seat adjustment MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 146 of 909
F1–58
TROUBLESHOOTING
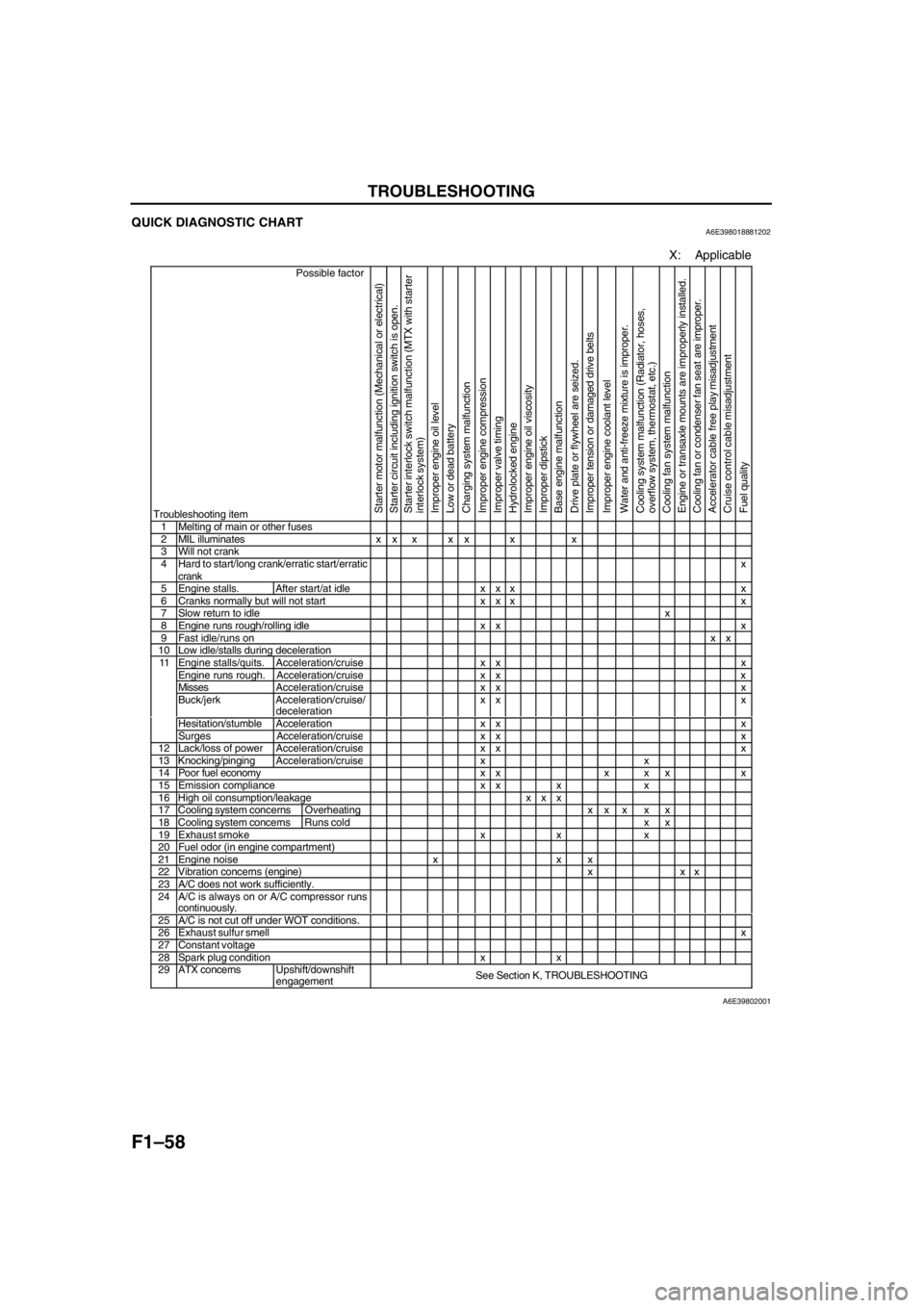
QUICK DIAGNOSTIC CHARTA6E398018881202
X: Applicable
Possible factor
Troubleshooting item
Starter motor malfunction (Mechanical or electrical)
Starter circuit including ignition switch is open.
Starter interlock switch malfunction (MTX with starter
interlock system)
Improper engine oil level
Low or dead battery
Charging system malfunction
Improper engine compression
Improper valve timing
Hydrolocked engine
Improper engine oil viscosity
Improper dipstick
Base engine malfunction
Drive plate or flywheel are seized.
Improper tension or damaged drive belts
Improper engine coolant level
Water and anti-freeze mixture is improper.
Cooling system malfunction (Radiator, hoses,
overflow system, thermostat, etc.)
Cooling fan system malfunction
Engine or transaxle mounts are improperly installed.
Cooling fan or condenser fan seat are improper.
Accelerator cable free play misadjustment
Cruise control cable misadjustment
Fuel quality
1 Melting of main or other fuses2 MIL illuminates x x x x x x x3 Will not crank4 Hard to start/long crank/erratic start/erratic
crankx
5 Engine stalls. After start/at idle x x x x6 Cranks normally but will not start x x x x7 Slow return to idlex8 Engine runs rough/rolling idle x x x9 Fast idle/runs onxx10 Low idle/stalls during decelerationEngine stalls/quits. Acceleration/cruise x x xEngine runs rough. Acceleration/cruise x x xMissesAcceleration/cruise x x xBuck/jerk Acceleration/cruise/
decelerationxx x
Hesitation/stumble Acceleration x x x
11
Surges Acceleration/cruis
exx x12 Lack/loss of powerAcceleration/cruisexx x13 Knocking/pingingAcceleration/cruisexx14 Poor fuel economy x x x x x x15 Emission compliance x x x x16 High oil consumption/leakage x x x17 Cooling system concerns Overheatingxx x x x18 Cooling system concernsRuns cold x x19 Exhaust smoke x x x20 Fuel odor (in engine compartment)21 Engine noise x x x22 Vibration concerns (engine) x x x23 A/C does not work sufficiently.24 A/C is always on or A/C compressor runs
continuously.
25 A/C is not cut off under WOT conditions.26 Exhaust sulfur smellx27 Constant voltage28 Spark plug condition x x29 ATX concernsUpshift/downshift
engagementSee Section K, TROUBLESHOOTING
A6E39802001
Page 329 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–177
F2
4 Does engine start normally after warm-up? Yes Inspect glow system operation.
(See T–19 RELAY INSPECTION)
Replace any malfunctioning part as necessary.
If glow system is okay, go to next step.
No Go to next step.
5 Is there any restriction in exhaust system or
catalyst converter?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
6 Inspect for fuel leakage from fuel pipe.
Is any fuel leakage found on fuel pipe?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
7 Inspect adjustment of accelerator position
sensor and idle switch.
(See F2–72 ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)
(See F2–70 IDLE SWITCH INSPECTION)
Are accelerator position sensor and idle switch
adjusted correctly?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust accelerator position sensor and idle switch
correctly.
(See F2–73 ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
ADJUSTMENT)
(See F2–71 IDLE SWITCH ADJUSTMENT)
8 Visually inspect CKP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CKP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
9 Measure gap between CKP sensor and teeth of
pulse wheel.
Specification
1.5—2.5 mm {0.059—0.098 in}
Is gap within specification?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust CKP sensor position.
10 Visually inspect CMP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CMP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Inspect following PIDs:
(See F2–65 PCM INSPECTION)
•ECT
•IAT
•MAF
•RPM
If PID value is not as specified, repair or replace
malfunctioning parts.
If PID value is okay, go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
11 Inspect fuel pressure sensor.
(See F2–79 FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
INSPECTION)
Is fuel pressure okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace common rail.
12 Inspect suction control valve.
(See F2–54 SUCTION CONTROL VALVE
INSPECTION)
Is suction control valve okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair supply pump.
(See F2–54 SUPPLY PUMP INSPECTION)
13 Is engine compression correct?
(See B2–8 COMPRESSION INSPECTION)Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for following:
•Damaged valve seat
•Worn valve stem and valve guide
•Worn or stuck piston ring
•Worn piston, piston ring or cylinder
Service as necessary.
14 Inspect fuel injector.
(See F2–56 FUEL INJECTOR INSPECTION)
Is fuel injector okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
15 Inspect EGR system operation.
Is EGR system operation normal?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning part according to
EGR system operation results.
16 Inspect IDM.
(See F2–84 INJECTOR DRIVER MODULE
(IDM) INSPECTION)
Is IDM okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
17 Inspect starting system.
Is starting system normal?Yes Inspect for loose connectors or poor terminal contact.
If okay, remove and inspect supply pump and common
rail.
No Repair or replace components as required. STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
Page 332 of 909

F2–180
TROUBLESHOOTING
15 Is there any restriction in exhaust system or
catalyst converter?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
16 Access RPM PID.
Is RPM PID indicating engine speed during
cranking engine?Yes Go to next step.
No Go to Step 19.
17Note
•The following test should be performed on
the vehicles with A/C system. If the
following test cannot be performed due to
engine stalling, go to next step.
•Go to next step for the vehicle without A/C
system.
Connect pressure gauge to A/C line.
Turn blower and A/C switches on.
Is pressure within specifications?Yes Go to next step.
NoA/C is always on:
Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.24 A/C ALWAYS
ON OR A/C COMPRESSOR RUNS
CONTINUOUSLY”.
Other symptoms:
Inspect following:
•Refrigerant charging amount
•Cooling fan No.1 and/or cooling fan No.2 operation
18 Inspect adjustment of accelerator position
sensor and idle switch.
(See F2–72 ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)
(See F2–70 IDLE SWITCH INSPECTION)
Are accelerator position sensor and idle switch
adjusted correctly?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust accelerator position sensor and idle switch
correctly.
(See F2–73 ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
ADJUSTMENT)
(See F2–71 IDLE SWITCH ADJUSTMENT)
19 Depress accelerator pedal slightly.
Crank engine.
Does engine start now?Yes Inspect idle speed.
(See F2–34 IDLE SPEED INSPECTION)
No Go to next step.
20 Inspect for fuel leakage from fuel pipe.
Is any fuel leakage found on fuel pipe?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
21 Visually inspect CKP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CKP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
22 Measure gap between CKP sensor and teeth of
pulse wheel.
Specification
1.5—2.5 mm {0.059—0.098 in}
Is gap within specification?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust CKP sensor position.
23 Visually inspect CMP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CMP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Inspect following PIDs:
(See F2–65 PCM INSPECTION)
•ECT
•IAT
•MAF
•RPM
If PID value is not as specified, repair or replace
malfunctioning parts.
If PID value is okay, go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
24 Inspect fuel pressure sensor.
(See F2–79 FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
INSPECTION)
Is fuel pressure okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace common rail.
25 Inspect suction control valve.
(See F2–54 SUCTION CONTROL VALVE
INSPECTION)
Is suction control valve okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair supply pump.
(See F2–54 SUPPLY PUMP INSPECTION)
26 Is engine compression correct?
(See B2–8 COMPRESSION INSPECTION)Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for following:
•Damaged valve seat
•Worn valve stem and valve guide
•Worn or stuck piston ring
•Worn piston, piston ring or cylinder
•Improper valve timing
Service as necessary.
27 Inspect fuel injector.
(See F2–56 FUEL INJECTOR INSPECTION)
Is fuel injector okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary. STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
Page 343 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–191
F2
5 Inspect adjustment of accelerator position
sensor and idle switch.
(See F2–72 ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)
(See F2–70 IDLE SWITCH INSPECTION)
Are accelerator position sensor and idle switch
adjusted correctly?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust accelerator position sensor and idle switch
correctly.
(See F2–73 ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
ADJUSTMENT)
(See F2–71 IDLE SWITCH ADJUSTMENT)
6 Measure voltage PCM terminal 33 and 56.
Is voltage okay?Yes Go to next step.
NoPCM terminal 33 does not specified:
Inspect clutch switch and related harness.
PCM terminal 56 does not specified:
Inspect neutral switch and related harness.
7 Visually inspect CKP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CKP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
8 Measure gap between CKP sensor and teeth of
pulse wheel.
Specification
1.5—2.5 mm {0.059—0.098 in}
Is gap within specification?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust CKP sensor position.
9 Visually inspect CMP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CMP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Inspect following PIDs:
(See F2–65 PCM INSPECTION)
•ECT
•IAT
•MAF
•RPM
If PID value is not as specified, repair or replace
malfunctioning parts.
If PID value is okay, go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
10 Inspect fuel pressure sensor.
(See F2–79 FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
INSPECTION)
Is fuel pressure okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace common rail.
11 Inspect suction control valve.
(See F2–54 SUCTION CONTROL VALVE
INSPECTION)
Is suction control valve okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair supply pump.
(See F2–54 SUPPLY PUMP INSPECTION)
12 Is engine compression correct?
(See B2–8 COMPRESSION INSPECTION)Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for following:
•Damaged valve seat
•Worn valve stem and valve guide
•Worn or stuck piston ring
•Worn piston, piston ring or cylinder
•Improper valve timing
Service as necessary.
13 Inspect fuel injector.
(See F2–56 FUEL INJECTOR INSPECTION)
Is fuel injector okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
14Note
•The following test should be performed on
the vehicles with A/C system. If the
following test cannot be performed due to
engine stalling, go to next step.
•Go to next step for the vehicle without A/C
system.
Connect pressure gauge to A/C line.
Turn blower and A/C switches on.
Is pressure within specifications?Yes Go to next step.
NoA/C is always on:
Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.24 A/C ALWAYS
ON OR A/C COMPRESSOR RUNS
CONTINUOUSLY”.
Other symptoms:
Inspect following:
•Refrigerant charging amount
•Cooling fan No.1 and/or cooling fan No.2 operation
15 Inspect EGR system operation.
Is EGR system operation normal?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning part according to
EGR system operation results.
16 Inspect glow system operation.
(See T–19 RELAY INSPECTION)
Is glow system operation normal?Yes Go to next step.
No Service as necessary. STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
Page 344 of 909

F2–192
TROUBLESHOOTING
End Of Sie
NO.11 ENGINE STALLS/QUITS, ENGINE RUNS ROUGH, MISSES, BUCK/JERK, HESITATION/STUMBLE,
SURGES
A6E408018881213
17 Inspect IDM.
(See F2–84 INJECTOR DRIVER MODULE
(IDM) INSPECTION)
Is IDM okay?Yes Remove and inspect supply pump and common rail.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
18 Verify test results.
•If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
•If malfunction remains, replace PCM. (See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION) STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
11ENGINE STALLS/QUITS, ENGINE RUNS ROUGH, MISSES, BUCK/JERK, HESITATION/STUMBLE,
SURGES
DESCRIPTION•Engine stops unexpectedly at beginning of acceleration or during cruise.
•Engine stops unexpectedly while cruising.
•Engine speed fluctuates during acceleration or cruising.
•Engine misses during acceleration or cruising.
•Vehicle bucks/jerks during acceleration, during or deceleration.
•Momentary pause at beginning of acceleration or during acceleration.
•Momentary minor irregularity in engine output.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Poor fuel quality
•Glow system malfunction
•Air leakage from intake-air system
•Intake-air system restriction or clogging
•Engine overheating
•A/C system improper operation
•Turbocharger malfunction
•Variable swirl control (VSC) system malfunction
•EGR system malfunction
•Neutral switch or related circuit malfunction
•Cooling fan No.1 or cooling fan No.2 seat are improper
•Fuel line clogging or restriction
•Fuel filter clogging or restriction
•Incorrect fuel injection timing
•Erratic signal from CKP sensor
•Erratic signal from CMP sensor
•ECT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Boost sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Accelerator position sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Idle switch or related circuit malfunction
•MAF/IAT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•IAT sensor No.2 or related circuit malfunction
•VSS or related circuit malfunction
•Incorrect adjustment accelerator position sensor and/or idle switch
•Incorrect idle speed
•Inadequate fuel pressure
•Fuel pressure sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Suction control valve malfunction (built-in supply pump)
•Fuel pressure limiter malfunction (built-in common rail)
•Supply pump malfunction
•Fuel injector malfunction
•Low engine compression
•Improper valve timing
•Exhaust system and/or catalyst converter restriction
•Clutch slippage
•IDM or related circuit malfunction
Warning
The following troubleshooting flow chart contains the fuel system diagnosis and repair
procedures. Read the following warnings before performing the fuel system services:
•Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep
sparks and flames away from fuel.
•Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injury or death
and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete “BEFORE
REPAIR PROCEDURE” and “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE” described in this manual.
Page 346 of 909

F2–194
TROUBLESHOOTING
End Of Sie
11 Inspect adjustment of accelerator position
sensor and idle switch.
(See F2–72 ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)
(See F2–70 IDLE SWITCH INSPECTION)
Are accelerator position sensor and idle switch
adjusted correctly?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust accelerator position sensor and idle switch
correctly.
(See F2–73 ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
ADJUSTMENT)
(See F2–71 IDLE SWITCH ADJUSTMENT)
12 Inspect adjustment of neutral switch.
(See F2–69 NEUTRAL SWITCH INSPECTION)
Is neutral switch adjusted correctly?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust neutral switch correctly.
13 Visually inspect CKP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CKP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
14 Measure gap between CKP sensor and teeth of
pulse wheel.
Specification
1.5—2.5 mm {0.059—0.098 in}
Is gap within specification?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust CKP sensor position.
15 Visually inspect CMP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CMP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Inspect following PIDs:
(See F2–65 PCM INSPECTION)
•ECT
•IAT
•MAF
•RPM
If PID value is not as specified, repair or replace
malfunctioning parts.
If PID value is okay, go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts.
16 Inspect fuel pressure sensor.
(See F2–79 FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
INSPECTION)
Is fuel pressure okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace common rail.
17 Inspect suction control valve.
(See F2–54 SUCTION CONTROL VALVE
INSPECTION)
Is suction control valve okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair supply pump.
(See F2–54 SUPPLY PUMP INSPECTION)
18 Is engine compression correct?
(See B2–8 COMPRESSION INSPECTION)Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for following:
•Damaged valve seat
•Worn valve stem and valve guide
•Worn or stuck piston ring
•Worn piston, piston ring or cylinder
•Improper valve timing
Service as necessary.
19 Inspect fuel injector.
(See F2–56 FUEL INJECTOR INSPECTION)
Is fuel injector okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
20 Inspect IDM.
(See F2–84 INJECTOR DRIVER MODULE
(IDM) INSPECTION)
Is IDM okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
21 Inspect timing belt for following:
•Chipping of gear teeth
•Low tension
•Breakage damage or cracks
Is timing belt okay?Yes Inspect following:
•Clutch slippage
•CKP sensor
•VSS
If okay, remove and inspect supply pump and common
rail.
No If timing is incorrect, adjust valve timing.
If timing belt is not okay, replace timing belt.
22 Verify test results.
•If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
•If malfunction remains, replace PCM. (See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION) STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
Page 347 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–195
F2
NO.12 LACK/LOSS OF POWER-ACCELERATION/CRUISEA6E408018881214
Diagnostic Procedure
12 LACK/LOSS OF POWER-ACCELERATION CRUISE
DESCRIPTION•Performance is poor under load (e.g., power down when climbing hills).
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Poor fuel quality
•Air leakage from intake-air system
•Intake-air system restriction or clogging
•Engine overheating
•A/C system improper operation
•Improper operation of A/C cut-off control
•Variable boost control (VBC) system malfunction
•Variable swirl control (VSC) system malfunction
•EGR system malfunction
•Vacuum leakage
•Clutch slippage
•Exhaust system and/or catalyst converter restriction
•Fuel line or clogging or restriction
•Fuel filter clogging or restriction
•Incorrect fuel injection timing
•Erratic signal from CKP sensor
•Erratic signal from CMP sensor
•ECT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Boost sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Accelerator position sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Idle switch or related circuit malfunction
•MAF/IAT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•IAT sensor No.2 or related circuit malfunction
•Incorrect adjustment accelerator position sensor and/or idle switch
•Incorrect idle speed
•Inadequate fuel pressure
•Fuel pressure sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Suction control valve malfunction (built-in supply pump)
•Fuel pressure limiter malfunction (built-in common rail)
•Supply pump malfunction
•Fuel injector malfunction
•Low engine compression
•Improper valve timing
•Cooling fan No.1 or cooling fan No.2 seat are improper
•Turbocharger malfunction
•Charge air cooler malfunction
•Brake system dragging
•Intake shutter valve malfunction
•Guide blade valve malfunction
•IDM or related circuit malfunction
Warning
The following troubleshooting flow chart contains the fuel system diagnosis and repair
procedures. Read the following warnings before performing the fuel system services:
•Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep
sparks and flames away from fuel.
•Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injury or death
and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete “BEFORE
REPAIR PROCEDURE” and “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE” described in this manual.
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1 Is idle speed stable? Yes Go to next step.
No Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.8 ENGINE RUNS
ROUGH/ROLLING IDLE”.
2 Is engine overheating? Yes Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.17 COOLING
SYSTEM CONCERNS—OVERHEATING”.
No Go to next step.
Page 355 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–203
F2
3 Perform self-test function using WDS or
equivalent.
Turn engine switch to ON.
Retrieve any DTC.
Is DTC displayed?YesDTC is displayed:
Go to appropriate DTC test.
Communication error message is displayed:
Inspect for following:
•Open circuit between PCM control relay and PCM
terminal 53 or 79
•Open circuit PCM control relay and PCM terminal
69
•PCM control relay stuck open
•Open or poor GND circuit (PCM terminal 65, 85,
103 or 104)
•Poor connection vehicle body GND
NoNo DTC is displayed:
Go to next step.
4Note
•The following test should be performed on
the vehicles with A/C system. If the
following test cannot be performed due to
engine stalling, go to next step.
•Go to next step for the vehicle without A/C
system.
Connect pressure gauge to A/C line.
Turn blower and A/C switches on.
Is pressure within specifications?Yes Go to next step
NoA/C is always on:
Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.24 A/C ALWAYS
ON OR A/C COMPRESSOR RUNS
CONTINUOUSLY”.
Other symptoms:
Inspect following:
•Refrigerant charging amount
•Cooling fan No.1 and/or cooling fan No.2
operation.
5 Access ECT PID.
Drive vehicle while monitoring PID.
Is PID within specification?Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for coolant leakage, cooling fan No.1 and
cooling fan No.2 operations or thermostat operation.
6 Inspect idle speed.
(See F2–34 IDLE SPEED INSPECTION)
Is idle speed okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.7 SLOW
RETURN TO IDLE”.
7 Perform EGR system inspection.
Is EGR system okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning part according to
EGR system operation results.
8 Inspect adjustment of accelerator position
sensor and idle switch.
(See F2–72 ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)
(See F2–70 IDLE SWITCH INSPECTION)
Are accelerator position sensor and idle switch
adjusted correctly?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust accelerator position sensor and idle switch
correctly.
(See F2–73 ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
ADJUSTMENT)
(See F2–71 IDLE SWITCH ADJUSTMENT)
9 Is engine compression correct?
(See B2–8 COMPRESSION INSPECTION)Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect for following:
•Damaged valve seat
•Worn valve stem and valve guide
•Worn or stuck piston ring
•Worn piston, piston ring or cylinder
•Improper valve timing
Service as necessary.
10 Inspect fuel injector.
(See F2–56 FUEL INJECTOR INSPECTION)
Is fuel injector okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
11 Perform turbocharger inspection.
(See F2–38 TURBOCHARGER INSPECTION)
Is turbocharger okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace turbocharger.
12 Inspect guide blade valve operation.
(See F2–229 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
OPERATION INSPECTION)
Is there any problem?Yes Repair or replace as necessary.
No Go to next step.
13 Visually inspect CKP sensor and teeth of pulse
wheel.
Are CKP sensor and teeth of pulse wheel okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace malfunctioning parts. STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
Page 372 of 909

F2–220
TROUBLESHOOTING
NO.22 VIBRATION CONCERNS (ENGINE)A6E408018881224
Diagnostic Procedure
22 VIBRATION CONCERNS (ENGINE)
DESCRIPTION•Vibration from under hood or driveline.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Loose attaching bolts or worn parts
•Cooling fan No.1 or cooling fan No.2 seat are improper
•Engine or transaxle mounts are improperly installed
•Components malfunction such as worn parts
•Erratic signal from CMP sensor
•ECT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Accelerator position sensor or related circuit malfunction
•MAF/IAT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Idle switch or related circuit malfunction
•Incorrect adjustment of accelerator position sensor and/or idle switch
•Fuel injector malfunction
•Vacuum leakage
•Improper tension or damaged drive belts
•Improper balance of wheels or tires
•Driveline malfunction
•Suspension malfunction
Warning
The following troubleshooting flow chart contains the fuel system diagnosis and repair
procedures. Read the following warnings before performing the fuel system services:
•Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep
sparks and flames away from fuel.
•Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injury or death
and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete “BEFORE
REPAIR PROCEDURE” and “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE” described in this manual.
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1 Inspect following components for loose attaching
bolts or worn parts:
•Cooling fan No.1
•Cooling fan No.2
•Cooling fan No.1 and cooling fan No.2 seat
•Drive belt and pulley
•Engine mounts
•Exhaust system
Are all items okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Readjust or retighten engine mount installation
position.
Service as necessary for other parts.
2 Inspect vacuum leakage.
Are vacuum hoses okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Service as necessary.
Repeat Step 2.
Page 691 of 909
REAR DIFFERENTIAL
M–61
M
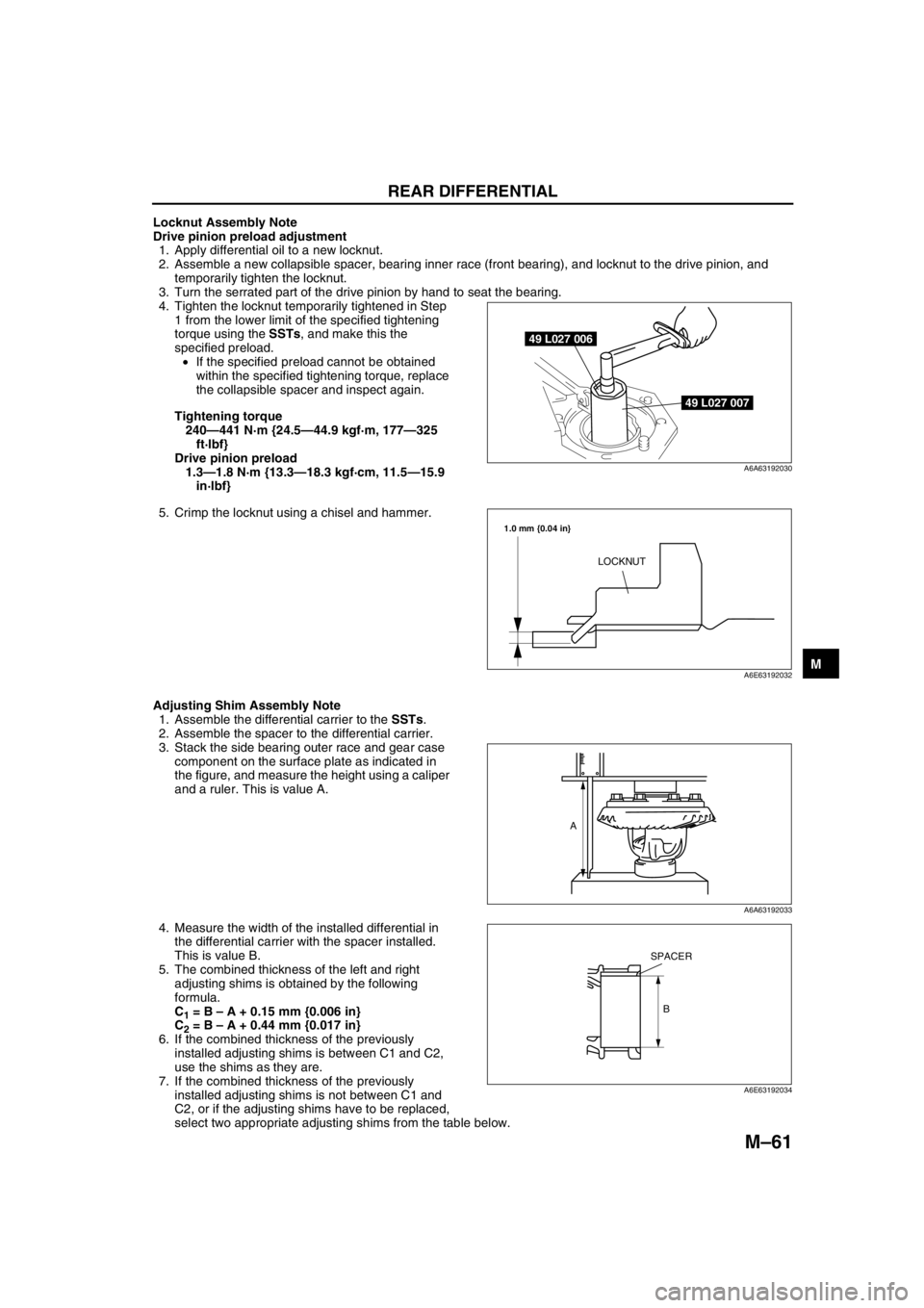
Locknut Assembly Note
Drive pinion preload adjustment
1. Apply differential oil to a new locknut.
2. Assemble a new collapsible spacer, bearing inner race (front bearing), and locknut to the drive pinion, and
temporarily tighten the locknut.
3. Turn the serrated part of the drive pinion by hand to seat the bearing.
4. Tighten the locknut temporarily tightened in Step
1 from the lower limit of the specified tightening
torque using the SSTs, and make this the
specified preload.
•If the specified preload cannot be obtained
within the specified tightening torque, replace
the collapsible spacer and inspect again.
Tightening torque
240—441 N·m {24.5—44.9 kgf·m, 177—325
ft·lbf}
Drive pinion preload
1.3—1.8 N·m {13.3—18.3 kgf·cm, 11.5—15.9
in·lbf}
5. Crimp the locknut using a chisel and hammer.
Adjusting Shim Assembly Note
1. Assemble the differential carrier to the SSTs.
2. Assemble the spacer to the differential carrier.
3. Stack the side bearing outer race and gear case
component on the surface plate as indicated in
the figure, and measure the height using a caliper
and a ruler. This is value A.
4. Measure the width of the installed differential in
the differential carrier with the spacer installed.
This is value B.
5. The combined thickness of the left and right
adjusting shims is obtained by the following
formula.
C
1 = B – A + 0.15 mm {0.006 in}
C
2 = B – A + 0.44 mm {0.017 in}
6. If the combined thickness of the previously
installed adjusting shims is between C1 and C2,
use the shims as they are.
7. If the combined thickness of the previously
installed adjusting shims is not between C1 and
C2, or if the adjusting shims have to be replaced,
select two appropriate adjusting shims from the table below.
49 L027 006
49 L027 007
A6A63192030
LOCKNUT
1.0 mm {0.04 in}
A6E63192032
A
A6A63192033
B
SPACER
A6E63192034