change time NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2001, Model line: X-TRAIL, Model: NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001Pages: 3833, PDF Size: 39.49 MB
Page 2 of 3833

FOREWORD
This manual contains maintenance and repair procedures for the NISSAN
X-TRAIL , model T30 series.
In order to assure your safety and the efficient functioning of the vehicle,
this manual should be read thoroughly. It is especially important that the
PRECAUTIONS in the GI section be completely understood before starting
any repair task.
All information in this manual is based on the latest product information
at the time of publication. The right is reserved to make changes in speci-
fications and methods at any time without notice.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
The proper performance of service is essential for both the safety of the
technician and the efficient functioning of the vehicle.
The service methods in this Service Manual are described in such a man-
ner that the service may be performed safely and accurately.
Service varies with the procedures used, the skills of the technician and the
tools and parts available. Accordingly, anyone using service procedures,
tools or parts which are not specifically recommended by NISSAN must
first be completely satisfied that neither personal safety nor the vehicle’s
safety will be jeopardized by the service method selected.
NISSAN EUROPE S.A.S.
Service Operations Section
Paris, France
Page 8 of 3833

GI-6
PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION:
●Do not use home heating oil, gasoline or other alternate fuels in your diesel engine. The use of
those can cause engine damage.
●Do not use summer fuel at temperatures below –7°C (20°F). The cold temperatures will cause wax
to form in the fuel. As a result, it may prevent the engine from running smoothly.
●Do not add gasoline or other alternate fuels to diesel fuel.
Precautions for Multiport Fuel Injection System or Engine Control SystemEAS000FT
●Before connecting or disconnecting any harness connector for
the multiport fuel injection system or ECM:
Turn ignition switch to “OFF” position.
Disconnect negative battery terminal.
Otherwise, there may be damage to ECM.
●Before disconnecting pressurized fuel line from fuel pump to
injectors, be sure to release fuel pressure.
●Be careful not to jar components such as ECM and mass air
flow sensor.
Precautions for Turbocharger (If Equipped)EAS000FU
The turbocharger turbine revolves at extremely high speeds and
becomes very hot. Therefore, it is essential to maintain a clean sup-
ply of oil flowing through the turbocharger and to follow all required
maintenance instructions and operating procedures.
●Always use the recommended oil. Follow the instructions for
proper time to change the oil and proper oil level.
●Avoid accelerating engine to a high rpm immediately after start-
ing.
●If engine had been operating at high rpm for an extended period
of time, let it idle for a few minutes prior to shutting if off.
Precautions for HosesEAS000FV
HOSE REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
●To prevent damage to rubber hose, do not pry off rubber hose
with tapered tool or screwdriver.
●To reinstall the rubber hose securely, make sure that hose inser-
tion length and orientation is correct. (If tube is equipped with
hose stopper, insert rubber hose into tube until it butts up
against hose stopper.)
SGI787
SGI292
SMA019D
SMA020D
Page 28 of 3833
GI-26
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Cold or Hot Start Up
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the car is started cold, or it may occur when
the car is restarted hot shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep the car overnight to
make a proper diagnosis.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
Introduction
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is approached in a logical and organized method.
Before beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thor-
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
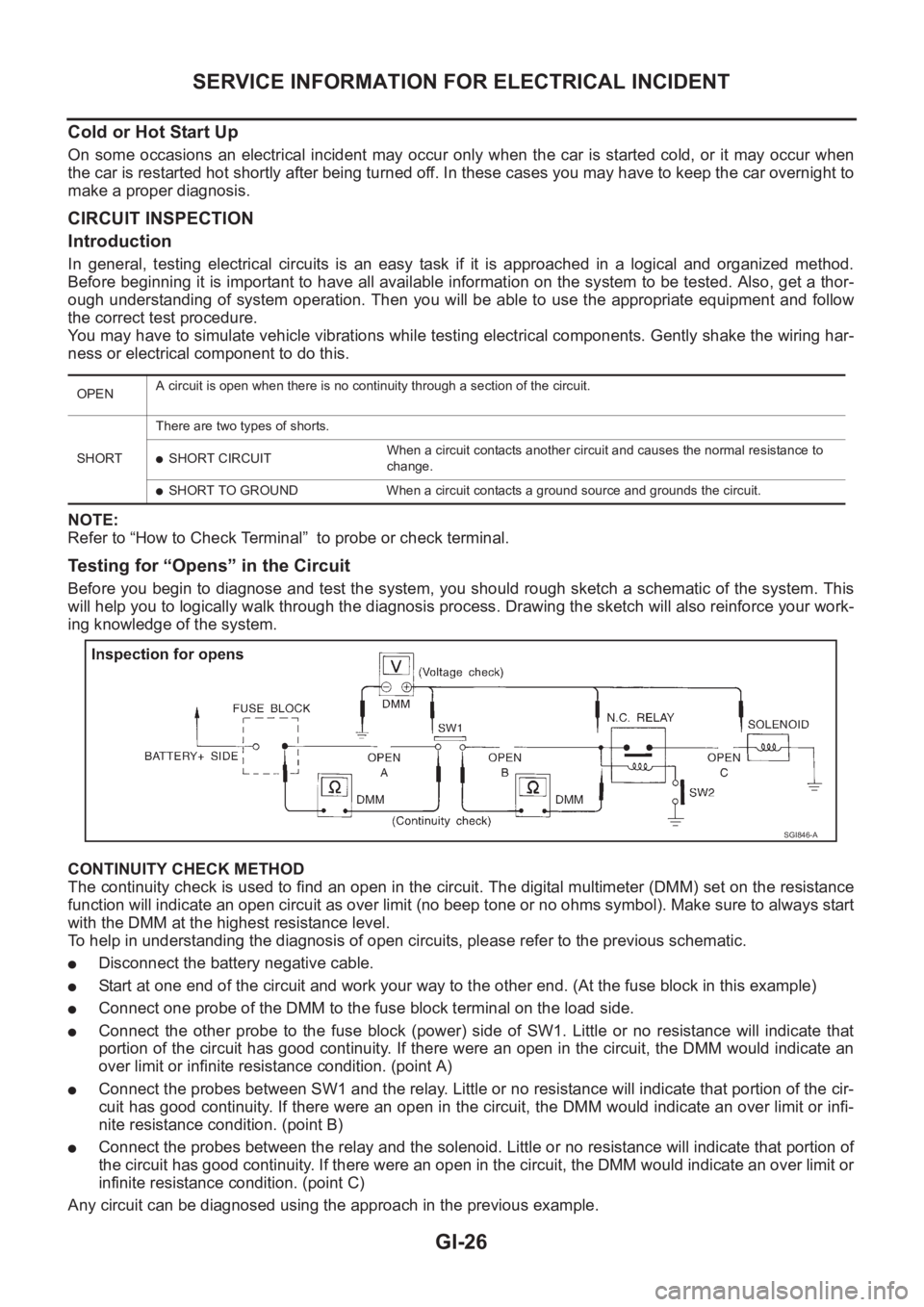
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbol). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits, please refer to the previous schematic.
●Disconnect the battery negative cable.
●Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
●Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
●Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that
portion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an
over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
●Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the cir-
cuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point B)
●Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of
the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or
infinite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
OPENA circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORTThere are two types of shorts.
●SHORT CIRCUITWhen a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
●SHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A
Page 37 of 3833

LIFTING POINT
GI-35
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
LIFTING POINTPFP:00000
Special Service Tools EAS000FH
CAUTION:
●Every time the vehicle is lifted up, maintain the complete vehicle curb condition.
●Since the vehicle's center of gravity changes when removing main parts on the front side (engine,
transmission, suspension etc.), support a jack up point on the rear side garage jack with a mission
jack or equivalent.
●Since the vehicle's center of gravity changes when removing main parts on the rear side (rear axle,
suspension, etc.), support a jack up point on the front side garage jack with a mission jack or
equivalent.
●Be careful not to smash or do not do anything that would affect piping parts.
Garage Jack and Safety Stand EAS000FI
WARNING:
●Park the vehicle on a level surface when using the jack. Make sure to avoid damaging pipes,
tubes, etc. under the vehicle.
●Never get under the vehicle while it is supported only by the jack. Always use safety stands when
you have to get under the vehicle.
Tool number
Tool nameDescription
LM4086-0200
Board on lift attachment
LM4519-0000
Safety stand attachment
S-NT001
S-NT002
Page 103 of 3833
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual CAMSHAFT
EM-53
[QR]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
Valve Lifter Hole Diameter
Using inside micrometer, measure diameter of valve lifter hole of cyl-
inder head.
Calculation of Valve Lifter Clearance
(Valve NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual CAMSHAFT
EM-53
[QR]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
Valve Lifter Hole Diameter
Using inside micrometer, measure diameter of valve lifter hole of cyl-
inder head.
Calculation of Valve Lifter Clearance
(Valve](/img/5/57405/w960_57405-102.png)
CAMSHAFT
EM-53
[QR]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
Valve Lifter Hole Diameter
Using inside micrometer, measure diameter of valve lifter hole of cyl-
inder head.
Calculation of Valve Lifter Clearance
(Valve lifter clearance) = (hole diameter of valve lifter) – (outer diam-
eter of valve lifter).
●When out of specified range, referring to each specification of
outer and inner diameter, replace either or both valve lifter and
cylinder head.
Va l v e C l e a r a n c eEBS00LS3
INSPECTION
Perform inspection as follows after removal, installation or replacement of camshaft or valve-related parts, or if
there is unusual engine conditions due to changes in valve clearance over time (starting, idling, and/or noise).
1. Warm up engine. Then stop it.
2. Remove splash cover on RH undercover.
3. Remove rocker cover. Refer to EM-35, "
ROCKER COVER" .
4. Turn crankshaft pulley in normal direction (clockwise when
viewed from front) to align TDC identification notch (without
paint mark) with timing indicator.
5. At this time, check that the both intake and exhaust cam noses
of No. 1 cylinder face outside.
●If they do not face outside, turn crankshaft pulley once more.
6. By referring to the figure, measure valve clearances at locations
marked X as shown in the table below (locations indicated with
black arrow in figure) with a feeler gauge.
●No. 1 cylinder compression TDC.Standard: 34.000 - 34.021 mm (1.3386 - 1.3394 in)
Standard: 0.020 - 0.056 mm (0.0008 - 0.0022 in)
PBIC0043E
KBIA0190E
KBIA0400J
Measuring position No.1 CYL. No.2 CYL. No.3 CYL. No.4 CYL.
No.1 cylinder at
TDCINT X X
EXH X X
SBIA0261E
Page 288 of 3833
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual LU-8
[QR]
ENGINE OIL
c. After warming up the engine, check for engine oil leakage with running engine.
Changing Engine OilEBS00KO4
WARNING:
●Be careful not to burn yourself, as the engine oil is hot NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual LU-8
[QR]
ENGINE OIL
c. After warming up the engine, check for engine oil leakage with running engine.
Changing Engine OilEBS00KO4
WARNING:
●Be careful not to burn yourself, as the engine oil is hot](/img/5/57405/w960_57405-287.png)
LU-8
[QR]
ENGINE OIL
c. After warming up the engine, check for engine oil leakage with running engine.
Changing Engine OilEBS00KO4
WARNING:
●Be careful not to burn yourself, as the engine oil is hot.
●Prolonged and repeated contact with used engine oil may
cause skin cancer. Try to avoid direct skin contact with
used engine oil. If skin contact is made, wash thoroughly
with soap or hand cleaner as soon as possible.
1. Warm up engine, put vehicle horizontally and check for engine
oil leakage from engine components.
2. Stop engine and wait for 10 minutes.
3. Remove drain plug and oil filler cap.
4. Drain engine oil.
●Install drain plug and refill with new engine oil.
Engine oil specifications and viscosity:
●API grade SG, SH, SJ or SL.
●ILSAC grade GF-I, GF-II or GF-III
●ACEA 96-A2
●Refer to MA-16, "RECOMMENDED FLUIDS AND LUBRICANTS" for further detail.
Engine oil capacity (Approximate):
Unit: (lmp qt)
CAUTION:
●Be sure to clean drain plug and install with new washer.
●The refill capacity depends on the engine oil temperature and drain time. Use these specifica-
tions for reference only.
●Always use the dipstick to the determine when the proper amount of engine oil is in the engine.
5. Warm up engine and check area around drain plug and oil filter for engine oil leakage.
6. Stop engine and wait for 10 minutes.
7. Check engine oil level. Refer to LU-7, "
ENGINE OIL LEVEL" . Oil pressure switch:
: 12.3 - 17.2 N·m (1.25 - 1.75 kg-m, 9 - 12 ft-lb)
PBIC0250E
Drain and refillWith oil filter change Approximately 3.9 (3-3/8)
Without oil filter change Approximately 3.5 (3-1/8)
Dry engine (engine overhaul)Approximately 4.5 (4)
Oil pan drain plug:
: 29.4 - 39.2 N·m (3.0 - 4.0 kg-m, 22 - 28 ft-lb)
Page 299 of 3833
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual ENGINE OIL
LU-19
[YD22DDTi]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
LUc. After warming up the engine, check for oil leakage with running engine.
Changing Engine OilEBS00B04
WARNING:
●Be careful not to burn yourself, NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual ENGINE OIL
LU-19
[YD22DDTi]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
LUc. After warming up the engine, check for oil leakage with running engine.
Changing Engine OilEBS00B04
WARNING:
●Be careful not to burn yourself,](/img/5/57405/w960_57405-298.png)
ENGINE OIL
LU-19
[YD22DDTi]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
LUc. After warming up the engine, check for oil leakage with running engine.
Changing Engine OilEBS00B04
WARNING:
●Be careful not to burn yourself, as the engine oil is hot.
●Prolonged and repeated contact with used engine oil may
cause skin cancer: try to avoid direct skin contact with
used engine oil. If skin contact is made, wash thoroughly
with soap or hand cleaner as soon as possible.
1. Warm up engine, put vehicle horizontally and check for engine
oil leakage from engine components.
2. Stop engine and wait for 10 minutes.
3. Remove drain plug and oil filler cap.
4. Drain engine oil.
●Install drain plug and refill with new engine oil.
Engine oil specification and viscosity:
●API grade CF-4.
●ACEA B1, B3, B4, B5
●Refer to MA-16, "RECOMMENDED FLUIDS AND LUBRI-
CANTS" .
Engine oil capacity (Approximate):
●The refill capacity depends on the engine oil temperature and drain time. Use these specifications for
reference only.
Always use the dipstick to the determine when the proper amount of engine oil is in the engine.
CAUTION:
●Be sure to clean drain plug and install with new washer.
●The refill capacity depends on the engine oil temperature and drain time. Use these specifica-
tions for reference only.
Always use the dipstick to the determine when the proper amount of engine oil is in the
engine.
5. Warm up engine and check area around drain plug and oil filter for engine oil leakage.
6. Stop engine and wait for 10 minutes.
7. Check engine oil level. Refer to LU-18, "
ENGINE OIL LEVEL AND MUDDINESS" . Oil pressure switch:
: 13.0 - 17.0 N·m (1.4 - 1.7 kg-m, 10 - 12 ft-lb)
PBIC0527E
Drain and refillWith oil filter change
5.2 (4-5/8 Imp qt)
Without oil filter change
4.9 (4-3/8 Imp qt)
Dry engine (engine overhaul)6.3 (5-1/2 Imp qt)
Oil pan drain plug:
: 29 - 39 N·m (3.0 - 4.0 kg-m, 22 - 29 ft-lb)
SBIA0122E
Page 385 of 3833
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
EC-35
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
inally designed. Both manufacturing differences (i.e., mass air flow sensor hot film) and characteristic changes
during oper NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
EC-35
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
inally designed. Both manufacturing differences (i.e., mass air flow sensor hot film) and characteristic changes
during oper](/img/5/57405/w960_57405-384.png)
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
EC-35
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
inally designed. Both manufacturing differences (i.e., mass air flow sensor hot film) and characteristic changes
during operation (i.e., injector clogging) directly affect mixture ratio.
Accordingly, the difference between the basic and theoretical mixture ratios is monitored in this system. This is
then computed in terms of “injection pulse duration” to automatically compensate for the difference between
the two ratios.
“Fuel trim” refers to the feedback compensation value compared against the basic injection duration. Fuel trim
includes short term fuel trim and long term fuel trim.
“Short term fuel trim” is the short-term fuel compensation used to maintain the mixture ratio at its theoretical
value. The signal from heated oxygen sensor 1 indicates whether the mixture ratio is RICH or LEAN compared
to the theoretical value. The signal then triggers a reduction in fuel volume if the mixture ratio is rich, and an
increase in fuel volume if it is lean.
“Long term fuel trim” is overall fuel compensation carried out long-term to compensate for continual deviation
of the short term fuel trim from the central value. Such deviation will occur due to individual engine differences,
wear over time and changes in the usage environment.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING
Two types of systems are used.
Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System
Fuel is injected into each cylinder during each engine cycle according to the firing order. This system is used
when the engine is running.
Simultaneous Multiport Fuel Injection System
Fuel is injected simultaneously into all four cylinders twice each engine cycle. In other words, pulse signals of
the same width are simultaneously transmitted from the ECM.
The four injectors will then receive the signals two times for each engine cycle.
This system is used when the engine is being started and/or if the fail-safe system (CPU) is operating.
FUEL SHUT-OFF
Fuel to each cylinder is cut off during deceleration or operation of the engine at excessively high speeds.
Electronic Ignition (EI) SystemEBS00M0D
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL CHART
SEF337W
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS)
Engine speed
Piston position
Ignition
timing con-
trolPower transistor Camshaft position sensor (PHASE)
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
Accelerator pedal position sensor Accelerator pedal position
Ignition switch Start signal
Knock sensor Engine knocking
Park/neutral position (PNP) switch Gear position
Battery Battery voltage
Wheel sensor Vehicle speed
Page 398 of 3833
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual EC-48
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
If a 1st trip DTC is stored in the ECM, the time data will be “[1t]”.
FREEZE FRAME DATA AND 1ST TRIP FREEZE FRAME DATA
The ECM records NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual EC-48
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
If a 1st trip DTC is stored in the ECM, the time data will be “[1t]”.
FREEZE FRAME DATA AND 1ST TRIP FREEZE FRAME DATA
The ECM records](/img/5/57405/w960_57405-397.png)
EC-48
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
If a 1st trip DTC is stored in the ECM, the time data will be “[1t]”.
FREEZE FRAME DATA AND 1ST TRIP FREEZE FRAME DATA
The ECM records the driving conditions such as fuel system status, calculated load value, engine coolant tem-
perature, short term fuel trim, long term fuel trim, engine speed, vehicle speed, base fuel schedule and intake
air temperature at the moment a malfunction is detected.
Data which are stored in the ECM memory, along with the 1st trip DTC, are called 1st trip freeze frame data.
The data, stored together with the DTC data, are called freeze frame data and displayed on CONSULT-II or
GST. The 1st trip freeze frame data can only be displayed on the CONSULT-II screen, not on the GST. For
details, see EC-97
.
Only one set of freeze frame data (either 1st trip freeze frame data or freeze frame data) can be stored in the
ECM. 1st trip freeze frame data is stored in the ECM memory along with the 1st trip DTC. There is no priority
for 1st trip freeze frame data and it is updated each time a different 1st trip DTC is detected. However, once
freeze frame data (2nd trip detection/MI on) is stored in the ECM memory, 1st trip freeze frame data is no
longer stored. Remember, only one set of freeze frame data can be stored in the ECM. The ECM has the fol-
lowing priorities to update the data.
For example, the EGR malfunction (Priority: 2) was detected and the freeze frame data was stored in the 2nd
trip. After that when the misfire (Priority: 1) is detected in another trip, the freeze frame data will be updated
from the EGR malfunction to the misfire. The 1st trip freeze frame data is updated each time a different mal-
function is detected. There is no priority for 1st trip freeze frame data. However, once freeze frame data is
stored in the ECM memory, 1st trip freeze data is no longer stored (because only one freeze frame data or 1st
trip freeze frame data can be stored in the ECM). If freeze frame data is stored in the ECM memory and freeze
frame data with the same priority occurs later, the first (original) freeze frame data remains unchanged in the
ECM memory.
Both 1st trip freeze frame data and freeze frame data (along with the DTCs) are cleared when the ECM mem-
ory is erased. Procedures for clearing the ECM memory are described in EC-56, "
HOW TO ERASE EMIS-
SION-RELATED DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION" .
SYSTEM READINESS TEST (SRT) CODE
System Readiness Test (SRT) code is specified in Mode 1 of ISO 15031-5.
As part of an enhanced emissions test for Inspection & Maintenance (I/M), certain states require the status of
SRT be used to indicate whether the ECM has completed self-diagnosis of major emission systems and com-
ponents. Completion must be verified in order for the emissions inspection to proceed.
If a vehicle is rejected for a State emissions inspection due to one or more SRT items indicating “INCMP”, use
the information in this Service Manual to set the SRT to “CMPLT”.
In most cases the ECM will automatically complete its self-diagnosis cycle during normal usage, and the SRT
status will indicate “CMPLT” for each application system. Once set as “CMPLT”, the SRT status remains
“CMPLT” until the self-diagnosis memory is erased.
Occasionally, certain portions of the self-diagnostic test may not be completed as a result of the customer's
normal driving pattern; the SRT will indicate “INCMP” for these items.
NOTE:
The SRT will also indicate “INCMP” if the self-diagnosis memory is erased for any reason or if the ECM mem-
ory power supply is interrupted for several hours.
PBIB0911E
Priority Items
1Freeze frame data Misfire — DTC: P0300 - P0304
Fuel Injection System Function — DTC: P0171, P0172
2 Except the above items (Includes A/T related items)
3 1st trip freeze frame data
Page 411 of 3833
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
EC-61
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to read a
code.
NISSAN X-TRAIL 2001 Service Repair Manual ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
EC-61
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to read a
code.](/img/5/57405/w960_57405-410.png)
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
EC-61
[QR25(WITH EURO-OBD)]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to read a
code.
A particular trouble code can be identified by the number of four-digit numeral flashes. The “zero” is indicated
by the number of ten flashes. The length of time the 1,000th-digit numeral flashes on and off is 1.2 seconds
consisting of an ON (0.6-second) - OFF (0.6-second) cycle.
The 100th-digit numeral and lower digit numerals consist of a 0.3-second ON and 0.3-second OFF cycle.
A change from one digit numeral to another occurs at an interval of 1.0-second OFF. In other words, the later
numeral appears on the display 1.3 seconds after the former numeral has disappeared.
A change from one trouble code to another occurs at an interval of 1.8-second OFF.
In this way, all the detected malfunctions are classified by their DTC numbers. The DTC “0000” refers to no
malfunction. (See EC-20, "
INDEX FOR DTC" )
How to Erase Diagnostic Test Mode II (Self-diagnostic Results)
The DTC can be erased from the back up memory in the ECM by depressing accelerator pedal. Refer to EC-
59, "HOW TO SWITCH DIAGNOSTIC TEST MODE" .
●If the battery is disconnected, the DTC will be lost from the backup memory after approx 24 hours.
●Be careful not to erase the stored memory before starting trouble diagnoses.
DIAGNOSTIC TEST MODE II — HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR 1 MONITOR
In this mode, the MI displays the condition of the fuel mixture (lean or rich) which is monitored by the heated
oxygen sensor 1.
*: Maintains conditions just before switching to open loop.
To check the heated oxygen sensor 1 function, start engine in the Diagnostic Test Mode II and warm it up until
engine coolant temperature indicator points to the middle of the gauge.
Next run engine at about 2,000 rpm for about 2 minutes under no-load conditions. Then make sure that the MI
comes ON more than 5 times within 10 seconds with engine running at 2,000 rpm under no-load.
OBD System Operation ChartEBS00M0R
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MI, 1ST TRIP DTC, DTC, AND DETECTABLE ITEMS
●When a malfunction is detected for the first time, the 1st trip DTC and the 1st trip freeze frame data are
stored in the ECM memory.
●When the same malfunction is detected in two consecutive trips, the DTC and the freeze frame data are
stored in the ECM memory, and the MI will come on. For details, refer to EC-44, "
Two Trip Detection
Logic" .
SEF952W
MI Fuel mixture condition in the exhaust gas Air-fuel ratio feedback control condition
ON Lean
Closed loop system
OFF Rich
*Remains ON or OFF Any condition Open loop system