compression ratio MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 25 of 909

OUTLINE
B1–3
B1
SPECIFICATIONSA6E220202000204
End Of Sie
ItemSpecification
New
Mazda6
(GG, GY)Current
Mazda6
(GG)New
Mazda6
(GG, GY)Current
Mazda6
(GG)New
Mazda6
(GG, GY)Current
Mazda6
(GG)
L8 LF L3
Type Gasoline, 4-cycle
Cylinder arrangement and number In-line, 4-cylinder
Combustion chamber Pentroof
Valve systemDOHC,
Timing chain driven, 16 valves
Displacement (ml {cc, cu in})1,798
{1,798, 109.7}1,999
{1,999, 121.9}2,261
{2,261, 137.9}
Bore × stroke (mm {in})83.0 × 83.1
{3.27 ×3.27}87.5 × 83.1
{3.44 ×3.27}87.5 × 94.0
{3.44 × 3.70}
Compression ratio 10.8:1 10.6:1
Compression pressure(kPa {kgf/cm
2,
psi}) [rpm]1,750
{17.85, 253.8}
[300]1,720
{17.54, 249.5}
[300]1,430
{14.58, 207.4}
[290]
Valve timingINOpenBTDC
(°)40—25
CloseABDC
(°)33 52 62—37
EXOpenBBDC
(°)37 42
CloseATDC
(°)45
Valve
clearance
[engine cold](mm {in})IN 0.22—0.28 {0.0087—0.0110} (0.25±0.03 {0.0098±0.0011})
EX 0.27—0.33 {0.0106 —0.0130} (0.30±0.03 {0.0118±0.0011})
Page 33 of 909

B2–2
OUTLINE
OUTLINE OF CONSTRUCTIONA6E230202000201•MZR-CD (RF Turbo) engine is newly adopted as Mazda6 (GG, GY).
•The construction of MZR-CD (RF Turbo) engine and operation which were newly adopted for the Mazda6 (GG,
GY) are the same as the current Mazda MPV(LW) MZR-CD (RF Turbo) engine model and current Mazda 323
(BJ) RF Turbo engine model except for the following components. (See Mazda MPV Workshop Manual
Supplement 1737-1*-02C.), (See Mazda 323 Workshop Manual Supplement 1633-10-98G.)
—Engine mount
•The construction and the operation of the engine mount for the new Mazda6 (GG, GY) MZR-CD (RF Turbo)
engine model is the same as the current Mazda6 (GG). (See Mazda6 Training Manual 3359-1*-02C)
End Of Sie
FEATURESA6E230202000202Improved engine performance
•Coated pistons have been adopted.
Reduced engine noise and vibration
•An aluminium alloy oil pan upper block has been adopted.
•An eight counter weight crankshaft has been adopted.
•A crankshaft pulley cover has been adopted.
•An engine cover with insulator has been adopted.
•A pendulum type engine mount has been adopted.
Improved serviceability
•A serpentine type drive belt has been adopted.
•An auto tensioner that automatically adjusts the drive belt tension has been adopted.
Improved design
•An engine cover has been adopted.
End Of Sie
SPECIFICATIONSA6E230202000203
End Of Sie
OUTLINE
ItemSpecifications
New Mazda6 (GG, GY) Current Mazda MPV (LW)
MZR-CD (RF Turbo) MZR-CD (RF Turbo)
TypeDiesel, 4-cycle
Cylinder arrangement and number In-line, 4-cylinder
Combustion chamber Direct injection
Valve system SOHC, belt-driven, 16-valve
Displacement (ml {cc, cu in}) 1,998 {1.998, 122.9}
Bore × stroke (mm {in}) 86.0 × 86.0 {3.39 × 3.39}
Compression ratio 18.4
Compression pressure
(kPa {kgf/cm
2, psi} [rpm])3,500 {35.7, 507.7} [250]
Valve timingINOpen BTDC (°)6
Close ABDC (°)30
EXOpen BBDC (°)41
Close ATDC (°)8
Valve clearance
[engine cold]IN (mm {in}) 0.12 —0.18 {0.005—0.007} (0.15±0.03 {0.006±0.0011})
EX (mm {in}) 0.32—0.38 {0.013—0.014} (0.35±0.03 {0.014±0.0011})
Page 146 of 909
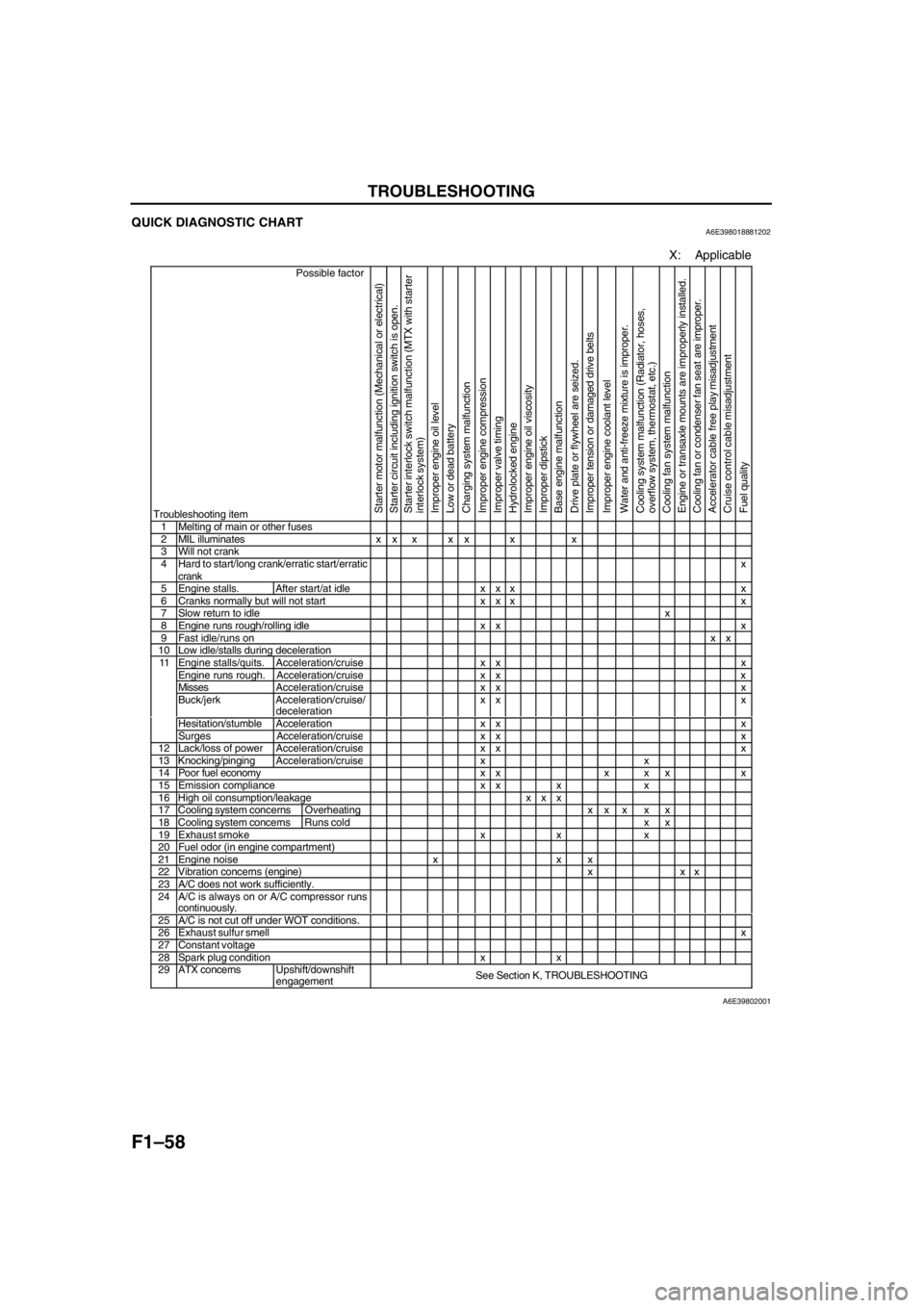
F1–58
TROUBLESHOOTING
QUICK DIAGNOSTIC CHARTA6E398018881202
X: Applicable
Possible factor
Troubleshooting item
Starter motor malfunction (Mechanical or electrical)
Starter circuit including ignition switch is open.
Starter interlock switch malfunction (MTX with starter
interlock system)
Improper engine oil level
Low or dead battery
Charging system malfunction
Improper engine compression
Improper valve timing
Hydrolocked engine
Improper engine oil viscosity
Improper dipstick
Base engine malfunction
Drive plate or flywheel are seized.
Improper tension or damaged drive belts
Improper engine coolant level
Water and anti-freeze mixture is improper.
Cooling system malfunction (Radiator, hoses,
overflow system, thermostat, etc.)
Cooling fan system malfunction
Engine or transaxle mounts are improperly installed.
Cooling fan or condenser fan seat are improper.
Accelerator cable free play misadjustment
Cruise control cable misadjustment
Fuel quality
1 Melting of main or other fuses2 MIL illuminates x x x x x x x3 Will not crank4 Hard to start/long crank/erratic start/erratic
crankx
5 Engine stalls. After start/at idle x x x x6 Cranks normally but will not start x x x x7 Slow return to idlex8 Engine runs rough/rolling idle x x x9 Fast idle/runs onxx10 Low idle/stalls during decelerationEngine stalls/quits. Acceleration/cruise x x xEngine runs rough. Acceleration/cruise x x xMissesAcceleration/cruise x x xBuck/jerk Acceleration/cruise/
decelerationxx x
Hesitation/stumble Acceleration x x x
11
Surges Acceleration/cruis
exx x12 Lack/loss of powerAcceleration/cruisexx x13 Knocking/pingingAcceleration/cruisexx14 Poor fuel economy x x x x x x15 Emission compliance x x x x16 High oil consumption/leakage x x x17 Cooling system concerns Overheatingxx x x x18 Cooling system concernsRuns cold x x19 Exhaust smoke x x x20 Fuel odor (in engine compartment)21 Engine noise x x x22 Vibration concerns (engine) x x x23 A/C does not work sufficiently.24 A/C is always on or A/C compressor runs
continuously.
25 A/C is not cut off under WOT conditions.26 Exhaust sulfur smellx27 Constant voltage28 Spark plug condition x x29 ATX concernsUpshift/downshift
engagementSee Section K, TROUBLESHOOTING
A6E39802001
Page 150 of 909

F1–62
TROUBLESHOOTING
NO.14 POOR FUEL ECONOMYA6E398018881203
Diagnostic procedure
14 POOR FUEL ECONOMY
DESCRIPTIONFuel economy is unsatisfactory.
POSSIBLE CAUSE•Contaminated air cleaner element
•VIS malfunction (if equipped)
•Engine cooling system malfunction
•Improper ATF level (ATX)
•Weak spark
•Poor fuel quality
•Erratic or no signal from CMP sensor
•Clutch slippage (MTX)
•VTCS malfunction
•Improper variable valve timing control system operation (if equipped)
•Improper coolant level
•Inadequate fuel pressure
•Spark plug malfunction
•PCV valve malfunction
•Brake dragging
•Improper valve timing due to jumping out of timing belt
•Contaminated MAF sensor
•Improper engine compression
•Exhaust system clogging
•Improper electrically controlled 4WD system operation
Warning
The following troubleshooting flow chart contains fuel system diagnosis and repair
procedures. Read following warnings before performing fuel system services:
•Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always
keep sparks and flames away from fuel.
•Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injuries or
death and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete
“BEFORE REPAIR PROCEDURE” and “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE” described in this
manual.
Caution
•Disconnecting/connecting quick release connector without cleaning it may possibly cause
damage to fuel pipe and quick release connector. Always clean quick release connector
joint area before disconnecting/connecting, and make sure that it is free of foreign material.
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1 Inspect for following:
•Air cleaner element for contamination
•ATF level
•Fuel quality
•Coolant level
•Brake dragging
•Clutch slippage
Are all items okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Service as necessary.
Repeat Step 1.
2 Connect WDS or equivalent to DLC-2.
Retrieve any continuous memory, KOEO and
KOER DTCs.
Are there any DTCs displayed?YesDTC is displayed:
Go to appropriate DTC test.
NoNo DTC is displayed:
Go to next step.
3 Access ECT PID.
Drive vehicle while monitoring PID.
(See F1–33 PCM INSPECTION (4WD).)
Is PID within specification?Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for coolant leakage, cooling fan and condenser
fan operations or thermostat operation.
Page 151 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F1–63
F1
End Of Sie
4 Is strong blue spark visible at each disconnected
high-tension lead while cranking engine?Yes Inspect for following:
•Spark plugs malfunction
•CMP sensor is improperly installed.
•Trigger wheel damage on camshaft
•Open or short circuit on CMP sensor
•Open or short circuit between CMP sensor and
PCM terminal 2J or 2M
Repair or replace malfunctioning parts.
If okay, go to next step.
No Inspect following:
•High-tension leads
•Ignition coil and connector
5 Install fuel pressure gauge between fuel pipe
and fuel distributor.
Start engine and run it at idle.
Measure fuel line pressure at idle.
Is fuel line pressure correct at idle?Yes Go to next step.
NoZero or low:
Inspect for clogged fuel line.
If okay, replace fuel pump unit
High:
Replace fuel pump unit.
6 Inspect for VTCS operation.
Does VTCS work properly?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning parts.
7Note
•The following test should be performed for
vehicles with variable valve timing control
system. Go to next step for vehicles
without variable valve timing control
system.
Inspect for variable valve timing control system
operation.
Does variable valve timing control system work
properly?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning parts.
8Note
•The following test should be performed for
vehicles with VIS. Go to next step for
vehicles without VIS.
Inspect for VIS operation.
Does VIS work properly?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning parts.
9 Remove and shake PCV valve.
Does PCV valve rattle?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace PCV valve.
10 Inspect for restriction in the exhaust system.
Is there any restriction?Yes Inspect exhaust system.
No Go to next step.
11 Inspect for contaminated MAF sensor.
Is there any contamination?Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for cause.
12 Inspect MAF sensor for contamination.
Is there any contamination?Yes Replace MAF sensor.
No Go to Step 14. (2WD)
Go to next step. (4WD)
13 Inspect electrically controlled 4WD system
operation.
Is operation of electrically controlled 4WD
system okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning parts.
14 Is engine compression correct? Yes Inspect valve timing.
No Inspect for cause.
15 Verify test results.
•If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
•If malfunction remains, replace PCM. STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
Page 319 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–167
F2
SYMPTOM QUICK DIAGNOSIS CHARTA6E408018881202
×: Applicable
Troubleshooting item
1 Melting of main or other fuses
2 MIL illuminates
3 Will not crank×× ×× × ×
4 Hard start/long crank/erratic start/erratic crank×× ×
5 Engine stalls After start/at idle××
6 Cranks normally but will not start××
7 Slow return to idle
8 Engine runs rough/rolling idle××
9 Fast idle/runs on
10 Low idle/stalls during deceleration××
11Engine stalls/quits Acceleration/cruise××
Engine runs rough Acceleration/cruise××
Misses Acceleration/cruise××
Buck/jerk Acceleration/cruise/ deceleration××
Hesitation/stumble Acceleration××
Surges Acceleration/cruise××
12 Lack/loss of power Acceleration/cruise××
13 Knocking/pinging××
14 Poor fuel economy××
15 Emissions compliance×× ×
16 High oil consumption/leakage××××
17 Cooling system concerns Overheating××
18 Cooling system concerns Runs cold
19 Excessive black smoke×
20 Fuel odor (in engine compartment)
21 Engine noise×× × ×
22 Vibration concerns (engine)×
23 A/C does not work sufficiently
24 A/C always on or A/C compressor runs continuously
25 A/C does not cut off under wide open throttle conditions
26 Constant voltage
Starter motor malfunction (Mechanical or electrical)Starter circuit including engine switch is openImproper engine oil levelLow or dead bateryCharging system malfunctionLow engine compressionImproper valve timingHydrolocked egineImproper engine oil viscosityImproper dipstickBase engine malfunctionSeized flywheelImproper tension or damaged drivebelts
Page 329 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–177
F2
4 Does engine start normally after warm-up? Yes Inspect glow system operation.
(See T–19 RELAY INSPECTION)
Replace any malfunctioning part as necessary.
If glow system is okay, go to next step.
No Go to next step.
5 Is there any restriction in exhaust system or
catalyst converter?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
6 Inspect for fuel leakage from fuel pipe.
Is any fuel leakage found on fuel pipe?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
7 Inspect adjustment of accelerator position
sensor and idle switch.
(See F2–72 ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)
(See F2–70 IDLE SWITCH INSPECTION)
Are accelerator position sensor and idle switch
adjusted correctly?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust accelerator position sensor and idle switch
correctly.
(See F2–73 ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
ADJUSTMENT)
(See F2–71 IDLE SWITCH ADJUSTMENT)
8 Visually inspect CKP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CKP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
9 Measure gap between CKP sensor and teeth of
pulse wheel.
Specification
1.5—2.5 mm {0.059—0.098 in}
Is gap within specification?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust CKP sensor position.
10 Visually inspect CMP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CMP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Inspect following PIDs:
(See F2–65 PCM INSPECTION)
•ECT
•IAT
•MAF
•RPM
If PID value is not as specified, repair or replace
malfunctioning parts.
If PID value is okay, go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
11 Inspect fuel pressure sensor.
(See F2–79 FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
INSPECTION)
Is fuel pressure okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace common rail.
12 Inspect suction control valve.
(See F2–54 SUCTION CONTROL VALVE
INSPECTION)
Is suction control valve okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair supply pump.
(See F2–54 SUPPLY PUMP INSPECTION)
13 Is engine compression correct?
(See B2–8 COMPRESSION INSPECTION)Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for following:
•Damaged valve seat
•Worn valve stem and valve guide
•Worn or stuck piston ring
•Worn piston, piston ring or cylinder
Service as necessary.
14 Inspect fuel injector.
(See F2–56 FUEL INJECTOR INSPECTION)
Is fuel injector okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
15 Inspect EGR system operation.
Is EGR system operation normal?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning part according to
EGR system operation results.
16 Inspect IDM.
(See F2–84 INJECTOR DRIVER MODULE
(IDM) INSPECTION)
Is IDM okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
17 Inspect starting system.
Is starting system normal?Yes Inspect for loose connectors or poor terminal contact.
If okay, remove and inspect supply pump and common
rail.
No Repair or replace components as required. STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
Page 330 of 909

F2–178
TROUBLESHOOTING
End Of Sie
NO.5 ENGINE STALLS-AFTER START/AT IDLEA6E408018881207
Diagnostic Procedure
18 Verify test results.
•If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
•If malfunction remains, replace PCM. (See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION) STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
5 ENGINE STALLS-AFTER START/AT IDLE
DESCRIPTION•Engine stops unexpectedly.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Poor fuel quality
•Intake-air system restriction or clogging
•Engine overheating
•A/C system improper operation
•Immobilizer system (PATS) and/or circuit malfunction (if equipped)
•PCM control relay malfunction
•Glow system malfunction
•Inadequate fuel pressure
•Fuel pressure sensor related circuit malfunction
•Suction control valve malfunction (built-in supply pump)
•Fuel pressure limiter malfunction (built-in common rail)
•Fuel leakage
•Fuel line clogging or restriction
•Fuel filter clogging or restriction
•Incorrect fuel injection timing
•Erratic signal from CKP sensor
•Erratic signal from CMP sensor
•Supply pump malfunction
•Fuel injector malfunction
•Low engine compression
•Improper valve timing
•Exhaust system and/or catalyst converter restriction or clogging
•EGR system malfunction
•ECT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Accelerator positions sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Accelerator positions sensor misadjustment
•MAF/IAT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•V-reference voltage supply circuit malfunction
•IDM or related circuit malfunction
Warning
The following troubleshooting flow chart contains the fuel system diagnosis and repair
procedures. Read the following warnings before performing the fuel system services:
•Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep
sparks and flames away from fuel.
•Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injury or death
and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete “BEFORE
REPAIR PROCEDURE” and “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE” described in this manual.
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1Note
•The following test should be perform for
vehicles with immobilizer system. Go to
Step 10 for vehicles without immobilizer
system.
Connect WDS or equivalent to DLC-2.
Do following conditions appear?
•Engine is not completely started.
•DTC B1681 is displayed.YesBoth conditions appear:
Go to Step 4.
NoEither or other condition appears:
Go to next step.
2 Is coil connector securely connected to coil? Yes Go to next step.
No Connect coil connector securely.
Return to Step 1.
3 Does security light illuminate? Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect instrument cluster and wiring harness.
Page 332 of 909

F2–180
TROUBLESHOOTING
15 Is there any restriction in exhaust system or
catalyst converter?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
16 Access RPM PID.
Is RPM PID indicating engine speed during
cranking engine?Yes Go to next step.
No Go to Step 19.
17Note
•The following test should be performed on
the vehicles with A/C system. If the
following test cannot be performed due to
engine stalling, go to next step.
•Go to next step for the vehicle without A/C
system.
Connect pressure gauge to A/C line.
Turn blower and A/C switches on.
Is pressure within specifications?Yes Go to next step.
NoA/C is always on:
Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.24 A/C ALWAYS
ON OR A/C COMPRESSOR RUNS
CONTINUOUSLY”.
Other symptoms:
Inspect following:
•Refrigerant charging amount
•Cooling fan No.1 and/or cooling fan No.2 operation
18 Inspect adjustment of accelerator position
sensor and idle switch.
(See F2–72 ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)
(See F2–70 IDLE SWITCH INSPECTION)
Are accelerator position sensor and idle switch
adjusted correctly?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust accelerator position sensor and idle switch
correctly.
(See F2–73 ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
ADJUSTMENT)
(See F2–71 IDLE SWITCH ADJUSTMENT)
19 Depress accelerator pedal slightly.
Crank engine.
Does engine start now?Yes Inspect idle speed.
(See F2–34 IDLE SPEED INSPECTION)
No Go to next step.
20 Inspect for fuel leakage from fuel pipe.
Is any fuel leakage found on fuel pipe?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
21 Visually inspect CKP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CKP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
22 Measure gap between CKP sensor and teeth of
pulse wheel.
Specification
1.5—2.5 mm {0.059—0.098 in}
Is gap within specification?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust CKP sensor position.
23 Visually inspect CMP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CMP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Inspect following PIDs:
(See F2–65 PCM INSPECTION)
•ECT
•IAT
•MAF
•RPM
If PID value is not as specified, repair or replace
malfunctioning parts.
If PID value is okay, go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
24 Inspect fuel pressure sensor.
(See F2–79 FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
INSPECTION)
Is fuel pressure okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace common rail.
25 Inspect suction control valve.
(See F2–54 SUCTION CONTROL VALVE
INSPECTION)
Is suction control valve okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair supply pump.
(See F2–54 SUPPLY PUMP INSPECTION)
26 Is engine compression correct?
(See B2–8 COMPRESSION INSPECTION)Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for following:
•Damaged valve seat
•Worn valve stem and valve guide
•Worn or stuck piston ring
•Worn piston, piston ring or cylinder
•Improper valve timing
Service as necessary.
27 Inspect fuel injector.
(See F2–56 FUEL INJECTOR INSPECTION)
Is fuel injector okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary. STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
Page 333 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–181
F2
End Of Sie
NO.6 CRANKS NORMALLY BUT WILL NOT STARTA6E408018881208
Diagnostic Procedure
28 Inspect IDM.
(See F2–84 INJECTOR DRIVER MODULE
(IDM) INSPECTION)
Is IDM okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
29 Inspect EGR system operation.
Is EGR system operation normal?Yes Remove and inspect supply pump and common rail.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning part according to
EGR system operation results.
30 Verify test results.
•If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
•If malfunction remains, replace PCM. (See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION) STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
6 CRANKS NORMALLY BUT WILL NOT START
DESCRIPTION•Starter cranks engine at normal speed but engine will not run.
•Refer to symptom troubleshooting “No.5 Engine stalls” if this symptom appears after engine stall.
•Fuel is in fuel tank.
•Battery is in normal condition.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Poor fuel quality
•Intake-air system restriction
•Fuel line restriction
•EGR system malfunction
•Glow system malfunction
•Fuel pressure sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Suction control valve malfunction (built-in supply pump)
•Fuel pressure limiter malfunction (built-in common rail)
•Fuel leakage
•Fuel filter clogging
•Incorrect fuel injection timing
•Erratic signal from CKP sensor
•Erratic signal from CMP sensor
•V-reference supply circuit malfunction
•ECT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Supply pump malfunction
•Fuel injector malfunction
•Immobilizer system (PATS) and/or circuit malfunction (if equipped)
•Low engine compression
•Improper valve timing
•IDM or related circuit malfunction
•PCM control repay malfunction
Warning
The following troubleshooting flow chart contains the fuel system diagnosis and repair
procedures. Read the following warnings before performing the fuel system services:
•Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep
sparks and flames away from fuel.
•Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injury or death
and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete “BEFORE
REPAIR PROCEDURE” and “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE” described in this manual.
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1Note
•The following test should be perform for
vehicles with immobilizer system. Go to
Step 10 for vehicles without immobilizer
system.
Connect WDS or equivalent to DLC-2.
Do following conditions appear?
•Engine is not completely started.
•DTC B1681 is displayed.YesBoth conditions appear:
Go to Step 4.
NoEither or other condition appears:
Go to next step.
2 Is coil connector securely connected to coil? Yes Go to next step.
No Connect coil connector securely.
Return to Step 1.