OPEL ASTRA 1991 Electronic Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1991, Model line: ASTRA, Model: OPEL ASTRA 1991Pages: 1070, PDF Size: 41.39 MB
Page 1061 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 8 IDLE SPEED CONTROL
Idle speed is controlled by means of the IACV (Idle Air
Control Valve) mounted on the throttle body assembly. The
IACV is driven by the IACSM (Idle Air Control Stepper Motor)
which is controlled by the ECU.
The IACV maintains constant idle speed (temperature depend-
ent) under all engine loads.
The ECU makes use of closed loop control algorithms to
ensure the best idle conditions for warm and cold engines.
Whenever the ignition is first switched the ECU selects a
pre-set idle position which is temperature dependent, there-
after it operates in the closed loop control mode.
Idle speed control is only possible with the throttle in the
closed position.
Timing advance support is utilised in the idle range to
enhance idle speed control. Spark timing is advanced by up
to 10ø if the idle speed drops below the set point, result-
ing in increased engine torque to offset the drop in speed.
If the idle speed rises above the set point the timing will
be retarded up to 10ø to reduce engine torque.
Correct idle speed control is not possible when the battery
voltage is below 9 volt.
Page 1062 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 9 IMMOBILISER OPERATION
The system contains an immobiliser function which prevents
hot-wiring. When the ignition is switched on the ECU will
wake up and prompt the ACU for its ID (Identification Code).
The ACU will respond by sending its ID to the ECU for com-
parison with an ID code stored in the ECU's ROM. Only if the
ACU's ID matches the ECU's ID normal engine
management
control will be allowed to take place.NO ENGINE CONTROL IS POSSIBLE IN THE ABSENCE OFTHE CORRECTACU ID.
Page 1063 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 10 DEFAULT MODE SELECTION
When the ECU detects a faulty signal from one of its sensors
it will substitute a default signal value to enable the
vehicle to be driven with degraded performance (see para-
graph 10.1).
Faulty sensor Substitute value/sensor
_____________________________________________________
______
EWT Warm engine - 100 øC
MAT 31 øC
Fuel map selector Zero percent enrichment
Timing map selector Map T1 - RON 87D
TPS Idle speed - 1,000 to
2,000 r.p.m.
MAP TPS and idle speed -
1,000 to 2,000 r.p.m.
Disable distributor
bypass operation and
fix spark timing at
10ø BTDC
CO potentiometer Zero percent
Page 1064 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 11 DIAGNOSTICS
Various possible methods of fault finding are listed below
to reduce down-time of the vehicle.
11.1 Diagnostic codes
The CPU continuously monitors its own activities and sensor
inputs. If a fault is detected during operation the diagnos-
tic lamp is turned on and a default signal value is used to
allow the car to be driven with slightly reduced perform-
ance. The fault code is stored in RAM for later evaluation
by the Dealer. If the fault disappears the unit will immedi-
ately use the sensor data instead of the default data, thus
ensuring optimum performance. The fault will be erased from
RAM after 7 starts (ignition turned on 7 times) during which
no fault was detected.
The fault stored in RAM could be accessed by grounding the
diagnostic initialisation input terminal. The fault will
then be flashed out by the diagnostic lamp.
Page 1065 of 1070
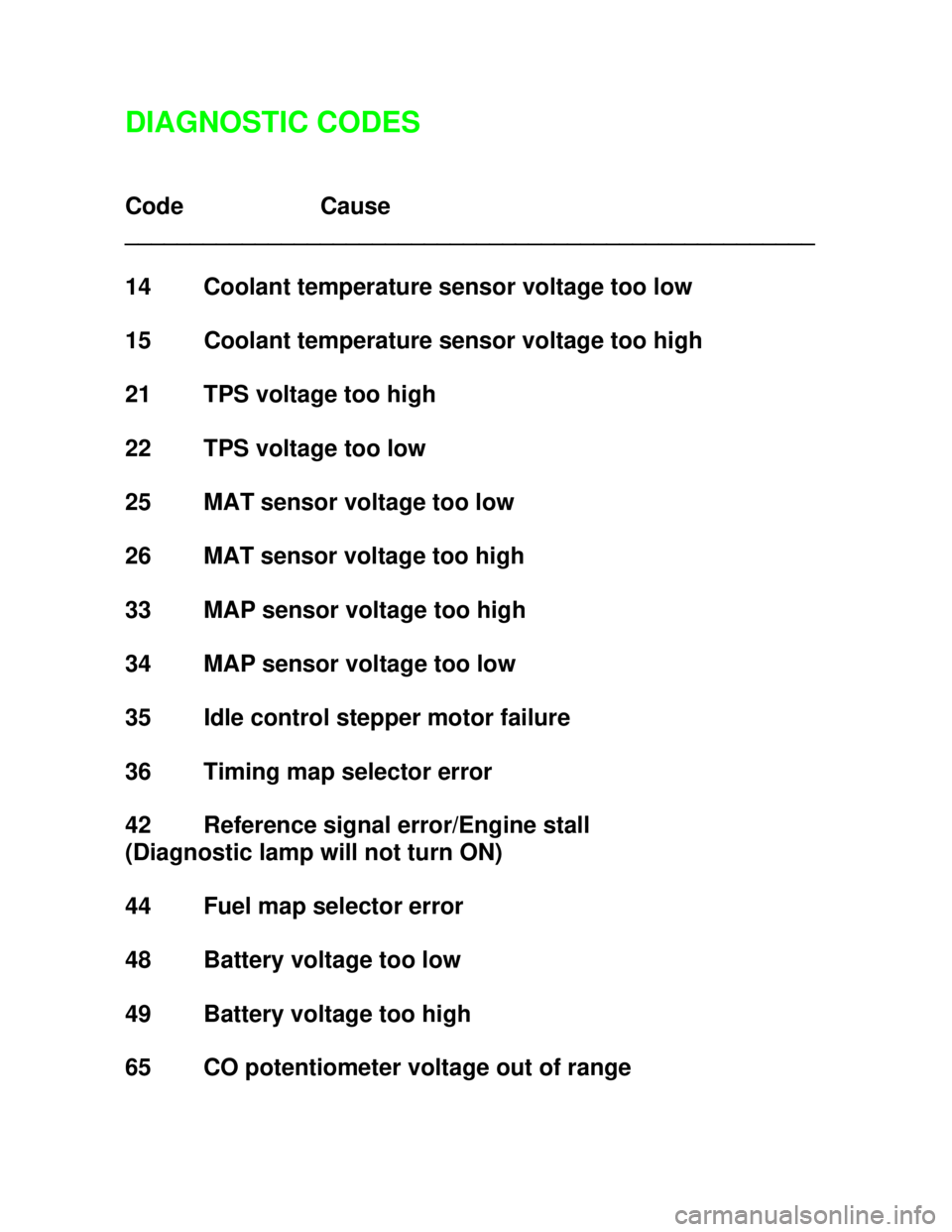
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DIAGNOSTIC CODES
Code Cause
_____________________________________________________
14 Coolant temperature sensor voltage too low
15 Coolant temperature sensor voltage too high
21 TPS voltage too high
22 TPS voltage too low
25 MAT sensor voltage too low
26 MAT sensor voltage too high
33 MAP sensor voltage too high
34 MAP sensor voltage too low
35 Idle control stepper motor failure
36 Timing map selector error
42 Reference signal error/Engine stall
(Diagnostic lamp will not turn ON)
44 Fuel map selector error
48 Battery voltage too low
49 Battery voltage too high
65 CO potentiometer voltage out of range
Page 1066 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 11.2 Volt- and ohmmeter
No repair work inside the ECU's is possible and
recommended.
A multimeter could however be used to ensure that the fol-
lowing inputs to the ECU are present:
11.2.1 Battery voltage:
11.2.2 The voltage measured between terminals
26B (pos) and 25B (neg) should be equal to the battery
voltage (6 and 16 VDC).
11.2.2 Ignition voltage: The voltage between terminal 22B
and
power ground should be equal to the battery voltage with
the ignition turned on.
11.2.3 TPS supply voltage: The voltage between terminal
09B
and signal ground should be between 4.6 and 5.2 volt.
11.2.4 TPS input signal voltage: The voltage between terminal
05B and signal ground should be:
Closed throttle 0.3 < VTPS < 1.0
Part load 1.0 < VTPS < 3.11
WOT 3.11 < VTPS < 5.2
Page 1067 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 11.2.5 CO potentiometer supply voltage: The voltage
between
terminal 23B and signal ground should be between 4.7 and
5.2 volt.
11.2.6 MAP sensor supply voltage: The voltage between
terminal
24B and signal ground should be between 4.7 and 5.2 volt.
11.2.7 MAP sensor signal voltage: The voltage between
terminal
15B and signal ground with ignition on should be:
MAP signal voltage Manifold absolute pressure
_____________________________________________________
___
1.00 20 kPa
2.00 40 kPa
3.00 60 kPa
4.00 80 kPa
4.50 90 kPa
5.00 100 kPa
A general tolerance of +/- 5% exists on the above voltages.
Page 1068 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 11.2.8 Timing map selector: The resistance between terminal
19B and 22B measured on the harness connector with the
ECU removed should be:
97 RON - 470 ohm
93 RON - 220 ohm
87 RON - 4,700 ohm
87D RON - 5,600 ohm
11.2.9 Fuel mixture selector: The resistance between terminal
18B and 11A measured on the harness connector with the
ECU removed should be:
-15% - 274 ohm
-10% - 340 ohm
-05% - 412 ohm
+05% - 619 ohm
+10% - 768 ohm
+15% - 931 ohm
+20% - 1180 ohm
+25% - 1500 ohm
Page 1069 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 11.2.10 EWT sensor: The resistance between terminal 16B and
11A
on the harness connector with the ECU removed should be:
EWT øC Resistance (ohm)
-20 19,700
-0 5,640
+20 2,410
40 1,177
60 565
80 308
100 186
Page 1070 of 1070

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 11.2.11 MAT sensor: The resistance between terminal 17B and
11A on the harness with the ECU removed should be:
MAT øC Resistance (ohm)
-12 9,977
-5 6,540
0 5,627
18 2,290
33 1,241
48 782
62 485