alternator MITSUBISHI LANCER 2005 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: LANCER, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER 2005Pages: 788, PDF Size: 45.98 MB
Page 72 of 788
CHARGING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-8
If the voltage is not within the standard value,
there is a malfunction of the voltage regulator or of
the alternator.
14.After the test, lower the engine speed to the idle
speed.
15.Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF)
position.
16.Remove the tachometer or the MUT-II/III.17.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
18.Disconnect the ammeter and voltmeter.
19.Connect the alternator output wire to the
alternator "B" terminal.
20.Remove the special tool, and return the connector
to the original condition.
21.Connect the negative battery cable.
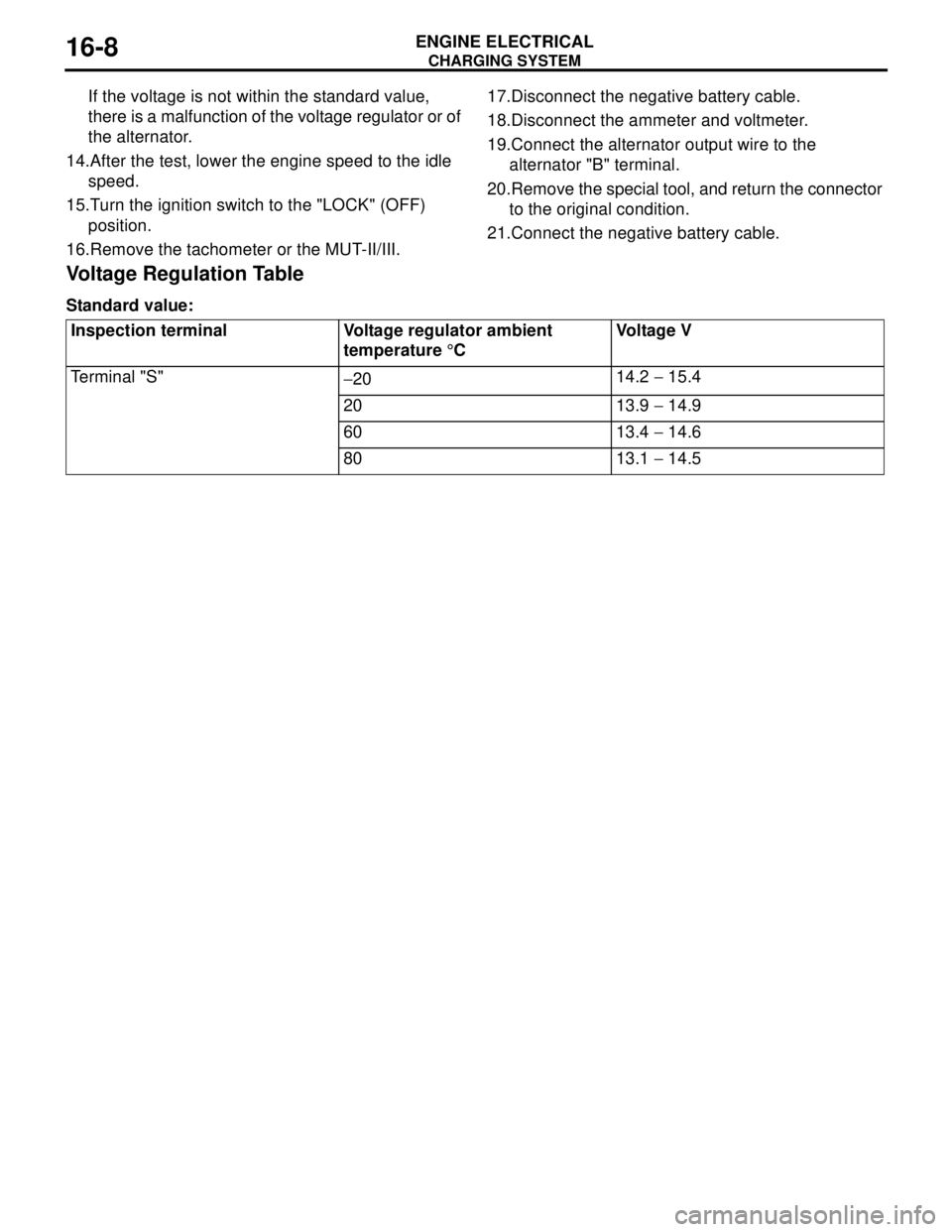
Voltage Regulation Table
Standard value:
Inspection terminal Voltage regulator ambient
temperature °CVoltage V
Terminal "S"
−2014.2 − 15.4
20 13.9 − 14.9
60 13.4 − 14.6
80 13.1 − 14.5
Page 73 of 788
CHARGING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-9
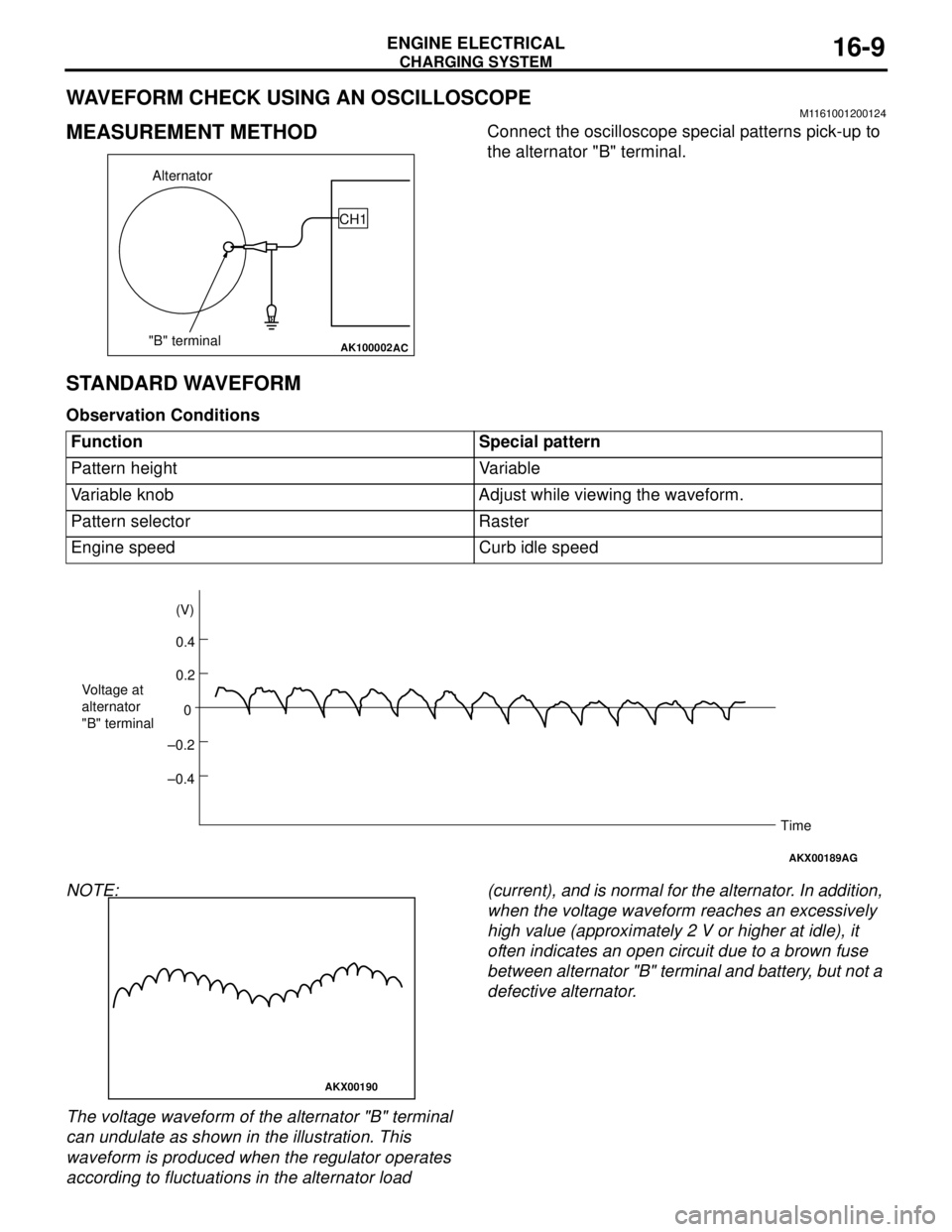
WAVEFORM CHECK USING AN OSCILLOSCOPEM1161001200124
MEASUREMENT METHODConnect the oscilloscope special patterns pick-up to
the alternator "B" terminal.
STANDARD WAVEFORM
Observation Conditions
NOTE:
The voltage waveform of the alternator "B" terminal
can undulate as shown in the illustration. This
waveform is produced when the regulator operates
according to fluctuations in the alternator load (current), and is normal for the alternator. In addition,
when the voltage waveform reaches an excessively
high value (approximately 2 V or higher at idle), it
often indicates an open circuit due to a brown fuse
between alternator "B" terminal and battery, but not a
defective alternator.
AK100002
Alternator
"B" terminalCH1
AC
Function Special pattern
Pattern height Variable
Variable knob Adjust while viewing the waveform.
Pattern selector Raster
Engine speed Curb idle speed
AKX00189
0.4 (V)
0.2
0
–0.2
–0.4 Voltage at
alternator
"B" terminal
Time
AG
AKX00190
Page 76 of 788
CHARGING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-12
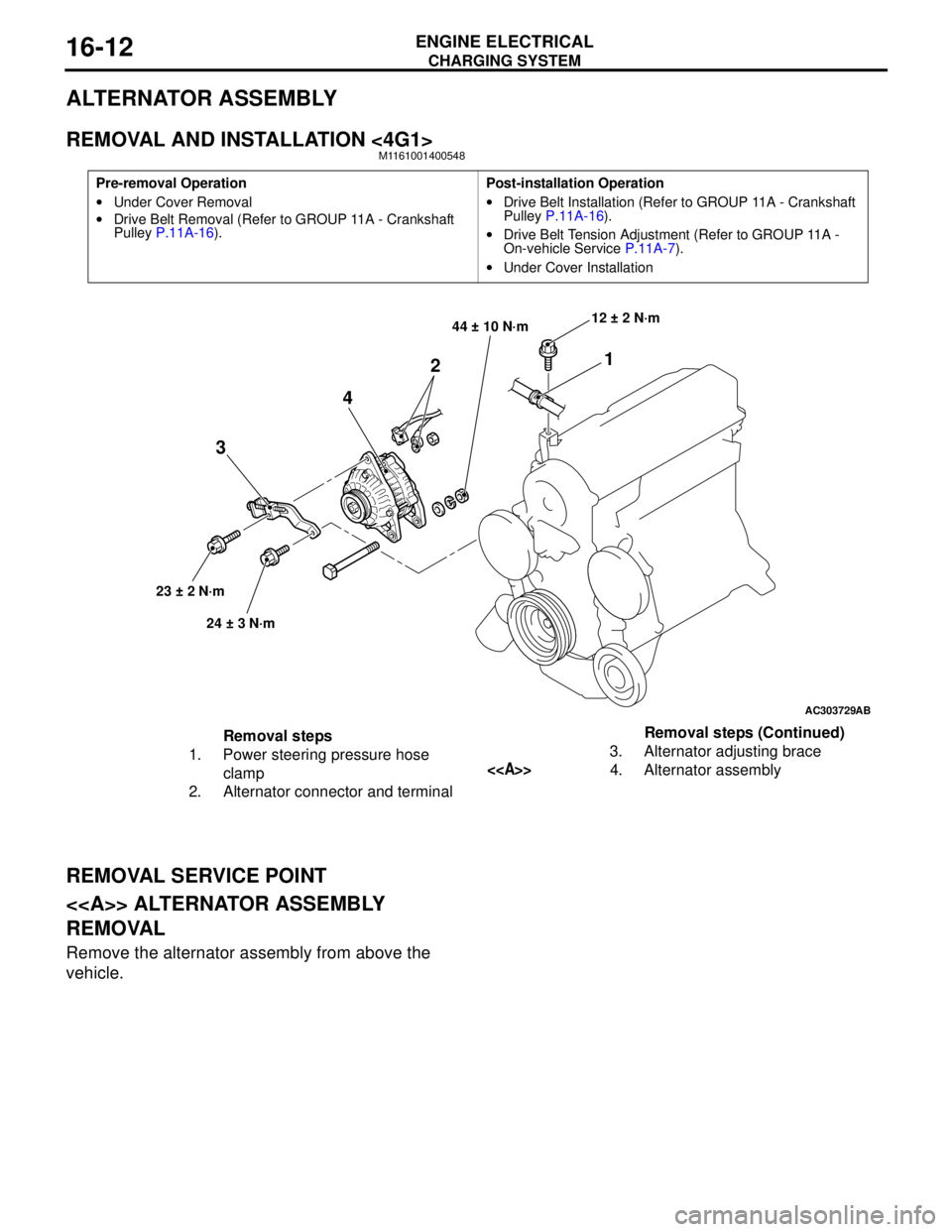
ALTERNATOR ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION <4G1>M1161001400548
REMOVAL SERVICE POINT
<> ALTERNATOR ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
Remove the alternator assembly from above the
vehicle.
Pre-removal Operation
•Under Cover Removal
•Drive Belt Removal (Refer to GROUP 11A - Crankshaft
Pulley P.11A-16).Post-installation Operation
•Drive Belt Installation (Refer to GROUP 11A - Crankshaft
Pulley P.11A-16).
•Drive Belt Tension Adjustment (Refer to GROUP 11A -
On-vehicle Service P.11A-7).
•Under Cover Installation
AC303729
1
2
4
3
44 ± 10 N·m
23 ± 2 N·m
24 ± 3 N·m12 ± 2 N·m
AB
Removal steps
1. Power steering pressure hose
clamp
2. Alternator connector and terminal3. Alternator adjusting brace
<>4. Alternator assemblyRemoval steps (Continued)
Page 78 of 788
Page 79 of 788
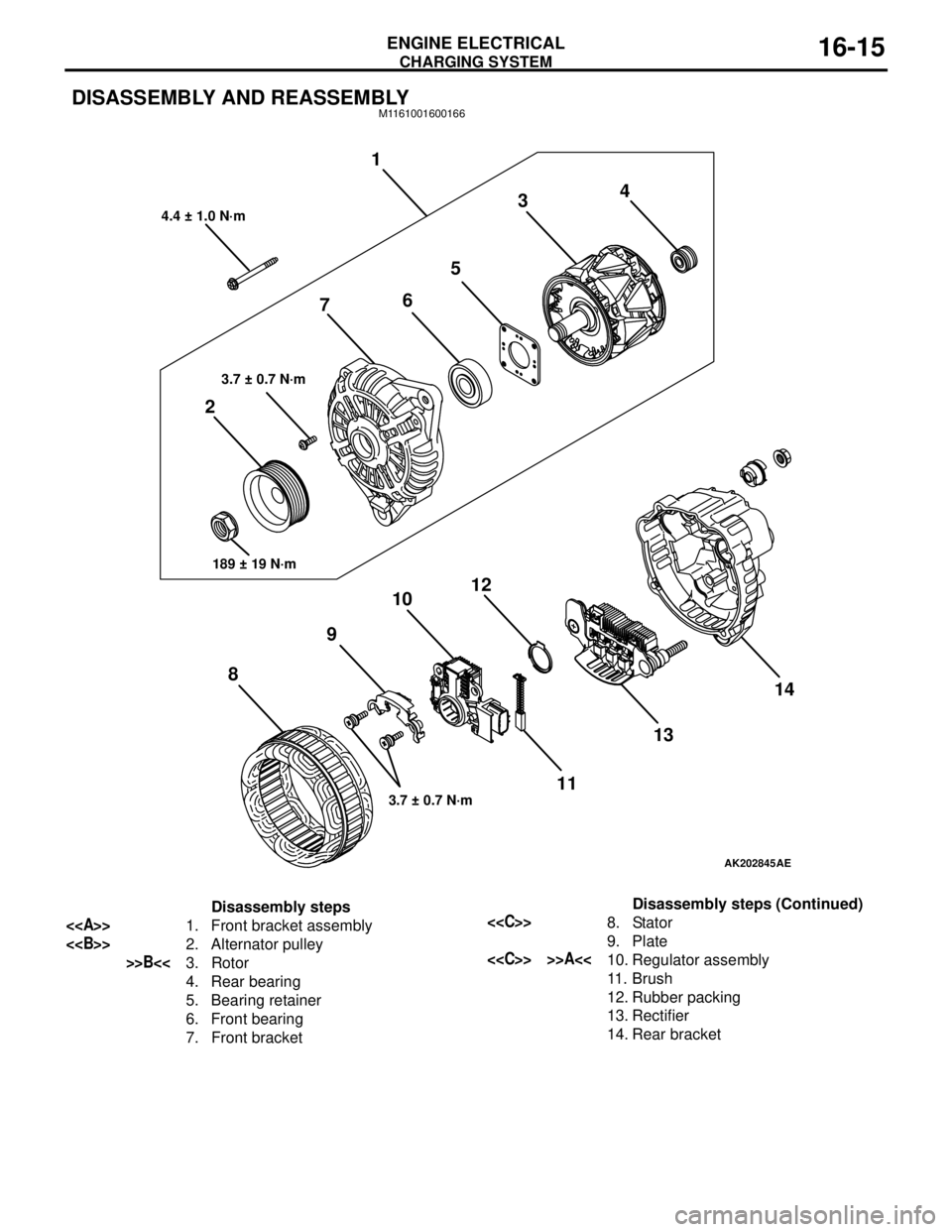
CHARGING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-15
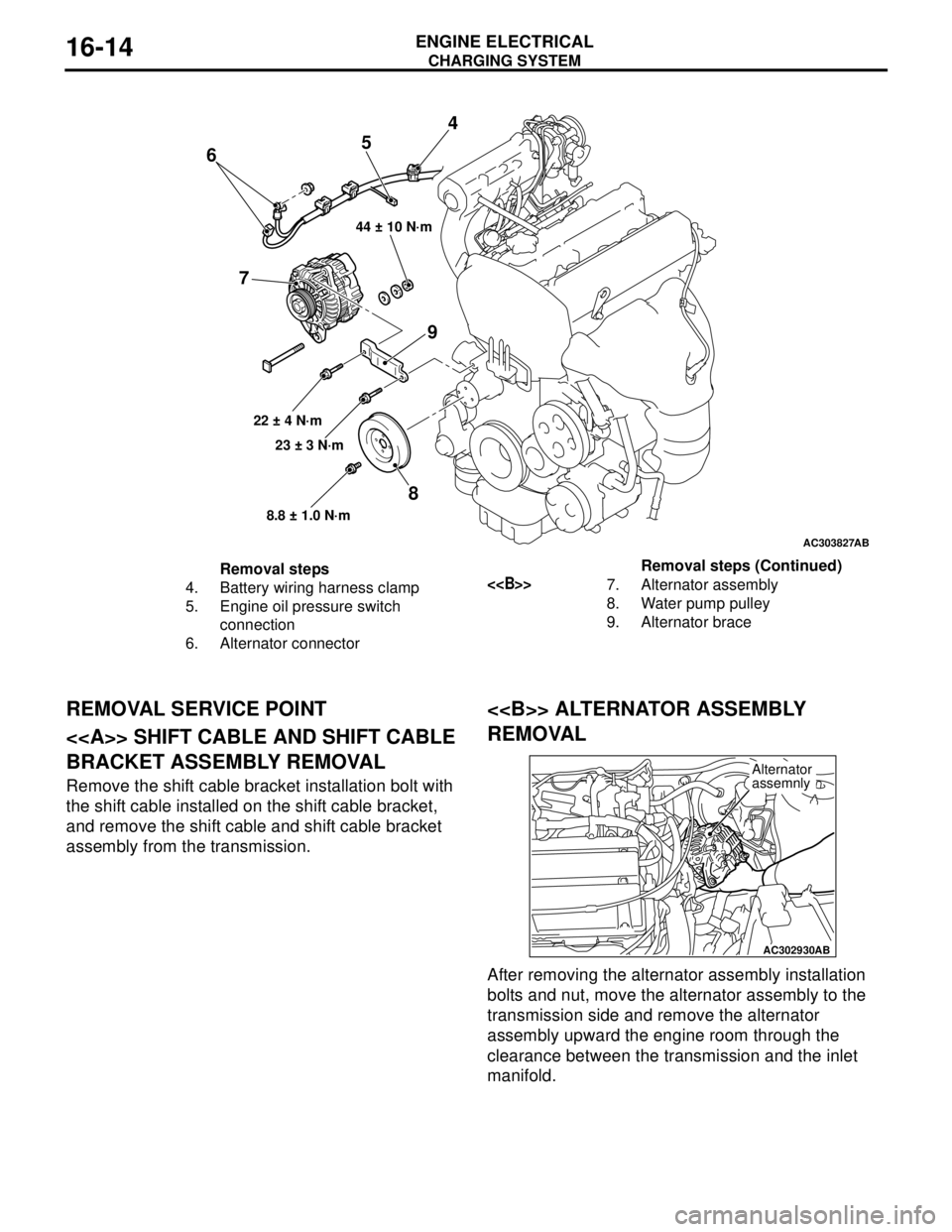
DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLYM1161001600166
AK202845
1
234
5
6
7
8910
11 12
1314
AE
4.4 ± 1.0 N·m
3.7 ± 0.7 N·m
189 ± 19 N·m
3.7 ± 0.7 N·m
Disassembly steps
<>1. Front bracket assembly
<>2. Alternator pulley
>>B<<3. Rotor
4. Rear bearing
5. Bearing retainer
6. Front bearing
7. Front bracket
<
9. Plate
<
11 . B r u s h
12. Rubber packing
13. Rectifier
14. Rear bracketDisassembly steps (Continued)
Page 80 of 788
Page 558 of 788

ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONER AND VENTILATION55-74
REFRIGERANT LEAK REPAIR
PROCEDURE
M1552001500277
LOST CHARGE
If the system has lost all charge due to a leak:
1. Evacuate the system (Refer to P.55-72).
2. Charge the system with approximately 480 − 520
g of refrigerant.
3. Check for leaks.
4. Discharge the system.
5. Repair leaks.
CAUTION
Replacement filter-drier units must be sealed
while in storage. The drier used in these units will
saturate water quickly upon exposure to the
atmosphere. When installing a drier, have all
tools and supplies ready for quick assembly to
avoid keeping the system open any longer than
necessary.
6. Replace receiver drier.
7. Evacuate and charge system.
LOW CHARGE
If the system has not lost all of its refrigerant charge;
locate and repair all leaks. If it is necessary to
increase the system pressure to find the leak
(because of an especially low charge) add
refrigerant. If it is possible to repair the leak without
discharging the refrigerant system, use the
procedure for correcting low refrigerant level.
HANDLING TUBING AND FITTINGS
Kinks in the refrigerant tubing or sharp bends in the
refrigerant hose lines will greatly reduce the capacity
of the entire system. High pressures are produced in
the system when it is operating. Extreme care must
be exercised to make sure that all connections are
pressure tight. Dirt and moisture can enter the
system when it is opened for repair or replacement of
lines or components. The following precautions must
be observed. The system must be completely
discharged before opening any fitting of connection
in the refrigeration system. Open fittings with caution
even after the system has been discharged. If any
pressure is noticed as a fitting is loosened, allow
trapped pressure to bleed off very slowly.
Never attempt to rebend formed lines to fit. Use the
correct line for the installation you are servicing. A
good rule for the flexible hose lines is keep the radius
of all bends at least 10 times the diameter of the
hose.Sharper bends will reduce the flow of refrigerant. The
flexible hose lines should be routed so that they are
at least 80 mm from the exhaust manifold. It is good
practice to inspect all flexible hose lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
On standard plumbing fittings with O-rings, these
O-rings are not reusable.
COMPRESSOR NOISE CHECKM1552008700272
You must first know the conditions when the noise
occurs. These conditions are: weather, vehicle
speed, in gear or neutral, engine temperature or any
other special conditions.
Noises that develop during A/C operation can often
be misleading. For example: what sounds like a
failed front bearing or connecting rod, may be
caused by loose bolts, nuts, mounting brackets, or a
loose clutch assembly. Verify accessory drive belt
tension (power steering or alternator).
Improper accessory drive belt tension can cause a
misleading noise when the compressor is engaged
and little or no noise when the compressor is
disengaged.
Drive belts are speed-sensitive. That is, at different
engine speeds, and depending upon belt tension,
belts can develop unusual noises that are often
mistaken for mechanical problems within the
compressor.
ADJUSTMENT
1. Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate
conditions as much as possible. Switch the
compressor on and off several times to clearly
identify compressor noise. To duplicate high
ambient conditions (high head pressure), restrict
air flow through the condenser. Install a manifold
gauge set to make sure discharge pressure
doesn't exceed 2,070 kPa.
2. Tighten all compressor mounting bolts, clutch
mounting bolt, and compressor drive belt. Check
to assure clutch coil is tight (no rotation or
wobble).
3. Check refrigerant hoses for rubbing or
interference that can cause unusual noises.
4. Check refrigerant charge (Refer to P.55-69).
5. Recheck compressor noise as in Step 1.
6. If noise still exists, loosen compressor mounting
bolts and retighten. Repeat Step 1.
7. If noise continues, replace compressor and repeat
Step 1.
Page 576 of 788
Page 593 of 788
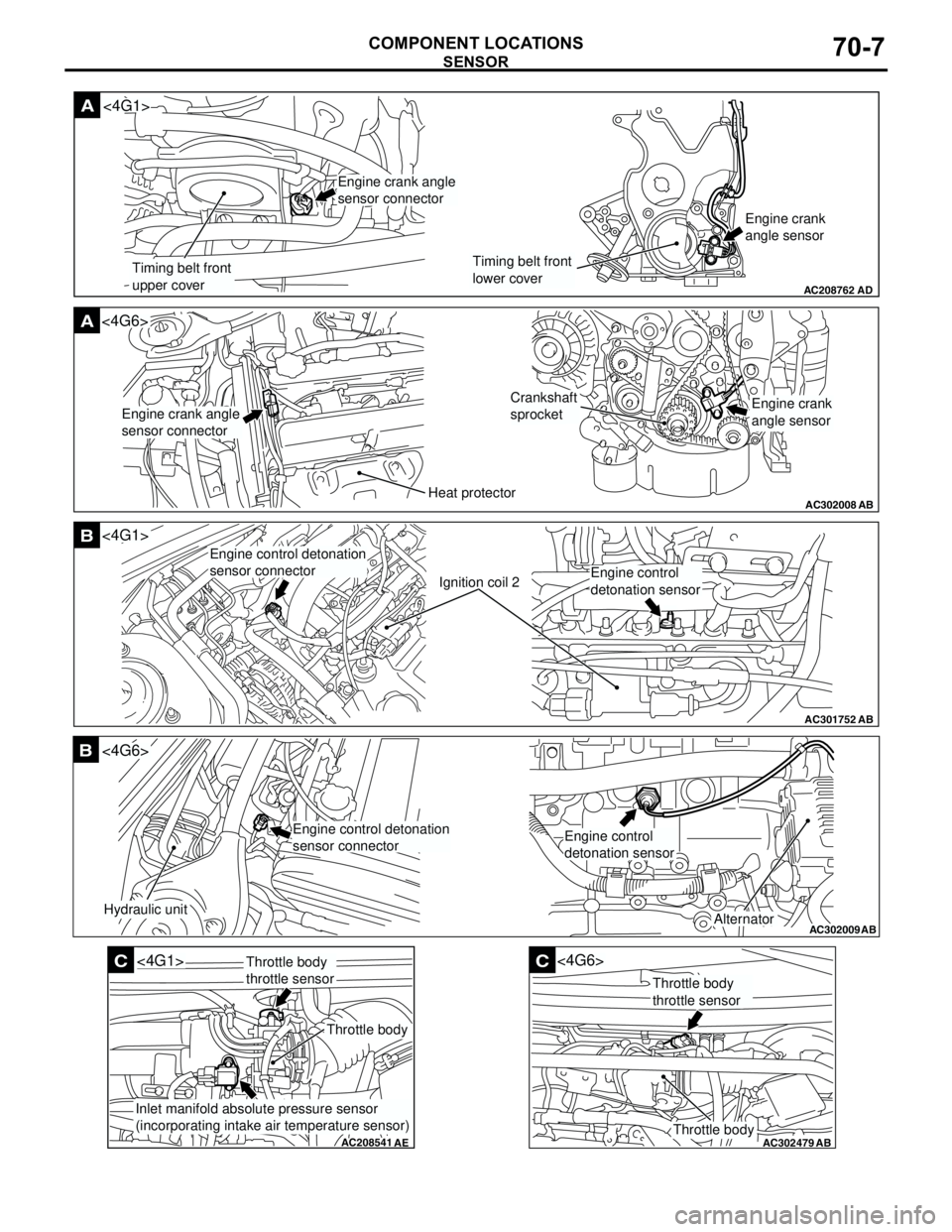
SENSOR
COMPONENT LOCATIONS70-7
AC208762
A
AD
Timing belt front
upper coverTiming belt front
lower coverEngine crank
angle sensor
<4G1>
Engine crank angle
sensor connector
AC302008
A<4G6>
ABHeat protector
Crankshaft
sprocket
Engine crank angle
sensor connectorEngine crank
angle sensor
AC301752
B
AB
Ignition coil 2
<4G1>
Engine control detonation
sensor connector
Engine control
detonation sensor
AC302009
B
AB
Hydraulic unit
<4G6>
Alternator
Engine control detonation
sensor connectorEngine control
detonation sensor
AC208541
C
AE
<4G1>
Throttle body
Throttle body
throttle sensor
Inlet manifold absolute pressure sensor
(incorporating intake air temperature sensor)
AC302479
AB
C
Throttle body
<4G6>
Throttle body
throttle sensor
Page 614 of 788
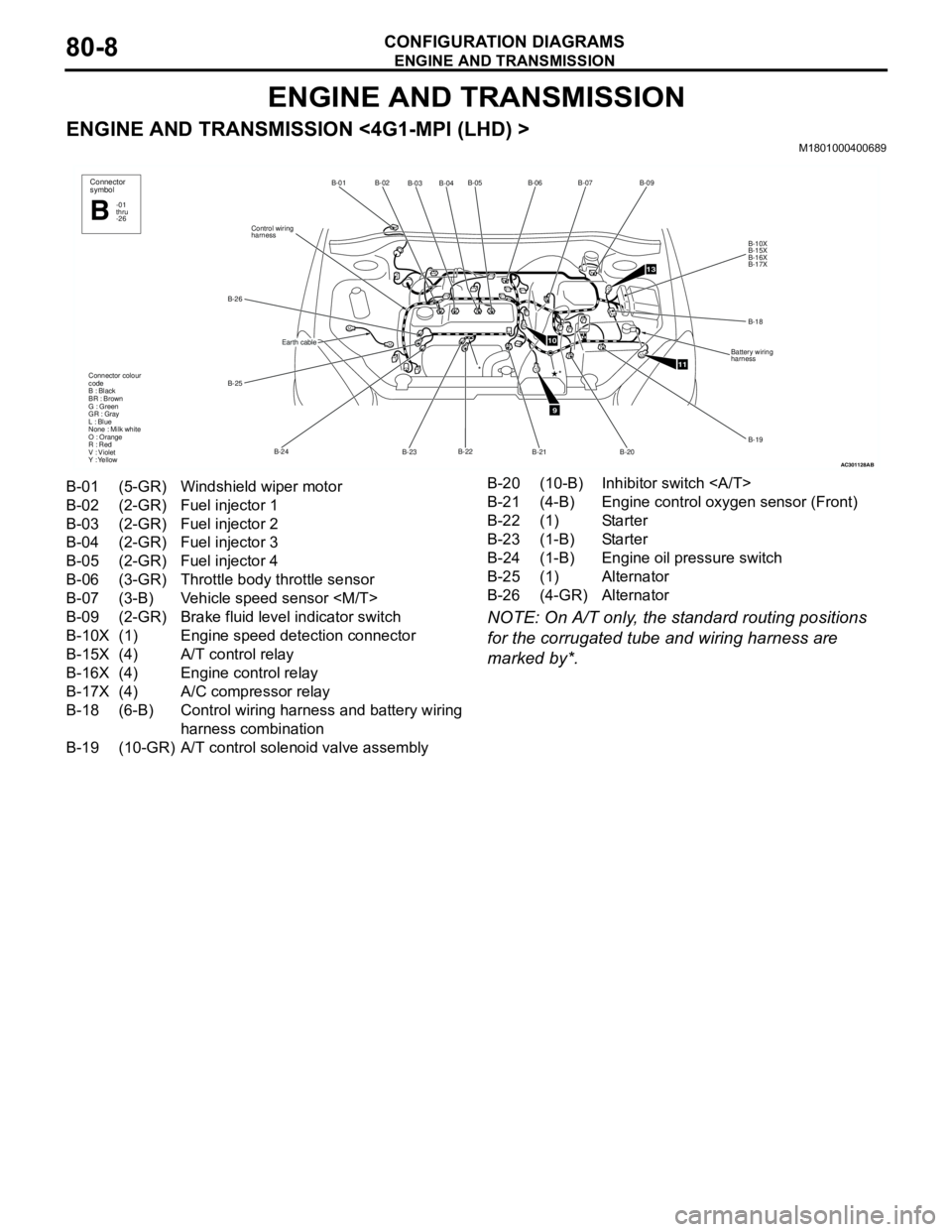
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION
CONFIGURATION DIAGRAMS80-8
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION <4G1-MPI (LHD) >M1801000400689
NOTE: On A/T only, the standard routing positions
for the corrugated tube and wiring harness are
marked by*.
AC301128
B-02
B-03B-04B-05
B-22
B-23 B-24 B-25 B-26Control wiring
harnessB-01
Connector colour
code
B : Black
BR : Brown
G : Green
GR : Gray
L : Blue
None : Milk white
O : Orange
R : Red
V : Violet
Y : Yellow*
Connector
symbol
-01
thru
-26B
Earth cable
AB
9
10
11
13
B-06B-07
B-09
B-10X
B-15X
B-16X
B-17X
B-18
Battery wiring
harness
B-19
B-20
B-21
*
B-01 (5-GR) Windshield wiper motor
B-02 (2-GR) Fuel injector 1
B-03 (2-GR) Fuel injector 2
B-04 (2-GR) Fuel injector 3
B-05 (2-GR) Fuel injector 4
B-06 (3-GR) Throttle body throttle sensor
B-07 (3-B) Vehicle speed sensor
B-09 (2-GR) Brake fluid level indicator switch
B-10X (1) Engine speed detection connector
B-15X (4) A/T control relay
B-16X (4) Engine control relay
B-17X (4) A/C compressor relay
B-18 (6-B) Control wiring harness and battery wiring
harness combination
B-19 (10-GR) A/T control solenoid valve assemblyB-20 (10-B) Inhibitor switch
B-21 (4-B) Engine control oxygen sensor (Front)
B-22 (1) Starter
B-23 (1-B) Starter
B-24 (1-B) Engine oil pressure switch
B-25 (1) Alternator
B-26 (4-GR) Alternator