change wheel OPEL GT-R 1973 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1973, Model line: GT-R, Model: OPEL GT-R 1973Pages: 625, PDF Size: 17.22 MB
Page 17 of 625
IoC-91973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
Figure OC-5 Brake Master Cylinder
I
Figure OC-6 Tire Rotation Methods
when the clutch pedal has in excess of 1
l/4 inch fr&
travel. See Figure OC-7.
Rear Axle
Change lubricant every
12,ooO miies when vehicle is
used for pulling a trailer.
Cooling SystemCheck at 12-month or
12,000~mile intervals, wash
radiator cap and filler neck with clean water, pres-
sure test system and radiator cap for proper pressure
holding capacity (tighten hose clamps and inspect
condition of all cooling and heater hoses). Replace
hoses every 24 months or 24,000 ,miles or earlier :if
checked, swollen or otherwise deteriorated.
Also each 12 months or
12,ooO miles, clean exteribr
of radiator core. Every 24 months or
24,OCO miles,Floor-Pan
-Clutch Pedal
Figure OC-7 GT Clutch Lash
drain, flush, and refill the cooline svstem with a new
coolant so&ion of permanent
6~; anti-freeze and
water for protection-of -20°F.
D-6 NOT REMOVE
RADIATOR CAP WHEN SOLUTION IS HOT
AND UNDER PRESSURE.
Wheel BearingsClean and repack front wheel bearings with a lubri-
cant as specified on the lubrication chart, Figure
oc-1.
Automatic Transmission FluidUnder normal driving conditions, change the trans-
mission fluid every 24,000 miles. Under unusual con-
ditions such as constant driving in heavy city traffic
during hot weather, trailer pulling, etc., this service
should be performed at
12,COO mile intervals.
General Motors DEXRON Automatic Transmis-
sion Fluid, which has been especially formulated and
tested for use in your automatic transmission, is
recommended. Other automatic transmission fluids
identified with the mark DEXRON are also recom-
mended.
Check the fluid level at each engine oil change
period. To make an accurate fluid level check:
1. Drive car several miles, making frequent starts and
stops, to bring transmission up to normal operating
temperature (approximately
180-190’F.)2. Park car on a level surface.
3. Place selector lever in “Park” and leave engine
running.
Page 18 of 625
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE OC-9
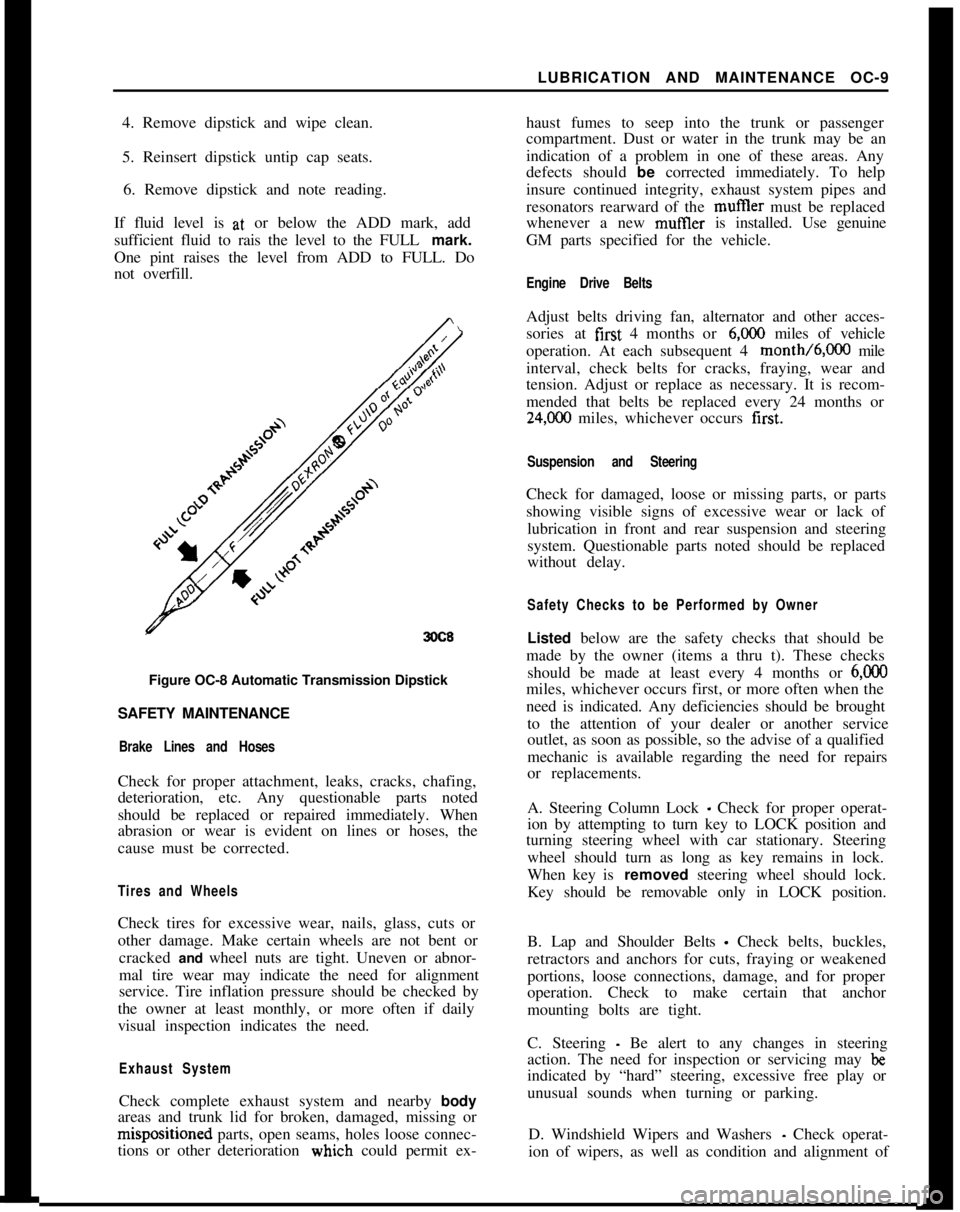
4. Remove dipstick and wipe clean.
5. Reinsert dipstick untip cap seats.
6. Remove dipstick and note reading.
If fluid level is at, or below the ADD mark, add
sufficient fluid to rais the level to the FULL mark.
One pint raises the level from ADD to FULL. Do
not overfill.
3OC8Figure OC-8 Automatic Transmission Dipstick
SAFETY MAINTENANCE
Brake Lines and HosesCheck for proper attachment, leaks, cracks, chafing,
deterioration, etc. Any questionable parts noted
should be replaced or repaired immediately. When
abrasion or wear is evident on lines or hoses, the
cause must be corrected.
Tires and WheelsCheck tires for excessive wear, nails, glass, cuts or
other damage. Make certain wheels are not bent or
cracked and wheel nuts are tight. Uneven or abnor-
mal tire wear may indicate the need for alignment
service. Tire inflation pressure should be checked by
the owner at least monthly, or more often if daily
visual inspection indicates the need.
Exhaust SystemCheck complete exhaust system and nearby body
areas and trunk lid for broken, damaged, missing orm&positioned parts, open seams, holes loose connec-
tions or other deterioration wiuch could permit ex-haust fumes to seep into the trunk or passenger
compartment. Dust or water in the trunk may be an
indication of a problem in one of these areas. Any
defects should be corrected immediately. To help
insure continued integrity, exhaust system pipes and
resonators rearward of the muftler must be replaced
whenever a new mufIler is installed. Use genuine
GM parts specified for the vehicle.
Engine Drive BeltsAdjust belts driving fan, alternator and other acces-
sories at first 4 months or
6,ooO miles of vehicle
operation. At each subsequent 4 month/6,000 mile
interval, check belts for cracks, fraying, wear and
tension. Adjust or replace as necessary. It is recom-
mended that belts be replaced every 24 months or
24,C00 miles, whichever occurs first.
Suspension and SteeringCheck for damaged, loose or missing parts, or parts
showing visible signs of excessive wear or lack of
lubrication in front and rear suspension and steering
system. Questionable parts noted should be replaced
without delay.
Safety Checks to be Performed by OwnerListed below are the safety checks that should be
made by the owner (items a thru t). These checks
should be made at least every 4 months or
6,ooOmiles, whichever occurs first, or more often when the
need is indicated. Any deficiencies should be brought
to the attention of your dealer or another service
outlet, as soon as possible, so the advise of a qualified
mechanic is available regarding the need for repairs
or replacements.
A. Steering Column Lock
_ Check for proper operat-
ion by attempting to turn key to LOCK position and
turning steering wheel with car stationary. Steering
wheel should turn as long as key remains in lock.
When key is removed steering wheel should lock.
Key should be removable only in LOCK position.
B. Lap and Shoulder Belts
- Check belts, buckles,
retractors and anchors for cuts, fraying or weakened
portions, loose connections, damage, and for proper
operation. Check to make certain that anchor
mounting bolts are tight.
C. Steering
- Be alert to any changes in steering
action. The need for inspection or servicing may
beindicated by “hard” steering, excessive free play or
unusual sounds when turning or parking.
D. Windshield Wipers and Washers
- Check operat-
ion of wipers, as well as condition and alignment of
Page 19 of 625

CC-10 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
wiper blades. Check amount and direction of fluid
sprayed by washers during use.,
E. Defrosters - Check performance by moving con-
trols to “DEF” and noting
am$nmt of air directed
against the windshield.
I
F. Wheel Alignment and
Balabce - In addition to
abnormal tire wear, the need fbr wheel alignment
service may be indicated by a pull to the right or
!eftwhen driving on a straight and level road. The need
for wheel balancing is usually
iddicated by a vibra-
tion of the steering wheel or
se;+ tihile driving at
normal highway speeds.I
IG. Brakes
- Be alert to illumiriation of the brake
warning light or changes in braking action,
SUCK as
repeated pulling to one side, unusual sounds when
braking or increased brake pedal travel. Any of thesecould indicate the need for
brakk system inspection
and/or service.
H. Parking Brake and Transmission “PARK”
Mechanism
- Check parking brake holding ability by
parking on a fairly steep hill and restraining the vehi-
cle with the parking brake only.
eon cars with auto-
matic transmissions, check the holding ability of the
“PARK” mechanism by releasing all brakes after
the transmission selector lever hak been placed in the“P” position.
I. Glass
- Check for broken, scrritched, dirty or da-
maged glass on vehicle that
coulld obscure vision’or
become an injury hazard.
J. Lights and Buzzers
- Check all instrument panel
illuminating and warning lights,’ seat belt reminder
light and buzzer, ignition key
b&er, interior lights,
license plate lights, side marker! lights, headlamps,
parking lamps, tail lamps, brake lights, turn signals,
backup lamps, and hazard warding flashers. Have
someone observe operation of
&ach exterior light
while you activate the controls: The operation of
instrument panel warning lights is covered in the
“Starting and Operating“ section of your
Own&%
Manual.K. Transmission Shift Indicator
‘- Check to be sure
automatic transmission shift
indiCator accurately i”-
dicates the shift position selected.
I
CAUTION: Before making thk check below,I
be sure to have a clear dist&e ahead and:
behind the car, set the parking brake and
firmly apply the foot brake.
Do not depress
accelerator pedal. Be prepared to
turn off ’
ignition switch
immediat+y if engine
should start.L. Starter Safety Switch (Automatic Transmissibn
Cars)
- Check starter safety switch by placing the
transmission in each of the driving gears while
at-tempting to start the engine. The starter should oper-ate only in the Park (“P”) or Neutral (“N”)
positions.
M. Horn
- Blow the horn occasionally to be sure thatit works. (Ignition switch must be in the “ON” posi-
tion.)
N. Seat Back Latches
- Check to see that seat back
latches are holding by pulling forward on the top of
each folding seat back.
0. Rearview Mirrors and Sun Visors
- Check that
friction joints are properly adjusted so mirrors and
sun visors stay in the selected position.
P. Door Latches
- Check for positive closing, latch-
ing and locking.
Q. Hood Latches - Check to make sure hood closesfirmly by pressing on the hood at the latching point
after each closing. Check also for broken, damaged
or missing parts which might prevent secure latch-
ing.R. Fluid Leaks
- Check for fuel, water, oil or other
fluid leaks by observing the ground beneath the vehi-cle after it has been parked for a while. If gasoline
fumes or fluid are noticed at any time, the cause
should be determined and corrected without delay
because of the possibility of fire.
S. Exhaust System
- Be alert to any change in the
sound of the exhaust system or a smell of fumes
which may indicate a leak.
Head Restraints
- Check that no head restraint
components are missing, damaged or loose. (Does
not apply to GT Models).
Disc BrakesCheck brake pads and condition of rotors while
wheels are removed during tire rotation. (Note belowregarding more frequent checks also applies to disc
brakes.)
Parking and Drum BrakesCheck drum
brake linings and other internal brake
components at each wheel (drums, wheel cylinders,
etc.). Parking brake adjustment also should be
checked whenever drum brake linings are checked.
NOTE: More frequent checks should be
made if driving conditions a.nd habits result
in frequent brake application. When brakes
require relining, it is recommended thatyou use those genuine General Motors
parts specified for your car,and Delco fluid
as required.
Page 67 of 625

1F. 46 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
’
/
Headlight High-Low Beam Control and Passing:
SignalI
When the headlights have been switched on, high
and low beam selection is made by raising the direc-
tional signal lever toward steering wheel. Each
ti&the lever is raised, beam position, will change.
When the headlights are not on, a flashing headlight
signal may be given by raising and lotiering the di-
rectional signal lever. With the headlights on and
inlow beam position, raising and lowering the direc-
tional signal lever will also cause the headlights to
flash.
Fog Light SwitchAll Rallye models are equipped with two white f?g
lights mounted below the front bumper.
The fog light toggle switch is located on the
insty-ment cluster to the left of the temperature and
fuelgauge cluster.
/
The fog lights can be turned off at any time by the
toggle switch, but can only be tyrned on when: :
1. The ignition switch on or the
?gine running.!
2. The fog light toggle switch lower half is pushed
in.3. The parking lights and/or low beam headlights
are
OKThe fog lights are automatically turned off if the
ignition switch is on and the headlights are switched
to high beam position.
Courtesy LightThe courtesy light illuminates the interior of the Car
when any door is opened. The courtesy light can also
be turned on with all doors closed by tilting the l&s.
GT Headlamp MechanismThe concealed headlamps are moved mechanically.
Pushing actuating lever on left side of console opens
headlamps and pulling lever closes headlamps. Two
(2) meshing gear segments convert the movement, of
the lever to a rotation of 180 degrees. The pivots of
the headlamps lie below the centerline so that with
headlamps in closed position, the headlamp housing
is flush with front sheet metal. Refer to Group 110,
Section “F”, for service procedures on the GT head-
lamp mechanism.
A white indicator lamp in the instrument panel lights
if the headlamps are not completely opened lorclosed The switches of the headlamp electrical sys-
tem are located behind the left headlamp operating,
mechanism.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTSHEADLAMP AIMING
The headlamps must be properly aimed in order to
obtain maximum road illumination and safety that
has been built into the headlighting equipment. With
the Guide T-3 type sealed beam units, proper aiming
is even more important because the increased range
and power of this lamp make even slight variations
from recommended aiming hazardous to approach-
ing motorists. The headlamps must be checked for
proper aim whenever a sealed beam unit is replaced
and after an adjustment or repairs of the front end
sheet metal assembly.
Regardless of method used for checking headlamp
aim, car must be at normal weight, that is, with gas,
oil, water, and spare tire. Tires must be uniformly
inflated to specified pressure. If car will regularly
carry an unusual load in rear compartment, or a
trailer, these loads should be on car when headlamps
are checked. Some States have special requirements
for headlamp aiming adjustment, and these require-
ments should be known and observed.
Horizontal and vertical aiming of each seal beam
unit is provided by two adjusting screws which move
the mounting ring in the body against the tension of
the coil spring. There is no adjustment for focus,
since the sealed beam unit is set for proper focus
during manufacturing assembly.
MAJOR REPAIRHEADLIGHT SWITCH
- OPEL 1900. MANTA
Removal1. Remove instrument cluster cover panel. See Sec-
tion H.
2. Compress retaining springs and pull switch out.
See Figure 1 F-
1.3. Pull multiple socket off switch.
Installation
1: Plug multiple socket in switch and push switch in
panel until clips lock in place.
2. Replace instrument cover and secure with two (2)
screws.
Page 75 of 625

lG- 54 1973 OPEL SERVICE’ MANtiAL/SIGNAL SYSTEMSCdNTENTS
9Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERAT!ON:
Directional Signal Lever
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Horn. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .HazardWarning
Flasher. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .BrakeSystemWarningLight
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .DIAGNOSIS:
SignalSystem,.......................
i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAINTENANCE AND ADJUS,TMENTS:
MAJOR REPAIR:
Directional Signal Switch
:. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
HornRemoval. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Removing Horn Contact
. . . . :.............................................
SPECIFICATIONS:
FuseChart. . . . . . I . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Page No.
1 G-54
1 G-54
1 G-55
lG-55 _1 G-55
1 G-55
16-551 G-55
1 G-56
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
DIRECTIONAL SIGNAL LEVERThe direction signal switch lever is a multi- purpose
lever controlling direction signals, passing signal,
and high and low beams. See Figure
lG-1.301Gl
Figure lG-1 Directional Signal Position for Headlamp
OperationThe direction signal lever is provided with a
two-step mechanism for operation of headlight high and
low beams, and passing signal (not in New Jersey).
With headlights off, moving the lever repeatedly to-
wards steering wheel flashes headlights as a passing
signal. With headlights on, moving the lever repeat-
edly towards steering wheel up to first stop also
flashes passing signal regardless whether or not the
direcl:ion signals are switched on. When the lever is
moved up to the second stop, the headlights are
changed from high to low beam
dr vice versa. On all
Rallye cars, when switching from low to high beam
position, with the fog lamp instrument panel switch
“ON” and ignition switch in “RUN” position, the
fog lights are automatically
switChed off. Direction
signals work in the normal manner; pushing the lever
up for right turn signal and pulling the lever down
for left turn signal.
The horn button is located in the center part of the
steering wheel. The horn is actuated by pushing
down on the ends of both spokes on Opel 1900 andManta’s or on the center horn button on the Rallye.
The button is provided with a spring-loaded plunger.See Figure
lG-2.
Page 176 of 625

FRONT SUSPENSION3A- 9
8. Press ball stud out of lower control arm.Removal Opel 1900 - MantaBefore raising vehicle, install Hooks J-23697 on re-
spective vehicle side to cross member and upper con-
trol arm. See Figure 3A-7.
1. Raise car and support at rear of front frame rails.
2. Remove front wheel.
3. At the lower control arm ball joint, remove castle
nut cotter pin and slacken back nut so that the thread
can no longer be damaged.
4. With a suitable drift, detach ball joint from steer-
ing knuckle. With jack, lift up lower control arm,
unscrew castle nut and remove Hooks J-23697.
5. Unscrew upper control arm ball joint and suspend
front wheel hub and brake caliper in wheel house. Do
not turn upper control arm ball joint flange, as this
would result in a change of camber.
6. Remove defective lower control arm ball joint
using Tools J-9519 and Receiver J-23754.
Installation GT
CAUTION:
Fasteners are important attachingparts in
that they could affect the performance of
vitaI com-
ponents and systems, and/or could result in
ma&r
repair expense. They must be replaced with one of
the same part
numer or with an equivalent part if
replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
re-
placement part of lesser quality or substitute design.
Torque values must be used as specified during reas-
sembly to assure proper retention of these parts.1. When pressing the ball joint in place, make certain
the locating notch in the lower rim of the ball joint
matches the alignment reference mark placed on the
lower control arm prior to removal. The notch in the
ball joint bottom plate, identifying the direction of
the elongated slot, must point towards the brake
drum backing plate. See Figure
3A-17. Alignment
must be within 2 degrees of lower control arm center-
line. If proper positioning of the ball joint is not
accomplished, the result is a limitation of the neces-
sary ball stud movement. If ball stud movement is
limited, an interference between the ball stud and
housing is created, and binding or even fracture may
occur. Replacement ball joints may or may not have
marking notch as shown in Figure
3A-20. If it does
not have a marking notch, the joint is completelysymetrical and may be installed in any position.
When pressing in ball joint do not press on bottom
plate, but on ball joint housing only.2. Install dust cap on lower ball joint and fill with
chassis lubricant. Attach dust cap retainer.
3. Press ball joint into steering knuckle. Use
J-9519-3 as installer and J-21690 as a supporting
sleeve.4. Install castle nut on ball joint stud and torque to
40
Ib.ft. Install new cotter pin.
5. Reconnect shock absorber to lower control arm
and torque to 30 lb.ft.
6. Remove spring compressor.
7. Install front wheel, and lower the car.
8. Always check caster and camber after ball joint
replacement.
Installation Opel 1900 - Manta
CAUTION:
Fasteners are important attachingparts in
that they could
aff’ect the performance of vital com-
ponents and systems, and/or could result in
ma&r
repair expense. They must be
rep/aced with one of
the same part number or with equivalent parts, if
rep/acement becomes necessary. Do not use a re-
p/acement part of lesser quality or substitute design.
Torque valves must be used as
specitied during reas-
sembIy to assure proper retention of these parts.1. Drive new ball joint into lower control arm using
Tools J-9519 as installer and J-23755 as a supporting
sleeve. Do not strike onto ball joint bottom.
The ball joint is maintenance-free. It is supplied as an
assembly only and cannot be disassembled further.
2. On new lower control arm ball joint, make sure
that the marking groove in the housing bottom in
alignment with the axis of the lower control arm.
Permissible deviation: minus 2 degrees to plus 2 de-
grees.This is required, to obtain the maximum freedom of
movement of the ball stud in the housing. See Figure
3A-18.3. Attach steering knuckle together with front wheel
hub and brake caliper to lower control arm ball joint.
Torque castle nut to 54
ft.lbs.4. Attach ball joint to upper control arm and torque
to 29
ft.lbs. Always use new self-locking nuts.
5. Install wheel and tighten nuts to a torque of 65
ft.lbs.6. Lower car and check caster and camber.
Page 177 of 625

3A- 101973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
Figure 3A-18 Lower Ball Joint Notch Opel 1900 -
MantaUPPER CONTROL ARM REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION
Removal GT1. Raise car and support at rear of front frame rails.
2. Remove front wheel.
3. Install spring compressor and compress spring
until there is 3-l/8” between compressor and lower
spring leaf.
4. Remove cotter pin and castle nut from upper ball
joint stud. Discard cotter pin.
5. Use tie rod remover J-21687 remove ball jointfrom.steering knuckle. 6. Support brake drum to
relieve tension on brake hose.
7. Remove hex nut from upper control arm shaft.
Remove shaft and washers from shock absorber sup
port. Do not damage threads on control arm shaft.
8. Remove control arm from car. Do not lose inner
toothed washers. Note size and location of toothed
washers.Removal
Opel 1900 . Manta
1, Raise car and support at rear of front frame rails.
2. Remove front wheel
3. Unscrew upper control arm to cross member
self-locking attaching nut.4. Unscrew ball joint from upper control arm. Do not
turn upper control arm ball joint flange, as this
would result in a change of camber.
5. Support front wheel hub so that brake hose is not
stressed.6. Pull out upper control shaft to cross member at-
taching bolt and remove control arm. Shims have to
be reinstalled in their original location to maintain
the proper caster setting.
Installation GT
CAUTION:
Fasteners are important attaching parts in
that they could affect the the
perfonmmce of vital
components and systems, and/or could result in ma-
jor repair expense. They must be replaced with one
of the same part number or with an equivalent part
if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a re-
placement part or lesser quality or substitute design.
Torque values must be used as specified during reas-
sembly to
assure proper retention of these parts.If rubber bushings on control arms are worn, arms
must be replaced.
1. Slide rubber rings over bushings. Slide rings over
inner sleeves of bushings. Place control arm in posi-
tion on shock absorber support, installing toothed
washers in their original positions. See Figure 3A-
19.2. From front to rear, install control arm shaft. If
necessary, align washers and control arm bushings
with a small drift prior to installing control arm
shaft. See Figure
3A-19.3. Tighten hex nut on control arm shaft finger tight.
4. Increase tension on spring compressor in order to
relieve tension on control arm shaft. Then torque hex
nut on control arm shaft to 33
Ib.ft.5. Press ball joint stud into steering knuckle and
torque castle nut to 29 lb.ft. Install new cotter pin.
6. Remove spring compressor and lower car.
7. Check front end alignment.
Installation Opel 1900. Manta
CAUTION:
Fasteners are important attaching parts in
that they could at?&
the performance of vital com-
ponents and systems, and/or
coo/d result in major
repair expense. They must be replaced with one of
the same part number or with equivalent parts, if
replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
re-
Page 190 of 625

FRONT END ALIGNMENT 3C-23
ing geometry, the following checks and inspections
must be made to insure correctness of alignment
equipment readings and alignment adjustments.
1. The front tires should have approximately the
same wear and all tires must be inflated to specified
pressures (see Wheel and Tire Specifications
- Sec-
tion 3G).
2. Check front wheel bearings for looseness and ad-
just if necessary (see Front Suspension Adjustments
- Section 3A).
3. Check for run-out of wheels and tires, (see Section
3G).
4. Check wheels and tires for balance and correct if
out-of-balance (See Section 3G).
5. Check for looseness at ball joints and tie
rdd ends;
if found excessive, it must be
corxcted before align-
ment readings will have any value.
Figure SC-Z Spring Compressor J-2 1689 Installed
6. Check shock absorber action and correct if neces-
sary. Consideration must be given the optional
equipment on the car, undercoating, dirt, etc.
7. It is advisable to check the condition and accuracy
of any equipment being used to check front end
alignment and to make certain that instructions of
the manufacturer are thoroughly understood.
ADJUSTING CASTER (GT)
4. Remove upper control arm shaft,
5. Remove upper control arm from shock absorber
support, being careful not to lose toothed washers.
6. Adjust caster by installing selective toothed wash-
ers on both sides of control arm shaft, between con-
trol arm and shock absorber support. Never use
CAUTION: Front suspension fasteners are impor- more than one washer at any one location. The total
tant attaching parts in that they could
affectthickness, front and rear washer, must equal .48”.
the performance of uital components and sys-
tems, and/or could result in major repair expense.
There are only two possible caster changes that can
be made.
They must be replaced with one of the same
part
number or with an equiualentpart ifreplacement
becomes necessary. Do not use a replacement part
Of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque
values must be used as specified during reassem-
bly to mure proper retention of these parts.
7. Using a drift to align holes, replace control arm
shaft in the direction as shown in Figure
3C-3.
Torque hex nut to 33 lb.ft. Make certain that crown
of both plate washers shows outward.
To change caster, three washers are available
- one
with a
.12” thickness, one that is .36” thick, and one
.24” thick. Toincrease caster place one of the thin
washers at the front of the control arm shaft and one
of the thick washers at the rear.
To decrease caster
place one thick washer at the front of the control
arm shaft and one thin washer at the rear.
1. Position jack below front suspension cross mem-
ber and raise front end of car. 8. Remove spring compressor, and install front
wheel and torque wheel nuts to 72 ft. Ibs.
9. Recheck caster.ADJUSTING CASTER (OPEL
1900. MANTA)
2. Place jack stands below front frame side members
and remove front wheel on side which caster is to be
adjusted. 1. Jack up vehicle and remove front wheel on the side
on which caster is to be adjusted.
3. Install front spring compressor J-21689 and com-
press spring. See Figure
3C-2.
2. Support vehicle below both lower control arms.
See Figure
3C-4.
3. Unscrew hex nut from upper control arm shaft
and pull out shaft.
4. Adjust caster by replacing washers (A) (front) and
Page 202 of 625

OPEL 1900 AND MANTA STEERING COLUMN ASSEMBLY 3E.35
II
OPEL 1900 AND MANTA STEERING COLUMN
ASSEMBLY
CONTENTS
SubjectPage No.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION:
Description and Operation of Directional Signal
Lever. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Description
andOperationofHorn. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Description of Steering Column Assembly
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .DIAGNOSIS: (Not Applicable)
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS: (Not
Applicable)
MAJOR REPAIR:
3E-353E-363E-36
Removal and Installation of Steering Column
Assembly
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RemovalandInstallationofSteeringWheel. . . . . . . . . . . .Disassembly and Reassembly of Direction Signal
Switch
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Disassembly and Reassembly of Steering and
Ignition Lock Cylinder, and Electrical Switch
from Mast Jacket Assembly
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .SPECIFICATIONS:
Steering
ColumnSpecifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3E-363E-383E-393E-403E-41
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONDESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OF
DIRECTIONAL SIGNAL LEVERhigh to low beam or vice versa. On all
19M) Rallye
cars, when switching from low to high beam posi-
tion, with the fog lamp instrument panel switch ON
The direction signal switch lever is a multi- purpose
lever controlling direction signals, passing signal and
headlight high and low beams. See Figure
3E-2.The dire&M signal lever is provided with a two-
step mechanism for operation of headlight high and
low beams, and passing signal (not in N.J.). With
headlights off, moving the lever repeatedly towards
steering wheel flashes headlights as a passing signal.
With headlights on, moving the lever repeatedly to-
wards steering wheel up to first stop also flashes
passing signal regardless whether or not the direction
signals are switched on. When the lever is moved up
to the second stop, the headlights are changed from
SE.2Figure
3E-2 Directional Signal Lever Position for
Headlamp Operation
Page 227 of 625

36. 601973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
severe or careless driver. Rapid acceleration and de-celeration, severe application of brakes, taking turns
at excessive speed, high-speed driving, and striking
curbs or other obstructions which lead to misalign-
ment are driving habits which will shorten the life of
any tire.hiaintenance of proper inflation pressure and peri-
odic interchanging of tires to equalize wear are
within the control of the driver. Underinflation
raises the internal temperature of a tire greatly due
to the continual friction caused by the flexing of the
side walls. Tire squealing on turns is an indication of
underinflation or excessive speed on the turns. A
combination of underinflation, high road tempera-
tures, and high-speed driving will quickly ruin the
best tire made.
High speed on straight highways or expressways nor-
mally causes more rapid wear on the rear than on thefront tires, although cupping of front tires can result
if the tires are not periodically switched from wheel
to wheel. Driving turns and curves at too high a rate
of speed causes the front tires to wear much faster
than the rear tires.
An inspection of the tires, together with information
as to locality in which the car has been operated willusually indicate whether abnormal wear is due to the
operating conditions described above or to mechani-cal faults which should be corrected.
The various types of
abnormal tire wear and their
causes are described in the following paragraphs.
Shoulder or Underinflation Tread WearWhen a tire is underinflated, the side walls and
shoulders of the tread carry the load, while the centerof tread folds in or compresses due to the low inter-
nal air pressure. This action causes the shoulders to
take all of the driving and braking load, resulting in
much faster wear of shoulders than of the center of
tread. See Figure 3G-7. For maximum results in han-dling, riding and tire life, tire inflation pressures
should never be allowed to go below the specified
minimum pressure.
Continuous high-speed driving on curves, right and
left, may produce tread wear very similar to underin-flation wear and might very easily be mistaken for
such. Side thrust when rounding turns causes wear
on the sides of tire tread. In making a turn to the left,especially at high speeds, the outside shoulder of the
right tire and the inside shoulder of the left tire take
the side thrust and naturally receive the most wear.
The only possible correction is to advise slower
speeds on curves. Do not increase tire inflation pres-
sures beyond specified limits, as this will cause centeror over-inflation wear. See paragraph below.
Canter or Overinflation Tread Wear
Excessive wheel camber, either positive or negative,causes the tire to run at such an angle to the road
surface that one side of the tread wears much more
than the other. See Figure
3G-7.When tire inflation pressures are maintained within
the specified limits, the tire will make a full contact
across the entire width of tread, thereby distributing
the wear evenly over the total surface of the tread
area.
Cross or Toe Tread WearWhen the front wheels have an excessive amount of
either toe-in or toe-out, the tires are actually draggedsideways when they travel straight down the road
and cross wear or scraping action takes place rapidly
wearing away the tread of tires. This cross wear con-dition will usually produce a tapered or feathered
edge on the ribs of the tire tread. See Figure
3G-7.In most cases, this can be detected by rubbing the
hand across the tire tread.
If the tapered or feathered edges are on the inner
sides of the ribs on one of both sides, it indicates thatone or both tires have excessive toe-in, while the
same condition in the outer sides of ribs indicates
excessive toe-out. Usually, excessive toe-in causes
excessive tire wear on the outer edge of the right
front tire and toe-out causes tire wear on the inner
edge of the left front tire. See Section 3C for toe-in
correction.Cornering wear caused by high-speed driving on
curves (see following paragraph) sometimes has the
appearance of toe wear. Care must be used to distin-guish between these two types of wear so that the
proper corrective measures will be used.
Side or Camber WearExcessive wheel camber, either positive or negative,
causes the tire to run at such an angle to the road
surface that one side of the tread wears much more
than the other. See Figure
3G-7.The amount or angle of the camber wear will be
governed by the amount of positive or negative cam-ber. Tire tread wear very similar in appearance to
camber wear may be caused by driving on turns at
excessive speeds. This “cornering” tread wear (see
paragraph below) cannot be corrected by change of
camber angle.
Adjustments for specified camber are covered in Sec-
tion 3C.