oil change MITSUBISHI MONTERO 1987 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1987, Model line: MONTERO, Model: MITSUBISHI MONTERO 1987 1.GPages: 284, PDF Size: 14.74 MB
Page 35 of 284
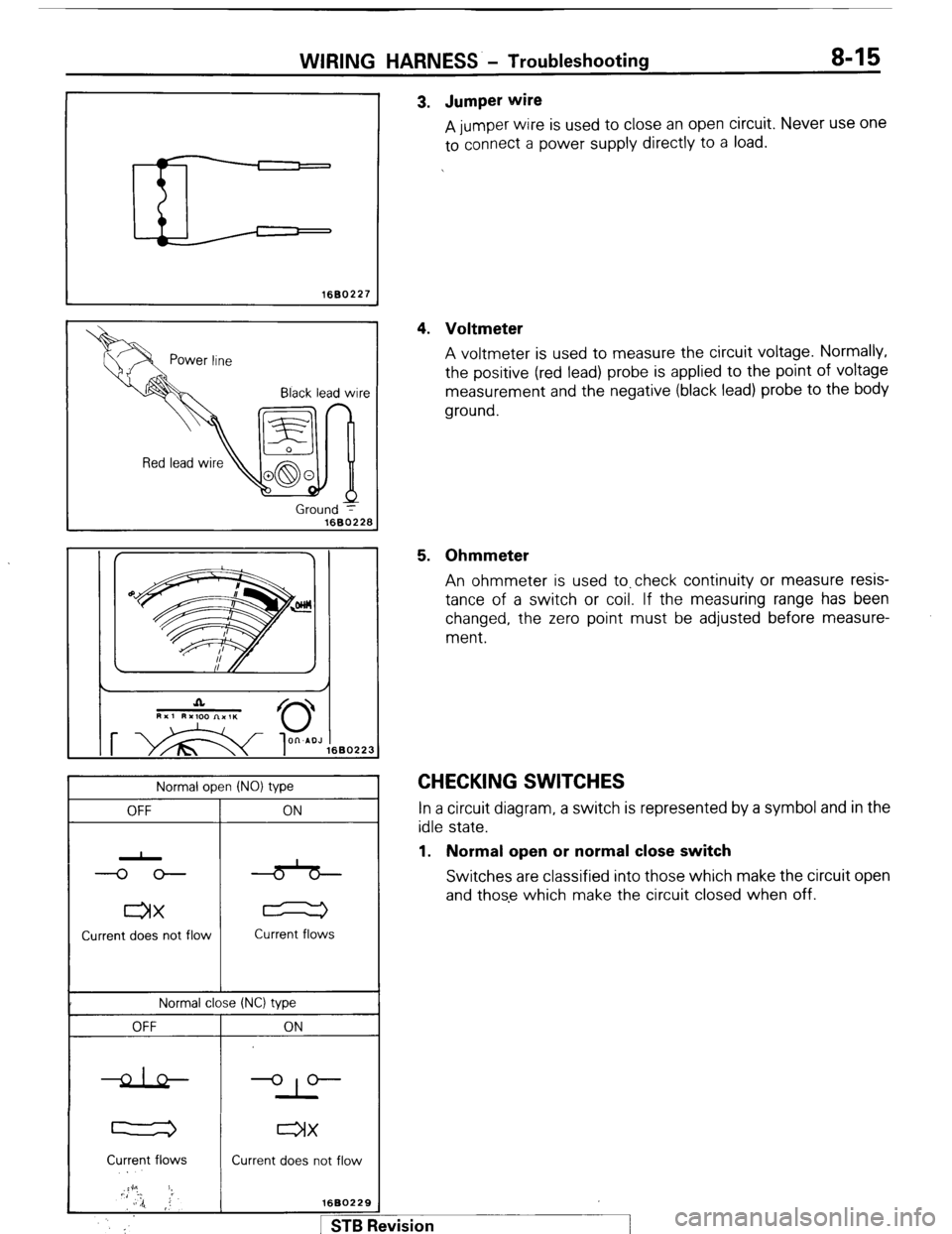
WIRING HARNESS - Troubleshooting 8-15
1660227
Black lead wire
Ground y
1680228
Normal open (NO) type
OFF
ax
Current does not flow ON
Current flows
Normal close (NC) type
OFF
l-2
Current flows ON
-op--
IX
Current does not flow
1680229
pm I 3. Jumper wire
A jumper wire is used to close an open circuit. Never use one
to connect a power supply directly to a load.
4. Voltmeter
A voltmeter is used to measure the circuit voltage. Normally,
the positive (red lead) probe is applied to the point of voltage
measurement and the negative (black lead) probe to the body
ground.
5. Ohmmeter
An ohmmeter is used to.check continuity or measure resis-
tance of a switch or coil. If the measuring range has been
changed, the zero point must be adjusted before measure-
ment.
CHECKING SWITCHES In a circuit diagram, a switch is represented by a symbol and in the
idle state.
1. Normal open or normal close switch
Switches are classified into those which make the circuit open
and those which make the circuit closed when off.
#vision
I
Page 213 of 284
AUDIO SYSTEM - Specifications 8-193
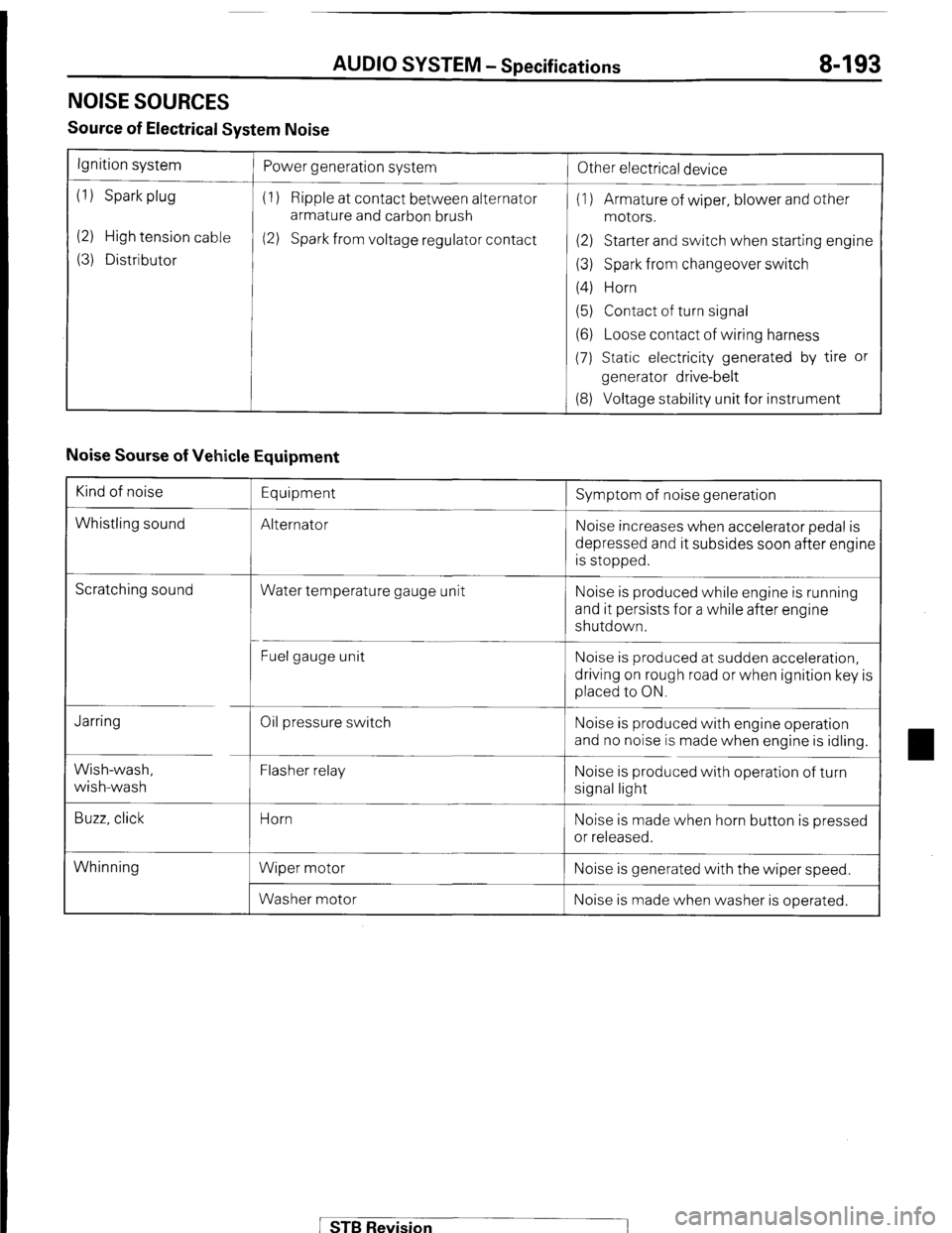
NOISE SOURCES
Source of Electrical System Noise
Ignition system
(1) Spark plug
(2) High tension cable
(3) Distributor Power generation system
(1) Ripple at contact between alternator
armature and carbon brush
(2) Spark from voltage regulator contact
!
Other electrical device
(1) Armature of wiper, blower and other
motors.
(2) Starter and switch when starting engine
(3) Spark from changeover switch
(4) Horn
(5) Contact of turn signal
(6) Loose contact of wiring harness
(7) Static electricity generated by tire or
generator drive-belt
(8) Voltage stability unit for instrument
Noise Sourse of Vehicle Equipment
Kind of noise
Whistling sound Equipment
Alternator Symptom of noise generation
Noise increases when accelerator pedal is
depressed and it subsides soon after engine
is stopped.
Scratching sound
Water temperature gauge unit Noise is produced while engine is running
and it persists for a while after engine
shutdown.
Fuel gauge unit Noise is produced at sudden acceleration,
driving on rough road or when ignition key is
placed to ON.
Jarring
Wish-wash,
wish-wash
Buzz, click Oil pressure switch
Flasher relay
Horn
Wiper motor
Washer motor Noise is produced with engine operation
and no noise is made when engine is idling.
Noise is produced with operation of turn
signal light
Noise is made when horn button is pressed
or released.
Whinning Noise is generated with the wiper speed.
Noise is made when washer is operated.
STB Revision
Page 231 of 284
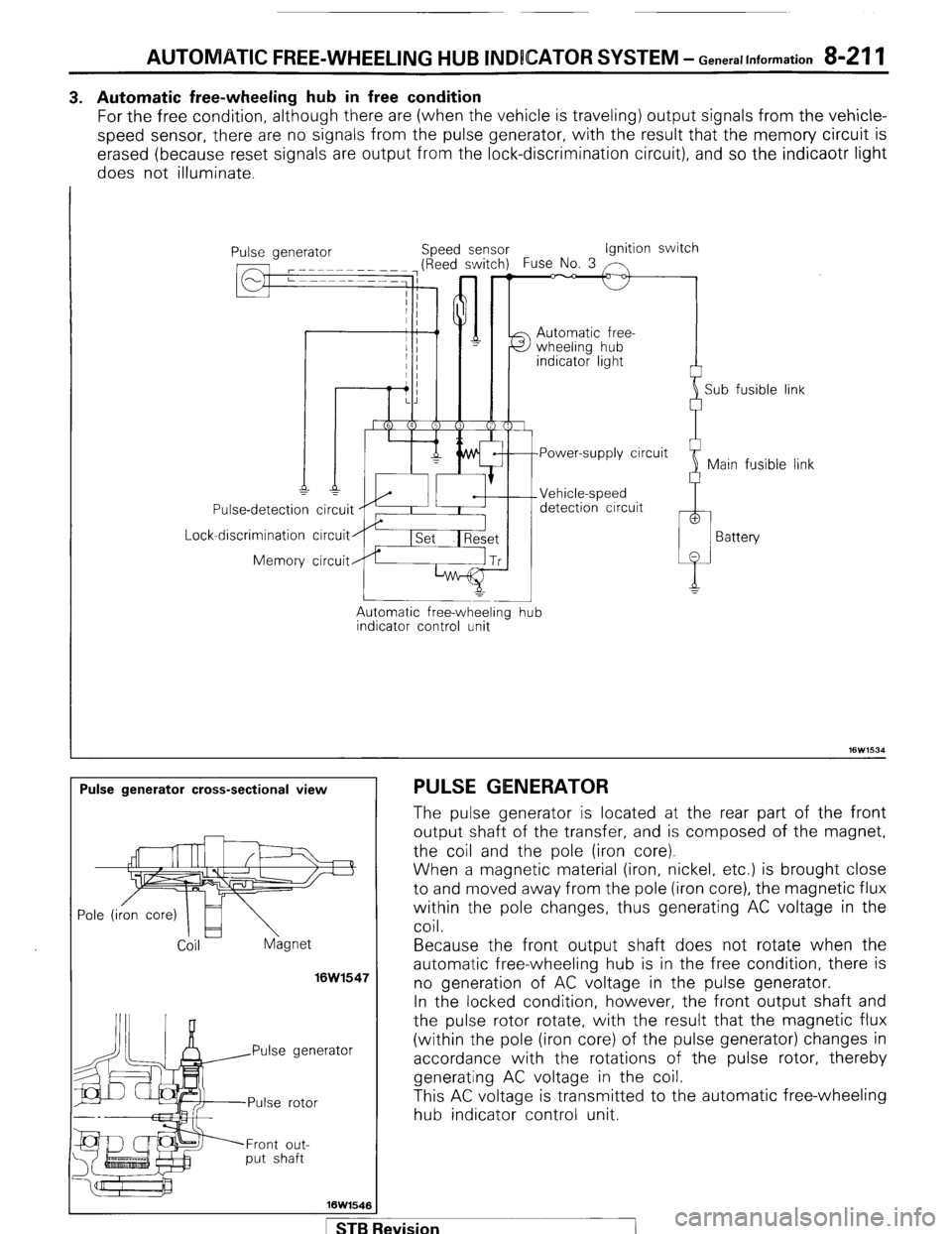
AUTOMATIC FREE-WHEELING HUB INDICATOR SYSTEM - Generallnformation 8-211
3. Automatic free-wheeling hub in free condition
For the free condition, although there are (when the vehicle is traveling) output signals from the vehicle-
speed sensor, there are no signals from the pulse generator, with the result that the memory circuit is
erased (because reset signals are output from the lock-discrimination circuit), and so the indicaotr light
does not illuminate.
I
Lock Use-detection
-discrimination
Memory ipeed sensor Ignition switch
Automatic free-
detection circuit
circuit
circuit
Automatic free-wheeling
indicator control unit -
hub i
Sub fusible link
link
Pulse generator cross-sectional view PULSE GENERATOR
Coil hgnet
16W1547
rator
Front out-
put shaft
16W1546 The pulse generator is located at the rear part of the front
output shaft of the transfer, and is composed of the magnet,
the coil and the pole (iron core).
When a magnetic material (iron, nickel, etc.) is brought close
to and moved away from the pole (iron core), the magnetic flux
within the pole changes, thus generating AC voltage in the
coil.
Because the front output shaft does not rotate when the
automatic free-wheeling hub is in the free condition, there is
no generation of AC voltage in the pulse generator.
In the locked condition, however, the front output shaft and
the pulse rotor rotate, with the result that the magnetic flux
(within the p o e I (’ Iron core) of the pulse generator) changes in
accordance with the rotations of the pulse rotor, thereby
generating AC voltage in the coil.
This AC voltage is transmitted to the automatic free-wheeling
hub indicator control unit.
STB Revision
Page 272 of 284
COllector
can
2OUO315
24-36 AIR-CONDITIONING-Service Adjustment Procedures
D&ARG,NG THE SYSTEM
Since the air conditioning refrigerant system is pressurized, it will
be necessary to completely discharge the system (in a well ven-
tilated area) before replacing any refrigerant component. The pro-
cedure is as follows:
(1) Install manifold gauge set. Make sure the gauge set valves are
closed before attaching the hoses to the refrigerant system.
(2) Install a long hose to the manifold gauge set connector. Run
this hose to the oil collector can near a shop exhaust system.
A good oil collector can may be made from a large empty
coffee can with a plastic top. Slit the plastic top in the form of
a Y to make an entrance for the refrigerant hose and an exit for
the gas.
(3) Open the compressor discharge and suction line pressure
valves and blow the refrigerant into the oil collect can. Watch
to make sure the hose does not blow out of the collector can.
(4) When the system has been completely discharged, measure
the amount of oil collected in the can. The amount of oil mea-
sured should be added to the refrigerant system before it is
re-charged. Add new oil-discard the used oil.
Caution
It is important to have the correct amount of oil in the refrig-
erant system.
Too little oil will provide inadequate compressor lubrication and
cause a compressor failure. Too much oil will increase discharge
air temperature.
When a 6P148 compressor is installed at the factory, it
contains 110 c.c. (3.7 U.S.fl.oz., 3.9 Imp.fl.oz.) of refrigerant oil.
While the air conditioning system is in operation, the oil is
carried through the entire system by the refrigerant. Some of
this oil will be trapped and retained in various parts of the
system.
When the following system components are changed, it is nec-
essary to add oil to the system to replace the oil being removed
with the component.
Compressor - 4Occ (1.4 U.S.fl.oz., 1.4 Imp.fl.oz.)
Condenser - 30 cc (1.0 U.S.fl.oz., 1.1 Imp.fl.oz.)
Evaporator - 60 cc (2.0 U.S.fl.oz., 2.1 Imp.fl.oz.)
Piping - 10 cc (.3 U.S.fl.oz., .4 Imp.fl.oz.)
Receiver drier - 0 cc (0 U.S.fl.oz., 0 Imp.fl.oz.)
EVACUATING THE SYSTEM
2OUO31
Whenever the system has been opened to the atmosphere, it is
absolutely essential that the system be evacuated or “vacuumed”
to remove all the air and moisture. Air in the refrigerant system
causes high compressor discharge pressures, a loss in system
performance, and oxidation of the compressor oil into gum and
varnish. Moisture in the refrigerant system can cause the expan-
sion valve to malfunction. Under certain conditions, water can
react with the refrigerant to form destructive acids. It is necessary
to adhere to the following procedure to keep air and moisture out
of the system.
(1) Install manifold gauge set. Make sure the gauge set valves are
closed before attaching the hoses to the refrigerant system.
(2) Discharge the system if the manifold gauge set indicates pres-
sure in the system.
(3) Connect a long test hoses from gauge set manifold center
connection to vacuum pump.
(4) Open both manifold gauge set valves.
/
/vision I