sensor NISSAN LATIO 2011 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2011, Model line: LATIO, Model: NISSAN LATIO 2011Pages: 3787, PDF Size: 78.35 MB
Page 47 of 3787
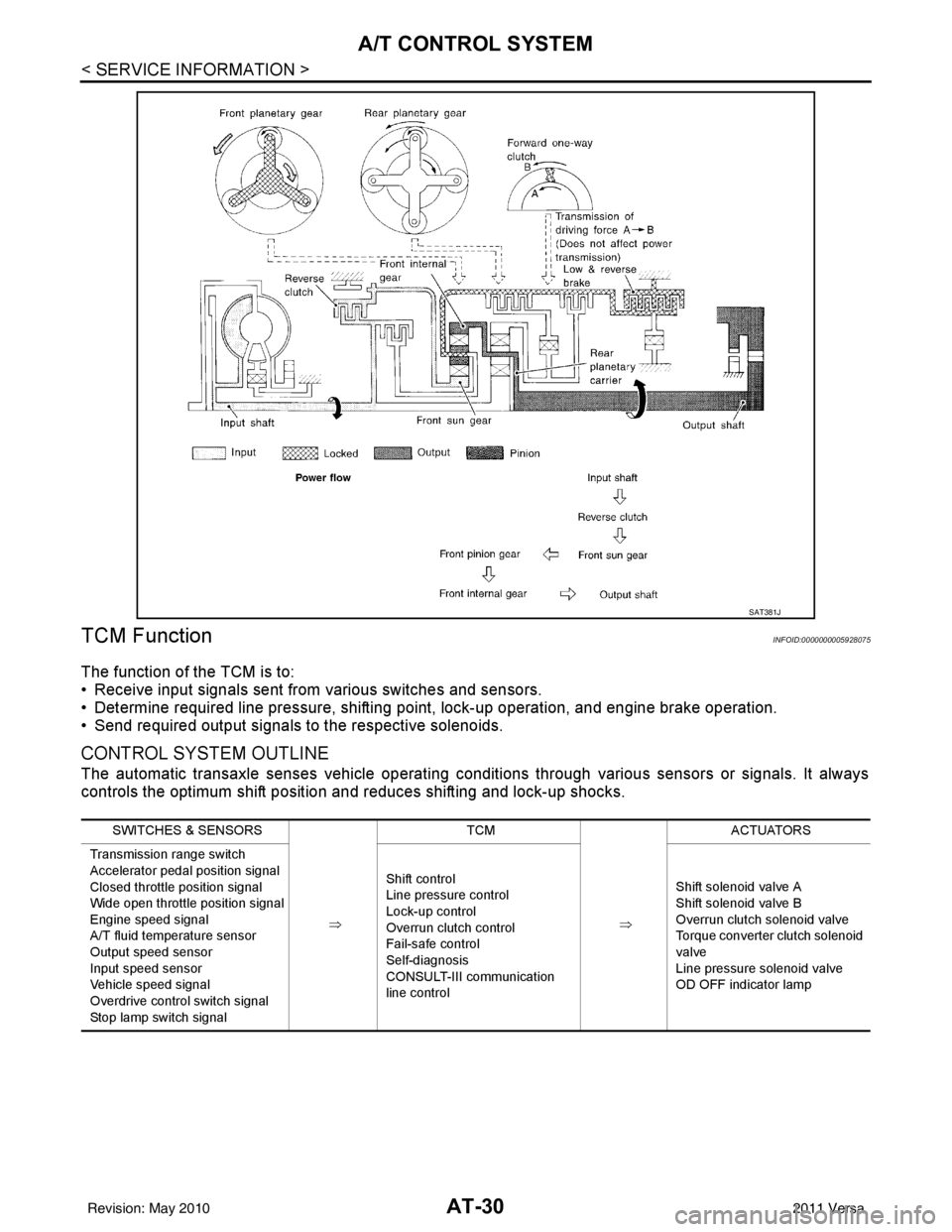
AT-30
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
A/T CONTROL SYSTEM
TCM Function
INFOID:0000000005928075
The function of the TCM is to:
• Receive input signals sent from various switches and sensors.
• Determine required line pressure, shifting poi nt, lock-up operation, and engine brake operation.
• Send required output signals to the respective solenoids.
CONTROL SYSTEM OUTLINE
The automatic transaxle senses vehicle operating conditions through various sensors or signals. It always
controls the optimum shift position and reduces shifting and lock-up shocks.
SAT381J
SWITCHES & SENSORS
⇒TCM
⇒ACTUATORS
Transmission range switch
Accelerator pedal position signal
Closed throttle position signal
Wide open throttle position signal
Engine speed signal
A/T fluid temperature sensor
Output speed sensor
Input speed sensor
Vehicle speed signal
Overdrive control switch signal
Stop lamp switch signal Shift control
Line pressure control
Lock-up control
Overrun clutch control
Fail-safe control
Self-diagnosis
CONSULT-III communication
line control
Shift solenoid valve A
Shift solenoid valve B
Overrun clutch solenoid valve
Torque converter clutch solenoid
valve
Line pressure solenoid valve
OD OFF indicator lamp
Revision: May 2010
2011 Versa
Page 48 of 3787
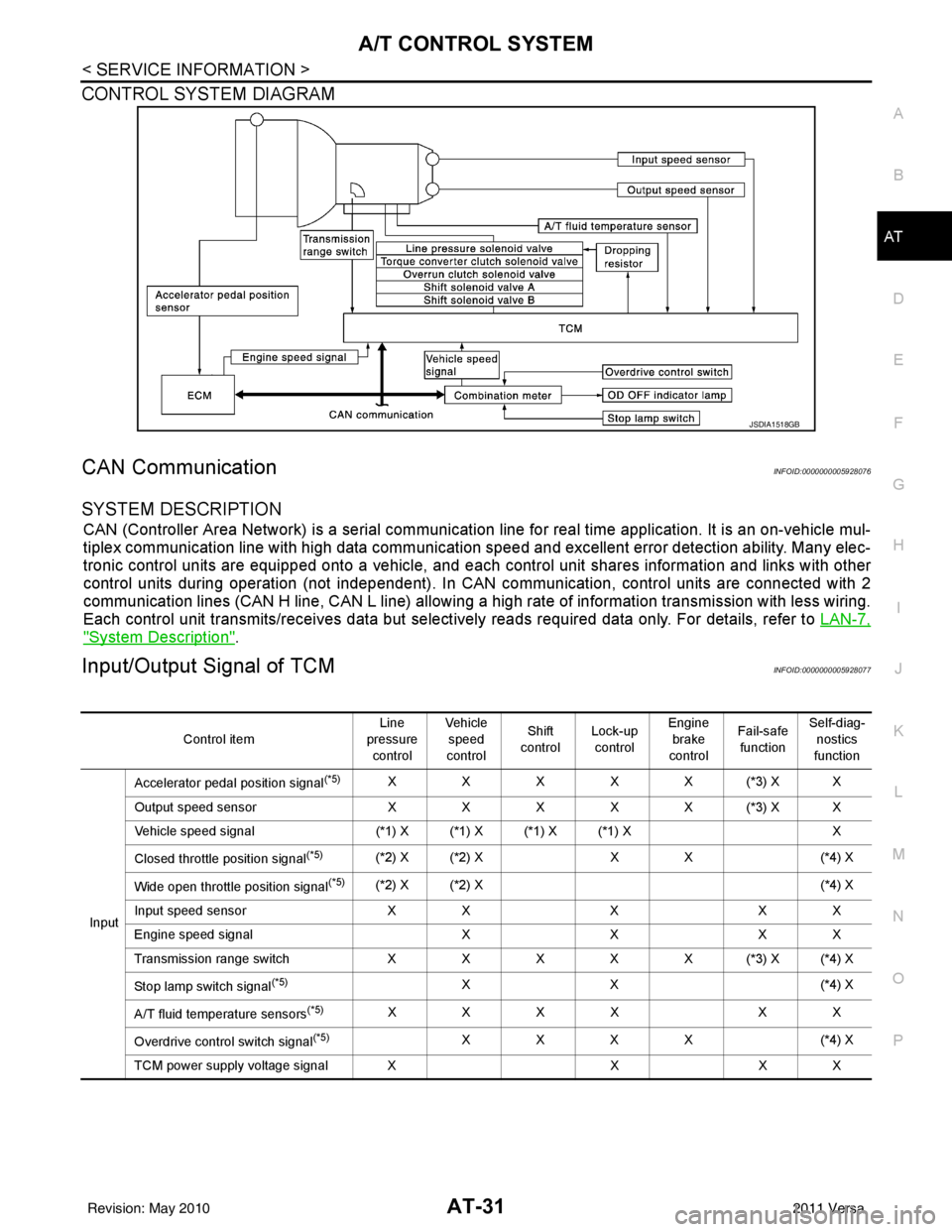
A/T CONTROL SYSTEMAT-31
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A
B
AT
N
O P
CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGRAM
CAN CommunicationINFOID:0000000005928076
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial communication line for real time application. It is an on-vehicle mul-
tiplex communication line with high data communication speed and excellent error detection ability. Many elec-
tronic control units are equipped onto a vehicle, and each control unit shares information and links with other
control units during operation (not independent). In CAN communication, control units are connected with 2
communication lines (CAN H line, CAN L line) allowing a high rate of information transmission with less wiring.
Each control unit transmits/receives data but selectively reads required data only. For details, refer to LAN-7,
"System Description".
Input/Output Signal of TCMINFOID:0000000005928077
JSDIA1518GB
Control itemLine
pressure control Veh icl e
speed
control Shift
control Lock-up
control Engine
brake
control Fail-safe
function Self-diag-
nostics
function
Input Accelerator pedal position signal
(*5)XXXXX(*3) XX
Output speed sensor X X X X X (*3) X X
Vehicle speed signal (*1) X (*1) X (*1) X (*1) X X
Closed throttle position signal
(*5)(*2) X (*2) X X X(*4) X
Wide open throttle position signal
(*5)(*2) X (*2) X (*4) X
Input speed sensor X XXX X
Engine speed signal XXX X
Transmission range sw itch XXXXX(*3) X(*4) X
Stop lamp switch signal
(*5)XX ( *4 ) X
A/T fluid temperature sensors
(*5)XXXX XX
Overdrive control switch signal
(*5)XXXX (*4) X
TCM power supply voltage signal X XX X
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 49 of 3787
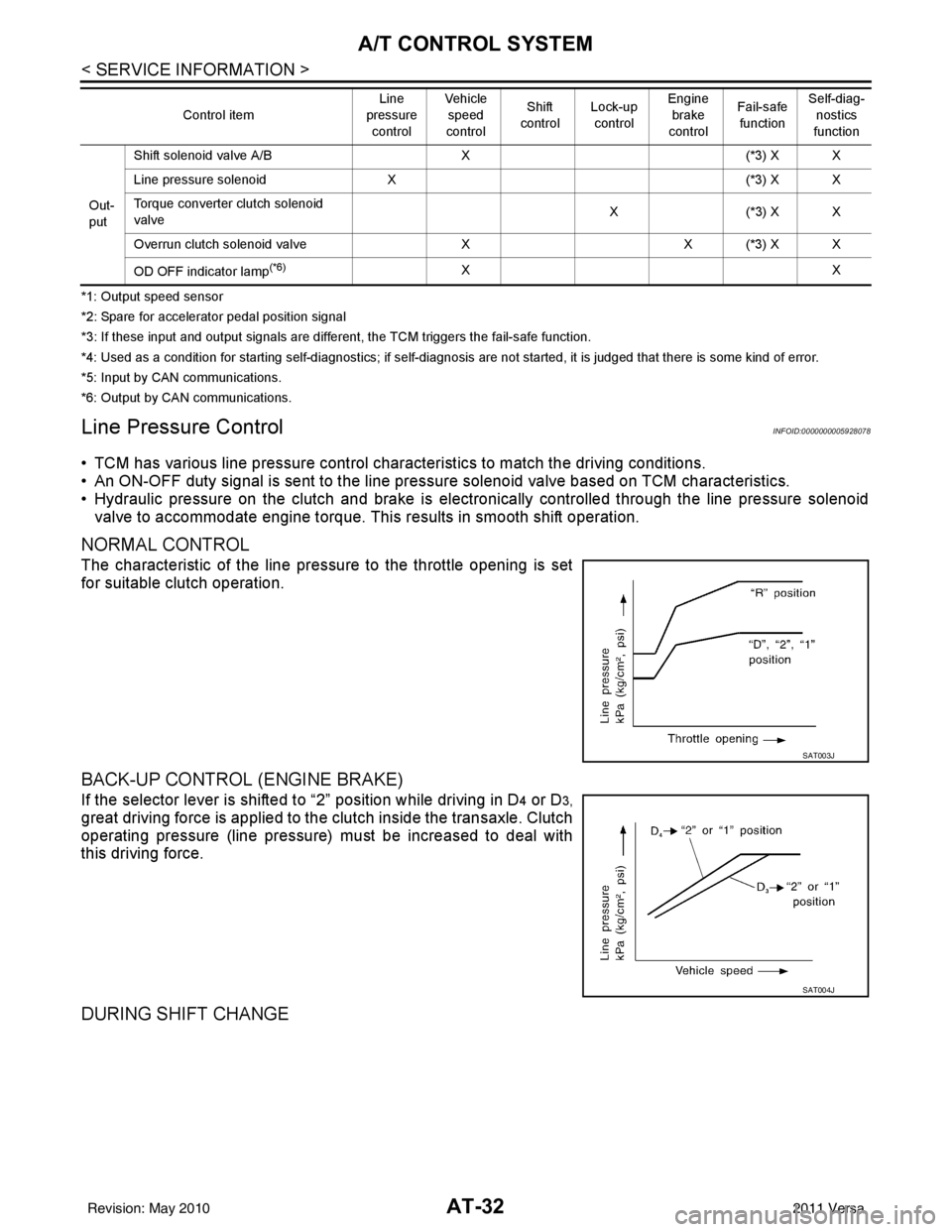
AT-32
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
A/T CONTROL SYSTEM
*1: Output speed sensor
*2: Spare for accelerator pedal position signal
*3: If these input and output signals are different, the TCM triggers the fail-safe function.
*4: Used as a condition for starting self-diagnostics; if self-diagnosis are not started, it is judged that there is some kind of error.
*5: Input by CAN communications.
*6: Output by CAN communications.
Line Pressure ControlINFOID:0000000005928078
• TCM has various line pressure control char acteristics to match the driving conditions.
• An ON-OFF duty signal is sent to the line pres sure solenoid valve based on TCM characteristics.
• Hydraulic pressure on the clutch and brake is electronically controlled through the line pressure solenoid valve to accommodate engine torque. This results in smooth shift operation.
NORMAL CONTROL
The characteristic of the line pressure to the throttle opening is set
for suitable clutch operation.
BACK-UP CONTROL (ENGINE BRAKE)
If the selector lever is shifted to “2” position while driving in D4 or D3,
great driving force is applied to the clutch inside the transaxle. Clutch
operating pressure (line pressure) must be increased to deal with
this driving force.
DURING SHIFT CHANGE
Out-
put Shift solenoid valve A/B
X(*3) X X
Line pressure solenoid X (*3) X X
Torque converter clutch solenoid
valve X(
*3 ) X X
Overrun clutch solenoid valve XX (*3) X X
OD OFF indicator lamp
(*6)XX
Control item
Line
pressure
control Vehicle
speed
control Shift
control Lock-up
control Engine
brake
control Fail-safe
function Self-diag-
nostics
function
SAT003J
SAT004J
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 50 of 3787

A/T CONTROL SYSTEMAT-33
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A
B
AT
N
O P
The line pressure is temporarily reduced corresponding to a change
in engine torque when shifting gears (that is, when the shift solenoid
valve is switched for clutch operation) to reduce shifting shock.
AT LOW FLUID TEMPERATURE
• A/T fluid viscosity and frictional characteristics of t he clutch facing change with A/T fluid temperature. Clutch
engaging or band-contacting pressure is compensated for, according to A/T fluid temperature, to stabilize
shifting quality.
• The line pressure is reduced below 60 °C (140° F) to prevent shift-
ing shock due to high viscosity of A/T fluid when temperature is
low.
• Line pressure is increased to a maximum irrespective of the throt- tle opening when A/T fluid temperature drops to −10° C (14° F). This
pressure rise is adopted to prevent a delay in clutch and brake
operation due to extreme drop of A/T fluid viscosity at low temper-
ature.
Shift ControlINFOID:0000000005928079
The shift is regulated entirely by electronic cont rol to accommodate vehicle speed and varying engine opera-
tions. This is accomplished by electrical signals trans mitted by the output speed sensor and the ECM (acceler-
ator pedal position sensor). This results in improved acceleration performance and fuel economy.
CONTROL OF SHIFT SOLENOID VALVES A AND B
The TCM activates shift solenoid valves A and B according to sig-
nals from the accelerator pedal position sensor and output speed
sensor to select the optimum gear position on the basis of the shift
schedule memorized in the TCM.
The shift solenoid valve performs simple ON-OFF operation. When
set to “ON”, the drain circuit closes and pilot pressure is applied to
the shift valve.
RELATION BETWEEN SHIFT SOLENOID VALVES A AND B AND GEAR POSITIONS
SCIA4828E
SCIA4829E
SCIA4830E
SAT008J
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 51 of 3787
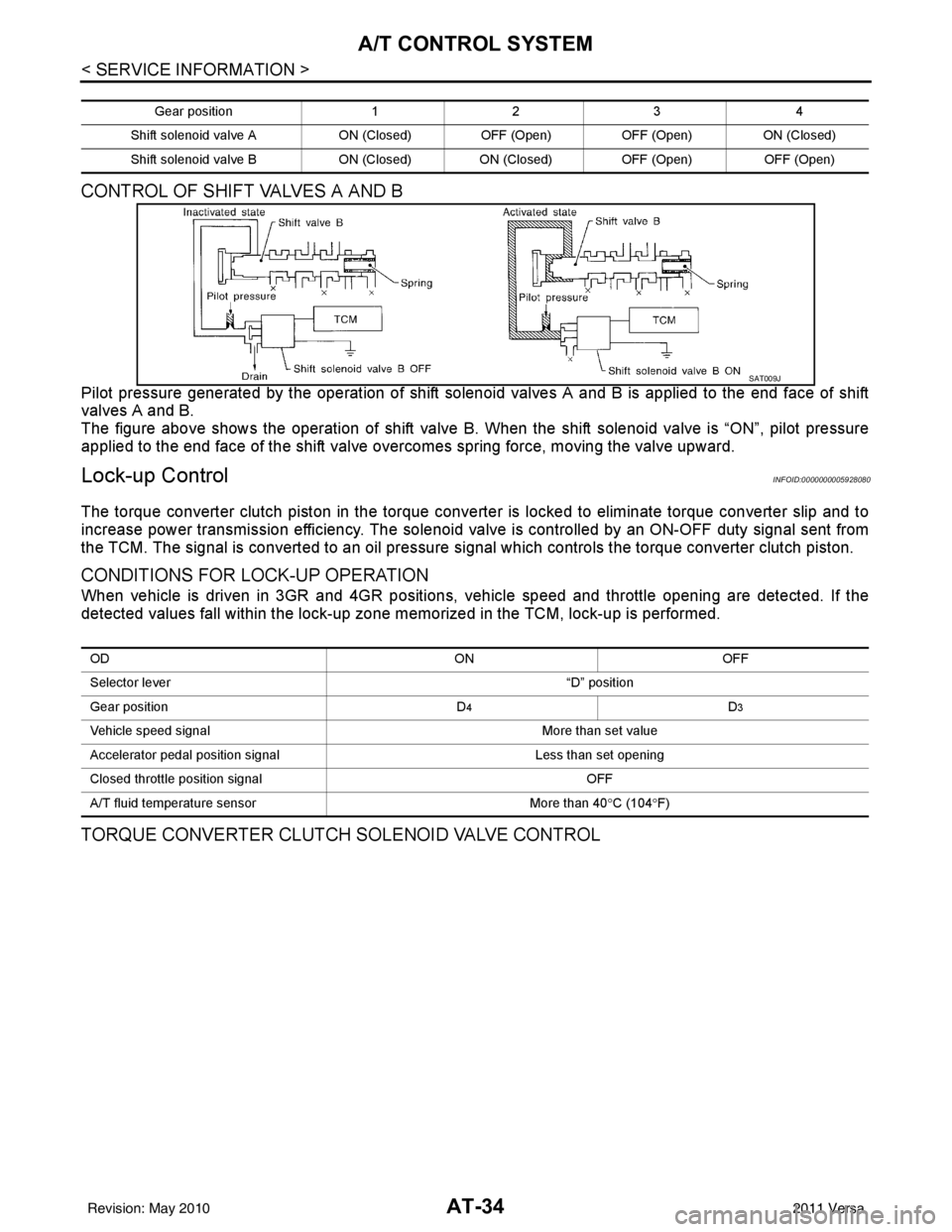
AT-34
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
A/T CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTROL OF SHIFT VALVES A AND B
Pilot pressure generated by the operation of shift solenoid valves A and B is applied to the end face of shift
valves A and B.
The figure above shows the operation of shift valve B. When the shift solenoid valve is “ON”, pilot pressure
applied to the end face of the shift valve overcomes spring force, moving the valve upward.
Lock-up ControlINFOID:0000000005928080
The torque converter clutch piston in the torque conver ter is locked to eliminate torque converter slip and to
increase power transmission efficiency. The solenoid va lve is controlled by an ON-OFF duty signal sent from
the TCM. The signal is converted to an oil pressure si gnal which controls the torque converter clutch piston.
CONDITIONS FOR LOCK-UP OPERATION
When vehicle is driven in 3GR and 4GR positions, v ehicle speed and throttle opening are detected. If the
detected values fall within the lock-up zone me morized in the TCM, lock-up is performed.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID VALVE CONTROL
Gear position123 4
Shift solenoid valve A ON (Closed)OFF (Open)OFF (Open) ON (Closed)
Shift solenoid valve B ON (Closed)ON (Closed) OFF (Open) OFF (Open)
SAT009J
OD ONOFF
Selector lever “D” position
Gear position D
4D3
Vehicle speed signal More than set value
Accelerator pedal position signal Less than set opening
Closed throttle position signal OFF
A/T fluid temperature sensor More than 40°C (104 °F)
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 56 of 3787

ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEMAT-39
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A
B
AT
N
O P
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
IntroductionINFOID:0000000005928084
A/T system has two self-diagnostic systems.
The first is emission-related on board diagnostic system (OBD-II) performed by the TCM in combination with
the ECM. The malfunction is indicated by the MIL (malf unction indicator lamp) and is stored as a DTC in the
ECM memory but not the TCM memory.
The second is the TCM original self-diagnosis indicated by the OD OFF indicator lamp. The malfunction is
stored in the TCM memory. The detected items are ov erlapped with OBD-II self-diagnostic items. For detail,
refer to AT-77, "
CONSULT-III Function (TRANSMISSION)" .
OBD-II Function for A/T SystemINFOID:0000000005928085
The ECM provides emission-related on board diagnostic (O BD-II) functions for the A/T system. One function
is to receive a signal from the TCM used with OBD-rela ted parts of the A/T system. The signal is sent to the
ECM when a malfunction occurs in the corresponding OBD-re lated part. The other function is to indicate a
diagnostic result by means of the MIL (malfunction indica tor lamp) on the instrument panel. Sensors, switches
and solenoid valves are used as sensing elements.
The MIL automatically illuminates in One or Two Trip Detection Logic when a malfunction is sensed in relation
to A/T system parts.
One or Two Trip Detection Logic of OBD-IIINFOID:0000000005928086
ONE TRIP DETECTION LOGIC
If a malfunction is sensed during the first test drive, the MIL will illuminate and the malfunction will be stored in
the ECM memory as a DTC. The TCM is not provided with such a memory function.
TWO TRIP DETECTION LOGIC
When a malfunction is sensed during the first test drive, it is stored in the ECM memory as a 1st trip DTC
(diagnostic trouble code) or 1st trip freeze frame data. At this point, the MIL will not illuminate. — 1st trip
If the same malfunction as that experienced during the fi rst test drive is sensed during the second test drive,
the MIL will illuminate. — 2nd trip
The “trip” in the “One or Two Trip Detection Logic” m eans a driving mode in which self-diagnosis is performed
during vehicle operation.
OBD-II Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)INFOID:0000000005928087
HOW TO READ DTC AND 1ST TRIP DTC
DTC and 1st trip DTC can be read by the following methods.
( with CONSULT-III or GST) CONSULT-III or GST (Generic Scan Tool) Examples: P0705, P0720 etc.
These DTC are prescribed by SAE J2012.
(CONSULT-III also displays the malfunctioning component or system.)
• 1st trip DTC No. is the same as DTC No.
• Output of the diagnostic trouble code indicates that the indicated circuit has a malfunction. How-
ever, in case of the Mode II and GST, they do not indicate whether the malfunction is still occurring or
occurred in the past and returned to normal.
CONSULT-III can identify them as shown below, therefore, CONS ULT-III (if available) is recom-
mended.
DTC or 1st trip DTC of a malfunction is displayed in SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS mode for “ENGINE” with
CONSULT-III. Time data indicates how many times the vehicle was driven after the last detection of a DTC.
If the DTC is being detected curr ently, the time data will be “0”.
If a 1st trip DTC is stored in the ECM, the time data will be “1t”.
Freeze Frame Data and 1st Trip Freeze Frame Data
The ECM has a memory function, which stores the driv ing condition such as fuel system status, calculated
load value, engine coolant temperature, short term f uel trim, long term fuel trim, engine speed and vehicle
speed at the moment the ECM detects a malfunction.
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 59 of 3787

AT-42
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
DTC Inspection Priority ChartINFOID:0000000005928089
If some DTCs are displayed at the same time, perform inspections one by one based on the following priority
chart.
NOTE:
If DTC “CAN COMM CIRCUIT” is displayed with other DTCs, first perform the trouble diagnosis for
DTC “CAN COMM CIRCUIT”. Refer to AT- 8 7
.
Fail-SafeINFOID:0000000005928090
The TCM has an electronic Fail-safe mode. This allows t he vehicle to be driven even if a major electrical input/
output device circuit is damaged.
Under Fail-Safe, the vehicle always runs in 3GR, even wit h a shift lever position of “1”, “2” or “D”. The cus-
tomer may complain of sluggish or poor acceleration.
Always follow the “ AT-43, "
How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate Repair" ”.
The SELF-DIAGNOSIS results will be as follows:
• The first SELF-DIAGNOSIS will indicate damage to the vehicle speed signal or the output speed sensor.
• During the next SELF-DIAGNOSIS, performed after checking the sensor, no damages will be indicated.
FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION
The following fail-safe functions allow vehicles to be driven even when sensor, switch or solenoid malfunction
occurs.
Output Speed Sensor
Vehicle speed signal is input from combination meter.
Accelerator Pedal Position Signal and Throttle Position Signal
TCM controls the throttle opening angle to a predetermined fixed position to enable driving if a malfunctioning
signal is input to TCM.
Transmission Range Switch
When the multiple transmission range switch signals are input to TCM, the priority of selector lever position
becomes “D”, “N”, “R”, “2” and “1” in order by internal TCM determination.
The use of 4GR is inhibited until normal operation resumes. Because the hydraulic circuit of the control valve
is switched by manual valve according to the selector lever position, however, actual operating condition of
vehicle becomes as follows.
Shift Solenoid Valve A and B
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, use of certain gears is limited. Refer to chart shown below.
Priority Detected items
1 CAN communication line
2 Except above
Actual lever positionTransmission range switch input signal Running status
“P” “P” position and other position signals P
“R” “R” position and other position signals R
“N” “N” position and other position signals N
“D” “D” position and other position signals D
1 ⇔ D2 ⇔ D3 ⇔ D4
“2” “2” position and other position signals (Except “1” position)
21 ⇔ 22 ⇔ 23
“2” position and “1” position signals 21 ⇔ 22
“1” “1” position and other position signals (Except “2” position)
11 ⇔ 12 ⇔ 13
“1” position and “2” position signals 11 ⇔ 12
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 60 of 3787

TROUBLE DIAGNOSISAT-43
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A
B
AT
N
O P
�z : Solenoid ON
× : Solenoid OFF
–: Non-standard condition
Line Pressure Solenoid Valve
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, line pre ssure solenoid valve is turned OFF to achieve maxi-
mum oil pressure.
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, torque conv erter clutch solenoid valve is turned OFF to release
lock-up.
Overrun Clutch Solenoid Valve
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, overr un clutch solenoid valve is turned OFF to engage overrun
clutch. This will result in more effective engine brake during deceleration.
How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate RepairINFOID:0000000005928091
INTRODUCTION
The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, accelera-
tor pedal position sensor or transmission range switch and provides
shift control or lock-up control via A/T solenoid valves.
The TCM also communicates with the ECM by means of a signal
sent from sensing elements used wit h the OBD-related parts of the
A/T system for malfunction-diagnostic purposes. The TCM is capa-
ble of diagnosing malfunctioning parts while the ECM can store mal-
functions in its memory.
Input and output signals must always be correct and stable in the
operation of the A/T system. T he A/T system must be in good oper-
ating condition and be free of valve seizure, solenoid valve malfunc-
tion, etc.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a malfunction that occurs intermittently rather than continuously. Most
intermittent malfunctions are caused by poor electric c onnections or improper wiring. In this case, careful
checking of suspected circuits may hel p prevent the replacement of good parts.
Shift positionNormal
Malfunction in solenoid
valve A Malfunction in solenoid
valve B Malfunction in solenoid
valves A and B
A BGearABGearABGearABGear
“D” position �z�z
1st –�z→×
3rd �z
→× –
3rd ––
3rd
×
�z2nd – �z→× ×–––
×× 3rd – x ×–––
�z ×4th – x �z→× –––
“2” position �z�z
1st –�z→× �z→× –––
× �z2nd – �z→× ×–––
×× 3rd – x ×–––
“1” position �z�z
1st –�z→× �z→× –––
× �z2nd – �z→× ×–––
×× 3rd – x ×–––
SAT631IA
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 64 of 3787
TROUBLE DIAGNOSISAT-47
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A
B
AT
N
O P
4. �† Perform “Road Test”. AT- 5 5
4-1. “Check Before Engine is Started” AT- 5 6
�†AT- 1 8 0 , "OD OFF Indicator Lamp Does Not Come On"
�† Perform self-diagnosis. Enter checks for detected items. AT- 7 7 , AT- 8 2 .
�† CAN COMM CIRCUIT AT- 8 7
.
�† TRANSMISSION RANGE SWITCH A AT- 9 0
.
�† TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR A AT- 9 5
.
�† OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR AT- 1 0 0
.
�† ENGINE SPEED AT- 1 0 5
.
�† 1GR INCORRECT RATIO AT- 1 0 9
�† 2GR INCORRECT RATIO AT- 11 2 .
�† 3GR INCORRECT RATIO AT- 11 5
.
�† 4GR INCORRECT RATIO AT- 11 8
.
�† TORQUE CONVERTER AT- 1 2 3
.
�† TORQUE CONVERTER AT- 1 2 8
.
�† PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID A AT- 1 3 3
.
�† SHIFT SOLENOID A AT- 1 3 8
.
�† SHIFT SOLENOID B AT- 1 4 3
.
�† OVERRUN CLUTCH SOLENOID AT- 1 4 8
.
�† VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL AT- 1 5 3
.
�† BATT/FLUID TEMP SEN AT- 1 5 6
.
�† INPUT SPEED SENSOR A AT- 1 6 2
.
�† CONTROL UNIT (RAM), CONTROL UNIT (ROM) AT- 1 6 7
.
�† MAIN POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND CIRCUIT AT- 1 6 8
.
4-2. “Check at Idle” AT- 5 6
�†AT- 1 8 2 , "Engine Cannot Be Started in "P" and "N" Position" .
�† AT- 1 8 3 , "
In "P" Position, Vehicle Moves Forward or Backward When Pushed" .
�† AT- 1 8 3 , "
In "N" Position, Vehicle Moves" .
�† AT- 1 8 4 , "
Large Shock "N" → "R" Position" .
�† AT- 1 8 5 , "
Vehicle Does Not Creep Backward in "R" Position" .
�† AT- 1 8 6 , "
Vehicle Does Not Creep Forward in "D", "2" or "1" Position" .
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 65 of 3787

AT-48
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
4. 4-3. “Cruise Test”AT- 5 8
Part 1
�†AT- 1 8 7 , "
Vehicle Cannot Be Started from D1" .
�† AT- 1 8 9 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D1→ D2or Does Not Kickdown: D4→ D2" .
�† AT- 1 9 0 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D2→ D3" .
�† AT- 1 9 2 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D3→ D4" .
�† AT- 1 9 3 , "
A/T Does Not Perform Lock-up" .
�† AT- 1 9 4 , "
A/T Does Not Hold Lock-up Condition" .
�† AT- 1 9 5 , "
Lock-up Is Not Released" .
�† AT- 1 9 6 , "
Engine Speed Does Not Return to Idle (Light Braking D4→ D3)" .
Part 2 AT- 6 1
�†AT- 1 8 7 , "Vehicle Cannot Be Started from D1" .
�† AT- 1 8 9 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D1→ D2or Does Not Kickdown: D4→ D2" .
�† AT- 1 9 0 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D2→ D3" .
�† AT- 1 9 2 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D3→ D4" .
Part 3 AT- 6 2
�†AT- 1 9 7 , "A/T Does Not Shift: D4→ D3, When OD OFF" .
�† AT- 1 9 8 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D3→ 22, When Selector Lever "D" → "2" Position" .
�† AT- 1 9 9 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: 22→ 11, When Selector Lever "2" → "1" Position" .
�† AT- 2 0 1 , "
Vehicle Does Not Decelerate by Engine Brake" .
�† Perform self-diagnosis. Enter checks for detected items. AT- 7 7
, AT- 8 2 .
�† CAN COMM CIRCUIT AT- 8 7
.
�† TRANSMISSION RANGE SWITCH A AT- 9 0
.
�† TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR A AT- 9 5
.
�† OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR AT- 1 0 0
.
�† ENGINE SPEED AT- 1 0 5
.
�† 1GR INCORRECT RATIO AT- 1 0 9
�† 2GR INCORRECT RATIO AT- 11 2 .
�† 3GR INCORRECT RATIO AT- 11 5
.
�† 4GR INCORRECT RATIO AT- 11 8
.
�† TORQUE CONVERTER AT-123
.
�† TORQUE CONVERTER AT-128
.
�† PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID A AT- 1 3 3
.
�† SHIFT SOLENOID A AT- 1 3 8
.
�† SHIFT SOLENOID B AT- 1 4 3
.
�† OVERRUN CLUTCH SOLENOID AT- 1 4 8
.
�† VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL AT- 1 5 3
.
�† BATT/FLUID TEMP SEN AT-156
.
�† INPUT SPEED SENSOR A AT- 1 6 2
.
�† CONTROL UNIT (RAM), CONTROL UNIT (ROM) AT-167
.
�† MAIN POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND CIRCUIT AT- 1 6 8
.
5. �† For self-diagnosis NG items, inspect each component. Repair or replace the damaged parts. AT- 7 7
,
AT- 8 2
6. �† Perform “Road Test”. AT- 5 5
7.�† Perform the Diagnostic Procedures for all remaining items marked NG. Repair or replace the damaged parts.
Refer to the Symptom Chart when you perform the procedures. (The chart also shows some other possible symp-
toms and the component inspection orders.) AT- 6 5
8.
�† Erase DTC from TCM and ECM memories. AT- 3 9,
AT- 8 2
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa