MAZDA MODEL TRIBUTE 2011 Owners Manual (in English)
Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2011, Model line: MODEL TRIBUTE, Model: MAZDA MODEL TRIBUTE 2011Pages: 320, PDF Size: 2.08 MB
Page 141 of 320

WARNING:Depending on where you secure a child restraint,
and depending on the child restraint design, you may block
access to certain seat belt buckle assemblies and/or LATCH lower
anchors, rendering those features potentially unusable. To avoid risk of
injury, occupants should only use seating positions where they are able
to be properly restrained.
WARNING:Make sure there are no seat belts or foreign objects
near or around the LATCH child-restraint system: Not following
the child-restraint system manufacturer’s instructions when installing
the child-restraint system is dangerous. If seat belts or a foreign object
prevent the child-restraint system from being securely attached to the
LATCH lower anchors and the child-restraint system is installed
improperly, the child-restraint system could move in a sudden stop or
collision causing serious injury or death to the child or other
occupants. When installing the child-restraint system, make sure there
are no seat belts or foreign objects near or around the LATCH lower
anchors. Always follow the child-restraint system manufacturer’s
instructions.
Use of inboard lower anchors from the outboard seating positions
(center seating use)
The lower anchors at the center of the second row rear seat are spaced
400 mm (16 inches) apart. The standardized spacing for LATCH lower
anchors is 280 mm (11 inches) center to center. A child seat with rigid
LATCH attachments cannot be installed at the center seating position.
LATCH compatible child seats (with attachments on belt webbing) can
only be used at this seating position provided that the child seat
manufacturer’s instructions permit use with the anchor spacing stated.
Do not attach a child seat to any lower anchor if an adjacent child seat is
attached to that anchor.
WARNING:The standardized spacing for LATCH lower anchors
is 280 mm (11 inches) center to center. Do not use LATCH
lower anchors for the center seating position unless the child seat
manufacturer’s instructions permit and specify using anchors spaced at
least as far apart as those of this vehicle.
Each time you use the safety seat, check that the seat is properly
attached to the lower anchors and tether anchor, if applicable. Tug the
Seating and Safety Restraints
141
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 142 of 320

child seat from side to side and forward and back where it is secured to
the vehicle. The seat should move less than one inch when you do this
for a proper installation.
If the safety seat is not anchored properly, the risk of a child being
injured in a crash greatly increases.
Combining seat belt and LATCH lower anchors for attaching child
safety seats
When used in combination, either the seat belt or the LATCH lower
anchors may be attached first, provided a proper installation is achieved.
Attach the tether strap afterward, if included with the child seat. Refer
toRecommendations for attaching child safety restraints for children
in this chapter.
Attaching child safety seats with tether straps
Many forward-facing child safety seats include a tether strap which
extends from the back of the child safety seat and hooks to an anchoring
point called the top tether anchor. Tether straps are available as an
accessory for many older safety seats. Contact the manufacturer of your
child seat for information about ordering a tether strap, or to obtain a
longer tether strap if the tether strap on your safety seat does not reach
the appropriate top tether anchor in the vehicle.
The rear seating positions of your vehicle are equipped with built-in
tether strap anchors located behind the seats on the roof panel in the
cargo area.
The tether strap anchors in your vehicle are in the following positions
(shown from top view):
Attach the tether strap only to the
appropriate tether anchor as shown.
The tether strap may not work
properly if attached somewhere
other than the correct tether
anchor.
Once the child safety seat has been
installed, using either the seat belt
or the lower anchors of the LATCH system, you can attach the top tether
strap.
If you install a child seat with rigid LATCH attachments, and have
attached the top tether strap to the proper top tether anchor, do not
tighten the tether strap enough to lift the child seat off the vehicle seat
Seating and Safety Restraints
142
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 143 of 320

cushion when the child is seated in it. Keep the tether strap just snug
without lifting the front of the child seat. Keeping the child seat just
touching the vehicle seat gives the best protection in a severe crash.
Perform the following steps to install a child safety seat with tether
anchors:
1. Route the child safety seat tether strap over the back of the seat.
For vehicles with adjustable head restraints, remove the head restraint
first, place under the front seat for storage, and then route the tether
strap over the top of the seatback.
2. Locate the correct anchor for
the selected seating position.
There are three tether anchors
located on the headliner at the rear
of the vehicle.
3. Clip the tether strap to the
anchor as shown.
The arrow in the above graphic
points toward the front of the
vehicle.
If the tether strap is clipped
incorrectly, the child safety seat may
not be retained properly in the
event of a collision.
4. Tighten the child safety seat
tether strap according to the
manufacturer’s instructions.
Seating and Safety Restraints
143
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 144 of 320

If the safety seat is not anchored properly, the risk of a child being
injured in a collision greatly increases.
If your child restraint system is equipped with a tether strap, and the
child restraint manufacturer recommends its use, Mazda also
recommends its use.
Child booster seats
The belt-positioning booster (booster seat) is used to improve the fit of
the vehicle seat belt. Children outgrow a typical child seat (e.g.,
convertible or toddler seat) when they weigh about 40 lb (18 kg) and are
around four (4) years of age. Consult your child safety seat owner
manual for the weight, height, and age limits specific to your child safety
seat. Keep your child in the child safety seat if it properly fits the child,
remains appropriate for their weight, height and age AND if properly
secured to the vehicle.
Although the lap/shoulder belt will provide some protection, children
who have outgrown a typical child seat are still too small for lap/shoulder
belts to fit properly, and wearing an improperly fitted vehicle seat belt
could increase the risk of serious injury in a crash. To improve the fit of
both the lap and shoulder belt on children who have outgrown child
safety seats, Mazda Motor Corporation recommends use of a
belt-positioning booster.
Booster seats position a child so that vehicle lap/shoulder seat belts fit
better. They lift the child up so that the lap belt rests low across the hips
and the knees bend comfortably at the edge of the cushion, while
minimizing slouching. Booster seats may also make the shoulder belt fit
better and more comfortably. Try to keep the belt near the middle of the
shoulder and across the center of the chest. Moving the child closer (a
few centimeters or inches) to the center of the vehicle, but remaining in
the same seating position, may help provide a good shoulder belt fit.
When children should use booster seats
Children need to use booster seats from the time they outgrow the
toddler seat until they are big enough for the vehicle seat and
lap/shoulder belt to fit properly. Generally this is when they reach a
height of at least 4 feet 9 inches (1.45 meters) tall (around age eight to
age twelve and between 40 lb (18 kg) and 80 lb (36 kg) or upward to
100 lb (45 kg) if recommended by your child restraint manufacturer).
Many state and provincial laws require that children use approved
booster seats until they reach age eight, a height of 4 feet 9 inches
(1.45 meters) tall, or 80 lb (36 kg).
Seating and Safety Restraints
144
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 145 of 320

Booster seats should be used until you can answer YES to ALL of these
questions when seated without a booster seat:
•Can the child sit all the way back
against the vehicle seat back with
knees bent comfortably at the
edge of the seat cushion?
•Can the child sit without
slouching?
•Does the lap belt rest low across the hips?
•Is the shoulder belt centered on the shoulder and chest?
•Can the child stay seated like this for the whole trip?
Types of booster seats
There are generally two types of belt-positioning booster seats: backless
and high back. Always use booster seats in conjunction with the vehicle
lap/shoulder belt.
•Backless booster seats
If your backless booster seat has a
removable shield, remove the
shield. If a vehicle seating position
has a low seat back or no head
restraint, a backless booster seat
may place your child’s head (as
measured at the tops of the ears)
above the top of the seat. In this
case, move the backless booster
to another seating position with a
higher seat back or head restraint and lap/shoulder belts, or consider
using a high back booster seat.
Seating and Safety Restraints
145
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 146 of 320
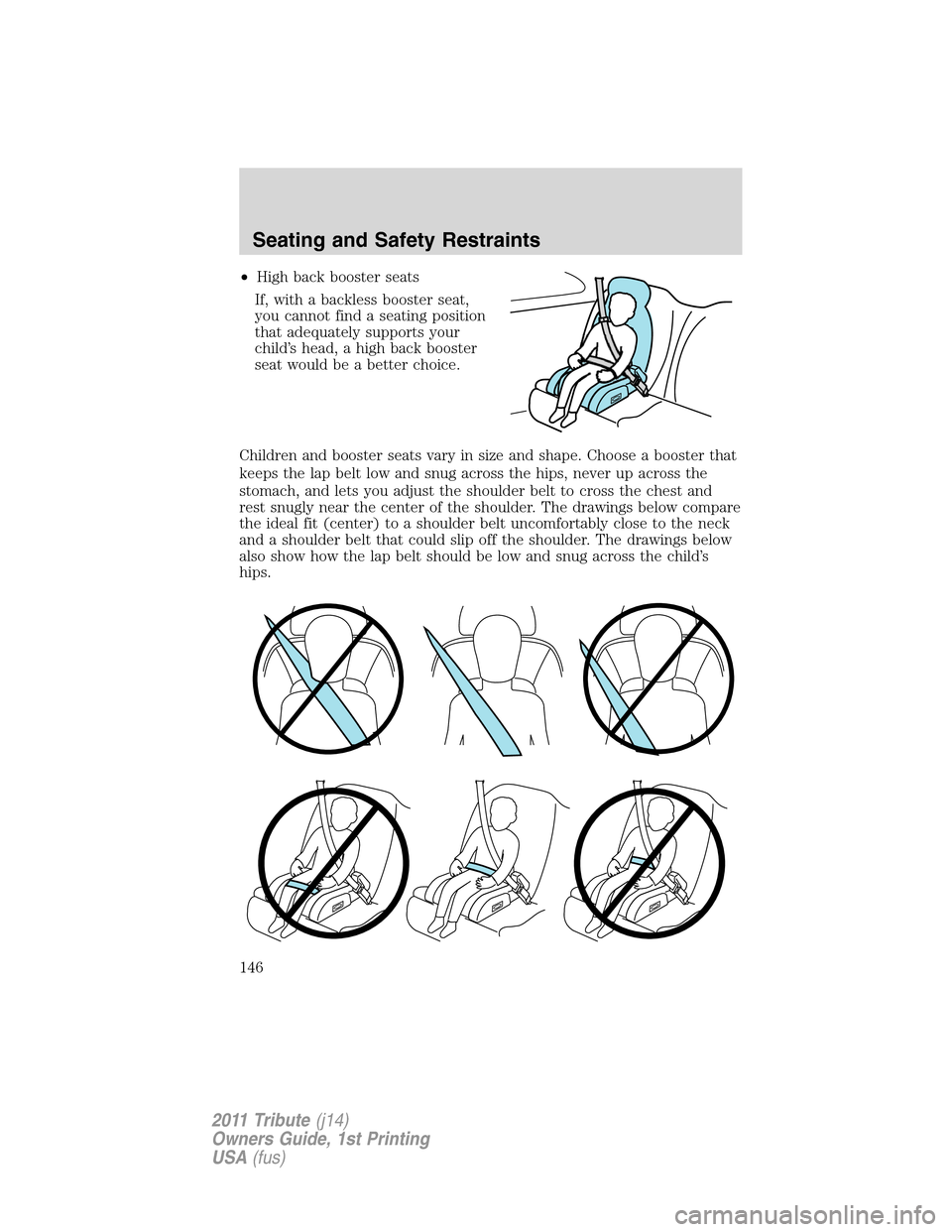
•High back booster seats
If, with a backless booster seat,
you cannot find a seating position
that adequately supports your
child’s head, a high back booster
seat would be a better choice.
Children and booster seats vary in size and shape. Choose a booster that
keeps the lap belt low and snug across the hips, never up across the
stomach, and lets you adjust the shoulder belt to cross the chest and
rest snugly near the center of the shoulder. The drawings below compare
the ideal fit (center) to a shoulder belt uncomfortably close to the neck
and a shoulder belt that could slip off the shoulder. The drawings below
also show how the lap belt should be low and snug across the child’s
hips.
Seating and Safety Restraints
146
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 147 of 320

If the booster seat slides on the vehicle seat, placing a rubberized mesh
sold as shelf or carpet liner under the booster seat may improve this
condition. Do not introduce any item thicker than this under the booster
seat. Check with the booster seat manufacturer’s instructions.
The importance of shoulder belts
Using a booster without a shoulder belt increases the risk of a child’s
head hitting a hard surface in a collision. For this reason, you should
never use a booster seat with a lap belt only. It is generally best to use a
booster seat with lap/shoulder belts in the back seat.
Move a child to a different seating location if the shoulder belt does not
stay positioned on the shoulder during use.
Follow all instructions provided by the manufacturer of the booster seat.
WARNING:Never place, or allow a child to place, the shoulder
belt under a child’s arm or behind the back because it reduces
the protection for the upper part of the body and may increase the risk
of injury or death in a collision.
Child restraint and seat belt maintenance
Inspect the seat belt systems periodically to make sure they work
properly and are not damaged.
NOTE:If unsure about the proper procedures, bring your vehicle to an
authorized Mazda dealership for inspection. Inspect the seat belts to
make sure there are no nicks, tears or cuts, replacing if necessary. Check
all emergency locking retractors on all outboard seating positions as well
as the automatic locking mode for child safety seats on all seats except
the driver’s seat. All seat belt assemblies, including retractors, buckles,
front seat belt buckle assemblies, buckle support assemblies (slide bar-if
equipped), shoulder belt height adjusters (if equipped), shoulder belt
guide on seatback (if equipped), child safety seat tether bracket
assemblies (if equipped), LATCH child seat tether anchors and lower
anchors (if equipped), and attaching hardware, should be inspected after
a collision. Mazda recommends that all seat belt assemblies used in
vehicles involved in a collision be replaced. However, if the collision was
minor and an authorized Mazda technician finds that the belts do not
show damage and continue to operate properly, they do not need to be
replaced. Seat belt assemblies not in use during a collision should also be
inspected and replaced if either damage or improper operation is noted.
Seating and Safety Restraints
147
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 148 of 320

The energy absorbing functions may have been activated in a collision so
the restraints should be examined; if the front airbags have deployed, the
pretensioners have also deployed and must be replaced — regardless of
whether there was an occupant in the passenger seat or not. The
optional side airbags are not connected to the pretensioners.
WARNING:Failure to inspect and if necessary replace the seat
belt assembly under the above conditions could result in severe
personal injuries in the event of a collision.
Refer toInteriorin theCleaningchapter.
Seating and Safety Restraints
148
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 149 of 320

NOTICE TO UTILITY VEHICLE AND TRUCK OWNERS
Utility vehicles and trucks handle
differently than passenger cars in
the various driving conditions that
are encountered on streets,
highways and off-road. Utility
vehicles and trucks are not designed
for cornering at speeds as high as
passenger cars any more than
low-slung sports cars are designed
to perform satisfactorily under
off-road conditions.
WARNING:Utility vehicles have a significantly higher rollover
rate than other types of vehicles. To reduce the risk of serious
injury or death from a rollover or other crash you must:
•Avoid sharp turns and abrupt maneuvers;
•Drive at safe speeds for the conditions;
•Keep tires properly inflated;
•Never overload or improperly load your vehicle; and
•Make sure every passenger is properly restrained.
WARNING:In a rollover crash, an unbelted person is
significantly more likely to die than a person wearing a seat belt.
All occupants must wear seat belts and children/infants must use
appropriate restraints to minimize the risk of injury or ejection.
Study your owner’s manual and any supplements for specific information
about equipment features, instructions for safe driving and additional
precautions to reduce the risk of an accident or serious injury.
Tires, Wheels and Loading
149
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 150 of 320

VEHICLE CHARACTERISTICS
4WD system (if equipped)
Your vehicle may be equipped with a four-wheel drive (4WD) system.
With the 4WD option, power will be delivered to the front wheels and
distributed to the rear wheels as needed. This increases traction which
may enable you to safely drive over terrain and road conditions that a
conventional two-wheel drive vehicle cannot. The 4WD system is active
all the time and requires no input from the operator.
For 4WD vehicles, a spare tire of a different size other than the tire
provided should never be used. A dissimilar spare tire size (other than
the spare tire provided) or major dissimilar tire sized between the front
and rear axles could cause the 4WD system to stop functioning and
default to front-wheel drive.
WARNING:Do not become overconfident in the ability of 4WD
vehicles. Although a 4WD vehicle may accelerate better than a
two-wheel drive vehicle in low traction situations, it won’t stop any
faster than two-wheel drive vehicles. Always drive at a safe speed.
How your vehicle differs from other vehicles
SUVs and trucks can differ from
some other vehicles in a few
noticeable ways. Your vehicle may
be:
•Higher – to allow higher load
carrying capacity and to allow it
to travel over rough terrain
without getting hung up or
damaging underbody components.
•Shorter – to give it the capability
to approach inclines and drive
over the crest of a hill without
getting hung up or damaging
underbody components. All other
things held equal, a shorter
wheelbase may make your vehicle
quicker to respond to steering inputs than a vehicle with a longer
wheelbase.
Tires, Wheels and Loading
150
2011 Tribute(j14)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)