Mercury Sable 2000 s Owners Manual
Manufacturer: MERCURY, Model Year: 2000, Model line: Sable, Model: Mercury Sable 2000Pages: 232, PDF Size: 2.09 MB
Page 91 of 232

One time disable
Anytime the safety belt is buckled and then unbuckled during an ignition
ON cycle, Belt Minder will be disabled for that ignition cycle only. The
safety belt needs to be latched for a minimum of 3 seconds before belt
minder is disabled.
Deactivating/activating the belt minder feature
Read steps1-9thoroughly before proceeding with the
deactivation/activation programming procedure.
The Belt Minder feature can be deactivated/activated by performing the
following procedure:
Before following the procedure, make sure that:
²the parking brake is set
²the gearshift is in P (Park) (automatic transmission).
²the ignition switch is in the OFF position
²all vehicle doors are closed
²the driver's safety belt is unbuckled
²the parklamps/headlamps are in OFF position (If vehicle is equipped
with Autolamps, this will not affect the procedure.)
To reduce the risk of injury, do not deactivate/activate the Belt
Minder feature while driving the vehicle.
1. Turn the ignition switch to the RUN (or ON) position. (DO NOT
START THE ENGINE)
2. Wait until the safety belt warning light turns off. (Approximately 1±2
minutes)
²Steps 3±5 must be completed within 60 seconds or the procedure will
have to be repeated.
3. Buckle then unbuckle the safety belt three times, ending with the
safety belt unbuckled. This can be done before or during Belt Minder
warning activation.
4. Turn on the parklamps/headlamps, turn off the parklamps/headlamps.
5. Buckle then unbuckle the safety belt three times, ending with the
safety belt unbuckled.
Seating and safety restraints
91
Page 92 of 232

²After step 5 the safety belt warning light will be turned on for three
seconds.
6. Within seven seconds of the safety belt warning light turning off,
buckle then unbuckle the safety belt.
²This will disable Belt Minder if it is currently enabled, or enable Belt
Minder if it is currently disabled.
7. Confirmation of disabling Belt Minder is provided by flashing the
safety belt warning light four times per second for three seconds.
8. Confirmation of enabling Belt Minder is provided by flashing the safety
belt warning light four times per second for three seconds, followed by
three seconds with the safety belt warning light off, then followed by
flashing the safety belt warning light four times per second for three
seconds again.
9. After receiving confirmation, the deactivation/activation procedure is
complete.
Safety belt maintenance
Inspect the safety belt systems periodically to make sure they work
properly and are not damaged. Inspect the safety belts to make sure
there are no nicks, wears or cuts, replacing if necessary. All safety belt
assemblies, including retractors, buckles, front seat belt buckle
assemblies, buckle support assemblies (slide bar-if equipped), shoulder
belt height adjusters (if equipped), shoulder belt guide on seatback (if
equipped), child safety seat tether bracket assemblies (if equipped), and
attaching hardware, should be inspected after a collision. Ford
recommends that all safety belt assemblies used in vehicles involved in a
collision be replaced. However, if the collision was minor and a qualified
technician finds that the belts do not show damage and continue to
operate properly, they do not need to be replaced. Safety belt assemblies
not in use during a collision should also be inspected and replaced if
either damage or improper operation is noted.
Failure to inspect and if necessary replace the safety belt
assembly under the above conditions could result in severe
personal injuries in the event of a collision.
Refer toCleaning and maintaining the safety beltsin the
Maintenance and caresection.
Seating and safety restraints
92
Page 93 of 232
AIR BAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM
Your vehicle is equipped with a crash sensing and diagnostic module
which records information about the air bag and sensor systems. In the
event of a collision this module may save information related to the
collision including information about the air bag system and impact
severity. This information will assist Ford in the servicing of your vehicle
and may help Ford better understand real world collisions and further
improve the safety of future vehicles.
The air bag supplemental restraint system is designed to work in
conjunction with the safety belts to help protect the driver and front
outboard passenger from certain upper body injuries. The term
ªsupplemental restraintº means the air bags are intended as a
supplement to the safety belts. Air bags alone cannot protect as well as
air bags plus safety belts in impacts for which the air bags are designed
to deploy, and air bags do not offer any protection in crashes for which
they do not deploy.
HOW DO THE AIR BAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINTS WORK?
The air bag supplemental restraint system consists of:
²driver and passenger dual stage air bag modules (which include the
inflators and air bags).
²side air bags (if equipped). Refer toSide air bag systemlater in this
chapter.
²one or more impact and safing sensors.
²the same indicator light, RCM (restraints control module) and
diagnostic unit used for the Personal safety system.
AVOL
PUSH ONAM
FM H
M
EJ TAPEBASS
TREB
BAL
FADE
SCAN REW
FF
RCOMP
OFF
A/C
MAX
A/CSHUFFLE
SIDE 1-2CD SEEK
TUNE
DISC 1-61 234 56
P!
BRAKE
+ –
CRUISERPMx1000ABS0 123
4
5
6
72060
14 0
18 0 10 0km/hP R N D 2 10000000000EFC HFUEL DOOR >THEFTLOW
COOLANT
ONSET+RESCST-OFF
Seating and safety restraints
93
Page 94 of 232

The air bag supplemental restraints are an intergral part of the Personal
Safety System. They are designed to be deployed in cases where the
Personal Safety System has determined the occupant conditions and
crash severity are appropriate to activate these devices. Refer to the
Personal Safety Systemsection in this chapter.
Important supplemental restraint system precautions
Air bags DO NOT inflate slowly or
gently and the risk of injury from a
deploying air bag is greatest close to
the trim covering the air bag
module.
All occupants of the vehicle, including the driver, should always
properly wear their safety belts, even when an air bag SRS is
provided.
Always transport children 12 years old and under in the back
seat and always properly use appropriate child restraints.
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
recommends a minimum distance of at least 25 cm (10 inches)
between an occupant's chest and the driver air bag module.
Never place your arm over the air bag module as a deploying air
bag can result in serious arm fractures or other injuries.
Steps you can take to properly position yourself away from the airbag:
²Move your seat to the rear as far as you can while still reaching the
pedals comfortably.
Seating and safety restraints
94
Page 95 of 232

²Recline the seat slightly (one or two degrees) from the upright
position.
Do not put anything on or over the air bag module. Placing
objects on or over the air bag inflation area may cause those
objects to be propelled by the air bag into your face and torso causing
serious injury.
Do not attempt to service, repair, or modify the Air Bag
Supplemental Restraint System or its fuses. See your Ford or
Lincoln-Mercury dealer.
Modifications to the front end of the vehicle, including frame,
bumper, front end body structure and tow hooks may effect the
performance of the air bag sensors increasing the risk of injury. Do not
modify the front end of the vehicle.
Children and air bags
For additional important safety
information, read all information on
safety restraints in this guide.
Children must always be properly
restrained. Accident statistics
suggest that children are safer when
properly restrained in the rear
seating positions than in the front
seating position. Failure to follow
these instructions may increase the
risk of injury in a collision.
Air bags can kill or injure a
child in a child seat.
NEVERplace a rear-facing child
seat in front of an active air bag. If
you must use a forward-facing
child seat in the front seat, move
the seat all the way back.
Seating and safety restraints
95
Page 96 of 232

Determining if the system is operational
The supplemental restraint system uses a warning indicator in the
instrument cluster or a back-up tone to indicate the condition of the
system. Refer to theRestraints Warning Indicatorsection in the
Instrumentationchapter. Routine maintenance of the air bag is not
required.
A difficulty with the system is indicated by one or more of the following:
²The readiness light (same light
for front and side air bag system)
will either flash or stay lit.
²The readiness light will not
illuminate immediately after ignition is turned on.
²A series of five beeps will be heard. The tone pattern will repeat
periodically until the problem and light are repaired.
If any of these things happen, even intermittently, have the supplemental
restraint system serviced at your dealership or by a qualified technician
immediately. Unless serviced, the system may not function properly in
the event of a collision.
How do the air bag supplemental restraints work?
The air bags inflate and deflate
rapidly upon activation. After air bag
deployment, it is normal to notice a
smoke-like, powdery residue or
smell the burnt propellant. This may
consist of cornstarch, talcum
powder (to lubricate the bag) or
sodium compounds (e.g., baking
soda) that result from the
combustion process that inflates the
air bag. Small amounts of sodium
hydroxide may be present which
may irritate the skin and eyes, but
none of the residue is toxic.
While the system is designed to help
reduce serious injuries, contact with
a deploying air bag may also cause abrasions, swelling or temporary
hearing loss. Because air bags must inflate rapidly and with considerable
force, there is the risk of death or serious injuries such as fractures,
Seating and safety restraints
96
Page 97 of 232

facial and eye injuries or internal injuries, particularly to occupants who
are not properly restrained or are otherwise out of position at the time
of air bag deployment. Thus, it is extremely important that occupants be
properly restrained as far away from the air bag module as possible while
maintaining vehicle control.
Several air bag system components get hot after inflation. Do not
touch them after inflation.
If the air bag is deployed,the air bag will not function again
and must be replaced immediately.If the air bag is not
replaced, the unrepaired area will increase the risk of injury in a
collision.
Side air bag system (if equipped)
Do not place objects or mount equipment on or near the air bag
cover on the side of the seatbacks of the front seats or in front
seat areas that may come into contact with a deploying air bag. Failure
to follow these instructions may increase the risk of personal injury in
the event of a collision.
Do not use accessory seat covers. The use of accessory seat
covers may prevent the deployment of the side air bags and
increase the risk of injury in an accident.
Do not lean your head on the door. The side air bag could injure
you as it deploys from the side of the seatback.
Do not attempt to service, repair, or modify the air bag
Supplemental Restraint System, its fuses or the seat cover on a
seat containing an air bag. See your Ford or Lincoln Mercury dealer.
All occupants of the vehicle including the driver should always
wear their safety belts even when an air bag SRS is provided.
Seating and safety restraints
97
Page 98 of 232
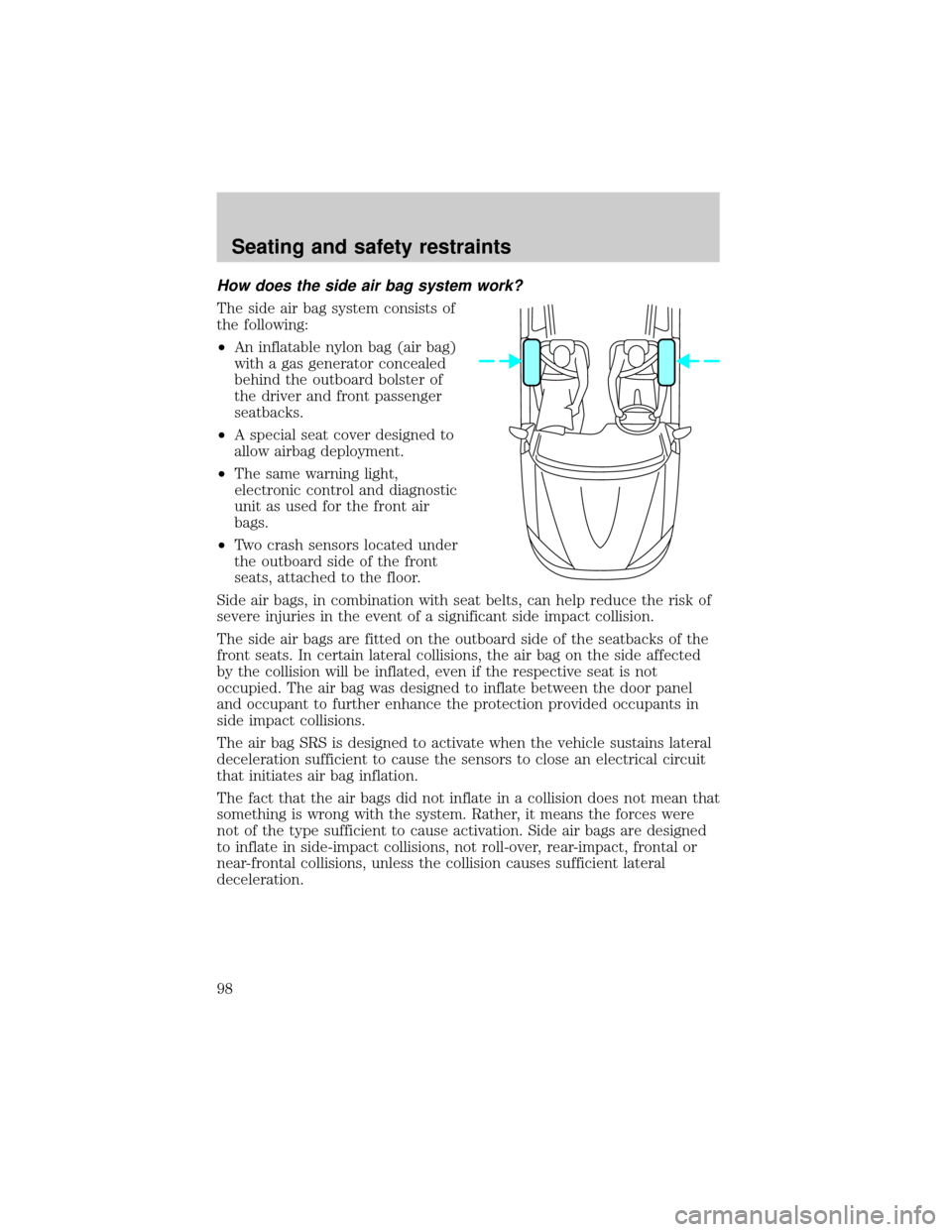
How does the side air bag system work?
The side air bag system consists of
the following:
²An inflatable nylon bag (air bag)
with a gas generator concealed
behind the outboard bolster of
the driver and front passenger
seatbacks.
²A special seat cover designed to
allow airbag deployment.
²The same warning light,
electronic control and diagnostic
unit as used for the front air
bags.
²Two crash sensors located under
the outboard side of the front
seats, attached to the floor.
Side air bags, in combination with seat belts, can help reduce the risk of
severe injuries in the event of a significant side impact collision.
The side air bags are fitted on the outboard side of the seatbacks of the
front seats. In certain lateral collisions, the air bag on the side affected
by the collision will be inflated, even if the respective seat is not
occupied. The air bag was designed to inflate between the door panel
and occupant to further enhance the protection provided occupants in
side impact collisions.
The air bag SRS is designed to activate when the vehicle sustains lateral
deceleration sufficient to cause the sensors to close an electrical circuit
that initiates air bag inflation.
The fact that the air bags did not inflate in a collision does not mean that
something is wrong with the system. Rather, it means the forces were
not of the type sufficient to cause activation. Side air bags are designed
to inflate in side-impact collisions, not roll-over, rear-impact, frontal or
near-frontal collisions, unless the collision causes sufficient lateral
deceleration.
Seating and safety restraints
98
Page 99 of 232

Several air bag system
components get hot after
inflation. Do not touch them after
inflation.
If the side air bag has
deployed,the air bag will
not function again. The side
air bag system (including the
seat) must be inspected and
serviced by a qualified
technician in accordance with
the vehicle service manual.If
the air bag is not replaced, the
unrepaired area will increase the
risk of injury in a collision.
Disposal of air bags and air bag equipped vehicles
For disposal of air bags or air bag equipped vehicles, see your local
dealership or qualified technician. Air bags MUST BE disposed of by
qualified personnel.
SAFETY RESTRAINTS FOR CHILDREN
See the following sections for directions on how to properly use safety
restraints for children. Also seeAir Bag Supplemental Restraint
System (SRS)in this chapter for special instructions about using air
bags.
Important child restraint precautions
You are required by law to use safety restraints for children in the U.S.
and Canada. If small children ride in your vehicle (generally children who
are four years old or younger and who weigh 18 kg [40 lbs] or less), you
must put them in safety seats made especially for children. Check your
local and state or provincial laws for specific requirements regarding the
safety of children in your vehicle.
Seating and safety restraints
99
Page 100 of 232

Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the
vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
Always follow the instructions and warnings that come with any infant or
child restraint you might use.
When possible, always place children under age 12 in the rear seat of
your vehicle. Accident statistics suggest that children are safer when
properly restrained in the rear seating positions than in the front seating
position.
Children and safety belts
If the child is the proper size, restrain the child in a safety seat.
Children who are too large for child safety seats (as specified by your
child safety seat manufacturer) should always wear safety belts.
Follow all the important safety restraint and air bag precautions that
apply to adult passengers in your vehicle.
If the shoulder belt portion of a combination lap and shoulder belt can
be positioned so it does not cross or rest in front of the child's face or
neck, the child should wear the lap and shoulder belt. Moving the child
closer to the center of the vehicle may help provide a good shoulder belt
fit.
Do not leave children, unreliable adults, or pets unattended in
your vehicle.
To improve the fit of lap and shoulder belts on children who have
outgrown child safety seats, Ford recommends use of a belt-positioning
booster seat that is labelled as conforming to all Federal motor vehicle
safety standards. Belt-positioning booster seats raise the child and
provide a shorter, firmer seating cushion that encourages safer seating
posture and better fit of lap and shoulder belts on the child.
A belt-positioning booster should be used if the shoulder belt rests in
front of the child's face or neck, or if the lap belt does not fit snugly on
both thighs, or if the thighs are too short to let the child sit all the way
back on the seat cushion when the lower legs hang over the edge of the
seat cushion. You may wish to discuss the special needs of your child
with your pediatrician.
Seating and safety restraints
100