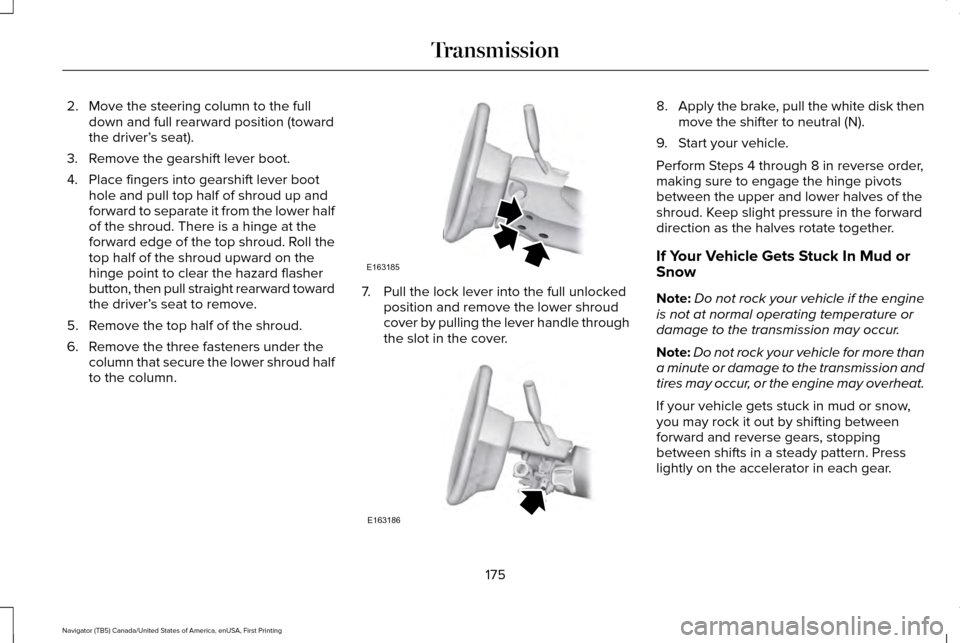
2. Move the steering column to the full
down and full rearward position (toward
the driver’ s seat).
3. Remove the gearshift lever boot.
4. Place fingers into gearshift lever boot hole and pull top half of shroud up and
forward to separate it from the lower half
of the shroud. There is a hinge at the
forward edge of the top shroud. Roll the
top half of the shroud upward on the
hinge point to clear the hazard flasher
button, then pull straight rearward toward
the driver’ s seat to remove.
5. Remove the top half of the shroud.
6. Remove the three fasteners under the column that secure the lower shroud half
to the column. 7. Pull the lock lever into the full unlocked
position and remove the lower shroud
cover by pulling the lever handle through
the slot in the cover. 8.
Apply the brake, pull the white disk then
move the shifter to neutral (N).
9. Start your vehicle.
Perform Steps 4 through 8 in reverse order,
making sure to engage the hinge pivots
between the upper and lower halves of the
shroud. Keep slight pressure in the forward
direction as the halves rotate together.
If Your Vehicle Gets Stuck In Mud or
Snow
Note: Do not rock your vehicle if the engine
is not at normal operating temperature or
damage to the transmission may occur.
Note: Do not rock your vehicle for more than
a minute or damage to the transmission and
tires may occur, or the engine may overheat.
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow,
you may rock it out by shifting between
forward and reverse gears, stopping
between shifts in a steady pattern. Press
lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
175
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing TransmissionE163185 E163186
Page 181 of 419

How Your Vehicle Differs From Other
Vehicles
WARNING
Vehicles with a higher center of gravity
such as utility and four-wheel drive
vehicles handle differently than vehicles with
a lower center of gravity. Utility and
four-wheel drive vehicles are not designed
for cornering at speeds as high as passenger
cars any more than low-slung sports cars are
designed to perform satisfactorily under
off-road conditions. Avoid sharp turns,
excessive speed and abrupt maneuvers in
these vehicles. Failure to drive cautiously
could result in an increased risk of loss of
vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal
injury and death. Truck and utility vehicles can differ from
some other vehicles. Your vehicle may be
higher to allow it to travel over rough terrain
without getting hung up or damaging
underbody components.
The differences that make your vehicle so
versatile also make it handle differently than
an ordinary passenger car. Maintain steering wheel control at all times,
especially in rough terrain. Since sudden
changes in terrain can result in abrupt
steering wheel motion, make sure you grip
the steering wheel from the outside. Do not
grip the spokes.
Drive cautiously to avoid vehicle damage
from concealed objects such as rocks and
stumps.
You should either know the terrain or
examine maps of the area before driving.
Map out your route before driving in the area.
To maintain steering and braking control of
your vehicle, you must have all four wheels
on the ground and they must be rolling, not
sliding or spinning.
Driving Off-Road With Truck and Utility
Vehicles
Note:
On some models, the initial shift from
two-wheel drive to four-wheel drive while
the vehicle is moving can cause some
momentary clunk and ratcheting sounds.
This is the front drivetrain coming up to
speed and the automatic locking hubs
engaging and is not cause for concern. Note:
Your vehicle may be equipped with a
front air dam that can become damaged
(due to reduced ground clearance) when
taking your vehicle off-road. This air dam
can be taken off by removing two bolts.
Four-wheel drive vehicles are specially
equipped for driving on sand, snow, mud and
rough terrain and have operating
characteristics that are somewhat different
from conventional vehicles, both on and off
the road.
Power is supplied to all four wheels through
a transfer case. On Four-wheel drive
vehicles, the transfer case allows you to
select different 4WD modes when necessary.
Information on transfer case operation and
shifting procedures can be found in this
chapter. Information on transfer case
maintenance can be found in the
Maintenance chapter. You should become
thoroughly familiar with this information
before you operate your vehicle.
178
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Four-Wheel Drive (If Equipped)
Page 182 of 419

Four-wheel drive (when you select a 4WD
mode) uses all four wheels to power the
vehicle. This increases traction, enabling you
to drive over terrain and road conditions that
a conventional two-wheel drive vehicle
cannot.
Basic Operating Principles
•
Do not use 4X4 mode on dry, hard
surfaced roads. Doing so will produce
excessive noise, increase tire wear and
may damage drive components. 4X4
mode is only intended for consistently
slippery or loose surfaces.
• Drive slower in strong crosswinds which
can affect the normal steering
characteristics of your vehicle.
• When driving your vehicle on surfaces
made slippery by loose sand, water,
gravel, snow or ice proceed with care. If Your Vehicle leaves the Road
If your vehicle leaves the road, reduce your
vehicle speed and avoid severe braking.
When your vehicle speed has been reduced
ease your vehicle back onto the road. Do
not turn the steering wheel sharply while
returning your vehicle to the road.
It may be safer to stay on the shoulder of the
road and slow down gradually before
returning to the road. You may lose control
if you do not slow down or if you turn the
steering wheel too sharply or abruptly.
It may be less risky to strike small objects,
such as freeway reflectors, with minor
damage to your vehicle rather than attempt
a sudden return to the road which could
cause your vehicle to slide sideways out of
control or roll over. Remember, your safety
and the safety of others should be your
primary concern. If your vehicle gets stuck WARNING
Do not spin the wheels at over 35 mph
(56 km/h). The tires may fail and injure
a passenger or bystander. Note:
Do not rock your vehicle if the engine
is not at normal operating temperature,
damage to the transmission may occur.
Note: Do not rock your vehicle for more than
a minute, damage to the transmission and
tires may occur or the engine may overheat.
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow it
may be rocked out by shifting between
forward and reverse gears, stopping
between shifts, in a steady pattern. Press
lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
Emergency Maneuvers
In an unavoidable emergency situation
where a sudden sharp turn must be made,
remember to avoid over-driving your vehicle
(i.e. turn the steering wheel only as rapidly
and as far as required to avoid the
emergency). Excessive steering can result
179
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Four-Wheel Drive (If Equipped)
Page 183 of 419

in loss of vehicle control. Apply smooth
pressure to the accelerator pedal or brake
pedal when changes in vehicle speed are
required. Avoid abrupt steering, acceleration
and braking. This could result in an increased
risk of vehicle roll over, loss of vehicle control
and personal injury. Use all available road
surface to bring your vehicle to a safe
direction of travel.
In the event of an emergency stop, avoid
skidding the tires and do not attempt any
sharp steering wheel movements.
If your vehicle goes from one type of surface
to another (i.e. from concrete to gravel) there
will be a change in the way your vehicle
responds to a maneuver (i.e. steering,
acceleration or braking).
Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four
wheels on the most solid area of the trail.
Avoid reducing the tire pressures but shift
to a lower gear and drive steadily through
the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly and
avoid excessive wheel slip.
Avoid driving at excessive speeds, this
causes vehicle momentum to work against
you and your vehicle could become stuck to
the point that assistance may be required
from another vehicle. Remember, you may
be able to back out the way you came if you
proceed with caution.
Mud and Water
Note:
Driving through deep water may
damage the vehicle.
If you must drive through high water, drive
slowly. Traction or brake capability may be
limited.
When driving through water, determine the
depth and avoid water higher than the
bottom of the hubs. If the ignition system
gets wet, your vehicle may stall.
Once through water, always try the brakes.
Wet brakes do not stop your vehicle as
effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be
improved by applying light pressure to the
brake pedal while moving slowly. Be cautious of sudden changes in vehicle
speed or direction when you are driving in
mud. Even 4WD vehicles can lose traction in
slick mud. As when you are driving over
sand, apply the accelerator slowly and avoid
spinning your wheels. If the vehicle does
slide, steer in the direction of the slide until
you regain control of the vehicle.
If the transmission, transfer case or front axle
are submerged in water, their fluids should
be checked and changed, if necessary.
If the front or rear axle is submerged in water,
the axle lubricant should be replaced.
After driving through mud, clean off residue
stuck to rotating driveshafts and tires. Excess
mud stuck on tires and rotating driveshafts
causes an imbalance that could damage
drive components.
180
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Four-Wheel Drive (If Equipped)E143950
Page 184 of 419

“Tread Lightly” is an educational program
designed to increase public awareness of
land-use regulations and responsibilities in
our nations wilderness areas. Ford Motor
Company joins the U.S. Forest Service and
the Bureau of Land Management in
encouraging you to help preserve our
national forest and other public and private
lands by “treading lightly”
.
Driving on Hilly or Sloping Terrain
Note: Avoid driving crosswise or turning on
steep slopes or hills.
Note: Avoid turning on steep slopes or hills.
A danger lies in losing traction, slipping
sideways and possible vehicle roll over.
Whenever driving on a hill, determine
beforehand the route you will use. Do not
drive over the crest of a hill without seeing
what conditions are on the other side. Do
not drive in reverse over a hill without the
aid of an observer.
Although natural obstacles may make it
necessary to travel diagonally up or down a
hill or steep incline, you should always try to
drive straight up or straight down. When climbing a steep slope or hill, start in
a lower gear rather than downshifting to a
lower gear from a higher gear once the
ascent has started. This reduces strain on
the engine and the possibility of stalling.
If your vehicle stalls, do not try to turn around
because this could cause vehicle roll over.
It is better to reverse back to a safe location.
Apply just enough power to the wheels to
climb the hill. Too much power will cause the
tires to slip, spin or lose traction, resulting in
loss of vehicle control. Descend a hill in the same gear you would
use to climb up the hill to avoid excessive
brake application and brake overheating. Do
not descend in neutral. Disengage overdrive
or move the transmission selector lever to a
lower gear. When descending a steep hill,
avoid sudden hard braking as you could lose
control. The front wheels have to be turning
in order to steer your vehicle.
If your vehicle has anti-lock brakes, apply the
brakes steadily. Do not pump the brakes.
Driving on Snow and Ice
WARNING
If you are driving in slippery conditions
that require tire chains or cables, then
it is critical that you drive cautiously. Keep
speeds down, allow for longer stopping
distances and avoid aggressive steering to
reduce the chances of a loss of vehicle
control which can lead to serious injury or
death. If the rear end of your vehicle slides
while cornering, steer in the direction of the
slide until you regain control of your vehicle. 181
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Four-Wheel Drive (If Equipped)E143949
Page 185 of 419

Note:
Excessive tire slippage can cause
transmission damage.
Four-wheel drive vehicles have advantages
over two-wheel drive vehicles in snow and
ice but can skid like any other vehicle.
Should you start to slide while driving on
snowy or icy roads, turn the steering wheel
in the direction of the slide until you regain
control.
Avoid sudden applications of power and
quick changes of direction on snow and ice.
Apply the accelerator slowly and steadily
when starting from a full stop.
Avoid sudden braking. Although a four-wheel
drive vehicle may accelerate better than a
two-wheel drive vehicle in snow and ice, it
will not stop any faster as braking occurs at
all four wheels. Do not become
overconfident as to road conditions.
Make sure you allow sufficient distance
between you and other vehicles for stopping.
Drive slower than usual and consider using
one of the lower gears. In emergency
stopping situations, apply the brake steadily.
Do not pump the brake pedal. See Hints on
Driving With Anti-Lock Brakes (page 184). Maintenance and Modifications
The suspension and steering systems on
your vehicle have been designed and tested
to provide predictable performance whether
loaded or empty. For this reason, we strongly
recommend that you do not make
modifications such as adding or removing
parts (i.e. lift kits or stabilizer bars) or by using
replacement parts not equivalent to the
original factory equipment.
We recommend that you use caution when
your vehicle has either a high load or device
(i.e. ladder or luggage racks). Any
modifications to your vehicle that raise the
center of gravity may cause your vehicle to
roll over when there is a loss of vehicle
control.
Failure to maintain your vehicle correctly may
void the warranty, increase your repair cost,
reduce vehicle performance and operational
capabilities and adversely affect you and
your passenger's safety. We recommend you
frequently inspect your vehicle's chassis
components when your vehicle is subject to
off road usage.
182
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Four-Wheel Drive
(If Equipped)
Page 187 of 419

GENERAL INFORMATION
Note:
Occasional brake noise is normal. If a
metal-to-metal, continuous grinding or
continuous squeal sound is present, the
brake linings may be worn-out and an
authorized dealer should check them. If the
vehicle has continuous vibration or shudder
in the steering wheel while braking, an
authorized dealer should check your vehicle.
Note: Brake dust may accumulate on the
wheels, even under normal driving
conditions. Some dust is inevitable as the
brakes wear and does not contribute to
brake noise. See Cleaning the Alloy Wheels
(page 292). See
Warning Lamps and
Indicators (page 101).
Wet brakes result in reduced braking
efficiency. Gently press the brake pedal a
few times when driving from a car wash or
standing water to dry the brakes. Brake Over Accelerator
In the event the accelerator pedal becomes
stuck or entrapped, apply steady and firm
pressure to the brake pedal to slow the
vehicle and reduce engine power. If you
experience this condition, apply the brakes
and bring your vehicle to a safe stop. Switch
the engine off, move the transmission to park
(P) and apply the parking brake. Inspect the
accelerator pedal and the area around it for
any items or debris that may be obstructing
its movement. If none are found and the
condition persists, have your vehicle towed
to the nearest authorized dealer.
Emergency Brake Assist
Emergency brake assist detects when you
brake heavily by measuring the rate at which
you press the brake pedal. It provides
maximum braking efficiency as long as you
press the pedal. Emergency brake assist can
reduce stopping distances in critical
situations.Anti-lock Brake System
This system helps you maintain steering
control during emergency stops by keeping
the brakes from locking. This lamp momentarily illuminates
when you switch the ignition on. If
the light does not illuminate during
start up, remains on or flashes, the anti-lock
braking system may be disabled. Have the
system checked by an authorized dealer. If
the anti-lock brake system is disabled,
normal braking is still effective. If the brake warning lamp
illuminates with the parking brake
released, have your brake system
serviced immediately.
HINTS ON DRIVING WITH ANTI-
LOCK BRAKES
Note: When the system is operating, the
brake pedal will pulse and may travel further.
Maintain pressure on the brake pedal. You
may also hear a noise from the system. This
is normal.
184
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing BrakesE138644 E138644
Page 192 of 419

PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
WARNINGS
Vehicle modifications involving braking
system, aftermarket roof racks,
suspension, steering system, tire
construction and wheel and tire size may
change the handling characteristics of your
vehicle and may adversely affect the
performance of the electronic stability control
system. In addition, installing any stereo
loudspeakers may interfere with and
adversely affect the electronic stability
control system. Install any aftermarket stereo
loudspeaker as far as possible from the front
center console, the tunnel, and the front
seats in order to minimize the risk of
interfering with the electronic stability control
sensors. Reducing the effectiveness of the
electronic stability control system could lead
to an increased risk of loss of vehicle control,
vehicle rollover, personal injury and death. WARNINGS
Remember that even advanced
technology cannot defy the laws of
physics. It’ s always possible to lose control
of a vehicle due to inappropriate driver input
for the conditions. Aggressive driving on any
road condition can cause you to lose control
of your vehicle increasing the risk of personal
injury or property damage. Activation of the
electronic stability control system is an
indication that at least some of the tires have
exceeded their ability to grip the road; this
could reduce the operator’ s ability to control
the vehicle potentially resulting in a loss of
vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal
injury and death. If your electronic stability
control system activates, SLOW DOWN. The system automatically turns on each time
you switch the ignition on.
If a driving condition activates either the
stability control or the traction control system
you may experience the following conditions:
•
The stability and traction control light
flashes.
• Your vehicle slows down. •
Reduced engine power.
• A vibration in the brake pedal.
• The brake pedal is stiffer than usual.
• If the driving condition is severe and your
foot is not on the brake, the brake pedal
may move as the systems applies higher
brake forces.
The stability control system has several
features built into it to help you maintain
control of your vehicle:
Electronic Stability Control
The system enhances your vehicle ’s ability
to prevent skids or lateral slides by applying
brakes to one or more of the wheels
individually and, if necessary, reducing
engine power.
Roll Stability Control
The system enhances your vehicle ’s ability
to prevent rollovers by detecting your
vehicle ’s roll motion and the rate at which it
changes by applying the brakes to one or
more wheels individually.
189
Navigator (TB5) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Stability Control