Electrical OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1134 of 6000

6E–17 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinouts
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red Connector – Row “A”
TS23344
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
A15 Volt Reference “A”RED5.0 V5.0 VAppropriate Sensor
A2Knock SensorYEL0.0 V DC
2mV AC0.0 V DC
18mV AC
(at idle)General Description and
Operation, Knock Sensor
A3Not Used————
A4Battery FeedWHTB+B+Chassis Electrical
A5Idle Air Control (IAC) “A”
HighBLUB+/0.8 VB+/0.8 VGeneral Description and
Operation, IAC
A6IAC “A” LowBLU/WHTB+/0.8 VB+/0.8 VGeneral Description and
Operation, IAC
A7IAC “B” LowBLU/BLKB+/0.8 VB+/0.8 VGeneral Description and
Operation, IAC
A8IAC “B” HighBLU/REDB+/0.8 VB+/0.8 VGeneral Description and
Operation, IAC
A9Automatic Transmission
Fluid (ATF) LampORN/BLUB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
A10Winter LampPNK/GRNB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
A11Power LampGRY/WHTB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
A12Antilock Brake System
(ABS)GRYB+B+Antilock Brake System
A13Malfunction Indicator
(Check Engine or MIL)
LampBLU0.0 VB+Chassis Electrical
A14“Check Transmission”
Lamp Driver (AT)ORN/BLKB+B+Chassis Electrical
Up Shift Lamp Driver (MT)ORN/BLU
Page 1136 of 6000
6E–19 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
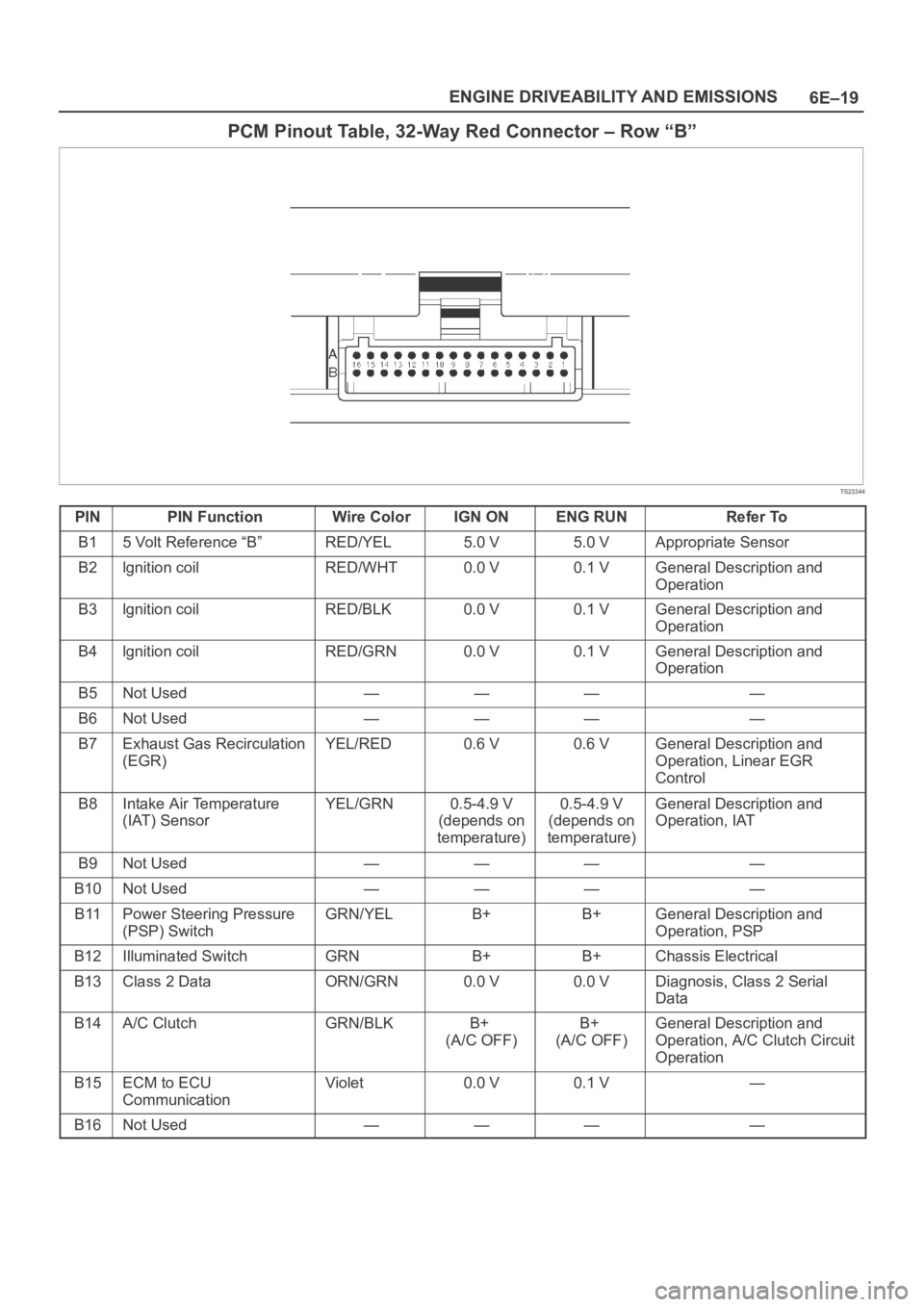
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red Connector – Row “B”
TS23344
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
B15 Volt Reference “B”RED/YEL5.0 V5.0 VAppropriate Sensor
B2lgnition coilRED/WHT0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B3lgnition coilRED/BLK0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B4lgnition coilRED/GRN0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B5Not Used————
B6Not Used————
B7Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR)YEL/RED0.6 V0.6 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Linear EGR
Control
B8Intake Air Temperature
(IAT) SensorYEL/GRN0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)General Description and
Operation, IAT
B9Not Used————
B10Not Used————
B11Power Steering Pressure
(PSP) SwitchGRN/YELB+B+General Description and
Operation, PSP
B12Illuminated SwitchGRNB+B+Chassis Electrical
B13Class 2 DataORN/GRN0.0 V0.0 VDiagnosis, Class 2 Serial
Data
B14A/C ClutchGRN/BLKB+
(A/C OFF)B+
(A/C OFF)General Description and
Operation, A/C Clutch Circuit
Operation
B15ECM to ECU
CommunicationViolet0.0 V0.1 V—
B16Not Used————
Page 1137 of 6000

6E–20
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White Connector – Row “C” (For EC)
TS23345
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
C1Injector Cylinder #4GRN/REDB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
C2Shift “B” SolenoidBRN/BLK0.0 V0.0 VAutomatic Transmission
(4L30E)
C3Injector Cylinder #6GRN/YELB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
C4Ignition Control (IC)
Cylinder #1RED0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
C5Crankshaft Position
Sensor, “A” CircuitYEL0.3 V to 5 V2.2 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Crankshaft
Position Sensor
C6Not Used————
C7PCM GroundYEL0.0 V0.0 VChassis Electrical
C8PCM GroundBLK/PNK0.0 V0.0 VChassis Electrical
C9PCM GroundBLK/BLU0.0 V0.0 VChassis Electrical
C10TachometerBLK/RED8.8 V10.0 V
(at idle)Chassis Electrical
C11Variable Intake ManifoldYEL/BLK0.0 VB+ (rpm
3600 over)Manual Transmission
C12Alternator Control GainWHT/BLU10.5 VB+Chassis Electrical
C13Fuel PWMBLU/PNKB+B+—
C14Bank 2 HO2S 1 HighPNK0.4 V0.1-0.9 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel HO2S 1
C15Bank 2 HO2S 1 LowBLU0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel HO2S 1
C16Not Used————
Page 1138 of 6000

6E–21 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White Connector – Row “C” (For except EC)
TS23345
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
C1Injector Cylinder #4GRN/REDB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
C2Shift “B” SolenoidBRN/BLK0.0 V0.0 VAutomatic Transmission
(4L30E)
C3Injector Cylinder #6GRN/YELB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
C4Ignition Control (IC)
Cylinder #1RED0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
C5Crankshaft Position
Sensor, “A” CircuitYEL0.3 V to 5 V2.2 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Crankshaft
Position Sensor
C6Not Used————
C7PCM GroundBLK/BLU0.0 V0.0 VChassis Electrical
C8PCM GroundBLK/PNK0.0 V0.0 VChassis Electrical
C9PCM GroundBLK/BLU0.0 V0.0 VChassis Electrical
C10TachometerBLK/RED8.8 V10.0 V
(at idle)Chassis Electrical
C11Variable Intake ManifoldYEL/BLK0.0 VB+ (rpm
3600 over)Manual Transmission
C12Not Used————
C13Not Used————
C14Not Used————
C15Not Used————
C16Not Used————
Page 1139 of 6000

6E–22
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White Connector – Row “D”
(For except EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA)
TS23345
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
D1Injector Cylinder #2GRN/ORNB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
D2Torque Converter Clutch
(TCC)BRN/BLU0.0 V0.0 VOn-Vehicle Service, Torque
Converter Clutch
D3Injector Cylinder #1GRN/WHTB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
D4Serial Data (8192)ORN5.0 V5.0 VChassis Electrical
D5Ignition Control, Cylinder
#5RED/YEL0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Ignition Coil
D6Ignition Control, Cylinder
#3RED/BLUE0.0 V0.0 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Ignition Coil
D7VSS Input / IMOB
ResponseWHT/BLK0.0 V0.1 V
(at rest)Chassis Electrical
D8Sensor Ground 5V
Reference A ReturnGRN0.0 V0.0 VAppropriate Sensor
D9Sensor Ground 5 V
Reference B ReturnGRY0.0 V0.0 VAppropriate Sensor
D10Mass Air Flow (MAF)YEL4.9 V4.2 VGeneral Description, Mass
Air Flow Sensor
D11Camshaft Position SensorWHT5.0 V or less
than 1.0 V4.6 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Camshaft
Position Sensor
D12Not Used————
D13Not Used————
D14Bank 1 HO2S 1 LowGRN0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel HO2S 1
D15Bank 1 HO2S 1 SignalRED0.4 V0.1-0.9 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel HO2S 1
D16Not Used————
Page 1140 of 6000

6E–23 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White Connector – Row “D”
(For EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA)
TS23345
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
D1Injector Cylinder #2GRN/ORNB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
D2Torque Converter Clutch
(TCC)BRN/BLU0.0 V0.0 VOn-Vehicle Service, Torque
Converter Clutch
D3Injector Cylinder #1GRN/WHTB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
D4Serial Data (8192)ORN5.0 V5.0 VChassis Electrical
D5Ignition Control, Cylinder
#5RED/YEL0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Ignition Coil
D6Ignition Control, Cylinder
#3RED/BLUE0.0 V0.0 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Ignition Coil
D7VSS Input / IMOB
ResponseLIGHT
GRN/WHT0.0 V0.1 V
(at rest)Chassis Electrical
D8Sensor Ground 5V
Reference A ReturnGRN0.0 V0.0 VAppropriate Sensor
D9Sensor Ground 5 V
Reference B ReturnGRY0.0 V0.0 VAppropriate Sensor
D10Mass Air Flow (MAF)YEL4.9 V4.2 VGeneral Description, Mass
Air Flow Sensor
D11Camshaft Position SensorWHT5.0 V or less
than 1.0 V4.6 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Camshaft
Position Sensor
D12Not Used————
D13Not Used————
D14Not Used————
D15Not Used————
D16Not Used————
Page 1150 of 6000

6E–33 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Undercarriage Component Locator Table (Manual Transmission)
Number
NameLocation
1Fuel Pump AssemblyInstalled in the top of the fuel tank
2Fuel Gauge UnitInstalled in the front edge of the right frame
rail, ahead of the rear axle
3Fuel FilterLocated along the inside of the right frame rail,
ahead of the rear axle
4Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)2WD: Protrudes from the transmission
housing, just ahead of the propeller shaft.
4WD: Protrudes from the rear output shaft
housing of the transfer case.
5Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, HO2S 1)Threaded into the exhaust pipe ahead of the
right-hand catalytic converter
6Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 2, HO2S 1)Threaded into the exhaust pipe ahead of the
left-hand catalytic converter
Fuse and Relay Panel (Underhood Electrical Center)
TS23336
Page 1154 of 6000

6E–37 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnosis
Strategy-Based Diagnostics
Strategy-Based Diagnostics
The strategy-based diagnostic is a uniform approach to
repair all Electrical/Electronic (E/E) systems. The
diagnostic flow can always be used to resolve an E/E
system problem and is a starting point when repairs are
necessary. The following steps will instruct the technician
how to proceed with a diagnosis:
1. Verify the customer complaint.
To verify the customer complaint, the technician
should know the normal operation of the system.
2. Perform preliminary checks.
Conduct a thorough visual inspection.
Review the service history.
Detect unusual sounds or odors.
Gather diagnostic trouble code information to
achieve an effective repair.
3. Check bulletins and other service information.
This includes videos, newsletters, etc.
4. Refer to service information (manual) system
check(s).
“System checks” contain information on a system
that may not be supported by one or more DTCs.
System checks verify proper operation of the
system. This will lead the technician in an
organized approach to diagnostics.
5. Refer to service diagnostics.
DTC Stored
Follow the designated DTC chart exactly to make an
effective repair.
No DTC
Select the symptom from the symptom tables. Follow the
diagnostic paths or suggestions to complete the repair.
You may refer to the applicable component/system check
in the system checks.
No Matching Symptom
1. Analyze the complaint.
2. Develop a plan for diagnostics.
3. Utilize the wiring diagrams and the theory of
operation.
Call technical assistance for similar cases where repair
history may be available. Combine technician knowledge
with efficient use of the available service information.
Intermittents
Conditions that are not always present are called
intermittents. To resolve intermittents, perform the
following steps:
1. Observe history DTCs, DTC modes, and freezeframe
data.
2. Evaluate the symptoms and the conditions described
by the customer.3. Use a check sheet or other method to identify the
circuit or electrical system component.
4. Follow the suggestions for intermittent diagnosis
found in the service documentation.
Most Tech 2s, such as the Tech II and the
5–8840–0285–0 (Fluke model 87 DVOM), have
data-capturing capabilities that can assist in detecting
intermittents.
No Trouble Found
This condition exists when the vehicle is found to operate
normally. The condition described by the customer may
be normal. Verify the customer complaint against another
vehicle that is operating normally. The condition may be
intermittent. Verify the complaint under the conditions
described by the customer before releasing the vehicle.
1. Re-examine the complaint.
When the Complaint cannot be successfully found or
isolated, a re-evaluation is necessary. The complaint
should be re-verified and could be intermittent as
defined in
Intermittents, or could be normal.
2. Repair and verify.
After isolating the cause, the repairs should be made.
Validate for proper operation and verify that the
symptom has been corrected. This may involve road
testing or other methods to verify that the complaint
has been resolved under the following conditions:
Conditions noted by the customer.
If a DTC was diagnosed, verify a repair by
duplicating conditions present when the DTC was
set as noted in the Failure Records or Freeze
Frame data.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of the vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with OBD system
diagnostics. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
IMPORTANT:Follow the steps below when you verify
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
1. Review and record the Failure Records and the
Freeze Frame data for the DTC which has been
diagnosed (Freeze Frame data will only be stored for
an A or B type diagnostic and only if the MIL(”Check
Engine” lamp) has been requested).
2. Clear the DTC(S).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the
Failure Records and Freeze Frame data.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Page 1169 of 6000

6E–52
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
10.This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes
an electrically erasable programmable read only
memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is replaced,
the new PCM must be programmed.
Refer to UBS
98 model year Immobilizer Workshop Manual.
Page 1172 of 6000

6E–55 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Damaged harness–Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to OK, observe the
A/C clutch while moving connectors and wiring
harnesses related to the A/C. A sudden clutch
malfunction will indicate the source of the intermittent
fault.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
This chart should be used for diagnosing the electrical
p o r t i o n o f t h e A / C c o m p r e s s o r c l u t c h c i r c u i t . A Te c h 2 w i l l
be used in diagnosing the system. The Tech 2 has the
ability to read the A/C request input to the PCM. The Tech
2 can display when the PCM has commanded the A/C
clutch “ON.” The Tech 2 should have the ability to
override the A/C request signal and energize the A/C
compressor relay.
Test Description
IMPORTANT:Do not engage the A/C compressor
clutch with the engine running if an A/C mode is not
selected at the A/C control switch.
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
Diagnostic Chart:3. This a test determine is the problem is with the
refrigerant system. If the switch is open, A/C
pressure gauges will be used to determine if the
pressure switch is faulty or if the system is partially
discharged or empty.
4. Although the normal complaint will be the A/C clutch
failing to engage, it is possible for a short circuit to
cause the clutch to run when A/C has not been
selected. This step is a test for that condition.
7. There is an extremely low probability that both relays
will fail at the same time, so the substitution process
is one way to check the A/C Thermostat relay. Use
a known good relay to do a substitution check.
9. The blower system furnishes a ground for the A/C
control circuit, and it also shares a power source
through the Heater and A/C Relay. The blower
must be “ON” in order to test the A/C system.
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any other DTCs stored?
—
Go to the
other DTC
chart(s) first
Go to Step 3
31. Disconnect the electrical connector at the pressure
switch located on the receiver/drier.
2. Use an ohmmeter to check continuity across the
pressure switch.
Is the pressure switch open?
—
Go to Air
Conditioning
to diagnose
the cause of
the open
pressure
switch
Go to Step 4
4IMPORTANT:Before continuing with the diagnosis, the
following conditions must be met:
The intake air temperature must be greater than
15
C. (60F).
The engine coolant temperature must be less
than 119
C (246F).
1. A/C “OFF.”
2. Start the engine and idle for 1 minute.
3. Observe the A/C compressor.
Is the A/C compressor clutch engaged even though
A/C has not been requested?
—Go to Step 45Go to Step 5
51. Idle the engine.
2. A/C “ON”.
3. Blower “ON”.
4. Observe the A/C compressor.
Is the A/C compressor magnetic clutch engaged?
—
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 6