change key battery OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1232 of 6000

6E–115 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108 MAP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
D06RW102
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP sensor signal voltage to the powertrain control
module (PCM) varies from below 2 volts at idle (high
vacuum) to above 4 volts with the key “ON,” engine not
running or at wide-open throttle (low vacuum).
The MAP sensor is used to determine manifold pressure
changes while the linear EGR flow test diagnostic is being
run (refer to
DTC P0401), to determine engine vacuum
level for some other diagnostics and to determine
barometric pressure (BARO). The PCM monitors the
MAP signals for voltages outside the normal range of the
MAP sensor. If the PCM detects a MAP signal voltage
that is excessively high, DTC P0108 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No TP sensor DTCs present.
Engine is running for more than 10 seconds.
Throttle position is below 3% if engine speed is below
1000 RPM.
Throttle position is below 10% if engine speed is above
1000 RPM.
The MAP sensor indicates an intermittent manifold
absolute pressure above 80kPa for a total of
approximately 10 seconds over a 16-second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will default to a BARO value of 79.3 kPa.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0108 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0108 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set. If
it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P1108 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 1253 of 6000
6E–136
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
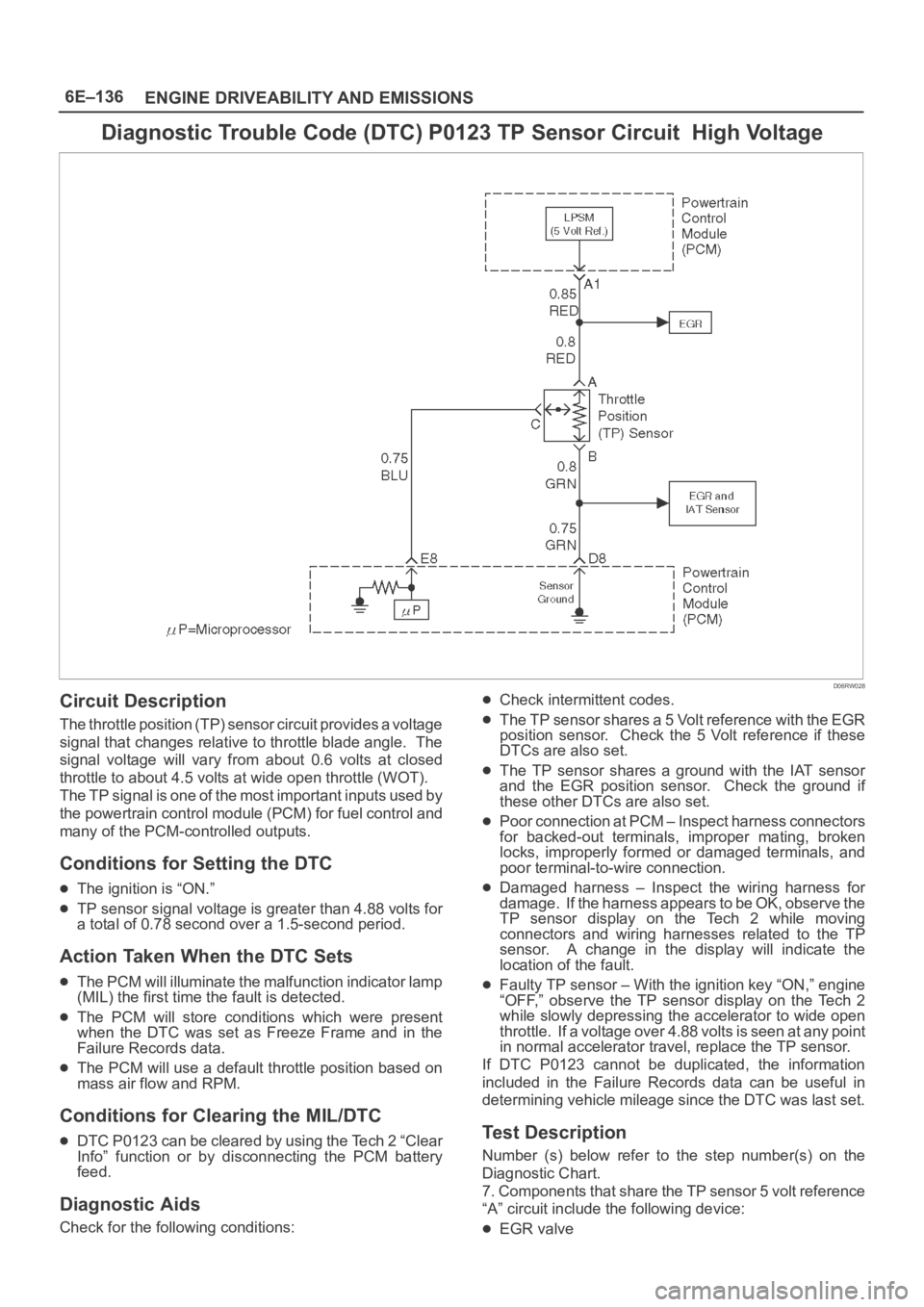
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0123 TP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
D06RW028
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to throttle blade angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about 0.6 volts at closed
throttle to about 4.5 volts at wide open throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is one of the most important inputs used by
the powertrain control module (PCM) for fuel control and
many of the PCM-controlled outputs.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ignition is “ON.”
TP sensor signal voltage is greater than 4.88 volts for
a total of 0.78 second over a 1.5-second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
The PCM will use a default throttle position based on
mass air flow and RPM.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0123 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Check intermittent codes.
The TP sensor shares a 5 Volt reference with the EGR
position sensor. Check the 5 Volt reference if these
DTCs are also set.
The TP sensor shares a ground with the IAT sensor
and the EGR position sensor. Check the ground if
these other DTCs are also set.
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
TP sensor display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the TP
sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Faulty TP sensor – With the ignition key “ON,” engine
“OFF,” observe the TP sensor display on the Tech 2
while slowly depressing the accelerator to wide open
throttle. If a voltage over 4.88 volts is seen at any point
in normal accelerator travel, replace the TP sensor.
If DTC P0123 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Test Description
Number (s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
7. Components that share the TP sensor 5 volt reference
“A” circuit include the following device:
EGR valve
Page 1460 of 6000

6E–343 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the
fuel injection system is called a “closed loop” system.
The PCM monitors signals from several sensors in order
to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called “modes.”
All modes are controlled by the PCM.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated
relief valve mounted on the fuel rail with fuel pump
pressure on one side and manifold pressure on the other
side. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel
pressure available to the injector at three times
barometric pressure adjusted for engine load. It may be
serviced separate.
If the pressure is too low, poor performance and a DTC
P0131, DTC P0151,DTC P0171 or DTC P1171 will be the
result. If the pressure is too high, excessive odor and/or a
DTC P0132, DTC P0152,DTC P0172 or DTC P0175 will
be the result. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis for
information on diagnosing fuel pressure conditions.
0011
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned “ON,” the PCM energizes the
fuel pump relay for two seconds to build up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the PCM shuts the fuel pump off and waits until
the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked and
the 58 X crankshaft position signal has been detected by
the PCM, the PCM supplies 12 volts to the fuel pump relay
to energize the electric in-tank fuel pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start” condition.
A fuel pump which does not provide enough pressure will
result in poor performance.
Fuel Rail
The fuel rail is mounted to the top of the engine and
distributes fuel to the individual injectors. Fuel is
delivered to the fuel inlet tube of the fuel rail by the fuel
lines. The fuel goes through the fuel rail to the fuel
pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator maintainsa constant fuel pressure at the injectors. Remaining fuel
is then returned to the fuel tank.
055RW009
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The purpose of the idle air control (IAC) valve is to control
engine idle speed, while preventing stalls due to changes
in engine load. The IAC valve, mounted in the throttle
body, controls bypass air around the throttle plate. By
moving the conical valve (pintle) in (to decrease air flow)
or out (to increase air flow), a controlled amount of air can
move around the throttle plate. If the RPM is too low, the
PCM will retract the IAC pintle, resulting in more air
moving past the throttle plate to increase the RPM. If the
RPM is too high, the PCM will extend the IAC pintle,
allowing less air to move past the throttle plate,
decreasing the RPM.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small steps called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the PCM based on battery voltage, coolant
temperature, engine load, and engine RPM. If the RPM
drops below a specified value, and the throttle plate is
closed, the PCM senses a near-stall condition. The PCM
will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve position to
prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with the
engine running, the idle RPM will be wrong. In this case,
the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the key is
cycled “ON” then “OFF.” When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “OFF.”
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-up
and the idle characteristics of the vehicle. If the IAC pintle
is fully open, too much air will be allowed into the manifold.
This results in high idle speed, along with possible hard
starting and a lean air/fuel ratio. DTC P0507 or DTC
P1509 may set. If the IAC pintle is stuck closed, too little
air will be allowed in the manifold. This results in a low idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and a rich air/fuel
ratio. DTC P0506 or DTC P1508 may set. If the IAC
pintle is stuck part-way open, the idle may be high or low
and will not respond to changes in the engine load.
Page 1968 of 6000

6E–75 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0123 (Flash DTC 21)
AP Sensor High Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The accelerator position (AP) sensor circuit provides a
voltage signal that changes relative to throttle blade
angle.
The TP signal is one of the most important inputs used by
the Engine Control Module ECM for fuel volume control
and many of the ECM-controlled outputs.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0123 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, brokenlocks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
AP sensor display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the TP
sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Faulty AP sensor – With the ignition key “ON,” engine
“OFF,” observe the AP sensor display on the Tech 2
while slowly depressing the accelerator to wide open
throttle. If a voltage over 4.88 volts is seen at any point
in normal accelerator travel, replace the AP sensor.
If DTC P0123 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Test Description
Number (s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
8. Components that share the AP sensor 5 volt reference
“A” circuit include the following device:
Page 2039 of 6000

6E–146
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1486 (Flash DTC 74)
ITP (Intake Throttle Position) Sensor High Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The intake throttle position (ITP) sensor circuit provides a
voltage signal that changes relative to throttle blade
angle.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1486 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
ITP sensor display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the TP
sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Faulty TP sensor – With the ignition key “ON,” engine
“OFF,” observe the TP sensor display on the Tech 2
while slowly depressing the accelerator to wide open
throttle.
If DTC P1486 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Page 2992 of 6000

WIRING SYSTEM 8D–399
1. Check to see if the battery voltage is normal.
2. Check to see if the fuse is normal.
3. Replace the anti–theft & keyless entry control unit with one reserved for test. If a trouble recurs even after replacing
the control unit, find out the cause of the trouble by referring to “System check procedure” and the following list.
ITEM MALFUNCTION POSSIBLE CAUSE DETECTING METHOD REMARKS
ANTI–THEFT
indicator light
does not flash
ANTI–THEFT
indicator light
does not turn off.
(Steadily on)
When door is
opened by pulling
up locking knob,
alarm does not
operate
Alarm does not
stop. Indicator light
does not change
to fully ON
condition, or does
not come on at
all.Burnt out indicator
light bulb possible.
Refer to “Connector
check table” in this
system.
Refer to “Connector
check table” in this
system.
Refer to “Connector
check table” in this
system.
Refer to “Connector
check table” in this
system.
Refer to “Connector
check table” in this
system.
Refer to “Connector
check table” in this
system. Defective contact of door switch,
or open circuit in door switch
wiring.
Short circuit in the detect switch.
Engine hood, doors and tailgate
are not fully closed and locked.
Defective door switch, or short
circuit in switch wiring.
Defective tamper switch, or short
circuit in wiring.
Defective lock switch, or short
circuit in wiring.
Defective engine hood switch, or
short circuit in wiring.
Defective tailgate switch, or short
circuit in wiring.
Defective control unit.
Poor contact of lock switch, or
open circuit in wiring.
Broken wire in wiring to headlight
and horn, or a blown fuse.
Defective contact of detect
switch, or damaged switch wiring.With door open, dome light and
courtesy light do not come on.
Check the control unit connector.
Check to see if doors are closed
and locked.
Dome light and courtesy light
remain lit on after closing doors.
Check the control unit connector.
Check the control unit connector.
Check the control unit connector.
Luggage room light remains lit
after closing tailgate.
Check alarm operation (See No.
46 of “System check procedure”),
possible cause is a poor contact
of lock switch of an open circuit in
wiring.
Check to see if headlights go out.
Check the control unit connector.
Check the control unit connector. A
C
D
E B
Page 3366 of 6000

SECURITY AND LOCKS8H–27
StepNo Ye s Action
41. Lock the door and unlock it three times.
2. Close the door and then open it.
NOTE: This step must be performed within ten seconds after step
3.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 5Finished
5Answer back mode changes.
Is this step complete?
Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
6The control unit makes lock/unlock response once with interval of
one second.
Is the response complete?
Finished—
7The control unit makes lock/unlock response three times with
interval of one second.
Is the response complete?
Finished—
Anti–theft & Keyless Entry Control
Unit/Transmitter Replacement
Anti–theft & Keyless Entry Control Unit
Replacement
1. Remove and install the control unit.
Refer to Anti–theft & Keyless Entry Control Unit
Removal and Installation in this section.
2. Register ID code.
Refer to ID Code Registration in this section.
3. Check that the keyless entry system works normally.
Transmitter Replacement
1. Prepare a new transmitter.
2. Regiter ID code.
Refer to ID Code Registration in this section.
3. Check that the keyless entry system works normally.
Transmitter Battery Replacement
1. Remove a screw to remove the cover.
2. Remove the batteries.
3. Set the new batteries into the transmitter.
4. Install the cover to the transmitter.
5. Check that the keyless entry system works normally.
Page 4772 of 6000

6E–115 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108 MAP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
D06RW102
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP sensor signal voltage to the powertrain control
module (PCM) varies from below 2 volts at idle (high
vacuum) to above 4 volts with the key “ON,” engine not
running or at wide-open throttle (low vacuum).
The MAP sensor is used to determine manifold pressure
changes while the linear EGR flow test diagnostic is being
run (refer to
DTC P0401), to determine engine vacuum
level for some other diagnostics and to determine
barometric pressure (BARO). The PCM monitors the
MAP signals for voltages outside the normal range of the
MAP sensor. If the PCM detects a MAP signal voltage
that is excessively high, DTC P0108 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No TP sensor DTCs present.
Engine is running for more than 10 seconds.
Throttle position is below 3% if engine speed is below
1000 RPM.
Throttle position is below 10% if engine speed is above
1000 RPM.
The MAP sensor indicates an intermittent manifold
absolute pressure above 80kPa for a total of
approximately 10 seconds over a 16-second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will default to a BARO value of 79.3 kPa.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0108 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0108 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set. If
it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P1108 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 4793 of 6000

6E–136
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0123 TP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
D06RW028
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to throttle blade angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about 0.6 volts at closed
throttle to about 4.5 volts at wide open throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is one of the most important inputs used by
the powertrain control module (PCM) for fuel control and
many of the PCM-controlled outputs.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ignition is “ON.”
TP sensor signal voltage is greater than 4.88 volts for
a total of 0.78 second over a 1.5-second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
The PCM will use a default throttle position based on
mass air flow and RPM.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0123 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Check intermittent codes.
The TP sensor shares a 5 Volt reference with the EGR
position sensor. Check the 5 Volt reference if these
DTCs are also set.
The TP sensor shares a ground with the IAT sensor
and the EGR position sensor. Check the ground if
these other DTCs are also set.
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
TP sensor display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the TP
sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Faulty TP sensor – With the ignition key “ON,” engine
“OFF,” observe the TP sensor display on the Tech 2
while slowly depressing the accelerator to wide open
throttle. If a voltage over 4.88 volts is seen at any point
in normal accelerator travel, replace the TP sensor.
If DTC P0123 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Test Description
Number (s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
7. Components that share the TP sensor 5 volt reference
“A” circuit include the following device:
EGR valve
Page 5000 of 6000

6E–343 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the
fuel injection system is called a “closed loop” system.
The PCM monitors signals from several sensors in order
to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called “modes.”
All modes are controlled by the PCM.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated
relief valve mounted on the fuel rail with fuel pump
pressure on one side and manifold pressure on the other
side. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel
pressure available to the injector at three times
barometric pressure adjusted for engine load. It may be
serviced separate.
If the pressure is too low, poor performance and a DTC
P0131, DTC P0151,DTC P0171 or DTC P1171 will be the
result. If the pressure is too high, excessive odor and/or a
DTC P0132, DTC P0152,DTC P0172 or DTC P0175 will
be the result. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis for
information on diagnosing fuel pressure conditions.
0011
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned “ON,” the PCM energizes the
fuel pump relay for two seconds to build up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the PCM shuts the fuel pump off and waits until
the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked and
the 58 X crankshaft position signal has been detected by
the PCM, the PCM supplies 12 volts to the fuel pump relay
to energize the electric in-tank fuel pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start” condition.
A fuel pump which does not provide enough pressure will
result in poor performance.
Fuel Rail
The fuel rail is mounted to the top of the engine and
distributes fuel to the individual injectors. Fuel is
delivered to the fuel inlet tube of the fuel rail by the fuel
lines. The fuel goes through the fuel rail to the fuel
pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator maintainsa constant fuel pressure at the injectors. Remaining fuel
is then returned to the fuel tank.
055RW009
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The purpose of the idle air control (IAC) valve is to control
engine idle speed, while preventing stalls due to changes
in engine load. The IAC valve, mounted in the throttle
body, controls bypass air around the throttle plate. By
moving the conical valve (pintle) in (to decrease air flow)
or out (to increase air flow), a controlled amount of air can
move around the throttle plate. If the RPM is too low, the
PCM will retract the IAC pintle, resulting in more air
moving past the throttle plate to increase the RPM. If the
RPM is too high, the PCM will extend the IAC pintle,
allowing less air to move past the throttle plate,
decreasing the RPM.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small steps called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the PCM based on battery voltage, coolant
temperature, engine load, and engine RPM. If the RPM
drops below a specified value, and the throttle plate is
closed, the PCM senses a near-stall condition. The PCM
will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve position to
prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with the
engine running, the idle RPM will be wrong. In this case,
the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the key is
cycled “ON” then “OFF.” When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “OFF.”
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-up
and the idle characteristics of the vehicle. If the IAC pintle
is fully open, too much air will be allowed into the manifold.
This results in high idle speed, along with possible hard
starting and a lean air/fuel ratio. DTC P0507 or DTC
P1509 may set. If the IAC pintle is stuck closed, too little
air will be allowed in the manifold. This results in a low idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and a rich air/fuel
ratio. DTC P0506 or DTC P1508 may set. If the IAC
pintle is stuck part-way open, the idle may be high or low
and will not respond to changes in the engine load.