check engine MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007Pages: 1449, PDF Size: 56.82 MB
Page 644 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-112
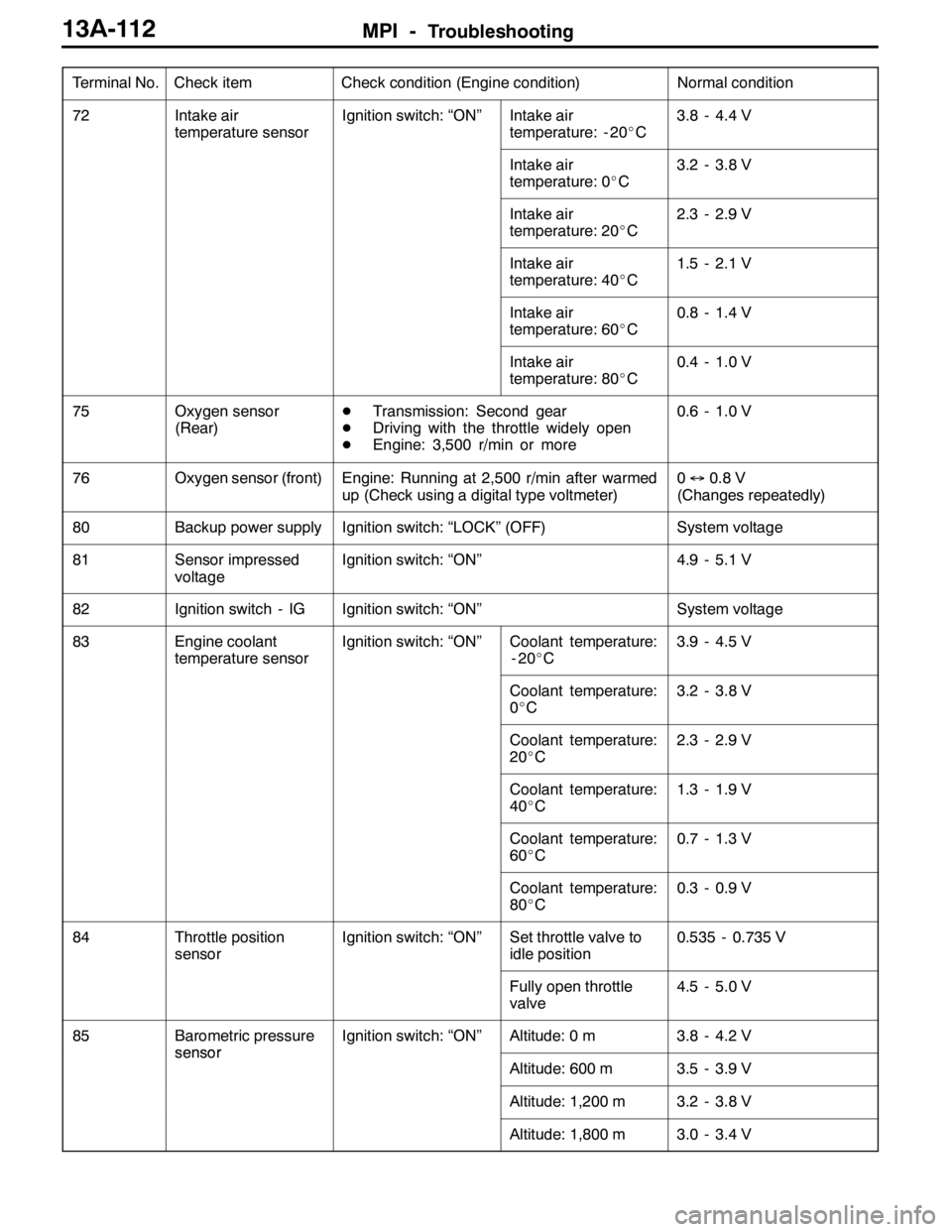
Terminal No.Normal condition Check condition (Engine condition) Check item
72Intake air
temperature sensorIgnition switch: “ON”Intake air
temperature: - 20_C3.8 - 4.4 V
Intake air
temperature: 0_C3.2 - 3.8 V
Intake air
temperature: 20_C2.3 - 2.9 V
Intake air
temperature: 40_C1.5 - 2.1 V
Intake air
temperature: 60_C0.8 - 1.4 V
Intake air
temperature: 80_C0.4 - 1.0 V
75Oxygen sensor
(Rear)DTransmission: Second gear
DDriving with the throttle widely open
DEngine: 3,500 r/min or more0.6 - 1.0 V
76Oxygen sensor (front)Engine: Running at 2,500 r/min after warmed
up (Check using a digital type voltmeter)0↔0.8 V
(Changes repeatedly)
80Backup power supplyIgnition switch: “LOCK” (OFF)System voltage
81Sensor impressed
voltageIgnition switch: “ON”4.9 - 5.1 V
82Ignition switch - IGIgnition switch: “ON”System voltage
83Engine coolant
temperature sensorIgnition switch: “ON”Coolant temperature:
-20_C3.9 - 4.5 V
Coolant temperature:
0_C3.2 - 3.8 V
Coolant temperature:
20_C2.3 - 2.9 V
Coolant temperature:
40_C1.3 - 1.9 V
Coolant temperature:
60_C0.7 - 1.3 V
Coolant temperature:
80_C0.3 - 0.9 V
84Throttle position
sensorIgnition switch: “ON”Set throttle valve to
idle position0.535 - 0.735 V
Fully open throttle
valve4.5 - 5.0 V
85Barometric pressure
sensor
Ignition switch: “ON”Altitude: 0 m3.8 - 4.2 V
sensor
Altitude: 600 m3.5 - 3.9 V
Altitude: 1,200 m3.2 - 3.8 V
Altitude: 1,800 m3.0 - 3.4 V
Page 645 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-113
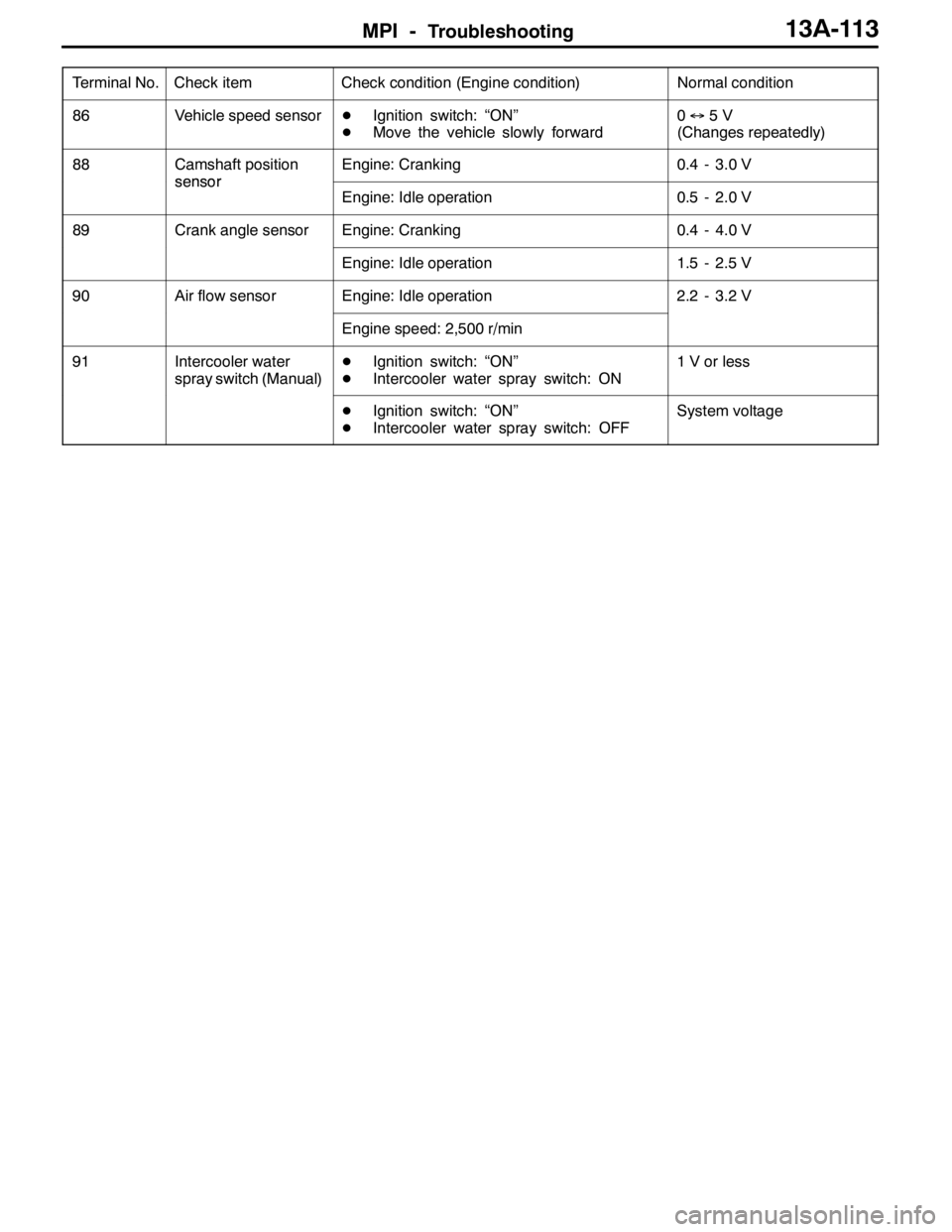
Terminal No.Normal condition Check condition (Engine condition) Check item
86Vehicle speed sensorDIgnition switch: “ON”
DMove the vehicle slowly forward0↔5V
(Changes repeatedly)
88Camshaft position
sensor
Engine: Cranking0.4 - 3.0 V
sensor
Engine: Idle operation0.5 - 2.0 V
89Crank angle sensorEngine: Cranking0.4 - 4.0 V
Engine: Idle operation1.5 - 2.5 V
90Air flow sensorEngine: Idle operation2.2 - 3.2 V
Engine speed: 2,500 r/min
91Intercooler water
spray switch (Manual)DIgnition switch: “ON”
DIntercooler water spray switch: ON1 V or less
DIgnition switch: “ON”
DIntercooler water spray switch: OFFSystem voltage
Page 646 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-114
CHECK CHART FOR RESISTANCE AND CONTINUITY
BETWEEN TERMINALS
1. Turn the ignition switch to “LOCK” (OFF) position.
2. Disconnect the engine-ECU connector.
3. Measure the resistance and check for continuity between
the terminals of the engine-ECU harness-side connector
while referring to the check chart.
NOTE
(1) When measuring resistance and checking continuity,
a harness for checking contact pin pressure should
be used instead of inserting a test probe.
(2) Checking need not be carried out in the order given
in the chart.
Caution
If the terminals that should be checked are mistaken,
or if connector terminals are not correctly shorted
to earth, damage may be caused to the vehicle wiring,
sensors, engine-ECU and/or ohmmeter.
Be careful to prevent this!
4. If the ohmmeter shows any deviation from the standard
value, check the corresponding sensor, actuator and
related electrical wiring, and then repair or replace.
5. After repair or replacement, recheck with the ohmmeter
to confirm that the repair or replacement has corrected
the problem.
Engine-ECU Harness Side Connector Terminal Arrangement
Terminal No.Inspection itemNormal condition (Check condition)
1-12No. 1 injector2-3Ω(at 20_C)
14 - 12No. 2 injector
2-12No. 3 injector
15 - 12No. 4 injector
Page 647 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-115
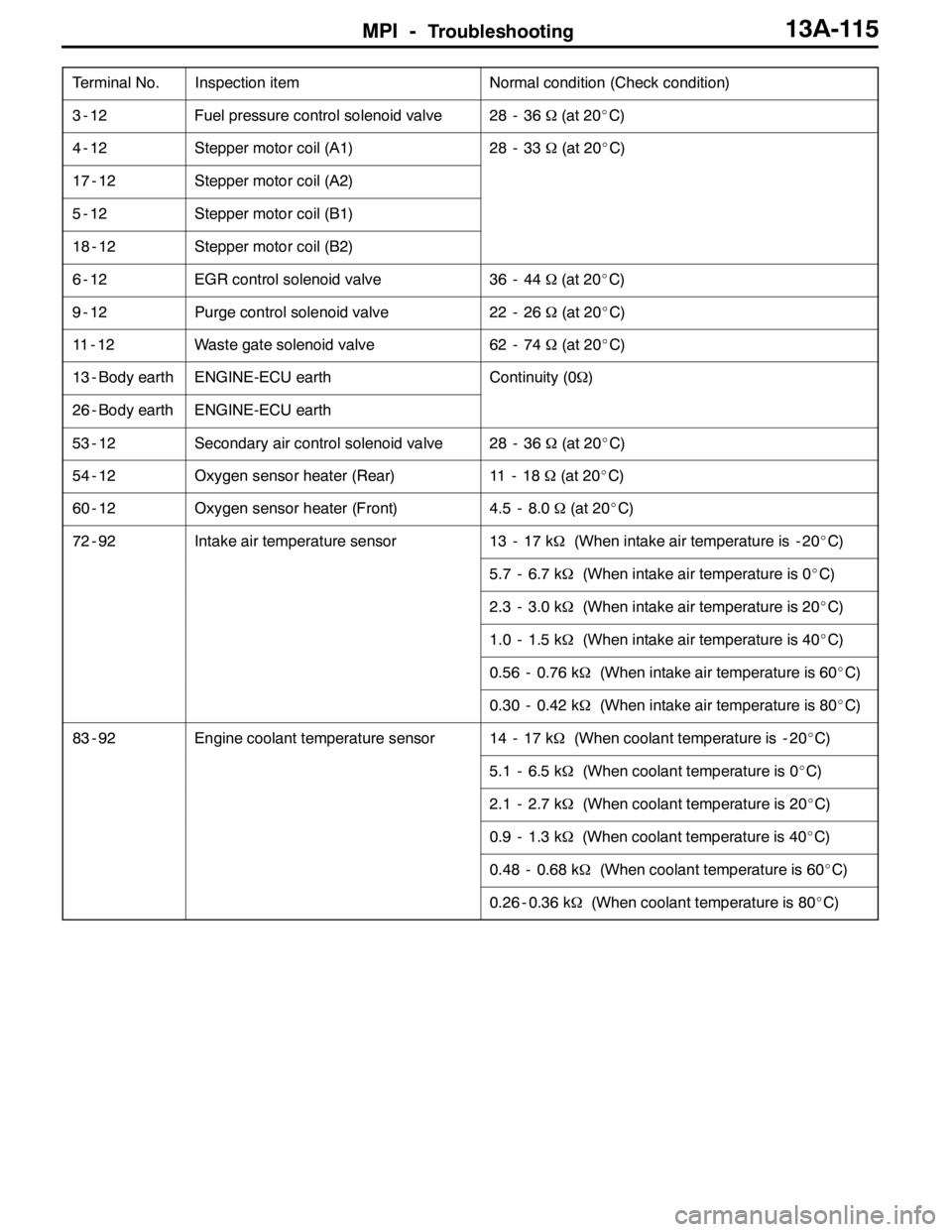
Terminal No. Normal condition (Check condition)Inspection item
3-12Fuel pressure control solenoid valve28 - 36Ω(at 20_C)
4-12Stepper motor coil (A1)28 - 33Ω(at 20_C)
17 - 12Stepper motor coil (A2)
5-12Stepper motor coil (B1)
18 - 12Stepper motor coil (B2)
6-12EGR control solenoid valve36 - 44Ω(at 20_C)
9-12Purge control solenoid valve22 - 26Ω(at 20_C)
11 - 1 2Waste gate solenoid valve62 - 74Ω(at 20_C)
13 - Body earthENGINE-ECU earthContinuity (0Ω)
26 - Body earthENGINE-ECU earth
53 - 12Secondary air control solenoid valve28 - 36Ω(at 20_C)
54 - 12Oxygen sensor heater (Rear)11 - 1 8Ω(at 20_C)
60 - 12Oxygen sensor heater (Front)4.5 - 8.0Ω(at 20_C)
72 - 92Intake air temperature sensor13 - 17 kΩ(When intake air temperature is - 20_C)
5.7 - 6.7 kΩ(When intake air temperature is 0_C)
2.3 - 3.0 kΩ(When intake air temperature is 20_C)
1.0 - 1.5 kΩ(When intake air temperature is 40_C)
0.56 - 0.76 kΩ(When intake air temperature is 60_C)
0.30 - 0.42 kΩ(When intake air temperature is 80_C)
83 - 92Engine coolant temperature sensor14 - 17 kΩ(When coolant temperature is - 20_C)
5.1 - 6.5 kΩ(When coolant temperature is 0_C)
2.1 - 2.7 kΩ(When coolant temperature is 20_C)
0.9 - 1.3 kΩ(When coolant temperature is 40_C)
0.48 - 0.68 kΩ(When coolant temperature is 60_C)
0.26 - 0.36 kΩ(When coolant temperature is 80_C)
Page 648 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-116
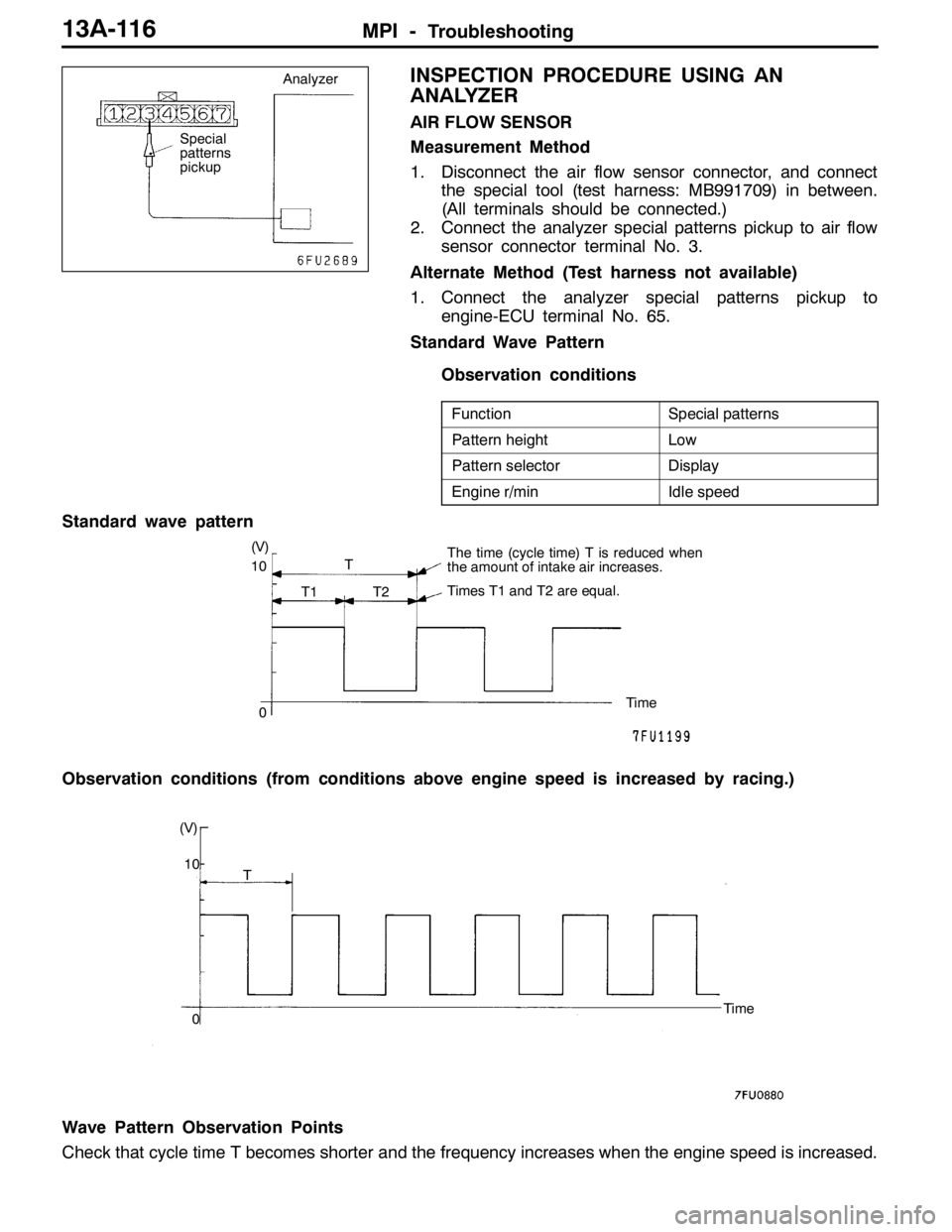
INSPECTION PROCEDURE USING AN
ANALYZER
AIR FLOW SENSOR
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the air flow sensor connector, and connect
the special tool (test harness: MB991709) in between.
(All terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to air flow
sensor connector terminal No. 3.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 65.
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation conditions
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightLow
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minIdle speed
Standard wave pattern
(V)
10
0The time (cycle time) T is reduced when
the amount of intake air increases.
Times T1 and T2 are equal.
Time T
T1 T2
Observation conditions (from conditions above engine speed is increased by racing.)
Time (V)
10
0T
Wave Pattern Observation Points
Check that cycle time T becomes shorter and the frequency increases when the engine speed is increased.
Analyzer
Special
patterns
pickup
Page 649 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-117
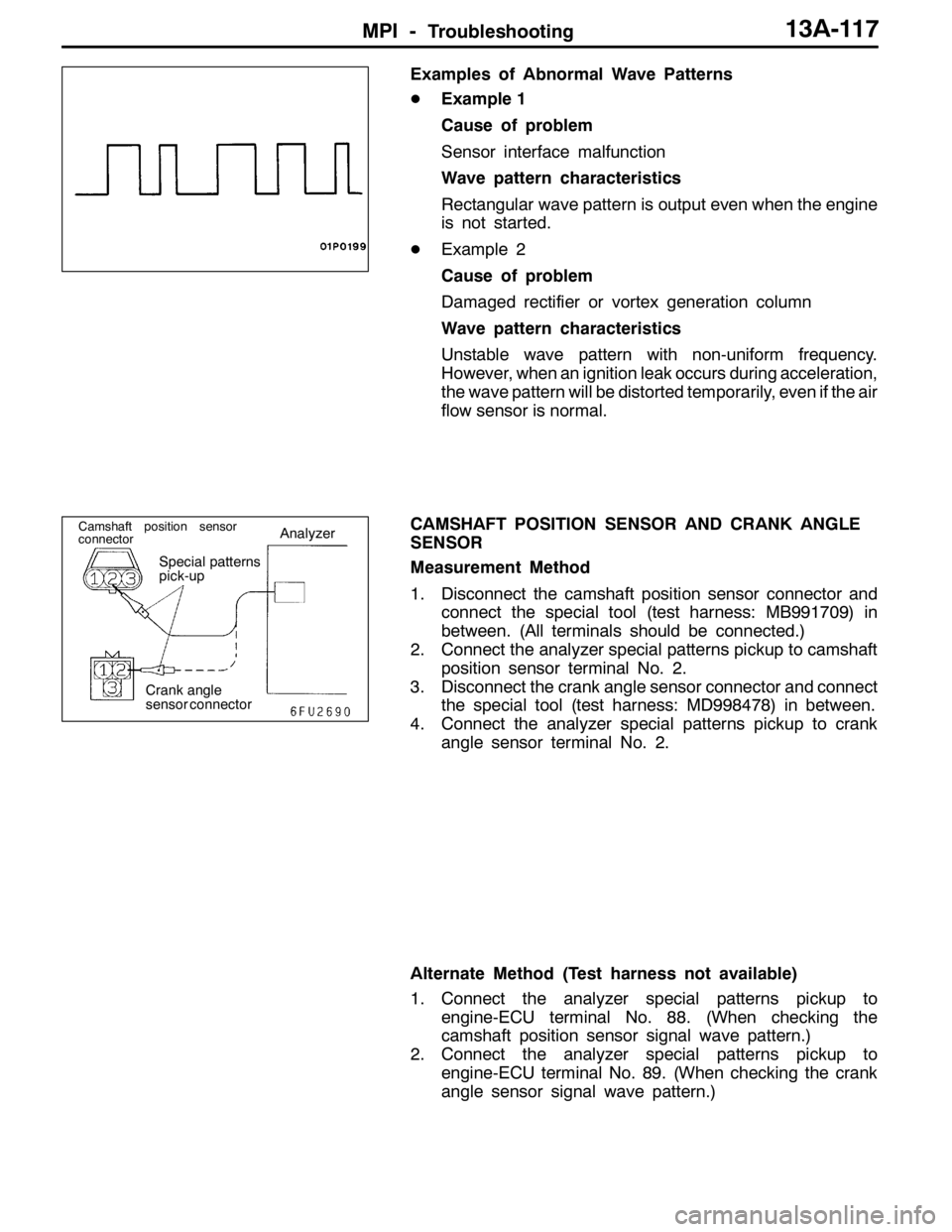
Examples of Abnormal Wave Patterns
DExample 1
Cause of problem
Sensor interface malfunction
Wave pattern characteristics
Rectangular wave pattern is output even when the engine
is not started.
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Damaged rectifier or vortex generation column
Wave pattern characteristics
Unstable wave pattern with non-uniform frequency.
However, when an ignition leak occurs during acceleration,
the wave pattern will be distorted temporarily, even if the air
flow sensor is normal.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR AND CRANK ANGLE
SENSOR
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the camshaft position sensor connector and
connect the special tool (test harness: MB991709) in
between. (All terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to camshaft
position sensor terminal No. 2.
3. Disconnect the crank angle sensor connector and connect
the special tool (test harness: MD998478) in between.
4. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to crank
angle sensor terminal No. 2.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 88. (When checking the
camshaft position sensor signal wave pattern.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 89. (When checking the crank
angle sensor signal wave pattern.)
Crank angle
sensor connector
Camshaft position sensor
connectorAnalyzer
Special patterns
pick-up
Page 650 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-118
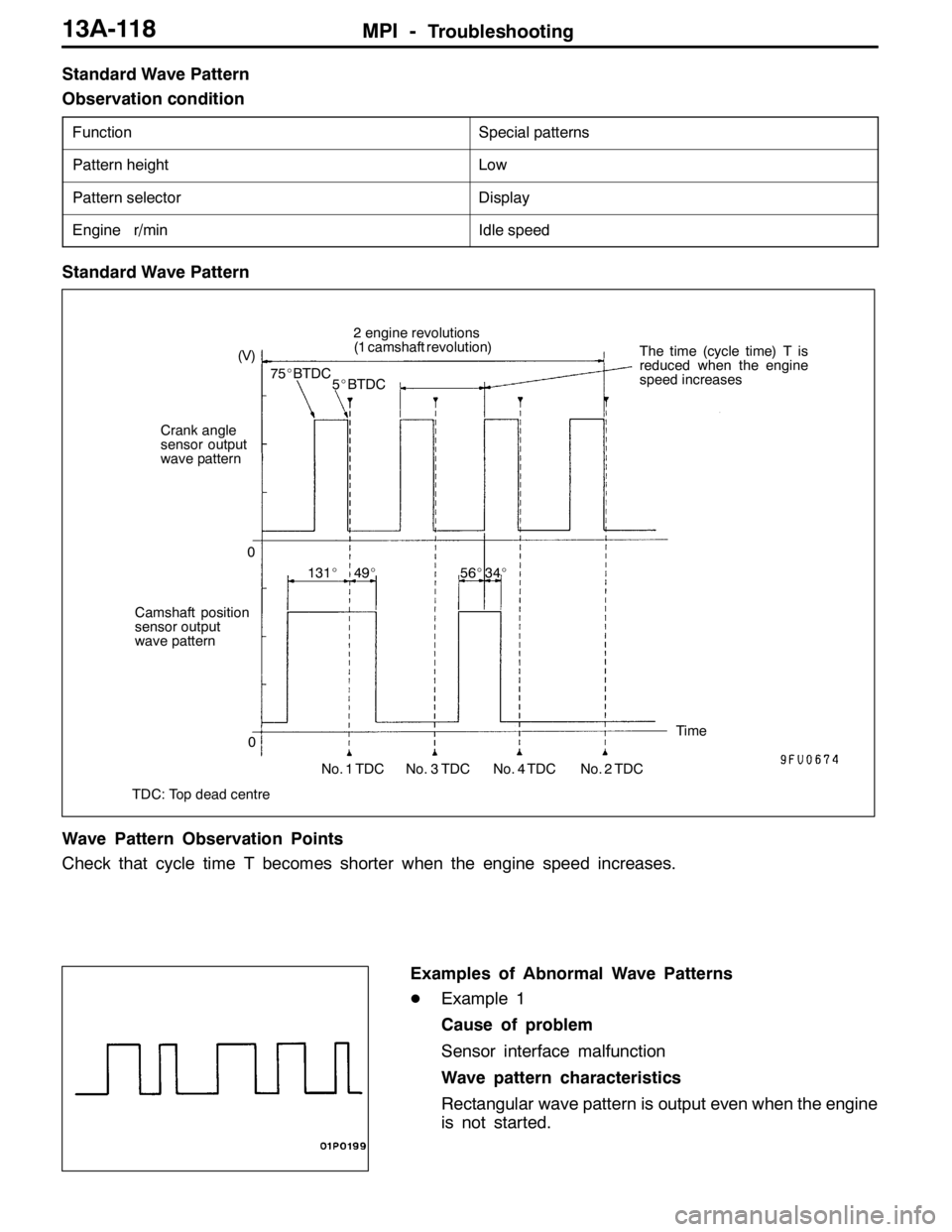
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation condition
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightLow
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minIdle speed
Standard Wave Pattern
Crank angle
sensor output
wave pattern(V)
75_BTDC2 engine revolutions
(1 camshaft revolution)
5_BTDCThe time (cycle time) T is
reduced when the engine
speed increases
0
Camshaft position
sensor output
wave pattern
TDC: Top dead centre131_49_
No. 1 TDC No. 3 TDC No. 4 TDC No. 2 TDCTime
056_34_
Wave Pattern Observation Points
Check that cycle time T becomes shorter when the engine speed increases.
Examples of Abnormal Wave Patterns
DExample 1
Cause of problem
Sensor interface malfunction
Wave pattern characteristics
Rectangular wave pattern is output even when the engine
is not started.
Page 651 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-119
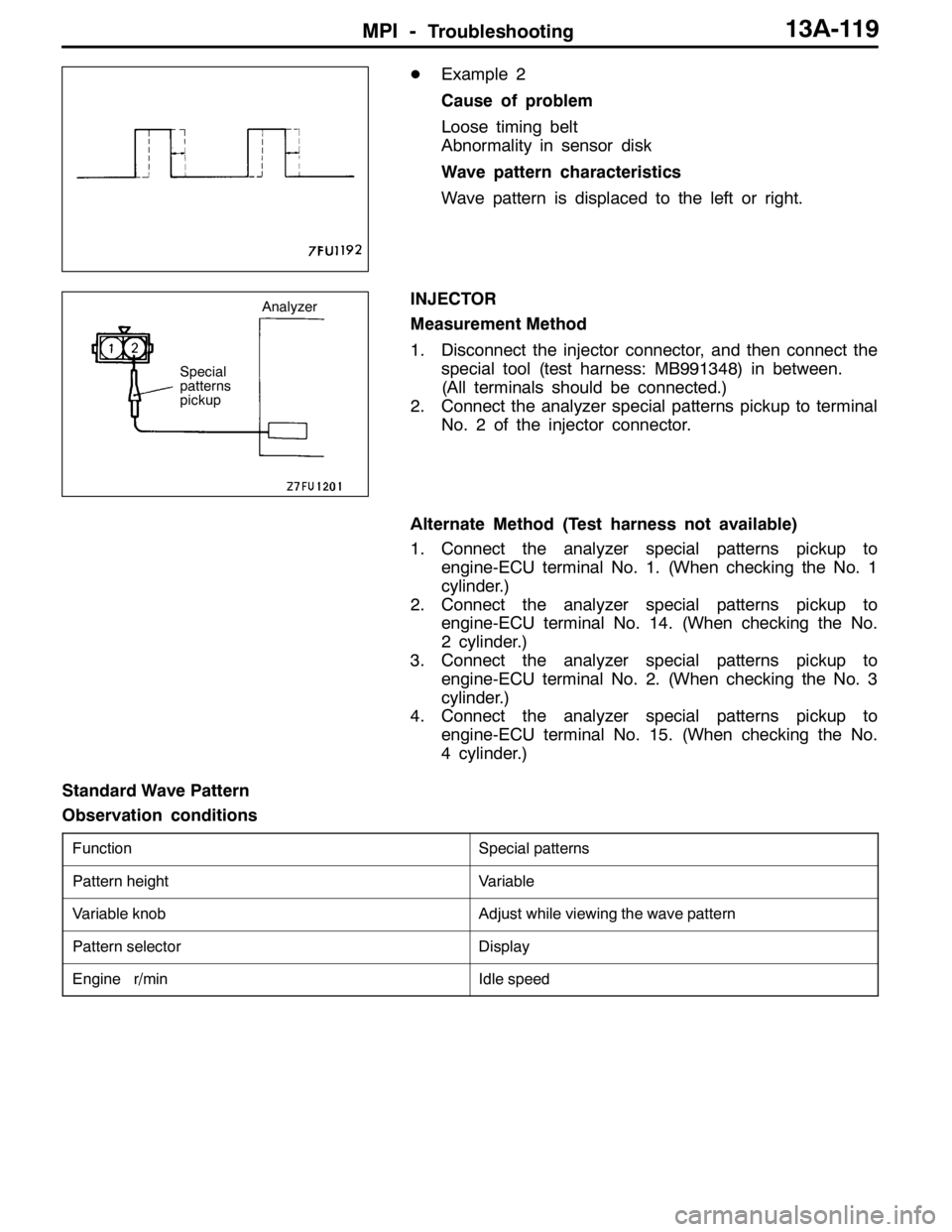
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Loose timing belt
Abnormality in sensor disk
Wave pattern characteristics
Wave pattern is displaced to the left or right.
INJECTOR
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the injector connector, and then connect the
special tool (test harness: MB991348) in between.
(All terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to terminal
No. 2 of the injector connector.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 1. (When checking the No. 1
cylinder.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 14. (When checking the No.
2 cylinder.)
3. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 2. (When checking the No. 3
cylinder.)
4. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 15. (When checking the No.
4 cylinder.)
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation conditions
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightVariable
Variable knobAdjust while viewing the wave pattern
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minIdle speed
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 654 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-122
Wave Pattern Observation Points
Check that the standard wave pattern appears when the stepper motor is operating.
Point A: Presence or absence of induced electromotive force from the motor turning. (Refer to the abnormal
wave pattern.)
Contrast with standard wave patternProbable cause
Induced electromotive force does not appear or is extremely small.Motor is malfunctioning
Point B: Height of coil reverse electromotive force
Contrast with standard wave patternProbable cause
Coil reverse electromotive force does not appear or is extremely small.Short in the coil
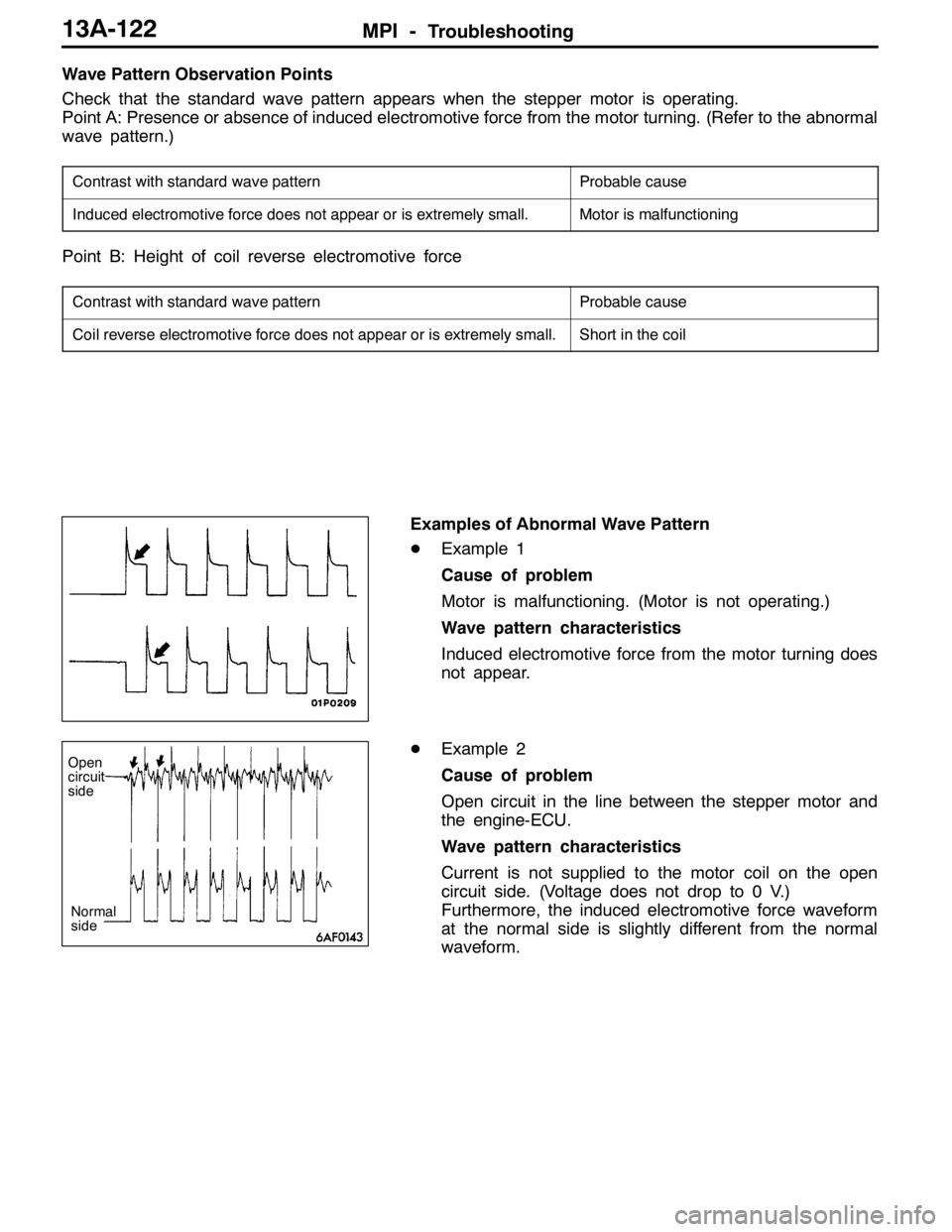
Examples of Abnormal Wave Pattern
DExample 1
Cause of problem
Motor is malfunctioning. (Motor is not operating.)
Wave pattern characteristics
Induced electromotive force from the motor turning does
not appear.
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Open circuit in the line between the stepper motor and
the engine-ECU.
Wave pattern characteristics
Current is not supplied to the motor coil on the open
circuit side. (Voltage does not drop to 0 V.)
Furthermore, the induced electromotive force waveform
at the normal side is slightly different from the normal
waveform.
Open
circuit
side
Normal
side
Page 657 of 1449

MPI -On-vehicle Service13A-125
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
FUEL PUMP CONNECTOR DISCONNECTION
(HOW TO REDUCE THE FUEL PRESSURE)
When removing the fuel pipe, hose, etc., since fuel pressure
in the fuel pipe line is high, do the following operation so
as to release the fuel pressure in the line and prevent fuel
from running out.
1. Remove the rear seat assembly. (Refer to GROUP 52A.)
2. Remove the protector.
3. Disconnect the fuel pump module connector.
4. After starting the engine and letting it run until it stops
naturally, turn the ignition switch to “LOOK” (OFF) position.
5. Connect the fuel pump module connector.
6. Install the protector and rear seat assembly.
(Refer to GROUP 52A.)
FUEL PUMP OPERATION CHECK
1. Check the operation of the fuel pump by using the MUT-II
to force-drive the fuel pump.
2. If the fuel pump will not operate, check by using the
following procedure, and if it is normal, check the drive
circuit.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to “LOOK” (OFF) position.
(2) Remove the rear seat assembly. (Refer to GROUP
52A.)
(3) Remove the protector.
(4) Disconnect the fuel pump module connector.
(5) When the fuel pump drive connector is attached
directly to the battery, check if the sound of the fuel
pump operation can be heard.
NOTE
As the fuel pump is an in-tank type, the fuel pump
sound is hard to hear, so remove the fuel filler cap
and check from the tank inlet.
(6) Check the fuel pressure by pinching the fuel hose
with the fingertips.
(7) Connect the fuel pump module connector.
(8) Install the protector and rear seat assembly. (Refer
to GROUP 52A.)