compression ratio OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 849 of 6000
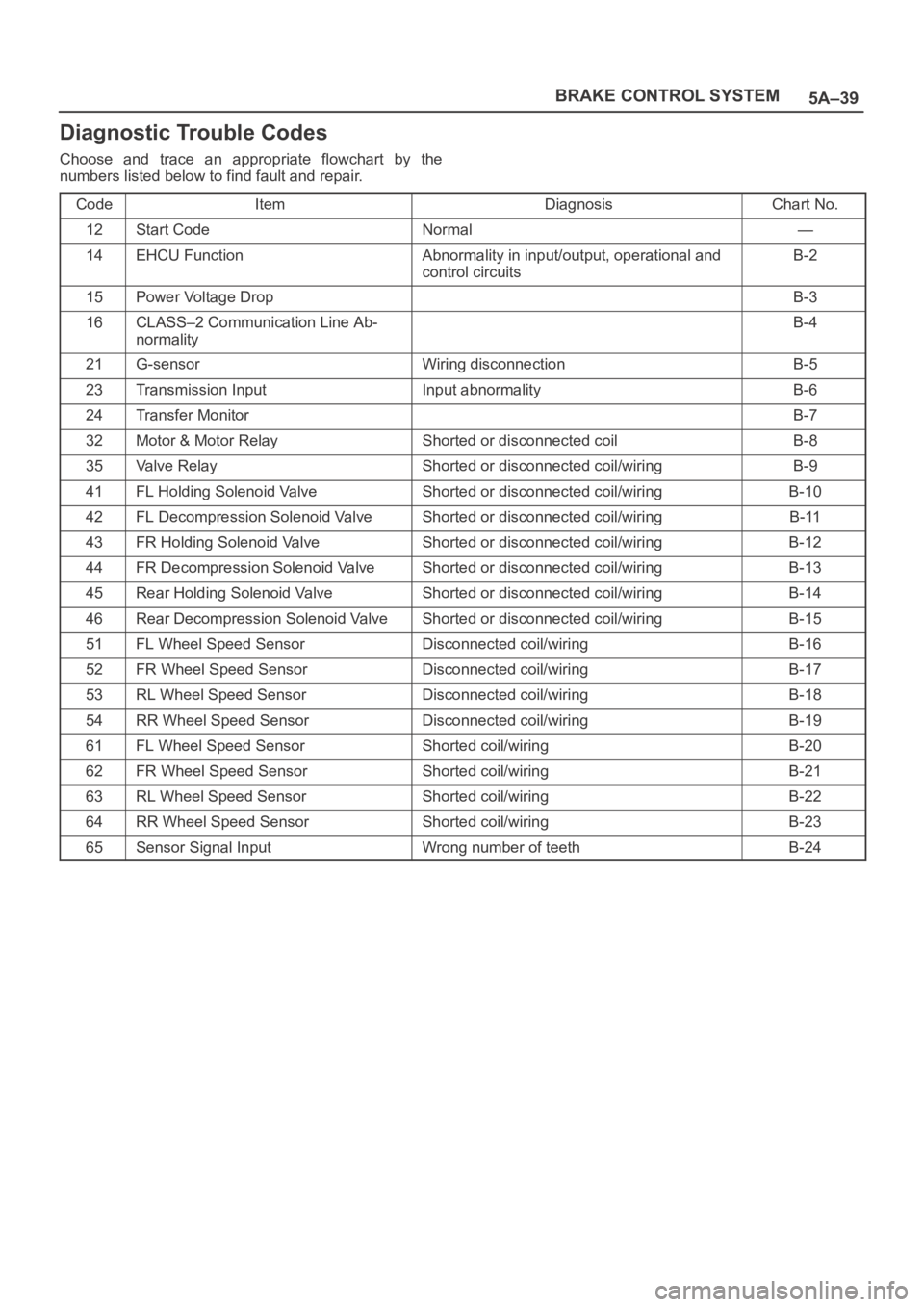
5A–39 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Choose and trace an appropriate flowchart by the
numbers listed below to find fault and repair.
Code
ItemDiagnosisChart No.
12Start CodeNormal—
14EHCU FunctionAbnormality in input/output, operational and
control circuitsB-2
15Power Voltage DropB-3
16CLASS–2 Communication Line Ab-
normalityB-4
21G-sensorWiring disconnectionB-5
23Transmission InputInput abnormalityB-6
24Transfer MonitorB-7
32Motor & Motor RelayShorted or disconnected coilB-8
35Valve RelayShorted or disconnected coil/wiringB-9
41FL Holding Solenoid ValveShorted or disconnected coil/wiringB-10
42FL Decompression Solenoid ValveShorted or disconnected coil/wiringB-11
43FR Holding Solenoid ValveShorted or disconnected coil/wiringB-12
44FR Decompression Solenoid ValveShorted or disconnected coil/wiringB-13
45Rear Holding Solenoid ValveShorted or disconnected coil/wiringB-14
46Rear Decompression Solenoid ValveShorted or disconnected coil/wiringB-15
51FL Wheel Speed SensorDisconnected coil/wiringB-16
52FR Wheel Speed SensorDisconnected coil/wiringB-17
53RL Wheel Speed SensorDisconnected coil/wiringB-18
54RR Wheel Speed SensorDisconnected coil/wiringB-19
61FL Wheel Speed SensorShorted coil/wiringB-20
62FR Wheel Speed SensorShorted coil/wiringB-21
63RL Wheel Speed SensorShorted coil/wiringB-22
64RR Wheel Speed SensorShorted coil/wiringB-23
65Sensor Signal InputWrong number of teethB-24
Page 959 of 6000

6A–3
ENGINE MECHANICAL
General Description
Engine Cleanliness And Care
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the thousandths of a
millimeter (ten thousandths of an inch). Accordingly,
when any internal engine parts are serviced, care and
cleanliness are important. Throughout this section, it
should be understood that proper cleaning and protection
of machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the
repair procedure. This is considered standard shop
practice even if not specifically stated.
A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to all
friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate
the surfaces on initial operation.
Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston
rings, connecting rods, rod bearings, and crankshaft
journal bearings are removed for service, they should
be retained in order.
At the time of installation, they should be installed in
the same locations and with the same mating
surfaces as when removed.
Battery cables should be disconnected before any
major work is performed on the engine. Failure to
disconnect cables may result in damage to wire
harness or other electrical parts.
The six cylinders of this engine are identified by
numbers; Right side cylinders 1, 3 and 5, Left side
cylinders 2, 4 and 6, as counted from crankshaft
pulley side to flywheel side.
General Information on Engine Service
The following information on engine service should be
noted carefully, as it is important in preventing damage
and contributing to reliable engine performance:
When raising or supporting the engine for any reason,
do not use a jack under the oil pan. Due to the small
clearance between the oil pan and the oil pump
strainer, jacking against the oil pan may cause
damage to the oil pick–up unit.
The 12–volt electrical system is capable of damaging
circuits. When performing any work where electrical
terminals could possibly be grounded, the ground
cable of the battery should be disconnected at the
battery.
Any time the intake air duct or air cleaner is removed,
the intake opening should be covered. This will
protect against accidental entrance of foreign
material into the cylinder which could cause extensive
damage when the engine is started.
Cylinder Block
The cylinder block is made of aluminum die–cast casting
for 75
V–type six cylinders. It has a rear plate integrated
structure and employs a deep skint. The cylinder liner is
cast and the liner inner diameter and crankshaft journal
diameter are classified into grades. The crankshaft is
supported by four bearings of which width of No.3 bearing
on the body side is different in order to support the thrust
bearing. The bearing cap is made of nodular cast iron and
each bearing cap uses four bolts and two side bolts.
Cylinder Head
The cylinder head, made of aluminum alloy casting
employs a pent–roof type combustion chamber with a
spark plug in the center. The intake and exhaust valves
are placed in V–type design. The ports are cross–flow
type.
Va l v e Tr a i n
Intake and exhaust camshaft on the both side of banks
are driven through an camshaft drive gear by timing belt.
The valves are operated by the camshaft and the valve
clearance is adjusted to select suitable thickness shim.
Intake Manifold
The intake manifold system is composed of the aluminum
cast common chamber and intake manifold attached with
six fuel injectors.
Exhaust Manifold
The exhaust manifold is made of nodular cast iron.
Pistons and Connecting Rods
Aluminum pistons are used after selecting the grade that
meets the cylinder bore diameter. Each piston has two
compression rings and one oil ring. The piston pin is made
of chromium steel is offset 1mm toward the thrust side,
and the thrust pressure of piston to the cylinder wall varies
gradually as the piston travels. The connecting rods are
made of forged steel. The connecting rod bearings are
graded for correct seze selection.
Crankshaft and Bearings
The crankshaft is made of Ductile cast–iron. Pins and
journals are graded for correct size selection for their
bearing.
Engine Lubrication
The oil discharged by a trochoid–type oil pump driven by
the crankshaft is fed through full–flow oil filter and to the oil
gallery provided under the crankshaft bearing cap. The oil
is then led to the crankshaft journals and cylinder head.
The crank pins are lubricated with oil from crankshaft
journals through oil holes. Also, an oil jet is fed to each
cylinder from crankshaft juornals on the connecting rod
for piston cleaning. The oil pan flange is dealed with liquid
packing only; do not deform or damage the flange surface
during removal or installation.
Page 1035 of 6000
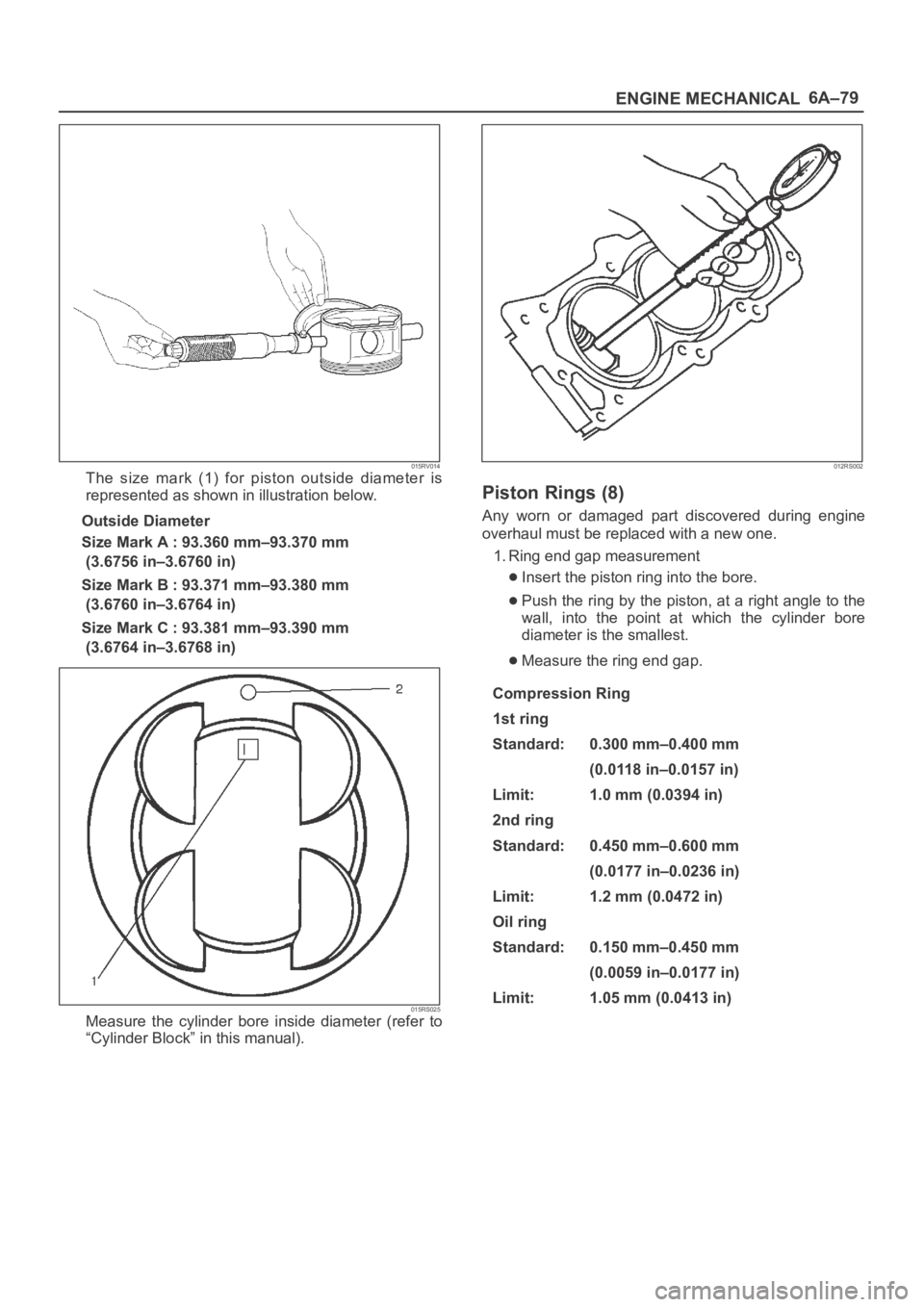
6A–79
ENGINE MECHANICAL
015RV014The size mark (1) for piston outside diameter is
represented as shown in illustration below.
Outside Diameter
Size Mark A : 93.360 mm–93.370 mm
(3.6756 in–3.6760 in)
Size Mark B : 93.371 mm–93.380 mm
(3.6760 in–3.6764 in)
Size Mark C : 93.381 mm–93.390 mm
(3.6764 in–3.6768 in)
015RS025Measure the cylinder bore inside diameter (refer to
“Cylinder Block” in this manual).
012RS002
Piston Rings (8)
Any worn or damaged part discovered during engine
overhaul must be replaced with a new one.
1. Ring end gap measurement
Insert the piston ring into the bore.
Push the ring by the piston, at a right angle to the
wall, into the point at which the cylinder bore
diameter is the smallest.
Measure the ring end gap.
Compression Ring
1st ring
Standard:
0.300 mm–0.400 mm
(0.0118 in–0.0157 in)
Limit: 1.0 mm (0.0394 in)
2nd ring
Standard: 0.450 mm–0.600 mm
(0.0177 in–0.0236 in)
Limit: 1.2 mm (0.0472 in)
Oil ring
Standard:
0.150 mm–0.450 mm
(0.0059 in–0.0177 in)
Limit: 1.05 mm (0.0413 in)
Page 1036 of 6000
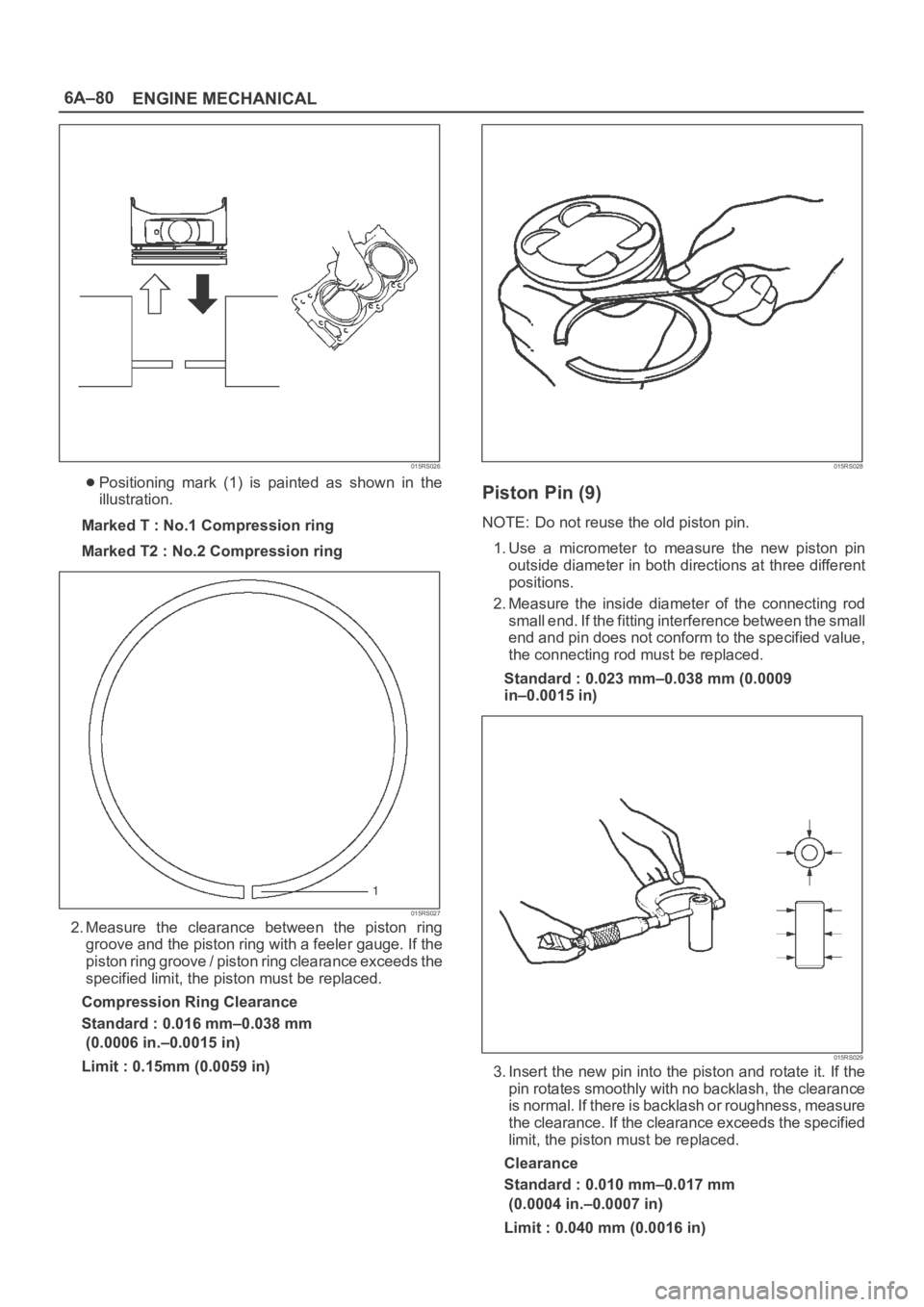
6A–80
ENGINE MECHANICAL
015RS026
Positioning mark (1) is painted as shown in the
illustration.
Marked T : No.1 Compression ring
Marked T2 : No.2 Compression ring
015RS027
2. Measure the clearance between the piston ring
groove and the piston ring with a feeler gauge. If the
piston ring groove / piston ring clearance exceeds the
specified limit, the piston must be replaced.
Compression Ring Clearance
Standard : 0.016 mm–0.038 mm
(0.0006 in.–0.0015 in)
Limit : 0.15mm (0.0059 in)
015RS028
Piston Pin (9)
NOTE: Do not reuse the old piston pin.
1. Use a micrometer to measure the new piston pin
outside diameter in both directions at three different
positions.
2. Measure the inside diameter of the connecting rod
small end. If the fitting interference between the small
end and pin does not conform to the specified value,
the connecting rod must be replaced.
Standard : 0.023 mm–0.038 mm (0.0009
in–0.0015 in)
015RS029
3. Insert the new pin into the piston and rotate it. If the
pin rotates smoothly with no backlash, the clearance
is normal. If there is backlash or roughness, measure
the clearance. If the clearance exceeds the specified
limit, the piston must be replaced.
Clearance
Standard : 0.010 mm–0.017 mm
(0.0004 in.–0.0007 in)
Limit : 0.040 mm (0.0016 in)
Page 1046 of 6000

6A–90
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Main Data and Specification
General Specification
ItemSpecificationsItem6VD16VE1
Engine type, number of cylinders and arrangementWater cooled, four cycle V6
Form of combustion chamberPent roof type
Valve mechanism4-Cams, 4-Valves, DOHC Gear & Belt Drive
Cylinder liner typeCasted in cylinder drive
Total piston displacement3165 cc3494 cc
Cylinder bore x stroke93.4mm x 77.0mm93.4mm x 85.0mm
(3.6772 in x 3.0315 in)(3.6772 in x 3.3465 in)
Compression ratio9.1 : 1
Compression pressure at 300rpm14.0 Kg/cm
Engine idling speed rpmNon adjustable (750)
Valve clearanceIntake: 0.28 mm (0.11 in)
Exhaust: 0.30mm (0.12in)
Oil capacity5.3 liters
Ignition timingNon adjustableNon adjustable
16 BTDC at idle rpm)(20 BTDC at idle rpm)
Spark plugK16PR–P11, PK16PR11, RC10PYP4
Plug gap1.0 mm–1.1 mm(0.0394 in – 0.0433 in)
Page 1381 of 6000

6E–264
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Hard Start Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
121. Remove spark plugs. Check for wet plugs, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check for a loose ignition coil ground.
Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Remove the ignition coils and check the ignition
coils for cracks or carbon tracking.
2. If a problem is found, replace affected coil(s) as
necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Check IAC operation. Perform the procedure in the
DTC P0506, Step 6 diagnostic table.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 16
161. Check for the following engine mechanical
problems (refer to
Engine Mechanical):
Low compression
Leaking cylinder head gaskets
Worn or incorrect camshaft
Camshaft drive belt slipped or stripped
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
171. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
All electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Page 1386 of 6000

6E–269 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Lack of Power, Sluggish or Spongy Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
111. Check the PCM grounds for the cleanliness,
tightness and proper locations. Refer to the PCM
wiring diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Check the exhaust system for possible restriction:
Inspect the exhaust system for damaged or
collapsed pipes.
Inspect the muffler for heat distress or possible
internal failure.
Check for a possible plugged three-way
catalytic converter by checking the exhaust
system back pressure. Refer to
Restricted
Exhaust System Check
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) for proper
operation. Refer to
4L30-E Transmission
Diagnosis
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Check for an engine mechanical problem. Check
for low compression, incorrect or worn camshaft,
loose timing belt, etc. Refer to
Engine Mechanical.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
All electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Page 1391 of 6000

6E–274
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
171. Check ignition coils for cracks or carbon tracking.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 18
18Using Tech 2, monitor the throttle position (TP) angle
with the engine idling.
Is the TP angle at the specified value and steady?
0%Go to Step 19
Refer to DTC
P0123
for
further
diagnosis
191. Check the positive crankcase ventilation (PCV)
valve for proper operation. Refer to
Crankcase
Ventilation System
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 20
201. Check the transmission range switch circuit. Use
Tech 2 and be sure Tech 2 indicates that the vehicle
is in drive with the gear selector in drive or overdrive.
2. If a problem is found, diagnose and repair the
transmission range switch as necessary (refer to
4L30-E Automatic Transmission Diagnosis).
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 21
211. Check for the following engine mechanical items.
Refer to
Engine Mechanical for diagnosis
procedures:
EGR valve mounted backward. Compare with
a known-good vehicle.
Low compression
Sticking or leaking valves
Worn camshaft lobe(s)
Camshaft drive belt slipped or stripped
Incorrect valve timing
Worn rocker arms
Broken valve springs
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 22
221. Check for faulty motor mounts. Refer to Engine
Mechanical
for inspection of mounts.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 23
231. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
All electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Page 1393 of 6000

6E–276
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Poor Fuel Economy Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
101. Check for an incorrect or faulty engine thermostat.
Refer to
Engine Cooling.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
111. Check for low engine compression. Refer to Engine
Mechanical
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Check the TCC operation. Refer to 4L30-E
Transmission Diagnosis
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check the exhaust system for possible restriction:
Inspect the exhaust system for damaged or
collapsed pipes.
Inspect the muffler for heat distress or possible
internal failure.
Check for a possible plugged three-way
catalytic converter by checking the exhaust
system back pressure. Refer to
Restricted
Exhaust System Check
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
14Check for proper calibration of the speedometer.
Does the speed indicated on the speedometer closely
match the vehicle speed displayed on Tech 2?
—Go to Step 16Go to Step 15
15Diagnose and repair an inaccurate speedometer
condition as necessary. Refer to
Vehicle Speed
Sensor
in Electrical Diagnosis.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair—
161. Check the air intake system and the crankcase for
air leaks. Refer to
Air Intake System and
Crankcase Ventilation System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
171. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. When all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
All connections within a suspected circuit
and/or system.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 18
18Perform the procedure in Fuel System Pressure Test.
Was the fuel pressure normal?
—
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance
Verify repair
Page 1401 of 6000

6E–284
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Cuts Out, Misses Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
171. Check ignition coils for cracks or carbon tracking.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 18
18Using Tech 2, monitor the TP angle with the engine
idling.
Is the TP angle at the specified value and steady?
0%Go to Step 19
Refer to DTC
P0123
for
further
diagnosis
191. Check the PCV valve for proper operation. Refer to
Crankcase Ventilation System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 20
201. Check the transmission range switch circuit. Use
Tech 2 and be sure Tech 2 indicates that the vehicle
is in drive with the gear selector in drive or overdrive.
2. If a problem is found, diagnose and repair the
transmission range switch as necessary (refer to
4L30-E Automatic Transmission Diagnosis).
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 21
211. Check the following engine mechanical items.
Refer to
Engine Mechanical for diagnosis
procedures:
Low compression
Sticking or leaking valves
Worn camshaft lobe(s)
Camshaft drive belt slipped or stripped
Incorrect valve timing
Worn rocker arms
Broken valve springs
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 22
221. Check for faulty motor mounts. Refer to Engine
Mechanical
for inspection of mounts.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 23
231. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
Visual/physical inspection
Te c h 2 d a t a
Freeze Frame data/Failure Records butter
All electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repair
Contact
Te c h n i c a l
Assistance