check engine light OPEL CALIBRA 1988 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1988, Model line: CALIBRA, Model: OPEL CALIBRA 1988Pages: 525, PDF Size: 58.26 MB
Page 71 of 525

Wiring diagrams 12•57
12
Key to wiring diagrams for 1992 and later models (continued)
NoDescriptionTrackNoDescriptionTrack
S20.2High pressure compressor switch925
S20.3High pressure blower compressor switch939
S21Fog lamps switch555 to 557
S22Rear fog lamp switch549 to 551
S24Air conditioning blower switch904 to 911
S29Coolant temperature switch118, 137, 357, 942, 957, 972
S30Left front heating mat switch660 to 662
S31Rear left door contact switch591
S32Rear right door contact switch592
S33Traction control switch1130, 1131
S37Window lifter switch868 to 894
S37.1Left window lifter switch868 to 870
S37.2Right window lifter switch886 to 888
S37.3Left rear window lifter switch874 to 876
S37.4Right rear window lifter switch892 to 894
S37.5Safety switch872, 873
S37.6Window anti-jam off switch890
S37.7Automatic window lifter control877 to 882
S39Left rear door window lifter switch878 to 880
S40Right rear door window lifter switch896 to 898
S41Driver door burglary locking switch800 to 802
S42Passenger door central locking switch805
S44Throttle valve switch316, 317
S47Driver door contact switch593, 594
S52Hazard warning switch569 to 573
S53First gear identification switch372
S55Right front heating mat switch664 to 666
S57Sun roof switch1170 to 1183
S63Computer switch
S63.1Function reset switch856
S63.2Clock hours adjustment switch857
S63.3Function select switch858
S63.4Clock minute adjustment switch859
S64Horn switch672
S68Outside mirror switch assy
S68.1Outside mirror adjustment switch638 to 640, 758 to 762
S68.3Left/right outside mirror switch637 to 641, 759 to 763
S68.4Parking position switch765
S82Washer fluid minimum capacity control switch736
S882 stage coolant temperature switch120, 121, 137, 138, 430, 431
S89Seat belt switch998
S93Coolant minimum capacity control switch737
S95Engine oil minuimum capacity control switch738
S98Headlamps levelling switch691 to 693
S99ZV driver door window lifter switch865
S100ZV passenger door window lifter switch883
S101Compressor switch926 to 928
S102Circulation switch918 to 920
S103Transmission temperature switch350
S104Kickdown switch493
S105Start-up assistance switch495 to 497
S106Economy power program switch492
S109Acceleration revolution pressure switch921
S115Coolant temperature switch487, 488
S116Stop lamp switch564, 565
S117Hydraulic pressure switch346
S120Engine compartment hood (anti-theft warning unit) switch835
S127Calibra tail gate central locking switch831
S128Coolant temperature switch936,937S131Defroster lever limit switch918
U2Computer851 to 862
U4ABS hydroaggregate1102 to 1122, 1146 to 1164
U4.1Pump motor relay1102, 1103, 1146, 1147
U4.2Solenoid valves relay1104, 1105, 1148, 1149
U4.3Pump motor1102,1146
U4.4Diode1105,1149
U4.5Left front solenoid valve1109,1153
U4.6Right front solenoid valve1111,1155
U4.7Rear axle solenoid valve1113,1157
U4.8ABS control unit1106 to 1122, 1150 to 1164
U4.9Solenoid valves plug1109 to 1113, 1153 to 1157
U5Check control display
U5.1Washer fluid minimum capacity telltale741
U5.2Oil minimum capacity telltale740
U5.3Coolant minimum capacity telltale739
U5.4Tail light & low beam telltale738
U5.5Stop light failure telltale737
U5.6Front brake lining telltale736
U12Filter heater
U12.1Temperature switch426, 452
U12.2Filter heater427, 453
U13Automatic transmission
U13.1Solenoid valve (shift 1)481
U13.2Solenoid valve (shift 2)482
U13.3Solenoid valve (lock up control)483
U13.4Solenoid valve (pressure control)484
U17Roof antenna amplifier795
V1Brake fluid test bulb diode712
V8Air conditioning compressor diode926
X1 onWiring connectorsVarious
X10Anti theft warning unit code837
X13Diagnostic link164, 165, 189, 190, 226, 270, 271, 258, 259,
309, 310, 370, 371, 343, 344, 473, 474, 573, 725, 836, 837, 860,
861, 1012, 1013, 1069, 1070, 1118, 1119, 1136, 1162, 1163
X15Octane number plug157, 158, 182, 183, 225, 226,
257, 258, 284, 285
X54Ignition coding plug310, 311, 1014, 1070, 1071
Y1Air conditioning compressor clutch925
Y4Headlamps washer solenoid valve620
Y5Fuel solenoid valve410, 445
Y7Fuel injection valves287 to 294,320 to 327,
384 to 391,1025 to 1032,1078 to 1089
Y10Hall sensor ignition distributor153 to 158
Y11Hot start solenoid valve375, 376
Y12Charging pressure control changeover valve377, 378
Y18Exhaust gas recirculation valve1093
Y23Inductive sensor distributor201 to 208
Y24Distributor (inductive discharge)
Y25Acceleration revolution solenoid valve155, 177
Y30Cold start acceleration solenoid valve 448
Y32Fuel injection valve212, 245
Y33Ignition distributor175 to 177, 268 to 270, 238 to 240,
301 to 303, 360 to 362
Y34Tank ventilation valve293, 331, 332, 379, 380,
1092, 1016, 1017,
Y35Circulation solenoid valve918
Y44Four wheel drive solenoid valve350
Y47Park brake shift lock lifting magnet469
Page 90 of 525

HEI (High Energy Ignition)
system
5This comprises of a breakerless distributor
and an electronic switching/amplifier module
along with the coil and spark plugs.
6The electrical impulse that is required to
switch off the low tension circuit is generated
by a magnetic trigger coil in the distributor. A
trigger wheel rotates within a magnetic stator,
the magnetic field being provided by a
permanent magnet. The magnetic field across
the two poles (stator arm and trigger wheel) is
dependent on the air gap between the two
poles. When the air gap is at its minimum, the
trigger wheel arm is directly opposite the
stator arm, and this is the trigger point. As the
magnetic flux between the stator arm and
trigger wheel varies, a voltage is induced in the
trigger coil mounted below the trigger wheel.
This voltage is sensed and then amplified by
the electronic module, and used to switch off
the low tension circuit. There is one trigger arm
and one stator arm for each cylinder.
7The ignition advance is a function of the
distributor, and is controlled both
mechanically and by a vacuum-operated
system. The mechanical governor mechanism
consists of two weights that move out from
the distributor shaft due to centrifugal force as
the engine speed rises. As the weights move
outwards, they rotate the trigger wheel
relative to the distributor shaft and so
advance the spark. The weights are held in
position by two light springs, and it is the
tension of the springs that is largely
responsible for correct spark advancement.
8The vacuum control consists of a
diaphragm, one side of which is connected by
way of a small-bore hose to the carburettor,
and the other side to the distributor.
Depression in the inlet manifold and
carburettor, which varies with engine speed
and throttle position, causes the diaphragm to
move, so moving the baseplate and
advancing or retarding the spark. A fine
degree of control is achieved by a spring in
the diaphragm assembly.
MSTS-i (Microprocessor-
controlled Spark Timing System)
9This system comprises a “Hall-effect”
distributor (or a crankshaft speed/position
sensor on X 16 SZ models), a manifold pressure
sensor, an oil temperature sensor, and a
module, along with the coil and spark plugs.
10On 1.6 litre models, the electrical impulse
that is required to switch off the low tension
circuit is generated by a sensor in the
distributor. A trigger vane rotates in the gap
between a permanent magnet and the sensor.
The trigger vane has four cut-outs, one for
each cylinder. When one of the trigger vane
cut-outs is in line with the sensor, magnetic
flux can pass between the magnet and the
sensor. When a trigger vane segment is in line
with the sensor, the magnetic flux is diverted
through the trigger vane away from thesensor. The sensor senses the change in
magnetic flux, and sends an impulse to the
MSTS-i module, which switches off the low
tension circuit.
11On 1.8 litre models, the electrical impulse
that is required to switch off the low tension
circuit is generated by a crankshaft
speed/position sensor, which is activated by a
toothed wheel on the crankshaft. The toothed
wheel has 35 equally spaced teeth, with a gap
in the 36th position. The gap is used by the
sensor to determine the crankshaft position
relative to TDC (top dead centre) of No 1 piston.
12Engine load information is supplied to the
MSTS-i module by a pressure sensor, which
is connected to the carburettor by a vacuum
pipe. Additional information is supplied by an
oil temperature sensor. The module selects
the optimum ignition advance setting based
on the information received from the sensors.
The degree of advance can thus be constantly
varied to suit the prevailing engine conditions.
Multec, with MSTS-i
13The ignition system is fully electronic in
operation and incorporates the Electronic
Control Unit (ECU) mounted in the driver’s
footwell. A distributor (driven off the camshaft
left-hand end and incorporating the amplifier
module) as well as the octane coding plug,
the spark plugs, HT leads, ignition HT coil and
associated wiring.
14The ECU controls both the ignition system
and the fuel injection system, integrating the
two in a complete engine management
system. Refer to Chapters 4B and 4C for
further information that is not detailed here.
15For ignition the ECU receives information
in the form of electrical impulses or signals
from the distributor (giving it the engine speed
and crankshaft position), from the coolant
temperature sensor (giving it the engine
temperature) and from the manifold absolute
pressure sensor (giving it the load on the
engine). In addition, the ECU receives input
from the octane coding plug (to provide
ignition timing appropriate to the grade of fuel
used) and from, where fitted, the automatic
transmission control unit (to smooth gear
changing by retarding the ignition as changes
are made).
16All these signals are compared by the
ECU with set values pre-programmed
(mapped) into its memory. Considering this
information, the ECU selects the ignition
timing appropriate to those values and
controls the ignition HT coil by way of the
amplifier module accordingly.
17The system is so sensitive that, at idle
speed, the ignition timing may be constantly
changing; this should be remembered if trying
to check the ignition timing.
18The system fitted to C18 NZ models, is
similar to that described above, except that
the amplifier module is separate. The ECU
determines engine speed and crankshaft
position using a sensor mounted in the
right-hand front end of the engine’s cylinderblock; this registers with a 58-toothed disc
mounted on the crankshaft so that the gap left
by the missing two teeth provides a reference
point, so enabling the ECU to recognise TDC.
19Note that this simplifies the distributor’s
function, which is merely to distribute the HT
pulse to the appropriate spark plug; it has no
effect whatsoever on the ignition timing.
DIS (Direct Ignition System)
20On all X16 SZ engines, and on C20 XE
(DOHC) engines from 1993-on, a DIS (Direct
Ignition System) module is used in place of
the distributor and coil. On the X16 SZ engine
the DIS module is attached to the camshaft
housing in the position normally occupied by
the distributor. On the C20 XE engine, a
camshaft phase sensor is attached to the
cylinder head at the non-driven end of the
exhaust camshaft, in the position normally
occupied by the distributor. The DIS module
is attached, by a bracket, to the cylinder head
at the non-driven end of the inlet camshaft.
21The DIS module consists of two ignition
coils and an electronic control module housed
in a cast casing. Each ignition coil supplies
two spark plugs with HT voltage. One spark is
provided in a cylinder with its piston on the
compression stroke, and one spark is
provided to a cylinder with its piston on the
exhaust stroke. This means that a “wasted
spark” is supplied to one cylinder during each
ignition cycle, but this has no detrimental
effect. This system has the advantage that
there are no moving parts (therefore there is
no wear), and the system is largely
maintenance-free.
Motronic M4.1 and M1.5
22This system controls both the ignition and
the fuel injection systems.
23The Motronic module receives information
from a crankshaft speed/position sensor, an
engine coolant temperature sensor mounted
in the thermostat housing. A throttle position
sensor, an airflow meter, and on models fitted
with a catalytic converter, an oxygen sensor
mounted in the exhaust system (Chapter 4C).
24The module provides outputs to control
the fuel pump, fuel injectors, idle speed and
ignition circuit. Using the inputs from the
various sensors, the module computes the
optimum ignition advance, and fuel injector
pulse duration, to suit the prevailing engine
conditions. This system gives very accurate
control of the engine under all conditions,
improving fuel consumption and driveability,
and reducing exhaust gas emissions.
25Further details of the fuel injection system
components are given in Chapter 4B.
Motronic M2.5 and M2.8
26The system is similar to that described for
SOHC models, with the following differences.
27Along with the crankshaft speed/position
sensor, a “Hall-effect” distributor is used
(similar to that described in this Section, with
the MSTS-i system).
Engine electrical systems 5•3
5
Page 92 of 525

5If the engine turns over at normal speed but
will not start, check the HT circuit by
connecting a timing light and turning the
engine over on the starter motor. If the light
flashes, voltage is reaching the spark plugs,
so these should be checked first. If the light
does not flash, check the HT leads
themselves followed by the distributor cap,
carbon brush and rotor arm.
6If there is a spark, check the fuel system for
faults as far as possible (Chapters 4A or 4B).
7If there is still no spark, check the voltage at
the ignition coil “+” or “15” terminal; it should
be the same as the battery voltage (i.e., at
least 11.7 volts). If the voltage at the coil is
more than 1 volt less than that at the battery,
check the connections back through the
ignition switch to the battery and its earth until
the fault is found. Note, however, that the
ECU controls the coil’s feed; do not attempt
to “test” the ECU with anything other than the
correct test equipment, which will be available
only to a Vauxhall dealer. If any of the wires
are to be checked which lead to the ECU,
always first unplug the relevant connector
from the ECU so that there is no risk of the
ECU being damaged by the application of
incorrect voltages from test equipment.
8If the feed to the ignition coil is sound,
check the coil’s primary and secondary
windings (refer to Section 16). Renew the coil
if faulty, but check the condition of the LT
connections themselves before doing so, to
ensure that the fault is not due to dirty or
poorly fastened connectors.
9If the ignition coil is in good condition, the
fault may be within the amplifier module or the
distributor on the C16 NZ and C16 NZ2
engines, or the amplifier or the crankshaft
speed/position sensor on the C18 NZ engine.
A quick check of these components can be
made by connecting a low-wattage bulb
across the ignition coil’s (disconnected) LT
terminals. If the bulb flickers or flashes when
the engine is turned over, the amplifier and
distributor (C16 NZ and C16 NZ2 engines), or
amplifier and crankshaft speed/position
sensor (C18 NZ engine), are sound.
10If this is the case, the entire LT circuit is in
good condition; the fault, if it lies in the
ignition system, must be in the HT circuit
components. These should be checked
carefully, as outlined above.
11If the indicator or bulb does not flash, the
fault is in either the amplifier or the distributor
(C16 NZ and C16 NZ2 engines), or the
amplifier or crankshaft speed/position sensor
(C18 NZ engine). Owners should note,
however, that by far the commonest cause of
“failure” of either of these is a poor
connection, either between the components
themselves or in the LT circuit wiring
connections. If such a fault is suspected, the
vehicle must be taken to a suitably equipped
Vauxhall dealer for testing; no information is
available to eliminate these components by
other means.12An irregular misfire suggests either a
loose connection or intermittent fault on the
primary circuit, or a HT fault on the coil side of
the rotor arm.
13With the ignition switched off, check
carefully through the system ensuring that all
connections are clean and securely fastened.
If the equipment is available, check the LT
circuit as described in paragraphs 7 to 11
above.
14Check that the HT coil, the distributor cap
and the HT leads are clean and dry. Check the
leads and the spark plugs (by substitution, if
necessary), then check the distributor cap,
carbon brush and rotor arm.
15Regular misfiring is almost certainly due to
a fault in the distributor cap, HT leads or spark
plugs. Use a timing light (paragraph 5, above)
to check whether HT voltage is present at all
leads.
16If HT voltage is not present on any
particular lead, the fault will be in that lead or
in the distributor cap. If HT is present on all
leads, the fault will be in the spark plugs;
check and renew them if there is any doubt
about their condition.
17If no HT voltage is present, check the
ignition coil; its secondary windings may be
breaking down under load.
18If all components have been checked for
signs of obvious faults but the system is still
thought to be faulty, take the vehicle to a
Vauxhall dealer for testing on special
equipment.
5Battery - testing and charging
2
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Testing
1Topping-up and testing of the electrolyte in
each cell is not possible. The condition of the
battery can therefore only be tested by
observing the battery condition indicator.
2The battery condition indicator is fitted in
the top of the battery casing, and indicates
the condition of the battery from its colour. If
the indicator shows green, then the battery is
in a good state of charge. If the indicator turns
darker, eventually to black, then the battery
requires charging, as described later in this
Section. If the indicator shows clear/yellow,
then the electrolyte level in the battery is too
low to allow further use, and the battery
should be renewed.
Charging
3Do not attempt to charge, load or jump start
a battery when the indicator shows
clear/yellow. If the battery is to be charged,
remove it from the vehicle and charge it as
follows.
4The maintenance-free type battery takes
considerably longer to fully recharge than the
standard type, the time taken being
dependent on the extent of discharge.5A constant-voltage type charger is required,
to be set, when connected, to 13.9 to 14.9
volts with a charger current below 25 amps.
6If the battery is to be charged from a fully
discharged state (less than 12.2 volts output),
have it recharged by a Vauxhall dealer or
battery specialist, as the charge rate will be
high and constant supervision during charging
is necessary.
6Battery - removal and refitting
2
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Removal
1The battery is located at the left-hand front
corner of the engine compartment.
2Disconnect the lead(s) at the negative
(earth) terminal by unscrewing the retaining
nut and removing the terminal clamp.
3Disconnect the positive terminal lead(s) in
the same way.
4Unscrew the clamp bolt sufficiently to
enable the battery to be lifted from its
location. Keep the battery in an upright
position, to avoid spilling electrolyte on the
bodywork.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but smear
petroleum jelly on the terminals when
reconnecting the leads, and always connect
the positive lead first and the negative lead
last.
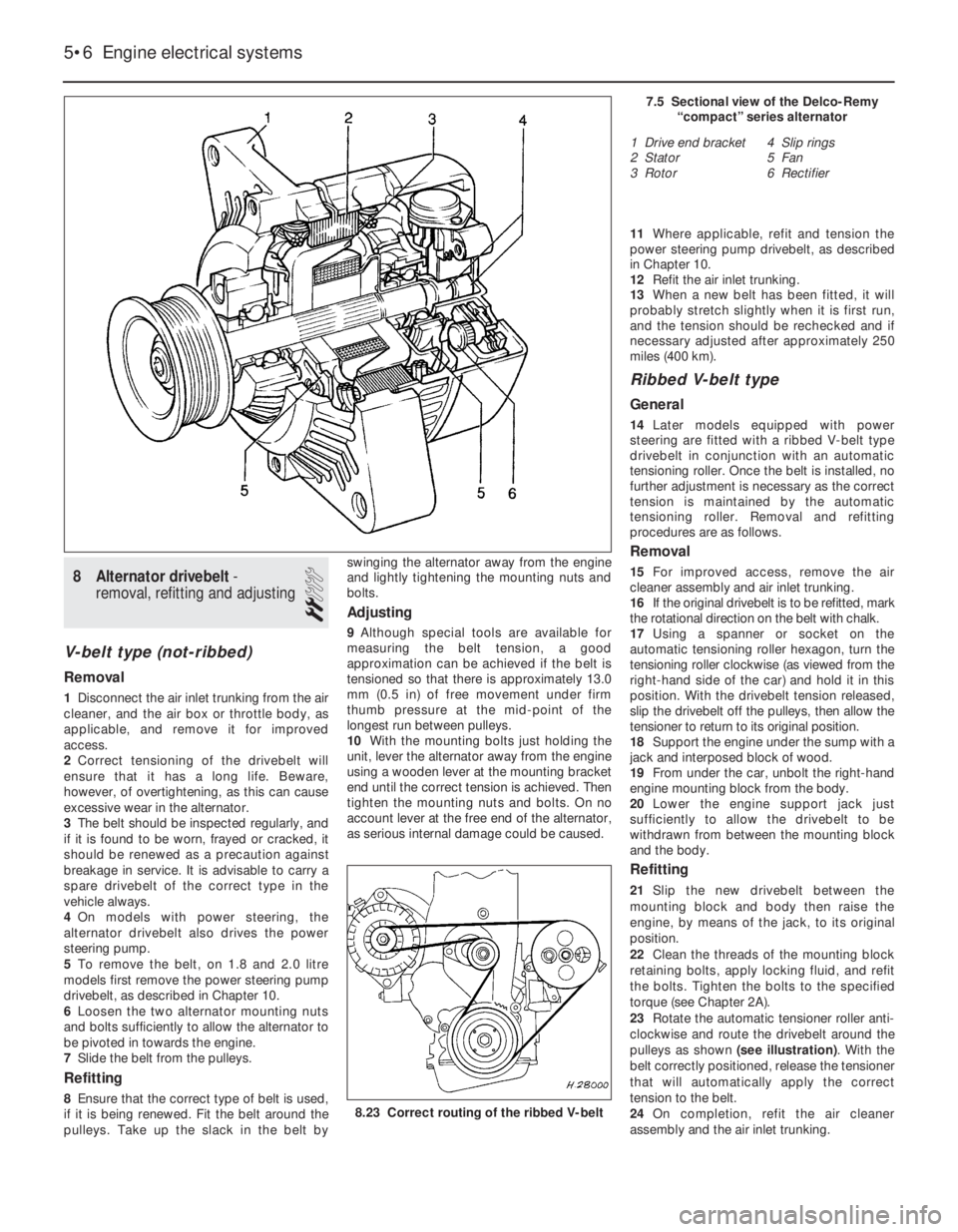
7Alternator - description
1A Delco-Remy or Bosch alternator may be
fitted, depending on model and engine
capacity. The maximum output of the
alternator varies accordingly.
2The alternator is belt-driven from the
crankshaft pulley. Cooling is provided by a
fan, mounted outside the casing on the end of
the rotor shaft. An integral voltage regulator is
incorporated, to control the output voltage.
3The alternator provides a charge to the
battery even at very low engine speed, and
consists of a coil-wound stator in which a
rotor rotates. The rotor shaft is supported in
ball-bearings, and slip rings are used to
conduct current to and from the field coils
through the carbon brushes.
4The alternator generates ac (alternating
current), which is rectified by an internal diode
circuit to dc (direct current) for supply to the
battery.
5Later models are fitted with a Delco-Remy,
‘compact’ series alternators (see illustration).
They use a ribbed V-belt type drivebelt with
automatic tensioner. They are rigidly mounted
to the engine.
Engine electrical systems 5•5
5
Page 93 of 525
8Alternator drivebelt -
removal, refitting and adjusting
2
V-belt type (not-ribbed)
Removal
1Disconnect the air inlet trunking from the air
cleaner, and the air box or throttle body, as
applicable, and remove it for improved
access.
2Correct tensioning of the drivebelt will
ensure that it has a long life. Beware,
however, of overtightening, as this can cause
excessive wear in the alternator.
3The belt should be inspected regularly, and
if it is found to be worn, frayed or cracked, it
should be renewed as a precaution against
breakage in service. It is advisable to carry a
spare drivebelt of the correct type in the
vehicle always.
4On models with power steering, the
alternator drivebelt also drives the power
steering pump.
5To remove the belt, on 1.8 and 2.0 litre
models first remove the power steering pump
drivebelt, as described in Chapter 10.
6Loosen the two alternator mounting nuts
and bolts sufficiently to allow the alternator to
be pivoted in towards the engine.
7Slide the belt from the pulleys.
Refitting
8Ensure that the correct type of belt is used,
if it is being renewed. Fit the belt around the
pulleys. Take up the slack in the belt byswinging the alternator away from the engine
and lightly tightening the mounting nuts and
bolts.
Adjusting
9Although special tools are available for
measuring the belt tension, a good
approximation can be achieved if the belt is
tensioned so that there is approximately 13.0
mm (0.5 in) of free movement under firm
thumb pressure at the mid-point of the
longest run between pulleys.
10With the mounting bolts just holding the
unit, lever the alternator away from the engine
using a wooden lever at the mounting bracket
end until the correct tension is achieved. Then
tighten the mounting nuts and bolts. On no
account lever at the free end of the alternator,
as serious internal damage could be caused.11Where applicable, refit and tension the
power steering pump drivebelt, as described
in Chapter 10.
12Refit the air inlet trunking.
13When a new belt has been fitted, it will
probably stretch slightly when it is first run,
and the tension should be rechecked and if
necessary adjusted after approximately 250
miles (400 km).
Ribbed V-belt type
General
14Later models equipped with power
steering are fitted with a ribbed V-belt type
drivebelt in conjunction with an automatic
tensioning roller. Once the belt is installed, no
further adjustment is necessary as the correct
tension is maintained by the automatic
tensioning roller. Removal and refitting
procedures are as follows.
Removal
15For improved access, remove the air
cleaner assembly and air inlet trunking.
16If the original drivebelt is to be refitted, mark
the rotational direction on the belt with chalk.
17Using a spanner or socket on the
automatic tensioning roller hexagon, turn the
tensioning roller clockwise (as viewed from the
right-hand side of the car) and hold it in this
position. With the drivebelt tension released,
slip the drivebelt off the pulleys, then allow the
tensioner to return to its original position.
18Support the engine under the sump with a
jack and interposed block of wood.
19From under the car, unbolt the right-hand
engine mounting block from the body.
20Lower the engine support jack just
sufficiently to allow the drivebelt to be
withdrawn from between the mounting block
and the body.
Refitting
21Slip the new drivebelt between the
mounting block and body then raise the
engine, by means of the jack, to its original
position.
22Clean the threads of the mounting block
retaining bolts, apply locking fluid, and refit
the bolts. Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque (see Chapter 2A).
23Rotate the automatic tensioner roller anti-
clockwise and route the drivebelt around the
pulleys as shown (see illustration). With the
belt correctly positioned, release the tensioner
that will automatically apply the correct
tension to the belt.
24On completion, refit the air cleaner
assembly and the air inlet trunking.
5•6Engine electrical systems
7.5 Sectional view of the Delco-Remy
“compact” series alternator
1 Drive end bracket
2 Stator
3 Rotor4 Slip rings
5 Fan
6 Rectifier
8.23 Correct routing of the ribbed V-belt
Page 95 of 525

6Remove the terminal screw and lift out the
diode assembly.
7Extract the two screws securing the brush
holder and voltage regulator to the slip ring
end housing, and remove the brush holder
assembly. Note the insulation washers under
the screw heads.
8Check that the brushes move freely in their
guides, and that the brush lengths are within
the limits given in the Specifications. If any
doubt exists regarding the condition of the
brushes, the best policy is to renew them.
9To fit new brushes, unsolder the old brush
leads from the brush holder, and solder on the
new leads in exactly the same place.
10Check that the new brushes move freely
in the guides.
Refitting
11Before refitting the brush holder
assembly, retain the brushes in the retracted
position using a stiff piece of wire or a twist
drill.
12Refit the brush holder assembly so that
the wire or drill protrudes through the slot in
the slip ring end housing, and tighten the
securing screws.
13Refit the diode assembly and the stator
assembly to the housing, ensuring that the
stator leads are in their correct positions, and
refit the terminal screw and nuts.
14Assemble the drive end housing and rotor
to the slip ring end housing, ensuring that the
previously made marks are aligned. Insert and
tighten the three through-bolts.
15Pull the wire or drill, as applicable, from
the slot in the slip ring end housing so that the
brushes rest on the rotor slip rings (see
illustration).
16Refit the alternator, as described in
Section 9
Bosch type alternator
Removal
17Disconnect the air trunking from the air
cleaner, and the air box or throttle body, as
applicable, and remove it for improved
access.
18Disconnect the battery leads.
19If desired, to improve access further, the
alternator can be removed, as described in
Section 920Remove the two securing screws, and
withdraw the brush holder/voltage regulator
assembly (see illustrations).
21Check that the brushes move freely in
their guides, and that the brush lengths are
within the limits given in the Specifications
(see illustration). If any doubt exists
regarding the condition of the brushes, the
best policy is to renew them as follows.
22Hold the brush wire with a pair of pliers,
and unsolder it from the brush holder. Lift away
the brush. Repeat for the remaining brush.
Refitting
23Note that whenever new brushes are
fitted, new brush springs should also be fitted.
24With the new springs fitted to the brush
holder, insert the new brushes, and check that
they move freely in their guides. If they bind,
lightly polish with a very fine file or glass
paper.
25Solder the brush wire ends to the brush
holder, taking care not to allow solder to pass
to the stranded wire.
26Check the condition of the slip rings, and
if necessary clean with a rag or very fine glass
paper (see illustration).
27Refit the brush holder/voltage regulator
assembly, and tighten the securing screws.
28Where applicable, refit the alternator, as
described in Section 9
29Reconnect the battery leads.
30Refit the air trunking.
Delco-Remy “compact” series
Removal
31Remove the alternator as described in
Section 9.
32Remove the plastic cover from the rear of
the alternator.
33Undo the two bolts securing the brush
holder to the rear of the alternator, noting that
one of the bolts also secures the suppression
capacitor.
34Remove the suppression capacitor then
withdraw the brush holder, noting the flat plug
on the side.
35Check that the brushes move freely in
their holder and that the brush lengths are
within the limits given in the Specifications. If
any doubt exists regarding the condition of
the brushes, the best policy is to renew them.36Check the condition of the slip rings, and
if necessary clean with a rag or very fine glass
paper.
Refitting
37Refitting the brushes is a reversal of
removal.
12Starter motor - general
1The starter motor is mounted at the rear of
the cylinder block, and may be of either
Delco-Remy or Bosch manufacture. Both
makes are of the pre-engaged type, i.e. the
drive pinion is brought into mesh with the
starter ring gear on the flywheel before the
main current is applied.
5•8Engine electrical systems
11.15 Withdrawing the twist drill used to
retain the brushes -
Delco-Remy alternator11.20B . . .and withdraw the brush
holder/voltage regulator assembly - Bosch
alternator
11.26 Alternator slip rings (arrowed) -
Bosch alternator
11.21 Measuring the length of an
alternator brush - Bosch alternator
11.20A Remove the securing screws . . .
Page 98 of 525

10Using an Allen key or hexagon bit, extract
the two securing screws and withdraw the
rotor arm, leaving the metal rotor hub in the
housing (see illustrations).
11Examine the O-ring on the plastic shield,
and renew if necessary.
Refitting
12Refitting is a reversal of removal, noting
that the rotor arm can only be fitted in one
position. If necessary, turn the metal rotor hub
so that the screw holes align with those in the
rotor arm and the end of the camshaft. Ensure
that the HT leads are correctly reconnected.
18Distributor (SOHC models) -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding. A
tachometer and a timing light will be required
to check the ignition timing on completion 14
NV and 16 SV
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the distributor cap, as described in
Section 17.
3Disconnect the distributor wiring plug (see
illustrations).
4On 14 NV models, disconnect the vacuum
pipe from the diaphragm unit on the side of
the distributor.
5If the original distributor is to be refitted,
make alignment marks between the
distributor body and the camshaft housing, sothat the distributor can be refitted in its
original position.
6Turn the crankshaft. This can be done by
either using a socket or spanner on the
crankshaft pulley bolt, or by engaging top
gear and pushing the vehicle backwards or
forwards. Bring No 1 cylinder to the firing
point. No 1 cylinder is at the firing point when:
a)The relevant timing marks are aligned. On
14 NV models, the pointer on the rear
timing belt cover should be aligned
halfway between the two notches in the
crankshaft pulley. On 16 NV models, the
pointer on the rear timing belt cover
should be aligned with the notch in the
crankshaft pulley
b)The tip of the rotor arm is pointing to the
position occupied by the No 1 cylinder HT
lead terminal in the distributor cap
c)On the Bosch distributor, the rotor arm is
aligned with the notch in the distributorbody (remove the rotor arm and plastic
shield, then refit the rotor arm to check
the alignment with the notch). On the
Lucas distributor, the rotor arm is
approximately aligned with the TDC arrow
stamped in the distributor body (see
illustration).
7Unscrew the clamp nut and remove the
clamp plate, then withdraw the distributor
from the camshaft housing (see illustrations).
8If desired, the distributor can be
dismantled, as described in Section 20.
9Check the condition of the O-ring on the
rear of the distributor body, and renew if
necessary.
Refitting
10Begin refitting by checking that No 1
cylinder is still at the firing point. The relevant
timing marks should be aligned. If the engine
has been turned whilst the distributor has
Engine electrical systems 5•11
18.6 TDC arrow on the Lucas distributor
body
18.7C . . .and withdraw the distributor18.7B . . .remove the clamp plate . . .18.7A Unscrew the clamp nut . . .
18.3B Disconnecting the distributor wiring
on the C16 NZ engine18.3A Disconnecting the distributor wiring
plug - 1.6 litre model (Bosch distributor)
17.10B . . .and withdraw the rotor arm -
2.0 litre model17.10A Extract the two securing
screws . . .
5
Page 99 of 525

been removed, check that No 1 cylinder is on
its firing stroke by removing No 1 cylinder
spark plug and placing a finger over the plug
hole. Turn the crankshaft until compression
can be felt, which indicates that No 1 piston is
rising on its compression stroke. Continue
turning the crankshaft until the relevant timing
marks are in alignment.
11Turn the rotor arm to the position noted in
paragraph 6c, and hold the rotor arm in this
position as the distributor is fitted. Note that
the distributor driveshaft will only engage with
the camshaft in one position. If the original
distributor is being refitted, align the marks
made on the distributor body and camshaft
housing before removal.
12Refit the clamp plate and nut, but do not
fully tighten the nut at this stage.
13On the Bosch distributor, remove the rotor
arm, then refit the plastic shield and the rotor
arm.
14On 14 NV models, reconnect the vacuum
pipe to the diaphragm unit.
15Reconnect the distributor wiring plug.
16Refit the distributor cap as described in
Section 17.
17Reconnect the battery negative lead.
18Check and if necessary adjust the ignition
timing, as described in Section 21.
19Distributor (DOHC models),
where applicable - removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the distributor cap, as described in
Section 17.
3Disconnect the distributor wiring plug.
4Unscrew the two securing bolts, and
remove the distributor from the cylinder head.
5Examine the O-ring on the rear of the
distributor, and renew if necessary.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal. However,
note that the distributor should be fitted so
that the wiring plug is positioned on the upper
left-hand side of the distributor body, when
viewed from the distributor cap end.
20Distributor - dismantling,
inspection and reassembly
3
Note: Before contemplating dismantling of a
distributor, check the cost and availability of
replacement parts. It may prove more
economical to renew the complete distributor
assembly
14 NV models
Dismantling
1With the distributor removed as described
in Section 18, continue as follows.
2Pull off the rotor arm, and remove the
plastic shield.
3The top bearing plate can be removed after
unscrewing the two securing screws, however
(other than the vacuum diaphragm unit), no
spares are available for the distributor and no
adjustments are required.
4If desired, the vacuum diaphragm unit can
be removed by extracting the two securing
screws and unhooking the operating arm from
the distributor baseplate. Note that the
screws are of differing lengths, the longer
screw also secures one of the distributor cap
clips.
Inspection
5The vacuum unit can be tested by applying
suction to the vacuum port, and checking that
the operating rod moves into the unit as
suction is applied. Remove the suction, and
check that the operating rod returns to its
original position. If the operating rod does not
move as described, renew the vacuum unit.
6Check the distributor cap for corrosion of
the segments, and for signs of tracking,
indicated by a thin black line between the
segments. Make sure that the carbon brush in
the centre of the cap moves freely and stands
proud of the surface of the cap. Renew the
cap if necessary.
7If the metal portion of the rotor arm is badly
burnt or loose, renew it. If slightly burnt or
corroded; it may be cleaned with a fine file.
8Examine the seal ring at the rear of the
distributor body, and renew if necessary.
Reassembly
9Reassembly is a reversal of dismantling,
ensuring that the vacuum unit operating arm
is correctly engaged with the peg on the
baseplate, several attempts may be required
to reconnect it.
10Refit the distributor as described in
Section 18, and then check and if necessary
adjust the ignition timing, as described in
Section 21.
16 SV models
Dismantling
11With the distributor removed as described
in Section 18, pull off the rotor arm and, on
the Bosch distributor, remove the plastic
shield.
12Using a pin punch, carefully drive out the
roll pin securing the plastic drive collar to the
rear of the distributor shaft (see illustration).
13Lift off the drive collar, and remove the
thrustwashers from the end of the shaft (see
illustration).
14Withdraw the shaft, complete with the
trigger vane, from the distributor body, and
recover the thrustwashers from the shaft (see
illustration).
15On the Lucas distributor, extract the
spring clip from inside the body, then
withdraw the terminal block. Pull the small
wiring plug from inside the terminal block (see
illustrations).
16Remove the screws, and lift the sensor
plate from the distributor body (see
illustrations).
5•12Engine electrical systems
20.15A Removing the spring clip . . .20.14 Recovering the thrustwashers from
the shaft - 1.6 litre (Bosch distributor)20.13 Removing the thrustwashers
20.12 Removing the drive collar roll pin -
1.6 litre models (Bosch distributor)
Page 100 of 525
Inspection
17Examine the distributor cap and rotor arm,
as described in paragraphs 6 and 7. Examine
the O-rings at the rear of the distributor body,
and on the rear of the shaft, and renew if
necessary.
Reassembly
18Reassembly is a reversal of dismantling,
ensuring that the thrustwashers are correctly
located. Note that the drive collar should be
refitted so that the drive peg on the collar is
aligned with the groove in the top of the
distributor shaft (it is possible to fit the drive
collar 180°out of position).
19Refit the distributor as described in
Section 18, and then check and if necessary
adjust the ignition timing, as described in
Section 21.
DOHC models (where
applicable)
20The distributor cap and rotor arm can be
examined as described in paragraphs 6 and 7.
21Ignition timing -checking and
adjustment
4
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding. A
tachometer and a timing light will be required
during this procedure. For details of ignition
timing adjustment required to operate vehicles
on unleaded petrol, refer to Section 22.
14 NV and 16 SV models
Checking
1Start the engine and run it until it reaches
normal operating temperature, then switch
off.
2On 14 NV models, disconnect the vacuum
pipe from the distributor vacuum diaphragm
unit.
3On all models use a spanner applied to the
crankshaft pulley bolt to rotate the crankshaft
clockwise until the notch in the pulley’s
inboard rim aligns with the pointer protruding
from the oil pump housing. On 14 NV models,
where two notches (indicating 10°and 5°
BTDC respectively) are found, rotate the
crankshaft until the second notch (in thedirection of rotation -i.e. 5°BTDC) aligns. Use
white paint or similar to emphasise the pointer
and notch, to make them easier to see.
4Connect a timing light to No 1 cylinder
(nearest the timing belt end of the engine) HT
lead, also a tachometer; follow the equipment
manufacturer’s instructions for connection.
5Start the engine and allow it to idle -the
speed should be between 700 and 1000 rpm.
6On 14 NV models, aim the timing light at the
pointer and check that it is aligned with the
crankshaft pulley notch.
7On early 16 SV models, disconnect the
ignition timing basic adjustment coding plug.
This can be identified by a length of Black
wire joining Brown/Red and Brown/Yellow
wires in a connector plug clipped to the wiring
or heater/cooling system hoses beneath the
battery/ignition coil (see illustration, 16.1). This
causes the MSTS-i module to adopt its basic
adjustment mode, sending a constant firing
signal corresponding to 10°BTDC and
eliminating any advance below 2000 rpm. Aim
the timing light at the pointer and check that it
is aligned with the crankshaft pulley notch.
8On later 16 SV, C 16 NZ and C 16 NZ2
models, the coding plugs are no longer fitted.
For accurate checking, special Vauxhall test
equipment must be used which causes the
MSTS module to adopt its basic adjustment
mode.
9Without access to such equipment, it is
possible to check and adjust the ignition
timing, accurate results cannot be
guaranteed. Owners are therefore advised to
have this work carried out by a suitably
equipped Vauxhall dealer; at the very least,
make the initial setting yourself and then have
it checked as soon as possible.
10If you do attempt to check the ignition
timing yourself, note that the fixed reference
mark is now an extended line embossed on
the timing belt lower outer cover.
Adjustment
11If the notch and pointer are not aligned,
loosen the distributor clamp nut and turn the
distributor body slightly in the required
direction to align.
12Tighten the distributor clamp nut, and
check that the notch and pointer are still
aligned. 13Stop the engine, and disconnect the
timing light and tachometer.
14On 16 SV models, reconnect the basic
adjustment coding plug. On 14 NV models,
reconnect the vacuum pipe to the distributor
vacuum diaphragm unit.
Other models
15No adjustment of the ignition timing is
possible on 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, as the
adjustment is carried out automatically by the
electronic control module.
16The ignition timing can be checked by a
Vauxhall dealer using specialist dedicated test
equipment, if a fault is suspected.
22Ignition timing -adjustment
for use with unleaded petrol
3
14 NV models
1All models with the 14 NV engine have the
ignition timing adjusted for use with 95 RON
unleaded petrol before they leave the factory,
and no further adjustment is required.
2Leaded petrol (98 RON) can be used if
desired, with no adverse effects.
1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 SOHC models
Note: Models equipped with a catalytic
converter must be operated on 95 R0N
unleaded petrol at all times, and although an
octane coding plug may be fitted, it should
not be tampered with
3Models, other than 14 NV, are equipped
with an octane coding plug, which is located
Engine electrical systems 5•13
20.16B . . .and withdraw the sensor plate -
1.6 litre (Bosch distributor)
20.16C Sensor plate screw (arrowed) -
1.6 litre (Lucas distributor)
20.16A Remove the securing screws . . .20.15B . . .and disconnecting the small
wiring plug - 1.6 litre (Lucas distributor)
5
Page 105 of 525

wax-based underbody protective coating, it is
a good idea to have the whole of the
underframe of the vehicle steam cleaned,
engine compartment included, so that a
thorough inspection can be carried out to see
what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary. Steam cleaning is available at
many garages and is necessary for removal of
the accumulation of oily grime that sometimes
is allowed to become thick in certain areas.
The dirt can then be simply hosed off. Note
that these methods should not be used on
vehicles with wax-based underbody
protective coating or the coating will be
removed. Such vehicles should be inspected
annually, preferably just before winter, when
the underbody should be washed down and
any damage to the wax coating repaired.
Ideally, a completely fresh coat should be
applied. It would also be worth considering
the use of such wax-based protection for
injection into door panels, sills, box sections,
etc., as an additional safeguard against rust
damage where such protection is not
provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish,
will give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheen
has dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to
be taken with metallic paintwork, as special
non-abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to
avoid damage to the finish.
Always check that the door and ventilator
opening drain holes and pipes are completely
clear so that water can be drained out. Bright
work should be treated in the same way as
paint work. Windscreens and windows can be
kept clear of the smeary film that often
appears, by using a glass cleaner. Never use
any form of wax or other body or chromium
polish on glass.
3Upholstery and carpets -
maintenance
1
Mats and carpets should be brushed or
vacuum cleaned regularly to keep them free of
grit. If they are badly stained remove them
from the vehicle for scrubbing or sponging
and make quite sure they are dry before
refitting. Seats and interior trim panels can be
kept clean by wiping with a damp cloth. If they
do become stained (which can be more
apparent on light coloured upholstery) use a
little liquid detergent and a soft nail brush to
scour the grime out of the grain of the
material. Do not forget to keep the headlining
clean in the same way as the upholstery.
When using liquid cleaners inside the vehicle
do not over-wet the surfaces being cleaned.Excessive damp could get into the seams and
padded interior causing stains, offensive
odours or even rot. If the inside of the vehicle
gets wet accidentally it is worthwhile taking
some trouble to dry it out properly, particularly
where carpets are involved. Do not leave oil or
electric heaters inside the vehicle for this
purpose.
4Minor body damage - repair
3
Repairs of minor scratches in
bodywork
If the scratch is very superficial, and does
not penetrate to the metal of the bodywork,
repair is very simple. Lightly rub the area of
the scratch with a paintwork renovator, to
remove loose paint from the scratch and to
clear the surrounding bodywork of wax polish.
Rinse the area with clean water.
Apply touch-up paint to the scratch using a
fine paint brush; continue to apply fine layers
of paint until the surface of the paint in the
scratch is level with the surrounding
paintwork. Allow the new paint at least two
weeks to harden: then blend it into the
surrounding paintwork by rubbing the scratch
area with a paintwork renovator or a very fine
cutting paste and apply wax polish.
Where the scratch has penetrated right
through to the metal of the bodywork, causing
the metal to rust, a different repair technique
is required. Remove any loose rust from the
bottom of the scratch with a penknife, then
apply rust inhibiting paint, to prevent the
formation of rust in the future. Using a rubber
or nylon applicator fill the scratch with
bodystopper paste. If required, this paste can
be mixed with cellulose thinners to provide a
very thin paste that is ideal for filling narrow
scratches. Before the stopper-paste in the
scratch hardens, wrap a piece of smooth
cotton rag around the top of a finger. Dip the
finger in cellulose thinners and then quickly
sweep it across the surface of the
stopper-paste in the scratch; this will ensure
that the surface of the stopper-paste is
slightly hollowed. The scratch can now be
painted over as described earlier in this
Section.
Repair of dents in bodywork
When deep denting of the vehicle’s
bodywork has taken place, the first task is to
pull the dent out, until the affected bodywork
almost attains its original shape. There is little
point in trying to restore the original shape
completely, as the metal in the damaged area
will have stretched on impact and cannot be
reshaped fully to its original contour. It is
better to bring the level of the dent up to a
point that is about 8 in (3 mm) below the level
of the surrounding bodywork. In cases where
the dent is very shallow anyway, it is not worthtrying to pull it out at all. If the underside of the
dent is accessible, it can be hammered out
gently from behind, using a mallet with a
wooden or plastic head. Whilst doing this,
hold a block of wood firmly against the
outside of the panel to absorb the impact
from the hammer blows and thus prevent a
large area of the bodywork from being
“belled-out”.
Should the dent be in a section of the
bodywork that has a double skin or some
other factor making it inaccessible from
behind, a different technique is called for. Drill
several small holes through the metal inside
the area particularly in the deeper section.
Then screw long self-tapping screws into the
holes just sufficiently for them to gain a good
purchase in the metal. Now the dent can be
pulled out by pulling on the protruding heads
of the screws with a pair of pliers.
The next stage of the repair is the removal
of the paint from the damaged area, and from
an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork. This is accomplished most easily
by using a wire brush or abrasive pad on a
power drill, although it can be done just as
effectively by hand using sheets of abrasive
paper. To complete the preparation for filling,
score the surface of the bare metal with a
screwdriver or the tang of a file, or
alternatively, drill small holes in the affected
area. This will provide a good “key” for the
filler paste.
To complete the repair see the Section on
filling and re-spraying.
Repair of rust holes or gashes in
bodywork
Remove all paint from the affected area and
from an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork, using an abrasive pad or a wire
brush on a power drill. If these are not
available a few sheets of abrasive paper will
do the job just as effectively. With the paint
removed you will be able to gauge the severity
of the corrosion and therefore decide whether
to renew the whole panel (if this is possible) or
to repair the affected area. New body panels
are not as expensive as most people think
and it is often quicker and more satisfactory
to fit a new panel than to attempt to repair
large areas of corrosion.
Remove all fittings from the affected area
except those which will act as a guide to the
original shape of the damaged bodywork (e.g.
headlamp shells, etc.). Then, using tin snips or
a hacksaw blade, remove all loose metal and
any other metal badly affected by corrosion.
Hammer the edges of the hole inwards to
create a slight depression for the filler paste.
Wire brush the affected area to remove the
powdery rust from the surface of the
remaining metal. Paint the affected area with
rust inhibiting paint. If the back of the rusted
area is accessible treat this also.
Before filling can take place it will be
necessary to block the hole in some way. This
can be achieved by using aluminium or plastic
mesh, or aluminium tape.
11•2Bodywork and fittings
Page 129 of 525

b)Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well maintained according to the
manufacturers schedule (see “Routine
maintenance” and the relevant Chapter).
In particular, ensure that the air cleaner
filter element, the fuel filter and the spark
plugs are renewed at the correct intervals.
If the inlet air/fuel mixture is allowed to
become too rich due to neglect, the
unburned surplus will enter and burn in
the catalytic converter, overheating the
element and eventually destroying the
converter.
c)If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the vehicle at all (or at least as little
as possible) until the fault is cured. The
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
d)The engine control indicator (the outline
of an engine with a lightning symbol
superimposed), will light when the ignition
is switched on and the engine is started,
then it will go out. While it may light briefly
while the engine is running, it should go
out again immediately and stays unlit. If it
lights and stays on while the engine is
running, seek the advice of a Vauxhall
dealer as soon as possible. A fault has
occurred in the fuel injection/ignition
system that, apart from increasing fuel
consumption and impairing the engine’s
performance, may damage the catalytic
converter.
e)DO NOT push or tow-start the vehicle.
This will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel causing it to overheat when
the engine does start see (b) above.
f)DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds. If the ignition is switched
off at anything above idle speed,
unburned fuel will enter the (very hot)
catalytic converter, with the possible risk
of its igniting on the element and
damaging the converter.
g)DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives.
These may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
h)DO NOT continue to use the vehicle if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke. The unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases the element will overheat.
i)Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures hence
the heat shields on the vehicle’s under-
body and the casing will become hot
enough to ignite combustible materials
that brush against it. DO NOT, therefore,
park the vehicle in dry undergrowth, over
long grass or over piles of dead leaves.
j)Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGlLE. Do not strike it with tools during
servicing work. Take great care when
working on the exhaust system. Ensure
that the converter is well clear of any
jacks or other lifting gear used to raise thevehicle. Do not drive the vehicle over
rough ground, road humps, etc., in such a
way as to ground the exhaust system.
k)In some cases, particularly when the
vehicle is new and/or is used for
stop/start driving, a sulphurous smell (like
that of rotten eggs) may be noticed from
the exhaust. This is common to many
catalytic converter-equipped vehicles and
seems to be due to the small amount of
sulphur found in some petrol’s reacting
with hydrogen in the exhaust to produce
hydrogen sulphide (CS) gas. While this
gas is toxic, it is not produced in sufficient
amounts to be a problem. Once the
vehicle has covered a few thousand miles
the problem should disappear. In the
meanwhile a change of driving style or of
the brand of petrol may effect a solution.
l)The catalytic converter, used on a
well-maintained and well-driven vehicle,
should last for between 50 000 and 100
000 miles. From this point on, careful
checks should be made at all specified
service intervals of the CO level to ensure
that the converter is still operating
efficiently. If the converter is no longer
effective it must be renewed.
11Carbon canister - removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands placed under the body side members
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
2Remove the front right hand wheel and
wheel arch liner.
3Note the hose and pipe connections to the
canister, or label them, to ensure that they are
reconnected to their original unions, then
disconnect them (see illustration). Unscrew
the two nuts securing the canister mounting
bracket to the vehicle body.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal, however
ensure correct fitment of hose and pipes.
12Oxygen sensor (catalytic
converter models) - removal
and refitting
3
Note: This sensor is also known as a Lambda
sensor.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the oxygen sensor wiring plug,
which is located behind the coolant expansion
tank.
3Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands placed under the body side members.
4On DOHC models, remove the engine
undershield, as described in Chapter 11.
5On models fitted with Multec injection
system, the sensor is screwed into the
exhaust manifold. Trace the wiring from the
sensor itself to the connector (either clipped
to the radiator cooling fan shroud or behind
the coolant expansion tank). Release it from
any clips or ties; disconnect the wiring before
unscrewing the sensor.
6On other models, unscrew the oxygen
sensor from the front section of the exhaust
system (see illustration). It is advisable to
wear gloves, as the exhaust system will be
extremely hot.
7Withdraw the oxygen sensor and its wiring,
taking care not to burn the wiring on the
exhaust system. If the sensor is to be re-used,
take care that the sealing ring is not lost, and
that the sensor is not dropped.
Refitting
8If a new sensor is being fitted, it will be
supplied with the threads coated in a special
grease to prevent it seizing in the exhaust
system.
9If the original sensor is being refitted,
ensure that the screw thread is clean. Coat
the thread with a lithium based copper grease
(i.e. Vauxhall Part No. 90295397).
10Refitting is a reversal of removal. Check
the exhaust system for leakage when the
engine is re-started.
4C•4Fuel and exhaust systems - exhaust and emissions
12.6 Oxygen sensor location in front
section of exhaust system - DOHC models
11.3 Charcoal canister
A Vent to atmosphere
B Vapour feed hose from filler pipe
C Vapour exhaust hose to inlet tract
D Control valve vacuum pipe from
throttle body