sensor OPEL CALIBRA 1988 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1988, Model line: CALIBRA, Model: OPEL CALIBRA 1988Pages: 525, PDF Size: 58.26 MB
Page 210 of 525
a)Inlet and exhaust manifolds (where
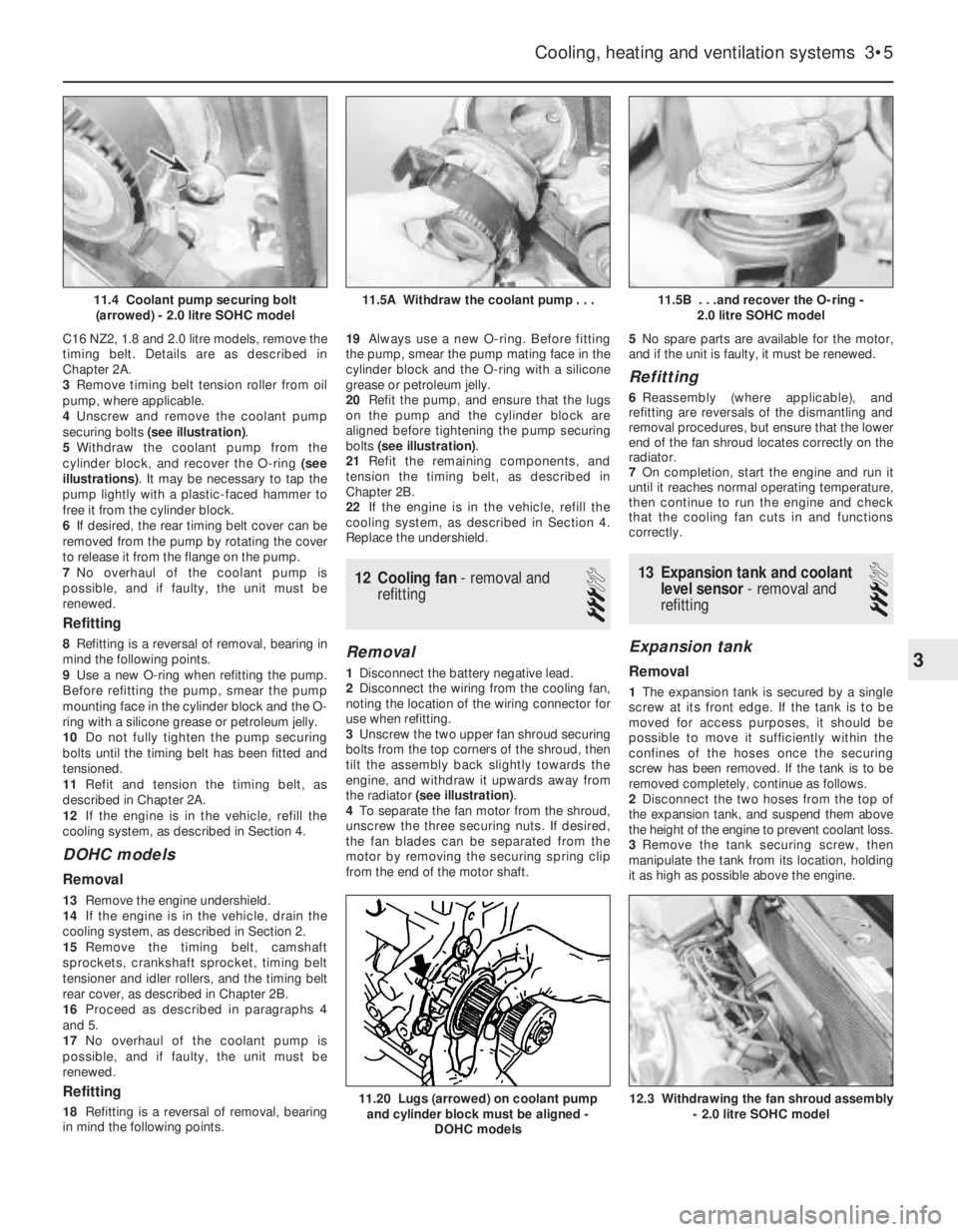
applicable)
b)Starter motor
c)Rear coolant gallery and hoses
d)Oil pressure switch
e)Oil temperature switch (where applicable)
f)Oil level sensor (where applicable)
g)Knock sensor (where applicable)
h)TDC sensor (where applicable)
i)Distributor components
j)Fuel pump (where applicable)
k)Thermostat/housing (N 16 NZ2, 1.8 and
2.0 litre models)
l)Power steering pump and mounting
bracket (where applicable)
m)Alternator mounting bracket
n)Engine lifting brackets
o)Dipstick/crankcase breather tube
p)Inlet manifold mounting bracket (where
applicable)
13To ensure maximum life, with minimum
trouble, from a rebuilt engine, not only must
everything be correctly assembled, but it must
also be spotlessly clean. All oilways and
coolant passages must be clear, and all
washers must be fitted in their original
positions. Oil all bearings and other moving
surfaces thoroughly with clean engine oil
during assembly.
14Before assembly begins, renew any bolts
or studs with damaged threads.
15Obtain a torque wrench, an angle-torque
gauge, sockets and bits, an oil can, clean
lint-free rag, and a set of engine gaskets and
oil seals, together with a new oil filter.16If they have been removed, new cylinder
head bolts, flywheel bolts, big-end bearing
cap bolts and main bearing cap bolts will also
be required.
17On completion of reassembly, refit the
applicable ancillary components listed in
paragraph 12.
18Follow procedure shown in Section 37.
11Timing belt and sprockets
(without automatic tensioner) -
removal, refitting and adjustment
3
Note: A two-legged puller may be required to
remove the crankshaft sprocket on N 16 NZ2,
1.8 and 2.0 litre models.Some of the later 1.4
and 1.6 litre engines, identifiable by the
squared-off top surfaces of the timing belt
covers, are fitted with spring-loaded auto-matic timing belt tensioners to ensure correct
belt tensioning on assembly.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2On models with power steering, remove the
pump drivebelt, see Chapters 1 and 10.
3Remove the alternator drivebelt, as
described in Chapter 5.
4On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models,
disconnect the wiring from the temperature
gauge sender.
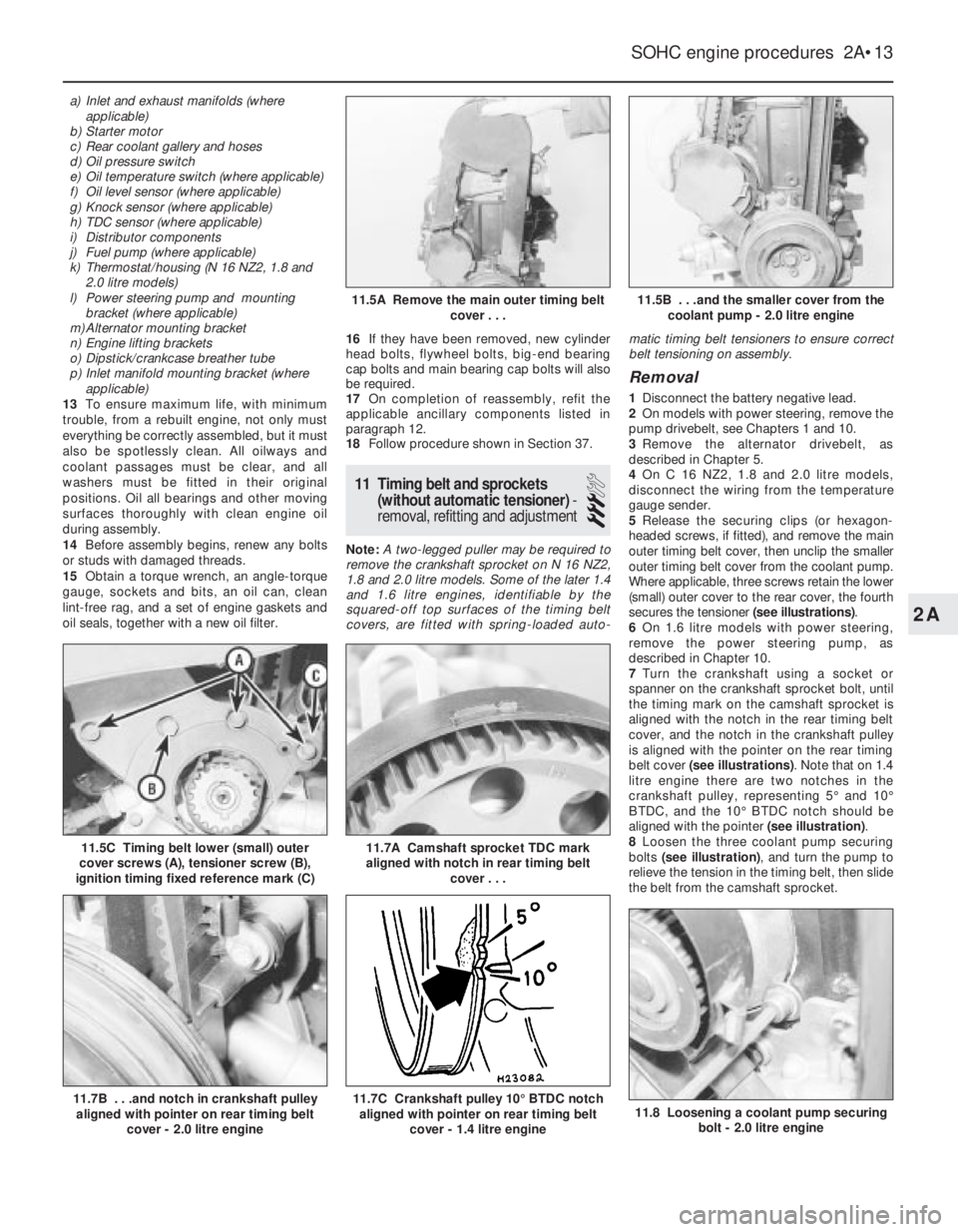
5Release the securing clips (or hexagon-
headed screws, if fitted), and remove the main
outer timing belt cover, then unclip the smaller
outer timing belt cover from the coolant pump.
Where applicable, three screws retain the lower
(small) outer cover to the rear cover, the fourth
secures the tensioner (see illustrations).
6On 1.6 litre models with power steering,
remove the power steering pump, as
described in Chapter 10.
7Turn the crankshaft using a socket or
spanner on the crankshaft sprocket bolt, until
the timing mark on the camshaft sprocket is
aligned with the notch in the rear timing belt
cover, and the notch in the crankshaft pulley
is aligned with the pointer on the rear timing
belt cover (see illustrations). Note that on 1.4
litre engine there are two notches in the
crankshaft pulley, representing 5°and 10°
BTDC, and the 10°BTDC notch should be
aligned with the pointer (see illustration).
8Loosen the three coolant pump securing
bolts (see illustration), and turn the pump to
relieve the tension in the timing belt, then slide
the belt from the camshaft sprocket.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•13
11.5C Timing belt lower (small) outer
cover screws (A), tensioner screw (B),
ignition timing fixed reference mark (C)
11.8 Loosening a coolant pump securing
bolt - 2.0 litre engine11.7C Crankshaft pulley 10°BTDC notch
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover - 1.4 litre engine11.7B . . .and notch in crankshaft pulley
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover - 2.0 litre engine
11.7A Camshaft sprocket TDC mark
aligned with notch in rear timing belt
cover . . .
11.5B . . .and the smaller cover from the
coolant pump - 2.0 litre engine11.5A Remove the main outer timing belt
cover . . .
2A
Page 211 of 525

9The crankshaft pulley must now be
removed. On 1.4 and 1.6 litre engines (except
C 16 NZ2), the pulley is secured by a single
bolt, which also secures the crankshaft
sprocket. On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre
engines, the pulley is secured by four bolts,
which must be unscrewed using an Allen key
or hexagon bit. On manual transmission
models, if the engine is in the vehicle, the
crankshaft can be prevented from turning by
having an assistant engage first gear and
depress the brake pedal. Alternatively, the
flywheel ring gear teeth can be jammed using
a large screwdriver or similar tool.
10With the crankshaft pulley removed, the
timing belt can be withdrawn.
11If desired, the sprockets and the rear
timing belt cover can be removed as follows,
otherwise go on to paragraph 23.
12To remove the camshaft sprocket, firstdisconnect the breather hose(s) from the
camshaft cover, then unscrew the securing
bolts noting the locations of the HT lead
brackets and any other wiring brackets, and
remove the camshaft cover.
13Recover the gasket. Prevent the camshaft
from turning by holding it with a spanner on
the flats provided between No’s 3 and 4
camshaft lobes, and unscrew the camshaft
sprocket bolt.
14Withdraw the sprocket from the end of the
camshaft.
15To remove the crankshaft sprocket on 1.4
and 1.6 litre engines (except C 16 NZ2), if
necessary, remove the lower securing bolts
from the main rear timing belt cover and use
two large screwdrivers behind the cover to
lever off the sprocket. Remove the Woodruff
key if it is loose.
16To remove the crankshaft sprocket on C
16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines, it will benecessary to prevent the crankshaft from
turning, as described in paragraph 9. Take
care when unscrewing the sprocket bolt, as it
is very tight. If necessary, use a two-legged
puller to remove the sprocket. Recover the
Woodruff key and the thrustwasher from the
end of the crankshaft.
17To remove the main rear timing belt cover
on C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models
disconnect the TDC sensor wiring plug and
unclip the wiring from the belt cover. Then
unscrew the two upper securing bolts and the
lower securing bolt(s) (one in the case of C 16
NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines, two on other
SOHC engines). Withdraw the cover,
manipulating it from the smaller rear belt
cover on the coolant pump (see illustrations).
18If desired, the smaller rear belt cover can
be removed from the coolant pump, after
unscrewing the securing bolt (see
illustration), by rotating it to disengage it from
the retaining flange on the pump.
Refitting
19Refit the rear timing belt cover(s) using a
reversal of the removal procedure, and
ensuring that the main cover engages correctly
with the smaller cover on the coolant pump.
20On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines,
refit the thrustwasher and the Woodruff key to
the end of the crankshaft. Then refit the
crankshaft sprocket, and tighten the securing
bolt to the specified torque in the two stages
given in the Specifications. Ensure that the
washer is in place under the bolt head, and
prevent the crankshaft from turning as during
removal (see illustrations).
2A•14SOHC engine procedures
11.17A Loosening the main rear timing
belt cover lower securing bolt -
2.0 litre engine11.18 Unscrewing the coolant pump rear
belt cover securing bolt - 2.0 litre engine
11.20E Tighten the bolt to the specified
torque . . .11.20D . . .and the washer and bolt11.20C . . .the crankshaft sprocket . . .
11.20B . . . the Woodruff key . . .11.20A Refit the thrustwasher . . .
11.17B Main rear timing belt cover lower
securing bolts (arrowed) - 1.6 SV engine
Page 224 of 525

28Crankshaft rear oil seal -
renewal
4
Renewal
1With the engine removed from the vehicle,
remove the flywheel, or flexplate (as
applicable) as described in Sections 25 and
26.
2Punch or drill a small hole in the centre of
the now-exposed oil seal. Screw in a
self-tapping screw, and pull on the screw with
pliers to extract the seal. Several attempts
may be necessary. Be careful not to damage
the sealing face of the crankshaft.
3Clean the oil seal seat with a wooden or
plastic scraper.4Grease the lips of the new seal, then tap the
seal into position using a tube, until flush with
the outer faces of the cylinder block and rear
main bearing cap (see illustration).
5Refit the flywheel or flexplate (if applicable),
as described in Sections 25 or 26.
29Sump - removal and refitting
4
Note: The sump gasket(s) must be renewed
on refitting and sealer will be required for use
on the oil pump and rear main bearing
cap-to-cylinder block joints
Removal
1If the engine is in the vehicle, continue as
follows, otherwise go on to paragraph 9.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Drain the engine oil, referring to Chapter 1 if
necessary, then refit and tighten the drain
plug.
4Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
5Remove the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
6Where applicable, disconnect the wiring
from the oil level sensor.
7Unscrew the securing bolts and remove the
engine-to-transmission blanking plate from
the bellhousing.8Remove the securing bolts, and withdraw
the sump. Note that on most models, the
sump baffle will probably be pulled away from
the cylinder block with the sump, but cannot
be removed until the oil pick-up pipe has been
removed.
9On 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, to remove
the sump baffle, it is necessary to unbolt the
bracket securing the oil pick-up pipe to the
cylinder block. The baffle can then be
manipulated over the oil pick-up pipe. On C
16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, prise the
rubber gasket from the sump baffle.
10If need be, the oil pick-up pipe can be
removed by unscrewing the single bolt
securing the support bracket to the cylinder
block (if not already done). Then remove the
two bolts securing the end of the pipe to the
oil pump. Recover the O-ring.
11Clean all traces of old gasket and sealing
compound from the mating faces of the
cylinder block, sump baffle (where
applicable), and sump.
Refitting
12Begin refitting by applying sealing
compound (Vauxhall part No 90485251 or
equivalent) to the joints between the oil pump
and cylinder block, and the rear main bearing
cap and cylinder block (see illustrations).
13On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre locate a
new rubber gasket over the sump baffle
flange, ensuring that it is seated correctly (see
illustration).
14On 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, offer the
sump baffle up to the cylinder block,
manipulating it over the oil pick-up pipe where
applicable.
15If the oil pick-up pipe has been removed,
refit it to the oil pump using a new O-ring and
tighten bolts to the specified torque (see
illustrations).
16Where applicable, refit the bracket
securing the oil pick-up pipe to the cylinder
block, ensuring that it passes through the
relevant hole in the sump baffle, if applicable
(see illustration).
17Coat the sump securing bolts with
thread-locking compound (i.e. Vauxhall part
No. 90167347), then refit the sump, and
tighten the bolts to the specified torque (see
illustrations).
SOHC engine procedures 2A•27
29.12B Applying sealing compound to the
joint between the oil pump and cylinder
block - 2.0 litre engine
29.15B . . .and tighten the securing bolts
to the specified torque - 2.0 litre engine29.15A Fit a new O-ring to the oil pick-up
pipe . . .29.13 Locate a new rubber gasket over
the sump baffle flange - 2.0 litre engine
29.12A Apply sealing compound (arrowed)
to oil pump and rear main bearing cap
joints before refitting sump
28.4 Fitting a new crankshaft rear oil seal -
2.0 litre engine
2A
Page 228 of 525

7If any of the ring end gaps exceed the
specified tolerance, the relevant rings will have
to be renewed, and if the ring grooves in the
pistons are worn, new pistons may be required.
8Clean out the piston ring grooves using a
piece of old piston ring as a scraper. Take
care not to scratch the surface of the pistons.
Protect your fingers, piston ring edges are
sharp. Also probe the groove oil return holes,
to ensure that they are not blocked.
9Check the cylinder bores for signs of wear
ridges towards the top of the bores. If wear
ridges are evident, and new piston rings are
being fitted, the top ring must be stepped to
clear the wear ridge, or the bore must be
de-ridged using a scraper.
10Fit the oil control ring sections with the
lower steel ring gap offset 25 to 50 mm to the
right of the spreader ring gap, and the upper
steel ring gap offset by the same distance to
the left of the spreader ring gap.
11Fit the lower compression ring, noting that
the ring is tapered or stepped. The ring should
be fitted with the word “TOP” uppermost.
12Fit the upper compression ring, and offset
the ring gap by 180°to the lower compression
ring gap. If a stepped ring is being fitted, fit
the ring with the smaller diameter of the step
uppermost.
13If new pistons are to be fitted, they must
be selected from the grades available, after
measuring the cylinder bores as described in
Section 36.
14Normally the appropriate oversize pistons
are supplied by the dealer when the block is
rebored.15Whenever new piston rings are being
installed, the glaze on the original cylinder
bores should be “broken”, using either
abrasive paper or a glaze-removing tool in an
electric drill. If abrasive paper is used, use
strokes at 60°to the bore centre line, to create
a cross-hatching effect.
34Crankshaft and bearings -
removal and refitting
4
Note: New main bearing cap bolts must be
used on refitting
Removal
1With the engine removed from the vehicle,
continue as follows.
2Remove the cylinder head, as described
previously in Section 20.
3Remove the sump, oil pick-up pipe and
sump baffle (where applicable), as described
in Section 29.
4Remove the oil pump, as described in
Section 30.
5Remove the flywheel or flexplate (if
applicable), as described in Sections 25 and
26.
6Remove the pistons and connecting rods,
as described in Section 32.
7Invert the engine so that it is standing on
the top face of the cylinder block.
8The main bearing caps are numbered 1 to 4
from the timing belt end of the engine. The
rear (flywheel end) cap is not marked. Toensure that the caps are refitted the correct
way round, note that the numbers are read
from the coolant pump side of the engine with
the engine inverted (see illustration).
9Unscrew and remove the main bearing cap
bolts, and tap off the bearing caps. If the
bearing shells are to be re-used, tape them to
their respective caps.
10Note that the centre bearing shell
incorporates thrust flanges to control
crankshaft endfloat.
11Lift the crankshaft (complete with timing
sensor wheel, if fitted), from the crankcase.
12Extract the upper bearing shells, and
identify them for position if they are to be
re-used.
13The crankshaft, bearings and sensor
wheel can be examined for wear and damage,
as described in Section 35, and the cylinder
block and bores can be examined as
described in Section 36.
Refitting
14Begin refitting by ensuring that the
crankcase and crankshaft are thoroughly
clean, and that all oilways are clear. If
possible, blow through the oil drillings with
compressed air, and inject clean engine oil
into them.
15If the crankshaft is being replaced, where
applicable, transfer the timing sensor wheel
and tighten to correct torque.
16Wipe clean the bearing shell seats in the
crankcase and the bearing caps, then fit the
upper bearing shells to their seats.
17Note that there is a tag on the back of
each bearing shell, which engages with a
groove in the relevant seat in the crankcase or
bearing cap (see illustration).
18If new bearing shells are being fitted, wipe
away all traces of protective grease.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•31
33.6 Measuring a piston ring end gap
using a feeler blade34.8 Main bearing cap identification mark
(arrowed) - 1.6 litre engine34.17 Main bearing shell tag (arrowed)
engages with groove in cylinder block -
2.0 litre SOHC engine
33.5C Sectional view showing correct
orientation of piston rings - all engines33.5B Removing the centre section of the
oil control ring - 2.0 litre SOHC engine
2A
A good alternative to
compressed air, is to use a
water dispersing lubricant
spray into each hole, using
the spout provided.
Page 230 of 525

31Refit the previously removed
components, referring to the relevant
Sections of this Chapter.
35Crankshaft and bearings -
examination
4
Examination
1Examine the crankpin and main journal
surfaces for signs of scoring or scratches, and
check the ovality and taper of the crankpins
and main journals. If the bearing surface
dimensions do not fall within the tolerance
ranges given in the Specifications at the
beginning of this Chapter, the crankpins
and/or main journals will have to be reground.
2Big-end and crankpin wear is accompanied
by distinct metallic knocking, particularly
noticeable when the engine is pulling from low
revs, and some loss of oil pressure.
3Main bearing and main journal wear is
accompanied by severe engine vibration rumble
- getting progressively worse as engine rev’s
increase - and again by loss of oil pressure.
4If the crankshaft requires regrinding, take it
to an engine reconditioning specialist, who
will machine it for you and supply the correct
undersize bearing shells.
5Inspect the big-end and main bearing shells
for signs of general wear, scoring, pitting and
scratches. The bearings should be matt grey
in colour. With leadindium bearings, should a
trace of copper colour be noticed, the
bearings are badly worn, as the lead bearing
material has worn away to expose the indium
underlay. Renew the bearings if they are in
this condition, or if there are any signs of
scoring or pitting. You are strongly advised
to renew the bearings - regardless of their
condition at time of major overhaul.
Refitting used bearings is a false economy.
6The undersizes available are designed to
correspond with crankshaft regrind sizes. Thebearings are in fact, slightly more than the
stated undersize, as running clearances have
been allowed for during their manufacture.
7Main and big-end bearing shells can be
identified as to size by the marking on the
back of the shell. Standard size shell bearings
are marked STD or .00, undersize shells are
marked with the undersize such as 0.020 u/s.
This marking method applies only to
replacement bearing shells, and not to those
used during production.
8An accurate method of determining bearing
wear is by using a Plastigage. The crankshaft
is located in the main bearings (and, if
necessary, the big-end bearings), and the
Plastigage filament is located across the
journal. Vauxhall recommend that the
crankshaft journal and bearing shells are
lightly lubricated, to prevent the Plastigage
from tearing as the bearing cap is removed.
The bearing cap should be fitted, and the
bolts tightened to the specified torque. The
cap is then removed, and the width of the
filament is checked against a scale that shows
the bearing running clearance. The clearance
should be compared with that given in the
Specifications.
9Where applicable, check the teeth of the
crankshaft TDC sensor wheel for damage
(see illustration). If evident, the crankshaft
must be renewed.
10Similarly, check the condition of the pins
in the front crankshaft balance weight, which
serve as detect points for the plug-in
diagnostic sensor used by Vauxhall dealers
(see illustration).
36Cylinder block and bores -
examination and renovation
4
Examination
1Examine the cylinder bores for taper,
ovality, scoring and scratches. Start bycarefully examining the top of the cylinder
bores. If they are at all worn, a very slight
ridge will be found on the thrust side. This
marks the top of the piston ring travel. The
owner will have a good indication of the bore
wear before dismantling the engine, or
removing the cylinder head. Excessive oil
consumption, accompanied by blue smoke
from the exhaust, is a sure sign of worn
cylinder bores and piston rings.
2Measure the bore diameter across the
block, and just below any ridge. This can be
done with an internal micrometer or a dial
gauge. Compare this with the diameter of the
bottom of the bore, which is not subject to
wear. If no measuring instruments are
available, use a piston from which the rings
have been removed, and measure the gap
between it and the cylinder wall with a feeler
blade. Refer to the Specifications. If the
cylinder wear exceeds the permitted
tolerances, then the cylinders will need
reboring, in which case note the following
points:
a)Piston and cylinder bores are closely
matched in production. The actual
diameter of the piston is indicated by
numbers on its crown; the same numbers
stamped on the crankcase indicate the
bore diameter
b)After reboring has taken place, the
cylinder bores should be measured
accurately and oversize pistons selected
from the grades available to give the
specified piston-to-bore clearance
c)For grading purposes, the piston diameter
is measured across the bottom of the skirt
3If the wear is marginal and within the
tolerances given, new special piston rings can
be fitted to offset the wear.
4Thoroughly examine the crankcase and
cylinder block for cracks and damage, and
use a piece of wire to probe all oilways and
waterways to ensure that they are
unobstructed.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•33
35.10 Check the condition of the pins (arrowed) in the front
crankshaft balance weight - 2.0 litre SOHC engine35.9 Check the condition of the TDC sensor wheel teeth at the
front of the crankshaft - 2.0 litre SOHC engine
2A
Page 231 of 525

5Note that the rubber plug located next to
the bellhousing flange on the cylinder block
covers the aperture for the installation of a
diagnostic TDC sensor. The sensor, when
connected to a monitoring unit, indicates TDC
from the position of the pins set into the
crankshaft balance weight.
37Examination and renovation
-general
4
General
1With the engine completely stripped, clean all
components and examine them for wear. Each
component should be checked, and where
necessary renewed or renovated, as described
in the relevant Sections of this Chapter.
2Renew main and big-end bearing shells as
a matter of course, unless it is known that
they have had little wear, and are in perfect
condition.
3If in doubt whether to renew a component
that is still just serviceable, consider the time
and effort that will be incurred should the
component fail at an early date after rebuild.
Obviously, the age and expected life of the
vehicle must influence the standards applied.4Gaskets, oil seals and O-rings must all be
renewed as a matter of routine. Flywheel,
cylinder head, and main and big-end bearing
cap bolts must be renewed, because of the
high stress to which they are subjected.
5Renew the engine core plugs while they are
easily accessible, if they show signs of
leakage. Knock out the old plugs with a
hammer and chisel or punch. Clean the plug
seats, smear the new plugs with sealing
compound, and tap them squarely into
position.
38Initial start-up after major
overhaul or repair
2
1Make a final check to ensure that
everything has been reconnected to the
engine, and that no rags or tools have been
left in the engine compartment.
2Check that oil and coolant levels are
correct.
3Start the engine. This may take a little longer
than usual, as fuel is pumped to the engine.
4Check that the oil pressure warning lamp
goes out when the engine starts. This may
take a few seconds as the new oil filter fills
with oil.5Run the engine at a fast tickover, and check
for leaks of oil, fuel and coolant. If a new
camshaft has been fitted, pay careful
attention to the running-in procedure given in
Section 18, paragraphs 17 and 18. Where
applicable, check the power steering and/or
automatic transmission fluid cooler unions for
leakage. Some smoke and odd smells may be
experienced, as assembly lubricants and
sealers burn off the various components.
6Bring the engine to normal operating
temperature. Check the ignition timing, idle
speed and the mixture (where applicable), as
described in Chapter 4A or 4B.
7Allow the engine to cool, then recheck the
oil and coolant levels. Top-up if necessary
8If new bearings, pistons, etc., have been
fitted, the engine should be run-in at reduced
speeds and loads for the first 500 miles (800
km) or so. It is beneficial to change the engine
oil and filter after this mileage.
2A•34SOHC engine procedures
Page 232 of 525

3
System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pressurised, with remote expansion tank. Coolant pump driven by
timing belt
Coolant
Type/specification (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Lubricants and fluidsin “Weekly checks”
Capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Specifications
Thermostat
Starts to open at (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92°C
Fully open at (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107°C
Operating temperature (approx.) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80°C
Expansion tank cap
Opening pressure (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.20 to 1.35 bar
Boiling point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125°C
Cooling fan switch
Switches on at (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C
Switches off at (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95°C
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Coolant pump bolts:
1.4 and 1.6 litre models
(except C16 NZ2), (M6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 6
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models (M8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Oil pipes to radiator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 16
Outlet to thermostat housing,
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 6
Temperature sender . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 8
Thermostat housing to cylinder head:
1.4 and 1.6 litre models (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 11
Chapter 3
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
Coolant mixture - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Coolant pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Cooling fan - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Cooling fan switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Cooling system - draining . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Cooling system - filling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Cooling system - flushing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Expansion tank and coolant level sensor - removal and refitting . . . .13
Facia ventilation nozzles - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1Heater blower motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Heater control panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Heater matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Radiator (automatic transmission) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .7
Radiator (manual transmission) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Radiator - inspection and cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Temperature gauge sender - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Thermostat - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Thermostat - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
3•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 236 of 525
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, remove the
timing belt. Details are as described in
Chapter 2A.
3Remove timing belt tension roller from oil
pump, where applicable.
4Unscrew and remove the coolant pump
securing bolts (see illustration).
5Withdraw the coolant pump from the
cylinder block, and recover the O-ring (see
illustrations). It may be necessary to tap the
pump lightly with a plastic-faced hammer to
free it from the cylinder block.
6If desired, the rear timing belt cover can be
removed from the pump by rotating the cover
to release it from the flange on the pump.
7No overhaul of the coolant pump is
possible, and if faulty, the unit must be
renewed.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing in
mind the following points.
9Use a new O-ring when refitting the pump.
Before refitting the pump, smear the pump
mounting face in the cylinder block and the O-
ring with a silicone grease or petroleum jelly.
10Do not fully tighten the pump securing
bolts until the timing belt has been fitted and
tensioned.
11Refit and tension the timing belt, as
described in Chapter 2A.
12If the engine is in the vehicle, refill the
cooling system, as described in Section 4.
DOHC models
Removal
13Remove the engine undershield.
14If the engine is in the vehicle, drain the
cooling system, as described in Section 2.
15Remove the timing belt, camshaft
sprockets, crankshaft sprocket, timing belt
tensioner and idler rollers, and the timing belt
rear cover, as described in Chapter 2B.
16Proceed as described in paragraphs 4
and 5.
17No overhaul of the coolant pump is
possible, and if faulty, the unit must be
renewed.
Refitting
18Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.19Always use a new O-ring. Before fitting
the pump, smear the pump mating face in the
cylinder block and the O-ring with a silicone
grease or petroleum jelly.
20Refit the pump, and ensure that the lugs
on the pump and the cylinder block are
aligned before tightening the pump securing
bolts (see illustration).
21Refit the remaining components, and
tension the timing belt, as described in
Chapter 2B.
22If the engine is in the vehicle, refill the
cooling system, as described in Section 4.
Replace the undershield.
12Cooling fan - removal and
refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the wiring from the cooling fan,
noting the location of the wiring connector for
use when refitting.
3Unscrew the two upper fan shroud securing
bolts from the top corners of the shroud, then
tilt the assembly back slightly towards the
engine, and withdraw it upwards away from
the radiator (see illustration).
4To separate the fan motor from the shroud,
unscrew the three securing nuts. If desired,
the fan blades can be separated from the
motor by removing the securing spring clip
from the end of the motor shaft.5No spare parts are available for the motor,
and if the unit is faulty, it must be renewed.
Refitting
6Reassembly (where applicable), and
refitting are reversals of the dismantling and
removal procedures, but ensure that the lower
end of the fan shroud locates correctly on the
radiator.
7On completion, start the engine and run it
until it reaches normal operating temperature,
then continue to run the engine and check
that the cooling fan cuts in and functions
correctly.
13Expansion tank and coolant
level sensor -removal and
refitting
3
Expansion tank
Removal
1The expansion tank is secured by a single
screw at its front edge. If the tank is to be
moved for access purposes, it should be
possible to move it sufficiently within the
confines of the hoses once the securing
screw has been removed. If the tank is to be
removed completely, continue as follows.
2Disconnect the two hoses from the top of
the expansion tank, and suspend them above
the height of the engine to prevent coolant loss.
3Remove the tank securing screw, then
manipulate the tank from its location, holding
it as high as possible above the engine.
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•5
11.5B . . .and recover the O-ring -
2.0 litre SOHC model
12.3 Withdrawing the fan shroud assembly
- 2.0 litre SOHC model11.20 Lugs (arrowed) on coolant pump
and cylinder block must be aligned -
DOHC models
11.5A Withdraw the coolant pump . . .11.4 Coolant pump securing bolt
(arrowed) - 2.0 litre SOHC model
3
Page 237 of 525

4Position a container beneath the tank, then
disconnect the bottom hose and allow the
contents of the tank to drain into the
container. Suspend the bottom hose as high
as possible above the engine to prevent
coolant loss.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but on
completion check and if necessary top-up the
coolant level, as described in Section 4. The
coolant drained from the expansion tank
during removal can be re-used, provided it
has not been contaminated.
Coolant level sensor
6The coolant level sensor, where fitted, is an
integral part of the expansion tank cap. If the
level sensor is faulty, the complete cap
assembly must be renewed.
14Temperature gauge sender -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1The sender is screwed into the inlet
manifold on 1.4 and 1.6 litre models (except
C16 NZ2), and into the thermostat housing
on C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models (see
illustrations).
2Partially drain the cooling system, as
described in Section 2, to minimise coolant
spillage.
3Disconnect the battery negative lead.4Disconnect the wiring from the switch, then
unscrew the switch from its location.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
6Coat the sender threads with sealant before
fitting.
7Top-up the cooling system, as described in
Section 4.
8On completion, start the engine and check
the operation of the temperature gauge. Also
check for coolant leaks.
15Cooling fan switch -removal
and refitting
3
Note: A new sealing ring should be used
when refitting the switch
Removal
1The cooling fan switch is located at the
bottom right-hand corner of the radiator (see
illustration).
2If a faulty switch is suspected, the circuit to
the fan motor can be tested by temporarily
bridging the terminals in the switch wiring
plug, and switching on the ignition. If the
cooling fan now operates, the switch is faulty
and should be renewed. To remove the
switch, continue as follows.
3Disconnect the battery negative lead, then
disconnect the switch wiring plug if not
already done.4Drain the cooling system, as described in
Section 2.
5Unscrew the switch from the radiator and
recover the sealing ring.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, but use a
new sealing ring, and refill the cooling system
as described in Section 4.
7On completion, start the engine and run it
until it reaches normal operating temperature,
then continue to run the engine and check
that the cooling fan cuts in and functions
correctly.
16Heater control panel -
removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the passenger side footwell trim,
the steering column shrouds, and the
instrument panel lower and upper trim panels,
as described in Chapter 11.
3Remove the clock or trip computer, as
applicable, from the facia, referring to Chapter
12 if necessary.
4Remove the two heater control panel
securing screws from the clock/trip computer
aperture, and the remaining securing screw
from the right-hand end of the panel (exposed
by removing the instrument panel lower trim
panel), (see illustrations).
3•6Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
14.1A Disconnecting the wiring from the
temperature gauge sender - 1.6 litre model14.1C Temperature gauge sender location
(arrowed) - 2.0 litre DOHC model
16.4B . . . and the remaining screw from
the right-hand end of the panel16.4A Remove the two heater control
panel securing screws from the clock/trip
computer aperture . . .15.1 Cooling fan switch location -
2.0 litre SOHC model viewed from below
14.1B Temperature gauge sender location
(arrowed) - 2.0 litre SOHC model
Page 262 of 525

Glossary of Technical Terms REF•23
JJump startStarting the engine of a vehicle
with a discharged or weak battery by
attaching jump leads from the weak battery to
a charged or helper battery.
LLoad Sensing Proportioning Valve (LSPV)A
brake hydraulic system control valve that
works like a proportioning valve, but also
takes into consideration the amount of weight
carried by the rear axle.
LocknutA nut used to lock an adjustment
nut, or other threaded component, in place.
For example, a locknut is employed to keep
the adjusting nut on the rocker arm in
position.
LockwasherA form of washer designed to
prevent an attaching nut from working loose.
MMacPherson strutA type of front
suspension system devised by Earle
MacPherson at Ford of England. In its original
form, a simple lateral link with the anti-roll bar
creates the lower control arm. A long strut - an
integral coil spring and shock absorber - is
mounted between the body and the steering
knuckle. Many modern so-called MacPherson
strut systems use a conventional lower A-arm
and don’t rely on the anti-roll bar for location.
MultimeterAn electrical test instrument with
the capability to measure voltage, current and
resistance.
NNOxOxides of Nitrogen. A common toxic
pollutant emitted by petrol and diesel engines
at higher temperatures.
OOhmThe unit of electrical resistance. One
volt applied to a resistance of one ohm will
produce a current of one amp.
OhmmeterAn instrument for measuring
electrical resistance.
O-ringA type of sealing ring made of a
special rubber-like material; in use, the O-ring
is compressed into a groove to provide the
sealing action.Overhead cam (ohc) engineAn engine with
the camshaft(s) located on top of the cylinder
head(s).
Overhead valve (ohv) engineAn engine with
the valves located in the cylinder head, but
with the camshaft located in the engine block.
Oxygen sensorA device installed in the
engine exhaust manifold, which senses the
oxygen content in the exhaust and converts
this information into an electric current. Also
called a Lambda sensor.
PPhillips screwA type of screw head having a
cross instead of a slot for a corresponding
type of screwdriver.
PlastigageA thin strip of plastic thread,
available in different sizes, used for measuring
clearances. For example, a strip of Plastigage
is laid across a bearing journal. The parts are
assembled and dismantled; the width of the
crushed strip indicates the clearance between
journal and bearing.
Propeller shaftThe long hollow tube with
universal joints at both ends that carries
power from the transmission to the differential
on front-engined rear wheel drive vehicles.
Proportioning valveA hydraulic control
valve which limits the amount of pressure to
the rear brakes during panic stops to prevent
wheel lock-up.
RRack-and-pinion steeringA steering system
with a pinion gear on the end of the steering
shaft that mates with a rack (think of a geared
wheel opened up and laid flat). When the
steering wheel is turned, the pinion turns,
moving the rack to the left or right. This
movement is transmitted through the track
rods to the steering arms at the wheels.
RadiatorA liquid-to-air heat transfer device
designed to reduce the temperature of the
coolant in an internal combustion engine
cooling system.
RefrigerantAny substance used as a heat
transfer agent in an air-conditioning system.
R-12 has been the principle refrigerant for
many years; recently, however, manufacturers
have begun using R-134a, a non-CFC
substance that is considered less harmful tothe ozone in the upper atmosphere.
Rocker armA lever arm that rocks on a shaft
or pivots on a stud. In an overhead valve
engine, the rocker arm converts the upward
movement of the pushrod into a downward
movement to open a valve.
RotorIn a distributor, the rotating device
inside the cap that connects the centre
electrode and the outer terminals as it turns,
distributing the high voltage from the coil
secondary winding to the proper spark plug.
Also, that part of an alternator which rotates
inside the stator. Also, the rotating assembly
of a turbocharger, including the compressor
wheel, shaft and turbine wheel.
RunoutThe amount of wobble (in-and-out
movement) of a gear or wheel as it’s rotated.
The amount a shaft rotates “out-of-true.” The
out-of-round condition of a rotating part.
SSealantA liquid or paste used to prevent
leakage at a joint. Sometimes used in
conjunction with a gasket.
Sealed beam lampAn older headlight design
which integrates the reflector, lens and
filaments into a hermetically-sealed one-piece
unit. When a filament burns out or the lens
cracks, the entire unit is simply replaced.
Serpentine drivebeltA single, long, wide
accessory drivebelt that’s used on some
newer vehicles to drive all the accessories,
instead of a series of smaller, shorter belts.
Serpentine drivebelts are usually tensioned by
an automatic tensioner.
ShimThin spacer, commonly used to adjust
the clearance or relative positions between
two parts. For example, shims inserted into or
under bucket tappets control valve
clearances. Clearance is adjusted by
changing the thickness of the shim.
Slide hammerA special puller that screws
into or hooks onto a component such as a
shaft or bearing; a heavy sliding handle on the
shaft bottoms against the end of the shaft to
knock the component free.
SprocketA tooth or projection on the
periphery of a wheel, shaped to engage with a
chain or drivebelt. Commonly used to refer to
the sprocket wheel itself.
Starter inhibitor switchOn vehicles with an
O-ring
Serpentine drivebelt
Plastigage
REF