seat adjustment OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1017 of 6000

6A–61
ENGINE MECHANICAL
5. Install lower valve spring seat, valve spring and upper
valve spring seat then put split collars on the upper
spring seat, using the 5–8840–2446–0 valve spring
compressor and 5–8840–2547–0 valve spring
compressor adapter to install the split collars.
014RW042
6. Install tappet with shim.
7. Install camshaft assembly.
Refer to installation procedure for Camshaft in this
manual.
Valve Clearance Adjustments
NOTE: To adjust valve clearance, apply engine oil to the
cam as well as to the adjusting shim (2) with the cylinder
head built on the cylinder block, give a few turns to the
camshaft by means of timing pulley tightening bolt, and
measure valve clearance when the nose of cam is just
opposite to maximum cam lift (1) as shown in illistration
below.
014RW081
Legend
(1) Cam
(2) Shim
(3) Tappet
Valve Clearance Standard Value (cold)
Intake: 0.23 mm–0.33 mm
(0.0091 in–0.0130 in)
Exhaust: 0.25 mm–0.35 mm
(0.0098 in–0.0138 in)
Selection of Adjusting Shim
Shim to be selected = (Thickness of removed shim) +
(Valve clearance measurement – Standard valve)
Based on the above formula, the best suited shim should
be selected from 41 sorts of shim (differently thick at
0.02mm (0.0008 in) intervals from 2.40mm (0.0945 in)
through 3.2mm (0.1260 in) thick). Install the shim and
check valve clearance.
Page 1458 of 6000

6E–341 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be diagnosed
in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the PCM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
TS23793
There are several ways for a person to become statically
charged. The most common methods of charging are by
friction and induction.
An example of charging by friction is a person sliding
across a vehicle seat.
Charge by induction occurs when a person with well
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentary touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components.
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
Do not touch the PCM connector pins or soldered
components on the PCM circuit board.
Do not touch the knock sensor module component
leads.
Do not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
Before removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
If the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.
Upshift Lamp
Refer to Manual Transmission.
General Description (Air Induction)
Air Induction System
The air induction system filters contaminants from the
outside air, and directs the progress of the air as it is
drawn into the engine. A remote-mounted air cleaner
prevents dirt and debris in the air from entering the
engine. The air duct assembly routes filtered air to the
throttle body. Air enters the engine by to following steps:
1. Through the throttle body.
2. Into the common chamber.
3. Through the cylinder head intake ports.
4. Into the cylinders.
055RV010
General Description (Fuel Metering)
Acceleration Mode
The PCM provides extra fuel when it detects a rapid
increase in the throttle position and the air flow.
Accelerator Controls
The accelerator control system is a cable-type system
with specific linkage adjustments.
Refer to
Cable Adjustment.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the PCM will compensate for
the weak spark by increasing the following:
The amount of fuel delivered.
The idle RPM.
Ignition dwell time.
CMP Signal
The PCM uses this signal to determine the position of the
number 1 piston during its power stroke, allowing the
Page 1465 of 6000
6E–348
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
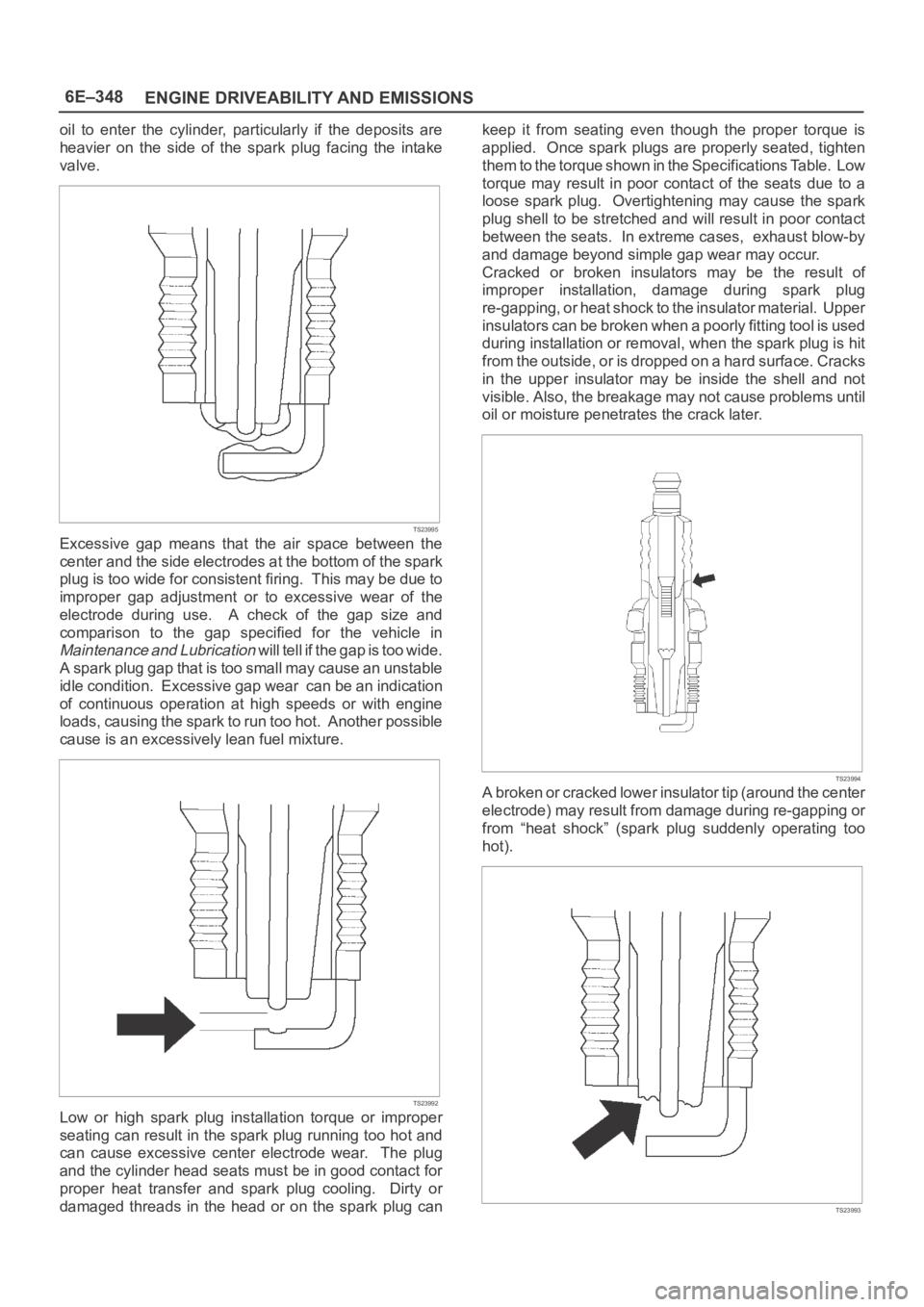
oil to enter the cylinder, particularly if the deposits are
heavier on the side of the spark plug facing the intake
valve.
TS23995
Excessive gap means that the air space between the
center and the side electrodes at the bottom of the spark
plug is too wide for consistent firing. This may be due to
improper gap adjustment or to excessive wear of the
electrode during use. A check of the gap size and
comparison to the gap specified for the vehicle in
Maintenance and Lubrication will tell if the gap is too wide.
A spark plug gap that is too small may cause an unstable
idle condition. Excessive gap wear can be an indication
of continuous operation at high speeds or with engine
loads, causing the spark to run too hot. Another possible
cause is an excessively lean fuel mixture.
TS23992
Low or high spark plug installation torque or improper
seating can result in the spark plug running too hot and
can cause excessive center electrode wear. The plug
and the cylinder head seats must be in good contact for
proper heat transfer and spark plug cooling. Dirty or
damaged threads in the head or on the spark plug cankeep it from seating even though the proper torque is
applied. Once spark plugs are properly seated, tighten
them to the torque shown in the Specifications Table. Low
torque may result in poor contact of the seats due to a
loose spark plug. Overtightening may cause the spark
plug shell to be stretched and will result in poor contact
between the seats. In extreme cases, exhaust blow-by
and damage beyond simple gap wear may occur.
Cracked or broken insulators may be the result of
improper installation, damage during spark plug
re-gapping, or heat shock to the insulator material. Upper
insulators can be broken when a poorly fitting tool is used
during installation or removal, when the spark plug is hit
from the outside, or is dropped on a hard surface. Cracks
in the upper insulator may be inside the shell and not
visible. Also, the breakage may not cause problems until
oil or moisture penetrates the crack later.
TS23994
A broken or cracked lower insulator tip (around the center
electrode) may result from damage during re-gapping or
from “heat shock” (spark plug suddenly operating too
hot).
TS23993
Page 2540 of 6000
LIGHTING SYSTEM8A–1
BODY AND ACCESSORIES
CONTENTS
Lighting System 8A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wiper/Washer System 8B. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Entertainment 8C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wiring System 8D. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Meter and Gauge 8E. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Body Structure 8F. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Seats 8G. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Security and Locks 8H. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sun Roof/Convertible Top 8I. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exterior/Interior Trim 8J. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LIGHTING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 8A–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Headlight Bulb 8A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Headlight 8A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Headlight and Associated Parts 8A–4. . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Headlight Adjustment 8A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fog Light Bulb 8A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fog Light Assembly 8A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fog Light Adjustment 8A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clarence Light Bulb 8A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Fog Light Bulb (RHD) 8A–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Taillight Bulb (Body) 8A–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Taillight Bulb (Bumper) 8A–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
License Plate Light Bulb (Body) 8A–8. . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
License Plate Light Bulb (Bumper) 8A–9. . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stoplight Bulb 8A–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal and Installation 8A–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . High Mount Stoplight 8A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Turn Signal Light Bulb 8A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Side Turn Signal Light Bulb 8A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Turn Signal Light Bulb 8A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Backup Light Bulb 8A–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dome Light Bulb 8A–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Luggage Room Light Bulb 8A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Courtesy Light Bulb 8A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Map Light Switch/Bulb 8A–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cigarette Lighter Illumination Bulb 8A–14. . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ashtray Illumination Bulb 8A–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Glove Box Illumination Bulb 8A–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal 8A–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 8A–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 3417 of 6000

8J–38EXTERIOR/INTERIOR TRIM
Power Door Mirror System
General Description
The circuit consists of the starter switch, door mirror
control switch, folding switch, defogger switch and door
mirrors on both sides.
The door mirror switch consists of the control switch,
folding switch and defogger switch.
When the control switch is operated with the starter
switch at either “ACC” or “ON” position, the motors
incorporated in the door mirrors on both sides rotates to
allow the horizontal and vertical adjustment of mirror
angles.
The folding switch can be used to fold the mirror and
return it to its original position.
When turning on the door mirror defogger switch with the
starter switch at “ON” position, built-in heater in the mirror
is activated to perform the defogger function.
Door Mirror Switch Assembly (Con-
trol Switch, Folding Switch and De-
fogger Switch) Removal
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
2. Remove the front console assembly(2).
Remove four screws.
Remove the transmission shift lever knob.
Remove the transfer shift lever knob.
Disconnect the seat heater switch connectors (if so
equipped).
Disconnect the door mirror switch connectors.
Disconnect the power & winter switch connectors.
(A/T only)
3. Remove the door mirror switch assembly(1).
Push the lock from the back side of the front
console.
825RS005
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following point.
1. Depress the switch with your fingers until it locks
securely.
Power Door Mirror
General Description
Mirrors contain two driving motors for the horizontal and
vertical movement of the mirror and one motor for folding
the mirror.
The movement of the mirror is controlled by the direction
of current running through these motors.
The housing portion of the mirror is provided with the
auto-stop mechanism which is interlocked with the motor
for folding the mirror. When the mirror moves to the stop
position (with the mirror folded or returned to its original
position), the current to the motor is shut off.
When the mirror cannot operate due to some obstacle
and the motor stops its rotation, the resistor prevents
current overflow.
720RS004
Removal and Installation
Refer to the Door Mirror removal and installation steps in
this section.
Page 4557 of 6000

6A–61
ENGINE MECHANICAL
5. Install lower valve spring seat, valve spring and upper
valve spring seat then put split collars on the upper
spring seat, using the 5–8840–2446–0 valve spring
compressor and 5–8840–2547–0 valve spring
compressor adapter to install the split collars.
014RW042
6. Install tappet with shim.
7. Install camshaft assembly.
Refer to installation procedure for Camshaft in this
manual.
Valve Clearance Adjustments
NOTE: To adjust valve clearance, apply engine oil to the
cam as well as to the adjusting shim (2) with the cylinder
head built on the cylinder block, give a few turns to the
camshaft by means of timing pulley tightening bolt, and
measure valve clearance when the nose of cam is just
opposite to maximum cam lift (1) as shown in illistration
below.
014RW081
Legend
(1) Cam
(2) Shim
(3) Tappet
Valve Clearance Standard Value (cold)
Intake: 0.23 mm–0.33 mm
(0.0091 in–0.0130 in)
Exhaust: 0.25 mm–0.35 mm
(0.0098 in–0.0138 in)
Selection of Adjusting Shim
Shim to be selected = (Thickness of removed shim) +
(Valve clearance measurement – Standard valve)
Based on the above formula, the best suited shim should
be selected from 41 sorts of shim (differently thick at
0.02mm (0.0008 in) intervals from 2.40mm (0.0945 in)
through 3.2mm (0.1260 in) thick). Install the shim and
check valve clearance.
Page 4998 of 6000

6E–341 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be diagnosed
in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the PCM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
TS23793
There are several ways for a person to become statically
charged. The most common methods of charging are by
friction and induction.
An example of charging by friction is a person sliding
across a vehicle seat.
Charge by induction occurs when a person with well
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentary touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components.
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
Do not touch the PCM connector pins or soldered
components on the PCM circuit board.
Do not touch the knock sensor module component
leads.
Do not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
Before removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
If the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.
Upshift Lamp
Refer to Manual Transmission.
General Description (Air Induction)
Air Induction System
The air induction system filters contaminants from the
outside air, and directs the progress of the air as it is
drawn into the engine. A remote-mounted air cleaner
prevents dirt and debris in the air from entering the
engine. The air duct assembly routes filtered air to the
throttle body. Air enters the engine by to following steps:
1. Through the throttle body.
2. Into the common chamber.
3. Through the cylinder head intake ports.
4. Into the cylinders.
055RV010
General Description (Fuel Metering)
Acceleration Mode
The PCM provides extra fuel when it detects a rapid
increase in the throttle position and the air flow.
Accelerator Controls
The accelerator control system is a cable-type system
with specific linkage adjustments.
Refer to
Cable Adjustment.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the PCM will compensate for
the weak spark by increasing the following:
The amount of fuel delivered.
The idle RPM.
Ignition dwell time.
CMP Signal
The PCM uses this signal to determine the position of the
number 1 piston during its power stroke, allowing the
Page 5005 of 6000

6E–348
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
oil to enter the cylinder, particularly if the deposits are
heavier on the side of the spark plug facing the intake
valve.
TS23995
Excessive gap means that the air space between the
center and the side electrodes at the bottom of the spark
plug is too wide for consistent firing. This may be due to
improper gap adjustment or to excessive wear of the
electrode during use. A check of the gap size and
comparison to the gap specified for the vehicle in
Maintenance and Lubrication will tell if the gap is too wide.
A spark plug gap that is too small may cause an unstable
idle condition. Excessive gap wear can be an indication
of continuous operation at high speeds or with engine
loads, causing the spark to run too hot. Another possible
cause is an excessively lean fuel mixture.
TS23992
Low or high spark plug installation torque or improper
seating can result in the spark plug running too hot and
can cause excessive center electrode wear. The plug
and the cylinder head seats must be in good contact for
proper heat transfer and spark plug cooling. Dirty or
damaged threads in the head or on the spark plug cankeep it from seating even though the proper torque is
applied. Once spark plugs are properly seated, tighten
them to the torque shown in the Specifications Table. Low
torque may result in poor contact of the seats due to a
loose spark plug. Overtightening may cause the spark
plug shell to be stretched and will result in poor contact
between the seats. In extreme cases, exhaust blow-by
and damage beyond simple gap wear may occur.
Cracked or broken insulators may be the result of
improper installation, damage during spark plug
re-gapping, or heat shock to the insulator material. Upper
insulators can be broken when a poorly fitting tool is used
during installation or removal, when the spark plug is hit
from the outside, or is dropped on a hard surface. Cracks
in the upper insulator may be inside the shell and not
visible. Also, the breakage may not cause problems until
oil or moisture penetrates the crack later.
TS23994
A broken or cracked lower insulator tip (around the center
electrode) may result from damage during re-gapping or
from “heat shock” (spark plug suddenly operating too
hot).
TS23993