brakes MITSUBISHI MONTERO 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: MONTERO, Model: MITSUBISHI MONTERO 2000Pages: 1839, PDF Size: 29.19 MB
Page 319 of 1839
GDI -Troubleshooting
DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE
Caution
When shifting the select lever to D range, the brakes should be applied so that the vehicle does
not move forward.
NOTE
*
1: Within four minutes after starting the engine
*2: In a new vehicle [driven approximately 500 km or less], the injector drive time is sometimes 10%
longer than the standard time.
*
3: The accelerator pedal position switch normally turns off when the voltage of the accelerator pedal
position sensor (1st channel) is 200 - 600 mV higher than the voltage at the idle position. If the
accelerator pedal position switch turns back on after the accelerator pedal position sensor voltage
has risen by 100 mV and the throttle valve has opened, the accelerator pedal position switch and
the accelerator pedal position sensor (1st channel) need to be adjusted.
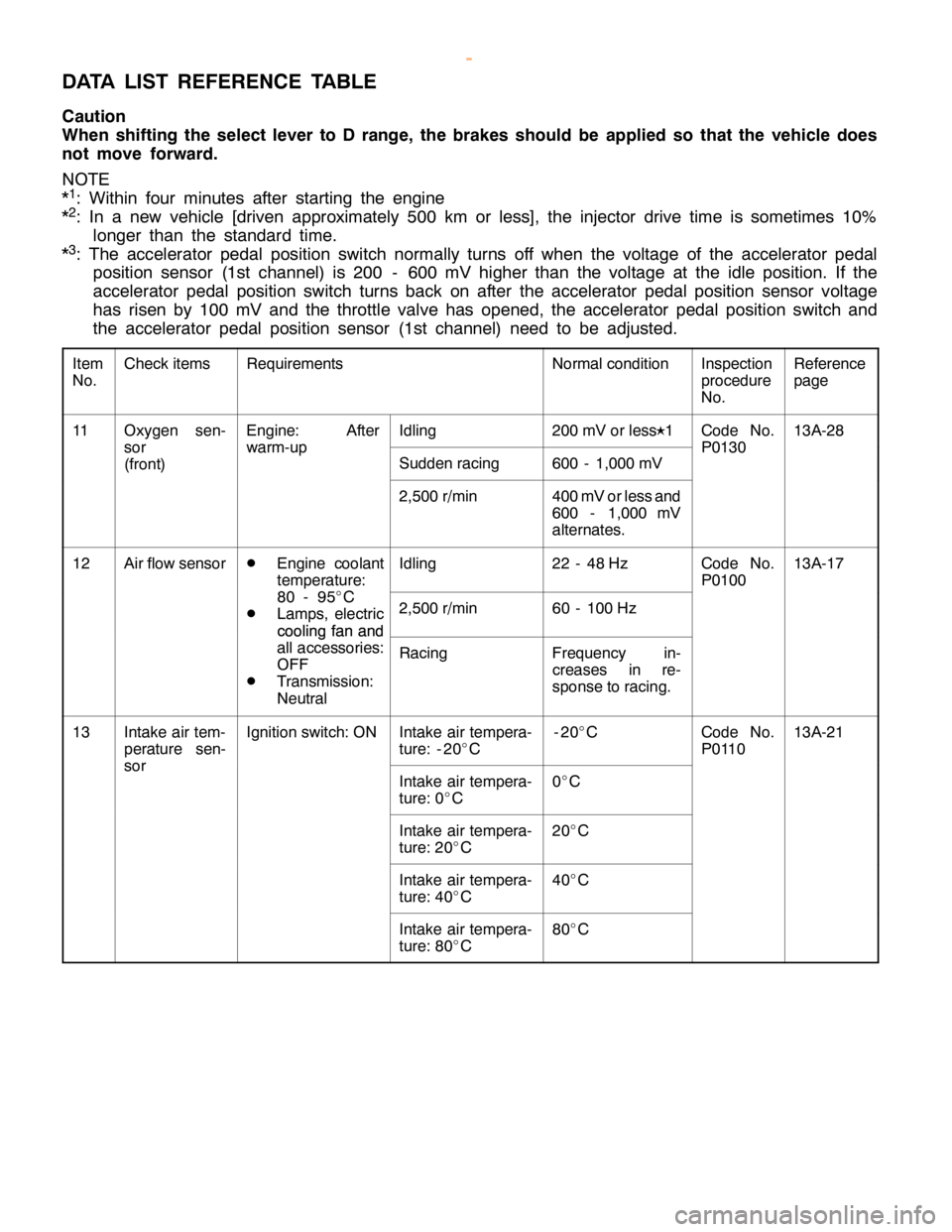
Item
No.Check itemsRequirementsNormal conditionInspection
procedure
No.Reference
page
11Oxygen sen-Engine: AfterIdling200 mV or lessK
1Code No.13A-28
sor
(front)warm-up
Sudden racing600 - 1,000 mV
P0130
2,500 r/min400 mV or less and
600 - 1,000 mV
alternates.
12Air flow sensorD
Engine coolant
temperature:Idling22 - 48 HzCode No.
P010013A-17
80 - 95_
C
D
Lamps, electric
cooling fan and2,500 r/min60 - 100 Hz
cooling fan and
all accessories:
OFF
D
Transmission:
Neutral
RacingFrequency in-
creases in re-
sponse to racing.
13Intake air tem-
perature sen-Ignition switch: ONIntake air tempera-
ture: - 20_
C-20_
CCode No.
P011013A-21
sor
Intake air tempera-
ture: 0_
C0_
C
Intake air tempera-
ture: 20_
C20_
C
Intake air tempera-
ture: 40_
C40_
C
Intake air tempera-
ture: 80_
C80_
C
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 412 of 1839
Page 1211 of 1839
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -General Information35A-3
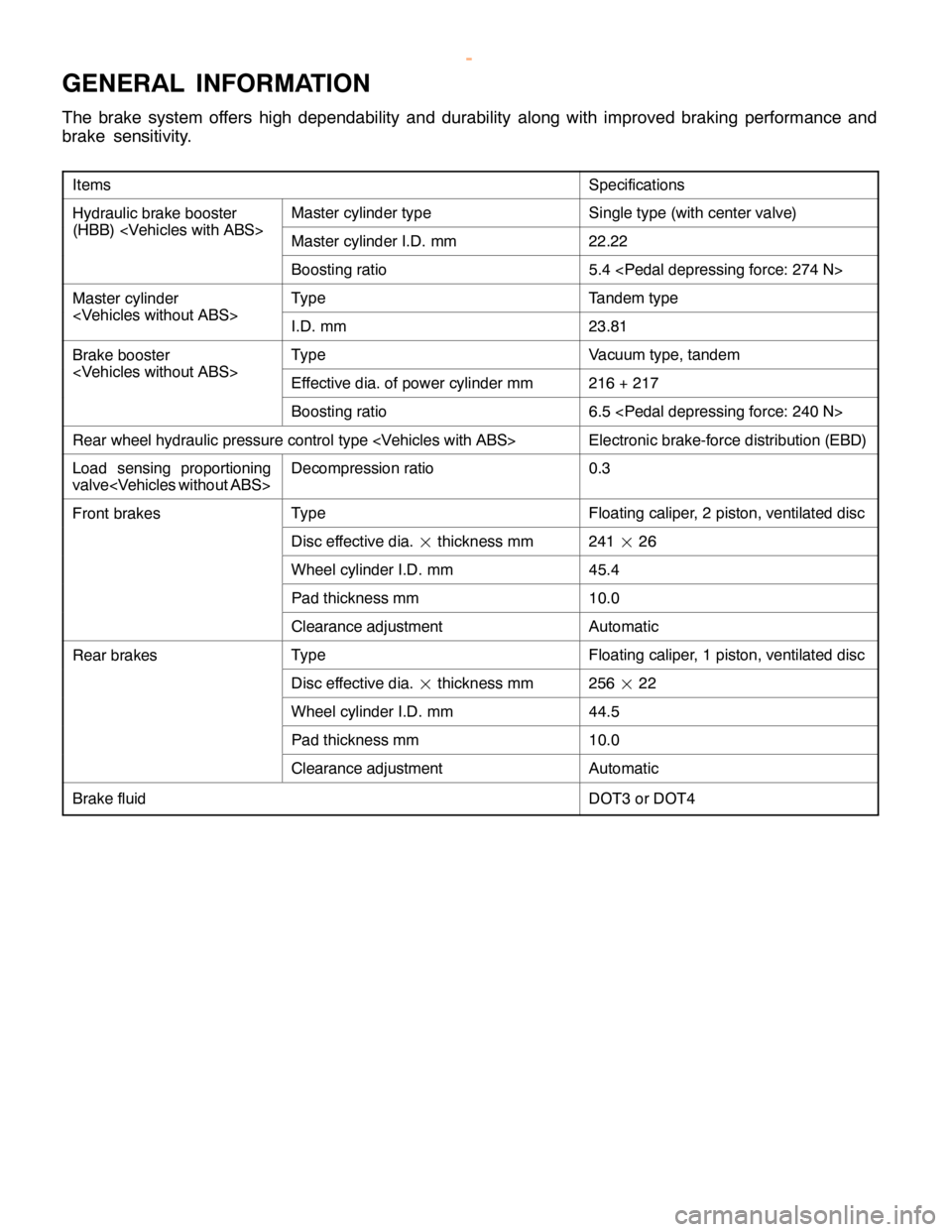
GENERAL INFORMATION
The brake system offers high dependability and durability along with improved braking performance and
brake sensitivity.
ItemsSpecifications
Hydraulic brake boosterMaster cylinder typeSingle type (with center valve)
(HBB)
Boosting ratio5.4
Master cylinderTypeTandem type
Brake boosterTypeVacuum type, tandem
Boosting ratio6.5
Rear wheel hydraulic pressure control type
Load sensing proportioning
valve
Front brakesTypeFloating caliper, 2 piston, ventilated disc
Disc effective dia.¢
thickness mm241¢
26
Wheel cylinder I.D. mm45.4
Pad thickness mm10.0
Clearance adjustmentAutomatic
Rear brakesTypeFloating caliper, 1 piston, ventilated disc
Disc effective dia.¢
thickness mm256¢
22
Wheel cylinder I.D. mm44.5
Pad thickness mm10.0
Clearance adjustmentAutomatic
Brake fluidDOT3 or DOT4
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1265 of 1839

ABS <4WD> -General Information35B-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
ABS has been adopted as standard equipment
in all vehicles to maintain directional stability and
steering performance during sudden braking.
The ABS control method used is a 4-sensor,
4-channel method (previous models: 4-sensor,
3- channel method
)which allows the brake
pressures for all four wheels to be controlled
independently of each other. The system has the
following features.
DEBD
*(Electronic Brake force Distribution
system) control has been added to provide the
ideal braking force for the rear wheels.DThe hydraulic unit function has been integrated
with the hydraulic brake booster (HBB).
DSelect solenoid valves (two valves for FL and
FR) have been adopted in order to reduce the
pedal kickback and improve the operation
feeling when the ABS is operating.
DIndependent 4-wheel control is carried out wile
the vehicle is turning in order to increase the
braking force.
NOTE
*EBD: Electronic Brake-force Distribution
EBD CONTROL
In ABS, electronic control method is used whereby
the rear wheel brake hydraulic pressure during
braking is regulated by rear wheel control solenoid
valves in accordance with the vehicle’s rate of
deceleration and the front and rear wheel slippage
which are calculated from the signals received from
the various wheel sensors. EBD control is a control
system which provides a high level of control for
both vehicle braking force and vehicle stability. The
system has the following features.
DBecause the system provides the optimum rear
wheel braking force regardless of the vehicle
laden condition and the condition of the road
surface, the system reduces the required pedal
depression force, particularly when the vehicle
is heavily laden or driving on road surfaces
with high frictional coefficients.DBecause the duty placed on the front brakes
has been reduced, the increases in pad
temperature can be controlled during front
brakes applying to improve the wear resistance
characteristics of the pad.
DControl valves such as the proportioning valve
are no longer required.
SPECIFICATIONS
ItemSpecifications
ABS control method4-sensor, 4-channel
No. of ABS rotor teethFront50
Rear50
ABS speed sensorTypeMagnet coil type
Gap between sensor and rotor mm0.9 (non-adjustable type)
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1300 of 1839

PARKING BRAKES
Click on the applicable bookmark to selected the required model year.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1301 of 1839

36-1
PARKING BRAKES
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 2..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 2.................
LUBRICANTS 2..............................
SEALANT 3..................................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 3.....................
Parking Brake Lever Stroke Check and
Adjustment 3..................................Parking Brake Switch Check 4..................
Lining Running-In 4............................
PARKING BRAKE LEVER 5..................
PARKING BRAKE CABLE 6..................
PARKING BRAKE DRUM 7...................
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk