NISSAN ALMERA TINO 2001 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2001, Model line: ALMERA TINO, Model: NISSAN ALMERA TINO 2001Pages: 3051, PDF Size: 46.38 MB
Page 2601 of 3051
HFC-134a (R-134a) Service Tools and
Equipment
=NLHA0120Never mix HFC-134a refrigerant and/or its specified lubricant with CFC-12 (R-12) refrigerant and/or its lubri-
cant.
Separate and non-interchangeable service equipment must be used for handling each type of refrigerant/
lubricant.
Refrigerant container fittings, service hose fittings and service equipment fittings (equipment which handles
refrigerant and/or lubricant) are different between CFC-12 (R-12) and HFC-134a (R-134a). This is to avoid
mixed use of the refrigerants/lubricant.
Adapters that convert one size fitting to another must never be used: refrigerant/lubricant contamination will
occur and compressor failure will result.
Tool number
Tool nameDescription
HFC-134a (R-134a)
refrigerant
NT196
Container color: Light blue
Container marking: HFC-134a (R-134a)
Fitting size: Thread size
+Large container 1/2″-16 ACME
KLH00-PAGR0
Nissan A/C System Oil
Type R
KLH00-PAGS0
Nissan A/C System Oil
Type S
NT197
Type: Poly alkylene glycol oil (PAG), type R
Application: HFC-134a (R-134a) vane rotary com-
pressors (Nissan only)
Type S
Application: HFC-134a (R-134a) swash plate com-
pressors (Nissan only)
Lubricity: 40 m!(1.4 Imp fl oz)
Recovery/Recycling
Recharging equipment
(ACR4)
NT195
Function: Refrigerant Recovery and Recycling and
Recharging
Electrical leak detector
NT198
Power supply:
+DC 12V (Cigarette lighter)
Manifold gauge set (with
hoses and couplers)
NT199
Identification:
+The gauge face indicates R-134a.
Fitting size: Thread size
+1/2″-16 ACME
PREPARATION
HFC-134a (R-134a) Service Tools and Equipment
HA-10
Page 2602 of 3051
Tool number
Tool nameDescription
Service hoses
+High side hose
+Low side hose
+Utility hose
NT201
Hose color:
+Low hose: Blue with black stripe
+High hose: Red with black stripe
+Utility hose: Yellow with black stripe or green
with black stripe
Hose fitting to gauge:
+1/2″-16 ACME
Service couplers
+High side coupler
+Low side coupler
NT202
Hose fitting to service hose:
+M14 x 1.5 fitting is optional or permanently
attached.
Refrigerant weight scale
NT200
For measuring of refrigerant
Fitting size: Thread size
+1/2″-16 ACME
Vacuum pump
(Including the isolator
valve)
NT203
Capacity:
+Air displacement: 4 CFM
+Micron rating: 20 microns
+Oil capacity: 482 g (17 oz)
Fitting size: Thread size
+1/2″-16 ACME
PREPARATION
HFC-134a (R-134a) Service Tools and Equipment (Cont’d)
HA-11
Page 2603 of 3051
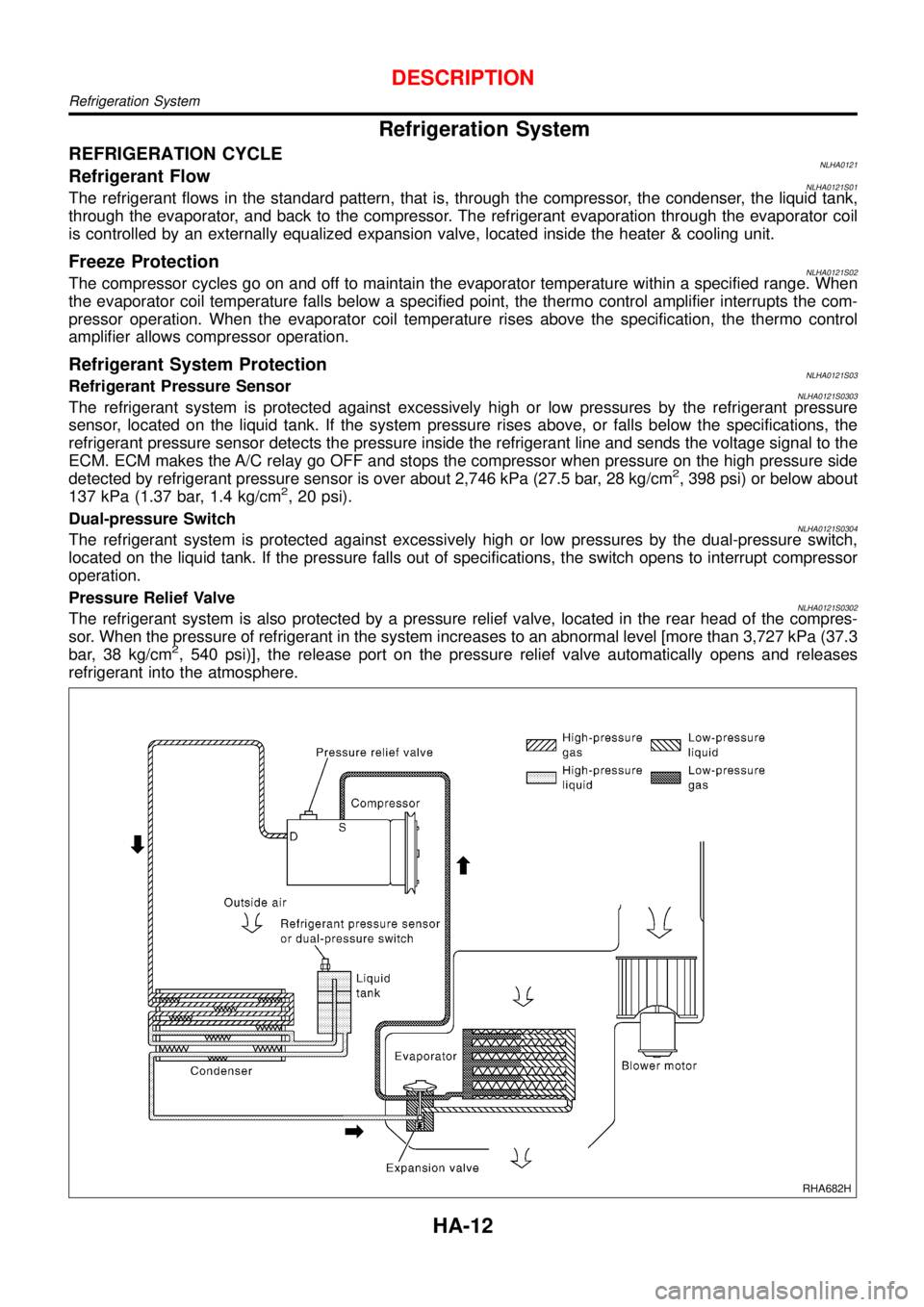
Refrigeration System
REFRIGERATION CYCLENLHA0121Refrigerant FlowNLHA0121S01The refrigerant flows in the standard pattern, that is, through the compressor, the condenser, the liquid tank,
through the evaporator, and back to the compressor. The refrigerant evaporation through the evaporator coil
is controlled by an externally equalized expansion valve, located inside the heater & cooling unit.
Freeze ProtectionNLHA0121S02The compressor cycles go on and off to maintain the evaporator temperature within a specified range. When
the evaporator coil temperature falls below a specified point, the thermo control amplifier interrupts the com-
pressor operation. When the evaporator coil temperature rises above the specification, the thermo control
amplifier allows compressor operation.
Refrigerant System ProtectionNLHA0121S03Refrigerant Pressure SensorNLHA0121S0303The refrigerant system is protected against excessively high or low pressures by the refrigerant pressure
sensor, located on the liquid tank. If the system pressure rises above, or falls below the specifications, the
refrigerant pressure sensor detects the pressure inside the refrigerant line and sends the voltage signal to the
ECM. ECM makes the A/C relay go OFF and stops the compressor when pressure on the high pressure side
detected by refrigerant pressure sensor is over about 2,746 kPa (27.5 bar, 28 kg/cm
2, 398 psi) or below about
137 kPa (1.37 bar, 1.4 kg/cm2, 20 psi).
Dual-pressure Switch
NLHA0121S0304The refrigerant system is protected against excessively high or low pressures by the dual-pressure switch,
located on the liquid tank. If the pressure falls out of specifications, the switch opens to interrupt compressor
operation.
Pressure Relief Valve
NLHA0121S0302The refrigerant system is also protected by a pressure relief valve, located in the rear head of the compres-
sor. When the pressure of refrigerant in the system increases to an abnormal level [more than 3,727 kPa (37.3
bar, 38 kg/cm
2, 540 psi)], the release port on the pressure relief valve automatically opens and releases
refrigerant into the atmosphere.
RHA682H
DESCRIPTION
Refrigeration System
HA-12
Page 2604 of 3051

CSV613 Variable Displacement Compressor
GENERAL INFORMATIONNLHA02061. The CSV613 compressor differs from previous units. The vent temperatures of the CSV613 compressor
do not drop too far below 5°C (41°F) when:
+evaporator intake air temperature is less than 20°C (68°F)
+engine is running at speeds less than 1,500 rpm.
This is because the CSV613 compressor provides a means of“capacity”control.
2. The CSV613 compressor provides refrigerant control under varying conditions. During cold winters, it may
not produce high refrigerant pressure discharge (compared to previous units) when used with air condi-
tioning systems.
3. A“clanking”sound may occasionally be heard during refrigerant charge. The sound indicates that the tilt
angle of the swash plate has changed and is not a problem.
4. For air conditioning systems with the CSV613 compressor, the clutch remains engaged unless: the sys-
tem main switch, fan switch or ignition switch is turned OFF. When ambient (outside) temperatures are
low or when the amount of refrigerant is insufficient, the clutch is disengaged to protect the compressor.
5. A constant range of suction pressure is maintained when engine speed is greater than a certain value. It
normally ranges from 147 to 177 kPa (1.47 to 1.77 bar, 1.5 to 1.8 kg/cm
2, 21 to 26 psi) under varying con-
ditions.
In previous compressors, however, suction pressure was reduced with increases in engine speed.
DESCRIPTION
CSV613 Variable Displacement Compressor
HA-13
Page 2605 of 3051
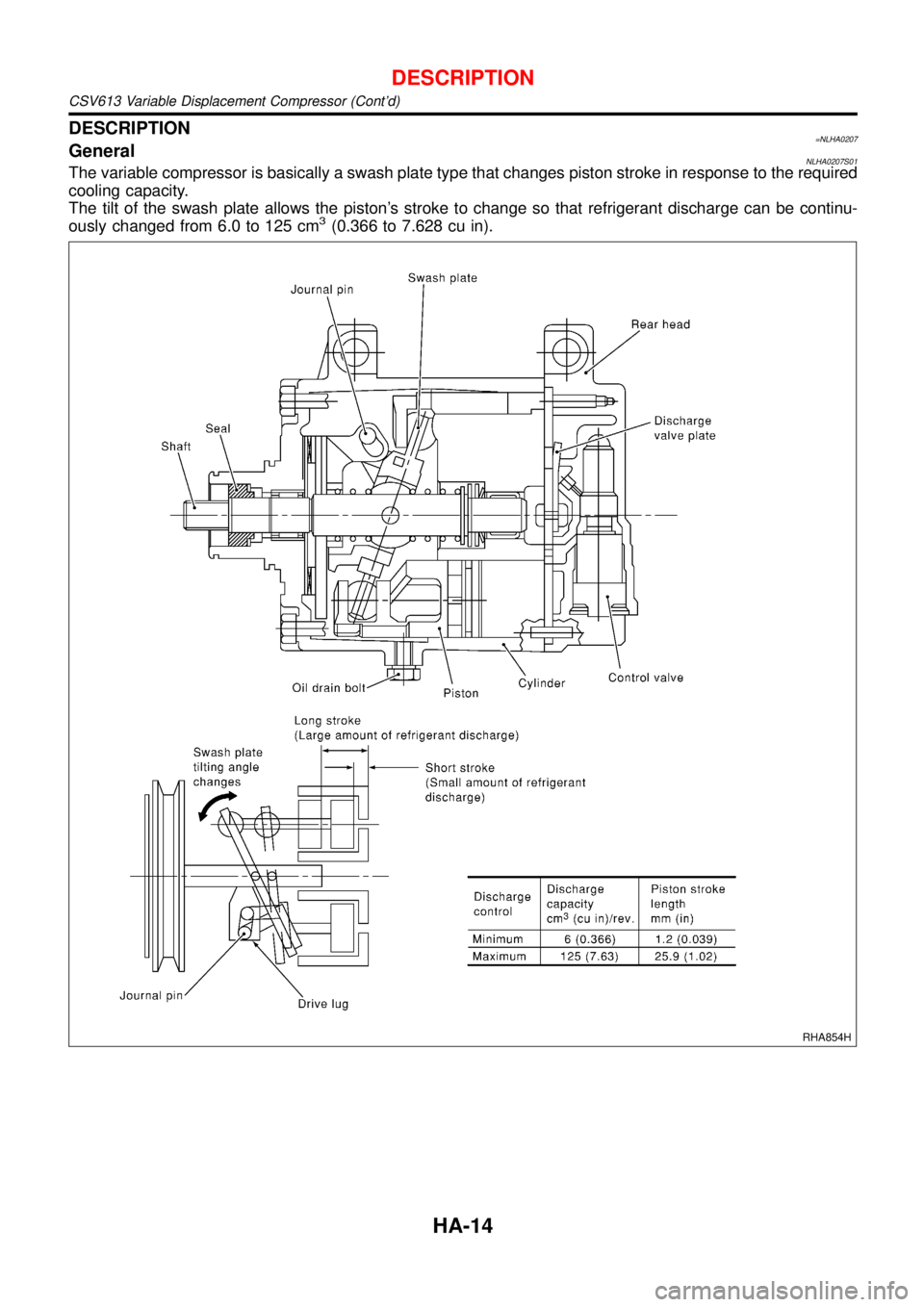
DESCRIPTION=NLHA0207GeneralNLHA0207S01The variable compressor is basically a swash plate type that changes piston stroke in response to the required
cooling capacity.
The tilt of the swash plate allows the piston’s stroke to change so that refrigerant discharge can be continu-
ously changed from 6.0 to 125 cm
3(0.366 to 7.628 cu in).
RHA854H
DESCRIPTION
CSV613 Variable Displacement Compressor (Cont’d)
HA-14
Page 2606 of 3051
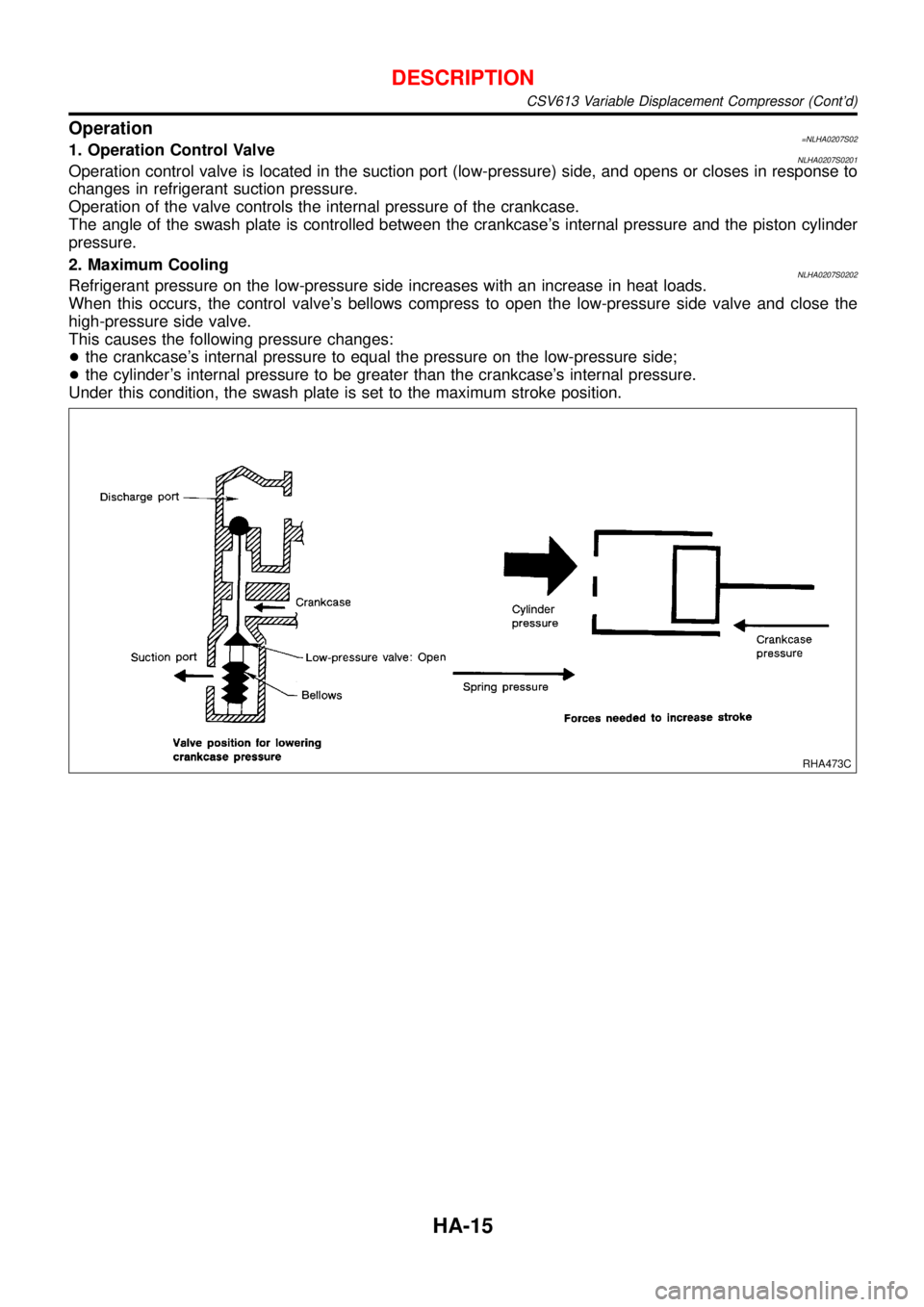
Operation=NLHA0207S021. Operation Control ValveNLHA0207S0201Operation control valve is located in the suction port (low-pressure) side, and opens or closes in response to
changes in refrigerant suction pressure.
Operation of the valve controls the internal pressure of the crankcase.
The angle of the swash plate is controlled between the crankcase’s internal pressure and the piston cylinder
pressure.
2. Maximum Cooling
NLHA0207S0202Refrigerant pressure on the low-pressure side increases with an increase in heat loads.
When this occurs, the control valve’s bellows compress to open the low-pressure side valve and close the
high-pressure side valve.
This causes the following pressure changes:
+the crankcase’s internal pressure to equal the pressure on the low-pressure side;
+the cylinder’s internal pressure to be greater than the crankcase’s internal pressure.
Under this condition, the swash plate is set to the maximum stroke position.
RHA473C
DESCRIPTION
CSV613 Variable Displacement Compressor (Cont’d)
HA-15
Page 2607 of 3051
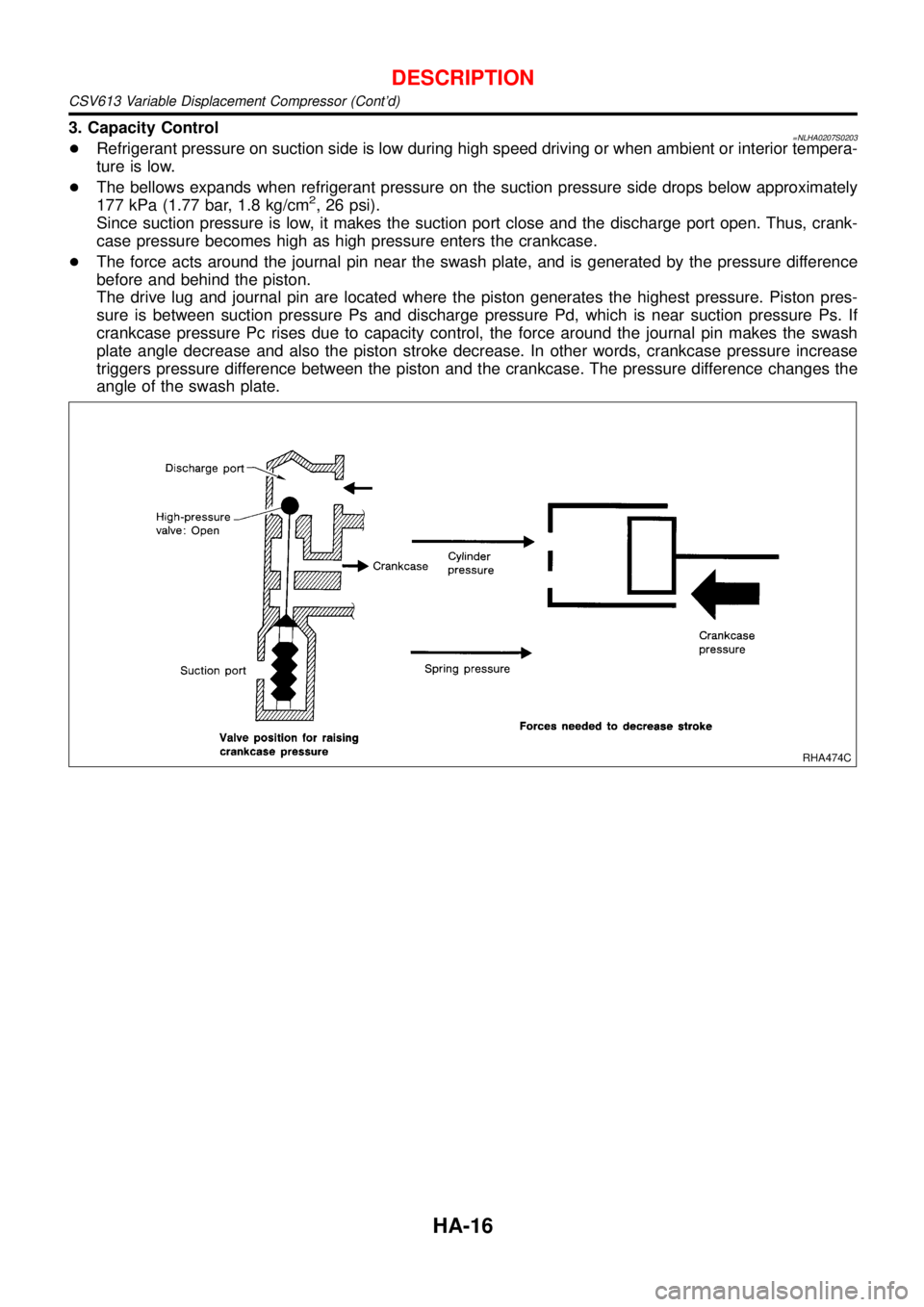
3. Capacity Control=NLHA0207S0203+Refrigerant pressure on suction side is low during high speed driving or when ambient or interior tempera-
ture is low.
+The bellows expands when refrigerant pressure on the suction pressure side drops below approximately
177 kPa (1.77 bar, 1.8 kg/cm
2, 26 psi).
Since suction pressure is low, it makes the suction port close and the discharge port open. Thus, crank-
case pressure becomes high as high pressure enters the crankcase.
+The force acts around the journal pin near the swash plate, and is generated by the pressure difference
before and behind the piston.
The drive lug and journal pin are located where the piston generates the highest pressure. Piston pres-
sure is between suction pressure Ps and discharge pressure Pd, which is near suction pressure Ps. If
crankcase pressure Pc rises due to capacity control, the force around the journal pin makes the swash
plate angle decrease and also the piston stroke decrease. In other words, crankcase pressure increase
triggers pressure difference between the piston and the crankcase. The pressure difference changes the
angle of the swash plate.
RHA474C
DESCRIPTION
CSV613 Variable Displacement Compressor (Cont’d)
HA-16
Page 2608 of 3051
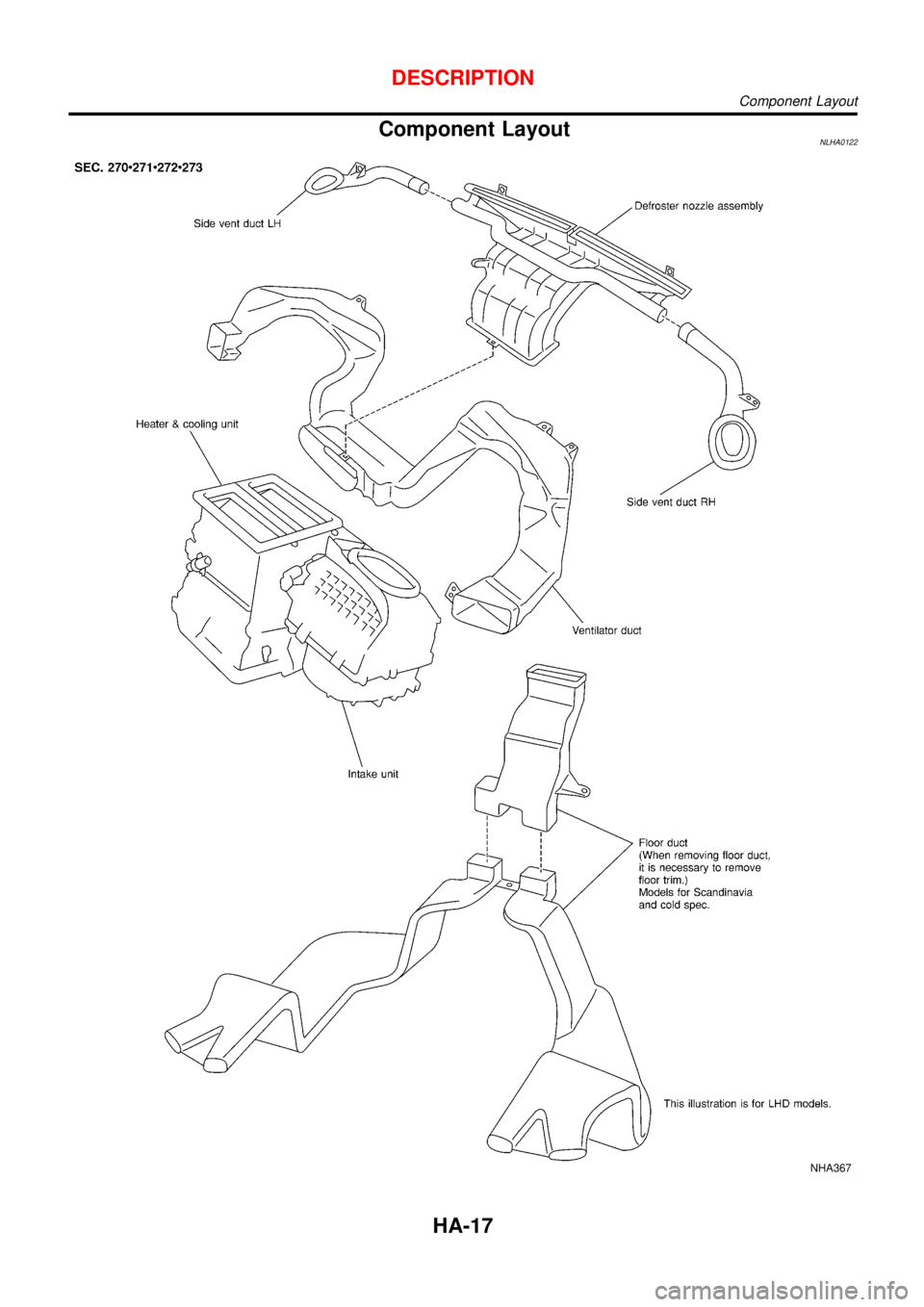
Component LayoutNLHA0122
NHA367
DESCRIPTION
Component Layout
HA-17
Page 2609 of 3051
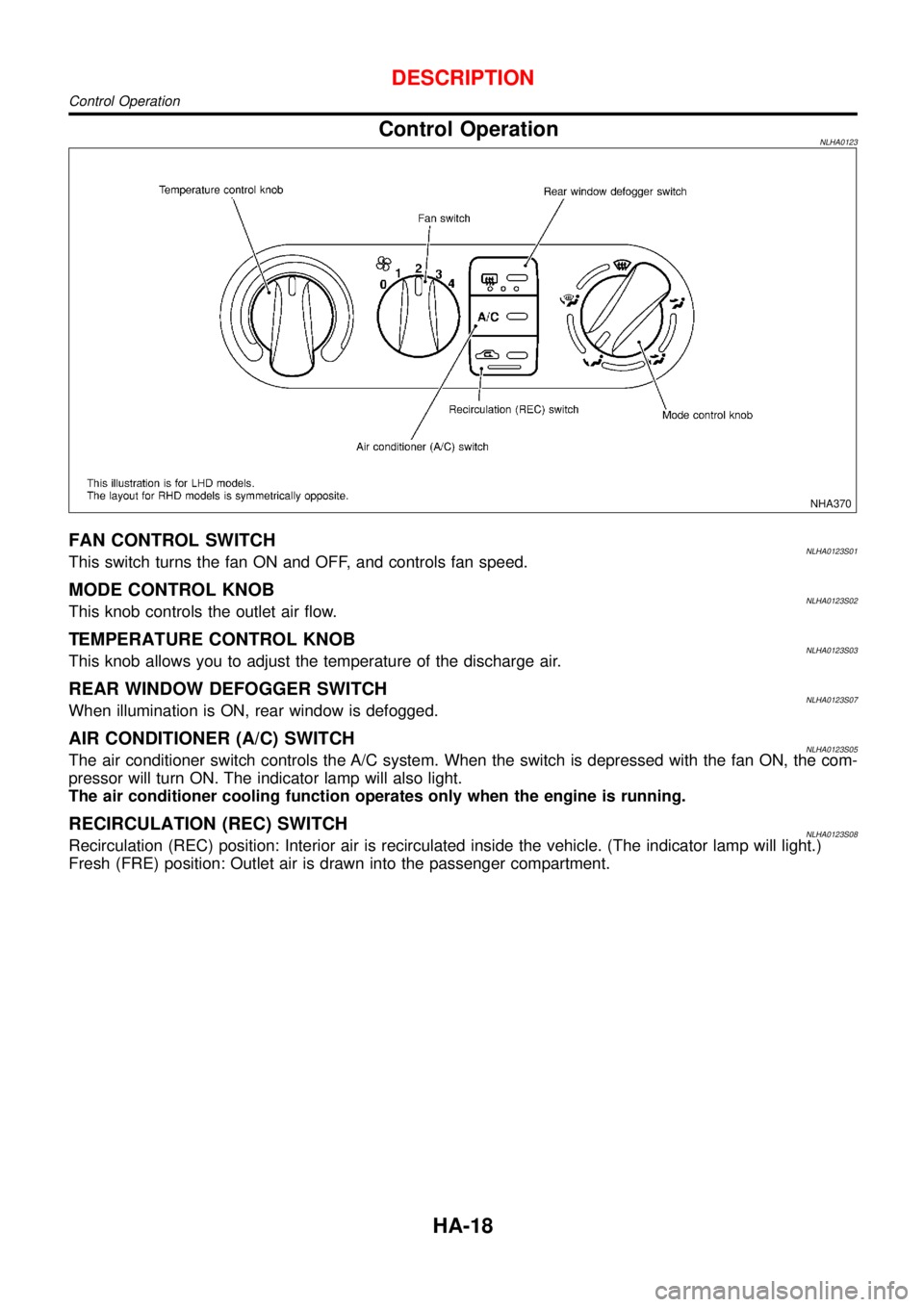
Control OperationNLHA0123
NHA370
FAN CONTROL SWITCHNLHA0123S01This switch turns the fan ON and OFF, and controls fan speed.
MODE CONTROL KNOBNLHA0123S02This knob controls the outlet air flow.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL KNOBNLHA0123S03This knob allows you to adjust the temperature of the discharge air.
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SWITCHNLHA0123S07When illumination is ON, rear window is defogged.
AIR CONDITIONER (A/C) SWITCHNLHA0123S05The air conditioner switch controls the A/C system. When the switch is depressed with the fan ON, the com-
pressor will turn ON. The indicator lamp will also light.
The air conditioner cooling function operates only when the engine is running.
RECIRCULATION (REC) SWITCHNLHA0123S08Recirculation (REC) position: Interior air is recirculated inside the vehicle. (The indicator lamp will light.)
Fresh (FRE) position: Outlet air is drawn into the passenger compartment.
DESCRIPTION
Control Operation
HA-18
Page 2610 of 3051
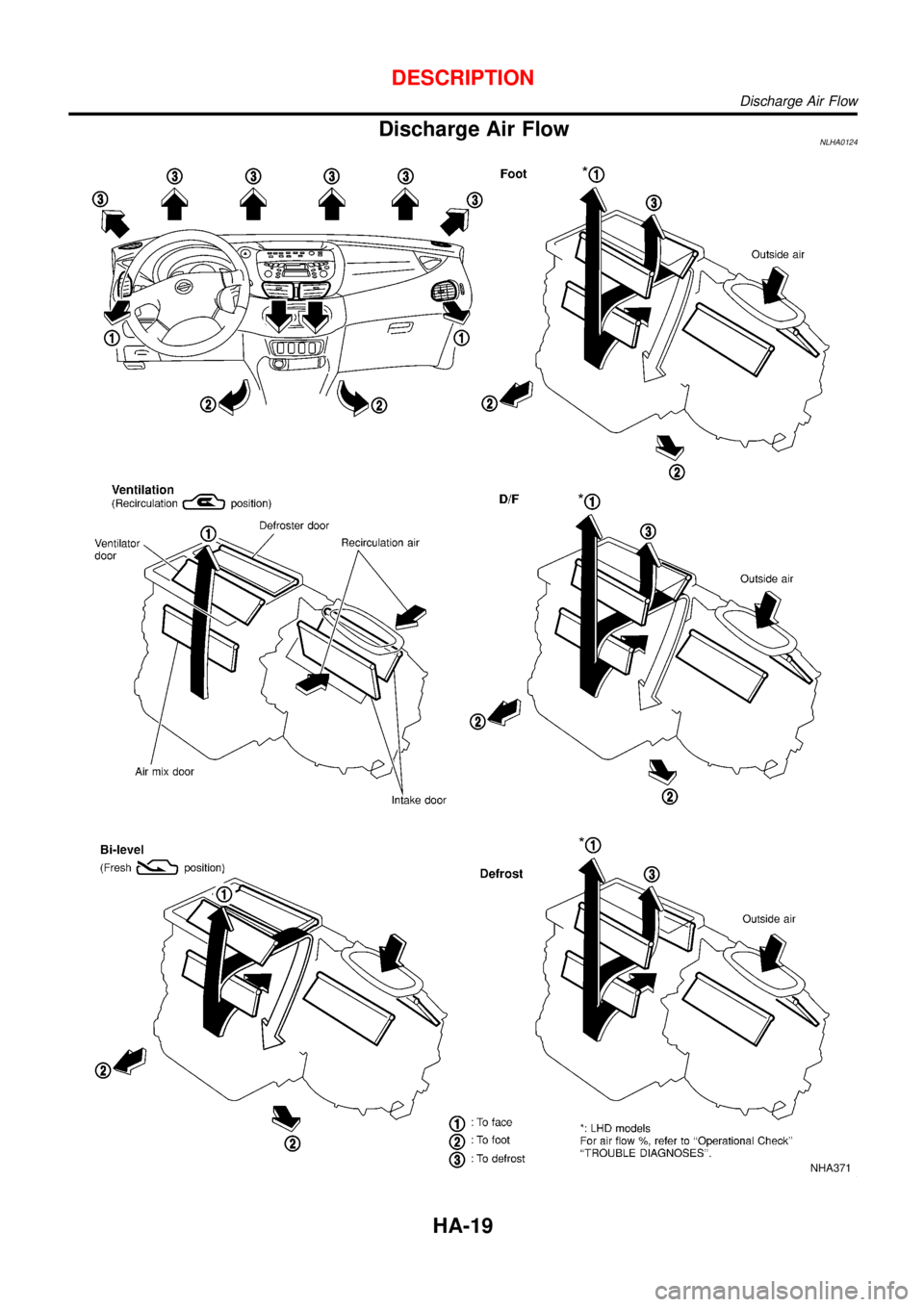
Discharge Air FlowNLHA0124
NHA371
DESCRIPTION
Discharge Air Flow
HA-19