compression ratio MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007Pages: 1449, PDF Size: 56.82 MB
Page 600 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-68
Inspection Procedure 11
Pulsation (Hesitation, sag), poor acceleration, stumbling,
surging
Probable cause
Causes shown on right are suspected.DAir/fuel ratio control system malfunction
DIgnition system malfunction
DFuel system malfunction
DIntake and exhaust system malfunction
DExhaust gas purifier system malfunction
DImproper compression pressure
DTurbocharger system malfunction
OK
To the next page
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 59: Oxygen sensor (rear) (Refer to P.13A-105.)
(Refer to P.13A-27.)
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 11: Oxygen sensor (front) (Refer to P.13A-102.)NGCheck the Code No. P0130: Oxygen sensor (front) system.
(Refer to P.13A-24.)
OK
Check the EGR valve for sticking.
(Refer to GROUP 17 - Exhaust Gas Purifier Check.)NGReplace the EGR valve.
OK
Check the EGR control solenoid valve.
(Refer to GROUP 17 - Exhaust Gas Purifier Check.)NGReplace the EGR control solenoid valve.
OK
Check the purge control solenoid valve.
(Refer to GROUP 17 - Exhaust Gas Purifier Check.)NGReplace the purge control solenoid valve.
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 13: Intake air temperature sensor
DNo. 14: Throttle position sensor
DNo. 21: Engine coolant temperature sensor
DNo. 25: Barometric pressure sensor
(Refer to P.13A-102.)
Proceed to OK if all service data values are correct.
Proceed to NG if there is even one abnormal service data value.NGRefer to inspections for diagnosis code of sensor showing
abnormal service data. (Refer to P.13A-12.)
OK
Check the injector operation sound. (Use sound scope.)NGCheck the Code No. P0201 - 204: Injector system for faulty
cylinder.
NO
Check the ignition timing.
(Refer to GROUP 11 - Engine Adjustment.)NGCheck mounting state of crank angle sensor and timing belt cover.
MUT-IISelf-Diag code
DIs a diagnosis code output?YESINSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSIS CODE
(Refer to P.13A-12.)
Page 607 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-75
Inspection Procedure 17
Abnormal odor, white smoke, black smoke, high CO or HC
concentration when idling
Probable cause
Causes shown on right are suspected.DAir/fuel ratio control system malfunction
DIgnition system malfunction
DFuel system malfunction
DIntake and exhaust system malfunction
DExhaust gas purifier system malfunction
DImproper compression pressure
DCatalyst defect
DEngine-ECU malfunction
OK
To the next page
OK
Check the fuel pressure. (Refer to P.13A-128.)
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 59: Oxygen sensor (rear)
(Refer to P.13A-105.)NGCheck the Code No. P0136: Oxygen sensor (rear) system.
(Refer to P.13A-27.)
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 11: Oxygen sensor (front) (Refer to P.13A-102.)NGCheck the Code No. P0130: Oxygen sensor (front) system.
(Refer to P.13A-24.)
OK
Check for exhaust gas leaks from exhaust manifold.NG
Repair
OK
Check the air intake from the intake hose and intake manifold.NG
Repair
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 12: Air flow sensor
DNo. 13: Intake air temperature sensor
DNo. 21: Engien coolant temperature sensor
DNo. 25: Barometric pressure sensor
(Refer to P.13A-102.)
Proceed to OK if all service data values are correct.
Proceed to NG if there is even one abnormal service data value.NGRefer to inspections for diagnosis code of sensor showing
abnormal service data. (Refer to P.13A-102.)
OK
Check the ignition timing.
(Refer to GROUP 11 - Engine Adjustment.)NGCheck the Inspection Procedure 15: Deviation of ignition interval
(Refer to P.13A-73.)
NO
MUT-IIActuator test
DNo. 01: No. 1 injector
DNo. 02: No. 2 injector
DNo. 03: No. 3 injector
DNo. 04: No. 4 injector
OK:The idling state changes.
DProceed to NG if the cylinder (NG cylinder) for which the idling
state did not change when injector was stopped is pinpointed.
DProceed to OK if all cylinders are OK, or if the NG cylinder
cannot be pinpointed.NGCheck the Code No. P0201: No. 1 injector system, P0202: No. 2
injector system, P0203: No. 3 injector system and P0204: No. 4
injector system. (Refer to P.13A-30, 31, 32, 33.)
MUT-IISelf-Diag code
DIs a diagnosis code output?YESINSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSIS CODE
(Refer to P.13A-12.)
Page 758 of 1449
ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Ignition System16-26
IGNITION SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
This system is equipped with two ignition coils (A
and B) with built-in power transistors for the No.
1 and No. 4 cylinders and the No. 2 and No. 3
cylinders respectively.
Interruption of the primary current flowing in the
primary side of ignition coil A generates a high
voltage in the secondary side of ignition coil A.
The high voltage thus generated is applied to the
spark plugs of No. 1 and No. 4 cylinders to generate
sparks. At the time that the sparks are generated
at both spark plugs, if one cylinder is at the
compression stroke, the other cylinder is at the
exhaust stroke, so that ignition of the compressed
air/fuel mixture occurs only for the cylinder which
is at the compression stroke.
In the same way, when the primary current flowing
in ignition coil B is interrupted, the high voltage
thus generated is applied to the spark plugs of
No. 2 and No. 3 cylinders.
The Engine-ECU turns the two power transistors
inside the ignition coils alternately on and off. Thiscauses the primary currents in the ignition coils
to be alternately interrupted and allowed to flow
to fire the cylinders in the order 1-3-4-2.
The Engine-ECU determines which ignition coil
should be controlled by means of the signals from
the camshaft position sensor which is incorporated
in the camshaft and from the crank angle sensor
which is incorporated in the crankshaft. It also
detects the crankshaft position in order to provide
ignition at the most appropriate timing in response
to the engine operation conditions. It also detects
the crankshaft position in order to provide ignition
at the most appropriate timing in response to the
engine operation conditions.
When the engine is cold or operated at high
altitudes, the ignition timing is slightly advanced
to provide optimum performance.
When the automatic transmission shifts gears, the
ignition timing is also retarded in order to reduce
output torque, thereby alleviating shifting shocks.
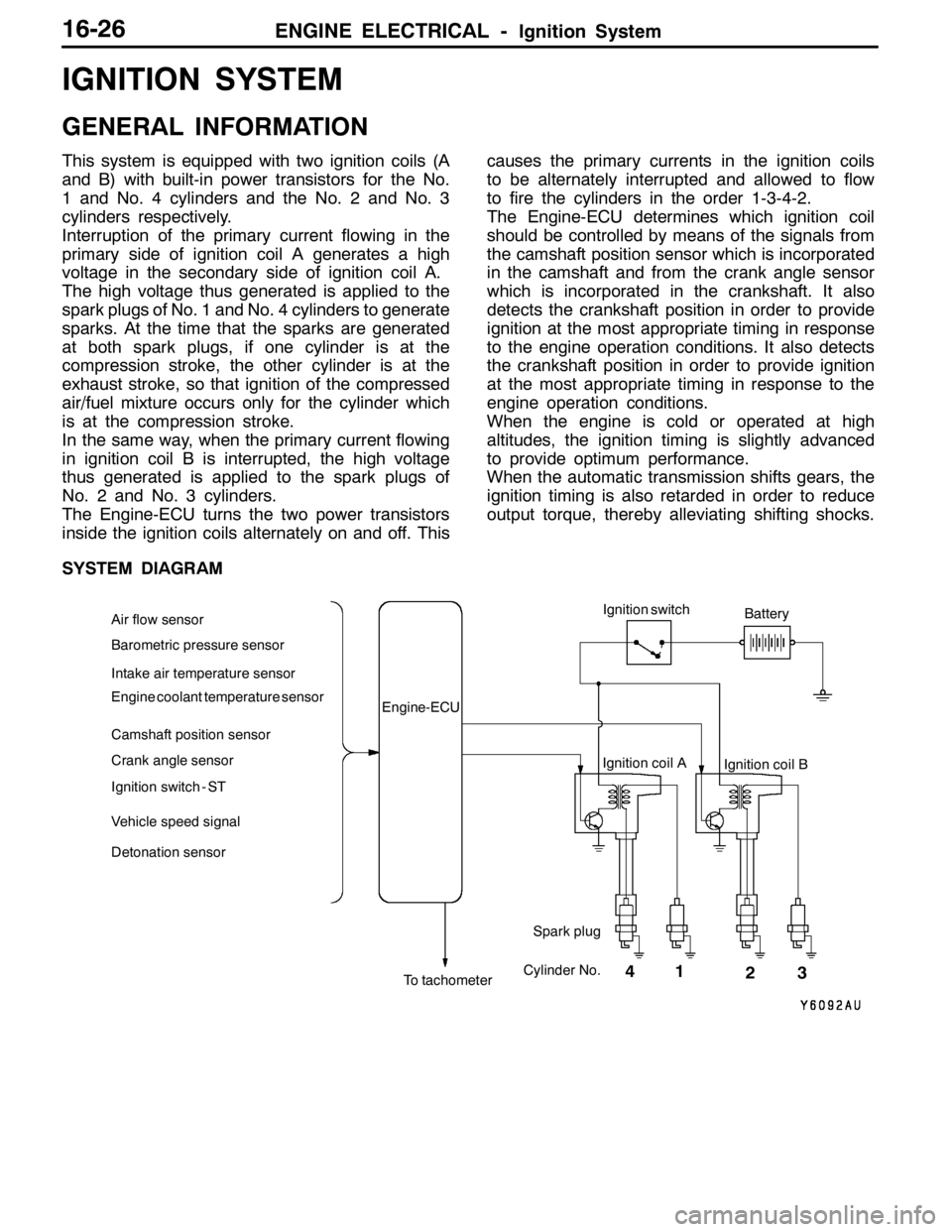
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Barometric pressure sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Camshaft position sensor
Crank angle sensor
Ignition switch - ST
Vehicle speed signalEngine-ECU
Ignition coil A
Ignition coil B Ignition switch
Spark plugBattery
To tachometerCylinder No. Air flow sensor
1 4
23
Detonation sensor
Page 764 of 1449
ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Ignition System16-32
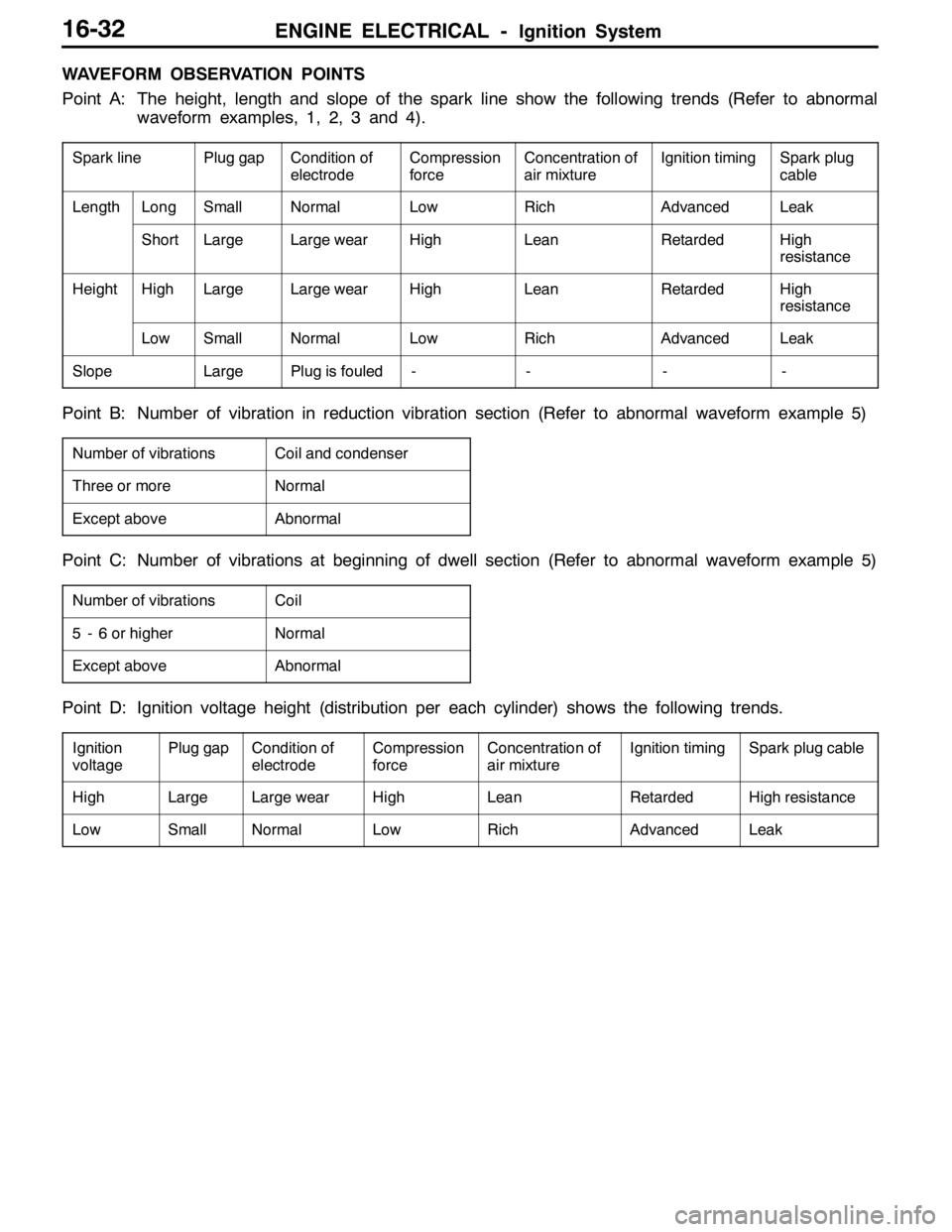
WAVEFORM OBSERVATION POINTS
Point A: The height, length and slope of the spark line show the following trends (Refer to abnormal
waveform examples, 1, 2, 3 and 4).
Spark linePlug gapCondition of
electrodeCompression
forceConcentration of
air mixtureIgnition timingSpark plug
cable
LengthLongSmallNormalLowRichAdvancedLeak
ShortLargeLarge wearHighLeanRetardedHigh
resistance
HeightHighLargeLarge wearHighLeanRetardedHigh
resistance
LowSmallNormalLowRichAdvancedLeak
SlopeLargePlug is fouled----
Point B: Number of vibration in reduction vibration section (Refer to abnormal waveform example 5)
Number of vibrationsCoil and condenser
Three or moreNormal
Except aboveAbnormal
Point C: Number of vibrations at beginning of dwell section (Refer to abnormal waveform example 5)
Number of vibrationsCoil
5 - 6 or higherNormal
Except aboveAbnormal
Point D: Ignition voltage height (distribution per each cylinder) shows the following trends.
Ignition
voltagePlug gapCondition of
electrodeCompression
forceConcentration of
air mixtureIgnition timingSpark plug cable
HighLargeLarge wearHighLeanRetardedHigh resistance
LowSmallNormalLowRichAdvancedLeak
Page 1045 of 1449
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -General Information35A-3
GENERAL INFORMATION
The brake system offers high dependability and durability along with improved braking performance and
brake sensitivity.
SERVICE PRECAUTION
Take care not to contact the parts or tools to the caliper because the paint of caliper will be scratched.
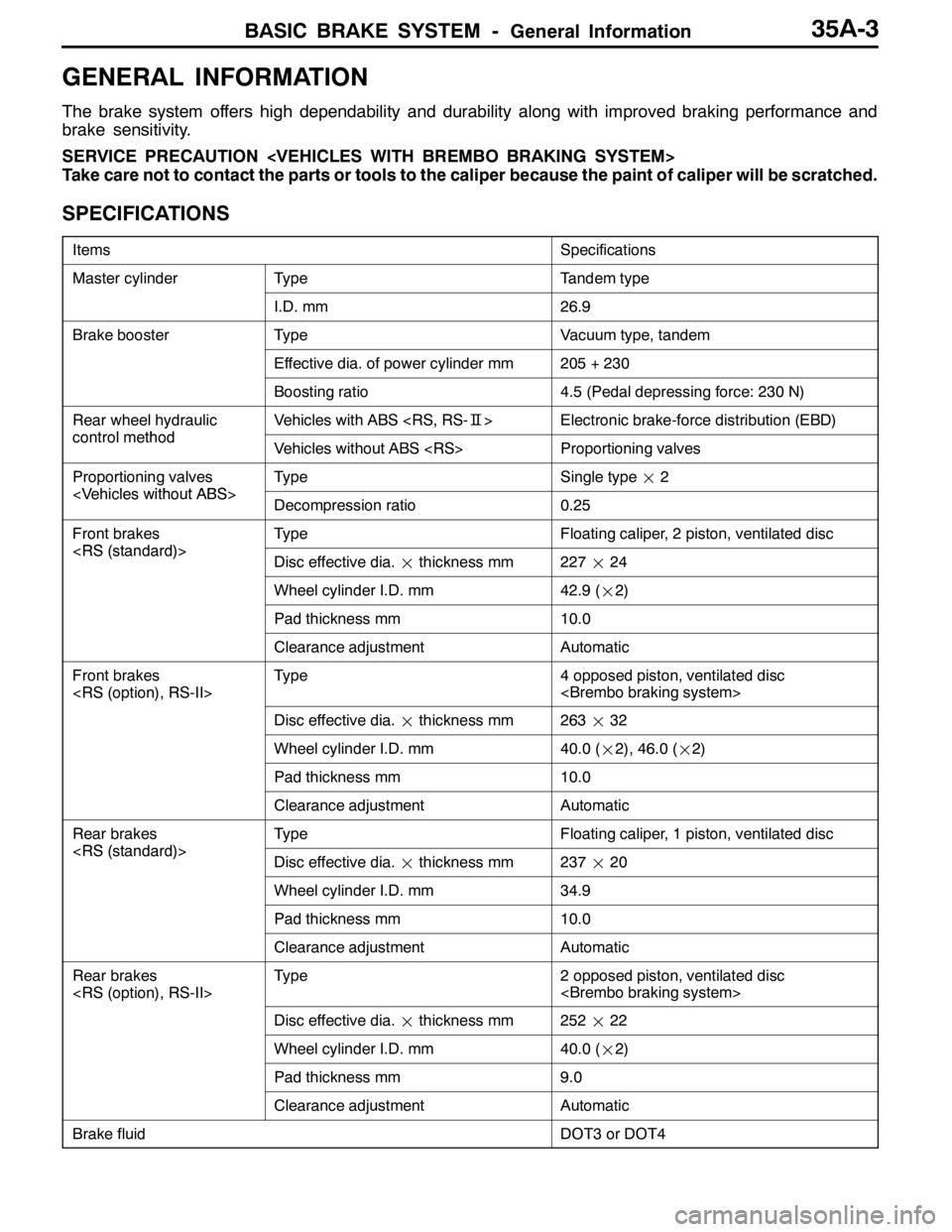
SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsSpecifications
Master cylinderTypeTandem type
I.D. mm26.9
Brake boosterTypeVacuum type, tandem
Effective dia. of power cylinder mm205 + 230
Boosting ratio4.5 (Pedal depressing force: 230 N)
Rear wheel hydraulic
controlmethod
Vehicles with ABS
control methodVehicles without ABS
Proportioning valves
VehicleswithoutABS
TypeSingle type¢2
Front brakes
RS(standard)
TypeFloating caliper, 2 piston, ventilated disc
Wheel cylinder I.D. mm42.9 (¢2)
Pad thickness mm10.0
Clearance adjustmentAutomatic
Front brakes
Disc effective dia.¢thickness mm263¢32
Wheel cylinder I.D. mm40.0 (¢2), 46.0 (¢2)
Pad thickness mm10.0
Clearance adjustmentAutomatic
Rear brakes
RS(standard)
TypeFloating caliper, 1 piston, ventilated disc
Wheel cylinder I.D. mm34.9
Pad thickness mm10.0
Clearance adjustmentAutomatic
Rear brakes
Disc effective dia.¢thickness mm252¢22
Wheel cylinder I.D. mm40.0 (¢2)
Pad thickness mm9.0
Clearance adjustmentAutomatic
Brake fluidDOT3 or DOT4
Page 1421 of 1449
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONER AND VENTILATION–On-vehicle Service HEATER, AIR CONDITIONER AND VENTILATION–On-vehicle Service55-19
8. Start the engine.
9. Operate the air conditioner and set at the lowest
temperature (MAX. COOL).
10. Fix the engine speed at 1,500 r/min.
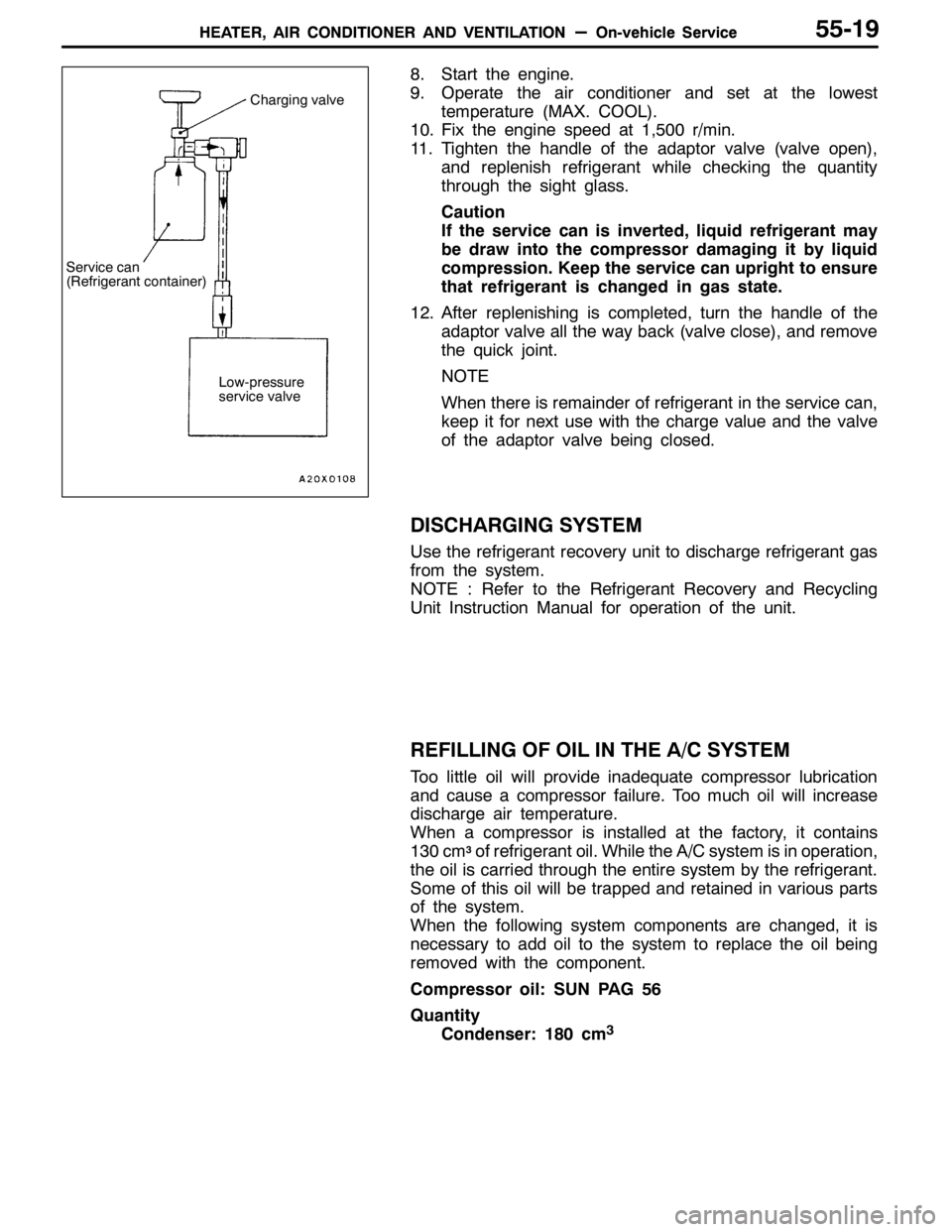
11. Tighten the handle of the adaptor valve (valve open),
and replenish refrigerant while checking the quantity
through the sight glass.
Caution
If the service can is inverted, liquid refrigerant may
be draw into the compressor damaging it by liquid
compression. Keep the service can upright to ensure
that refrigerant is changed in gas state.
12. After replenishing is completed, turn the handle of the
adaptor valve all the way back (valve close), and remove
the quick joint.
NOTE
When there is remainder of refrigerant in the service can,
keep it for next use with the charge value and the valve
of the adaptor valve being closed.
DISCHARGING SYSTEM
Use the refrigerant recovery unit to discharge refrigerant gas
from the system.
NOTE : Refer to the Refrigerant Recovery and Recycling
Unit Instruction Manual for operation of the unit.
REFILLING OF OIL IN THE A/C SYSTEM
Too little oil will provide inadequate compressor lubrication
and cause a compressor failure. Too much oil will increase
discharge air temperature.
When a compressor is installed at the factory, it contains
130 cm
3of refrigerant oil. While the A/C system is in operation,
the oil is carried through the entire system by the refrigerant.
Some of this oil will be trapped and retained in various parts
of the system.
When the following system components are changed, it is
necessary to add oil to the system to replace the oil being
removed with the component.
Compressor oil: SUN PAG 56
Quantity
Condenser: 180 cm
3
Charging valve
Service can
(Refrigerant container)
Low-pressure
service valve