inflation pressure OPEL GT-R 1973 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1973, Model line: GT-R, Model: OPEL GT-R 1973Pages: 625, PDF Size: 17.22 MB
Page 18 of 625
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE OC-9
4. Remove dipstick and wipe clean.
5. Reinsert dipstick untip cap seats.
6. Remove dipstick and note reading.
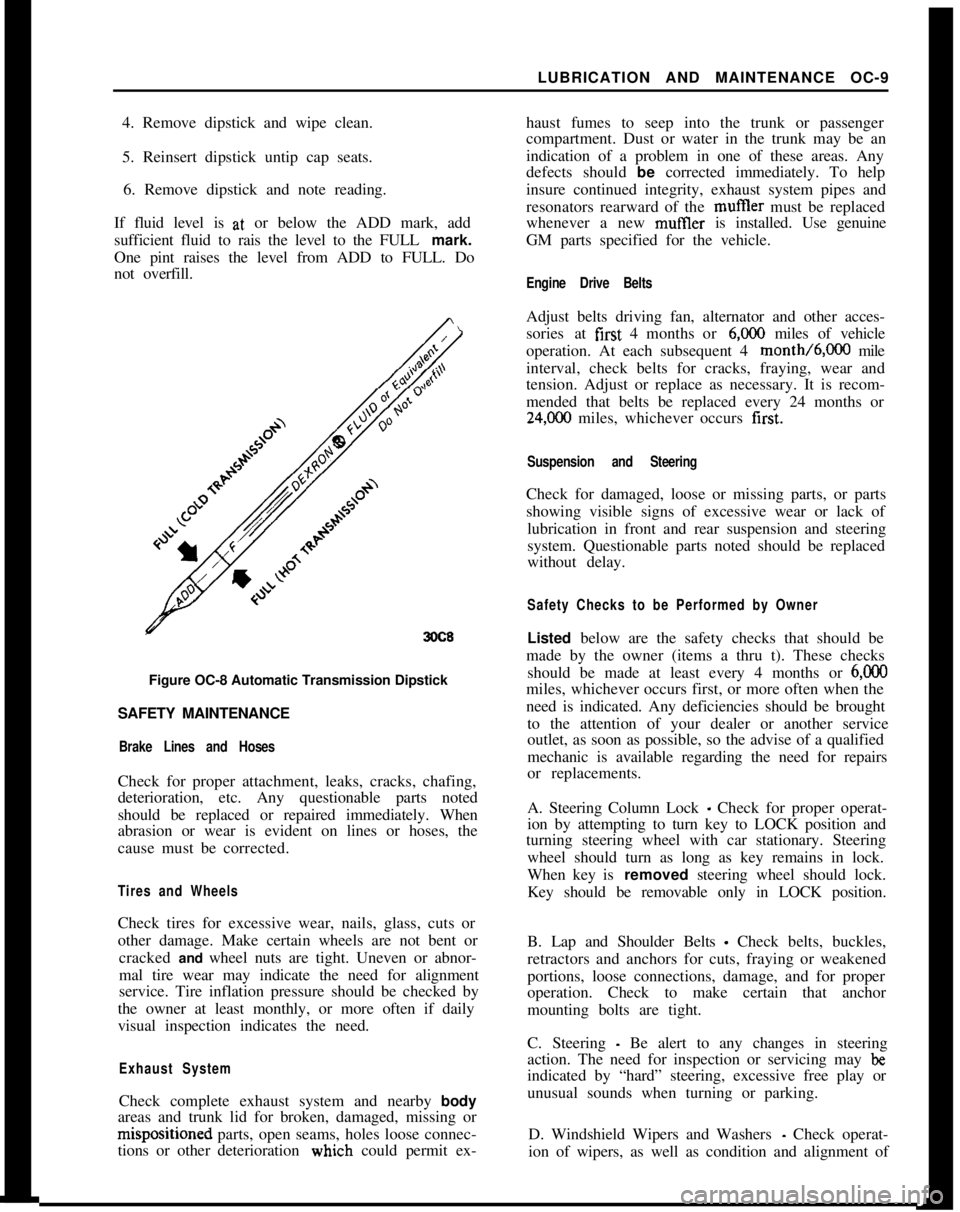
If fluid level is at, or below the ADD mark, add
sufficient fluid to rais the level to the FULL mark.
One pint raises the level from ADD to FULL. Do
not overfill.
3OC8Figure OC-8 Automatic Transmission Dipstick
SAFETY MAINTENANCE
Brake Lines and HosesCheck for proper attachment, leaks, cracks, chafing,
deterioration, etc. Any questionable parts noted
should be replaced or repaired immediately. When
abrasion or wear is evident on lines or hoses, the
cause must be corrected.
Tires and WheelsCheck tires for excessive wear, nails, glass, cuts or
other damage. Make certain wheels are not bent or
cracked and wheel nuts are tight. Uneven or abnor-
mal tire wear may indicate the need for alignment
service. Tire inflation pressure should be checked by
the owner at least monthly, or more often if daily
visual inspection indicates the need.
Exhaust SystemCheck complete exhaust system and nearby body
areas and trunk lid for broken, damaged, missing orm&positioned parts, open seams, holes loose connec-
tions or other deterioration wiuch could permit ex-haust fumes to seep into the trunk or passenger
compartment. Dust or water in the trunk may be an
indication of a problem in one of these areas. Any
defects should be corrected immediately. To help
insure continued integrity, exhaust system pipes and
resonators rearward of the muftler must be replaced
whenever a new mufIler is installed. Use genuine
GM parts specified for the vehicle.
Engine Drive BeltsAdjust belts driving fan, alternator and other acces-
sories at first 4 months or
6,ooO miles of vehicle
operation. At each subsequent 4 month/6,000 mile
interval, check belts for cracks, fraying, wear and
tension. Adjust or replace as necessary. It is recom-
mended that belts be replaced every 24 months or
24,C00 miles, whichever occurs first.
Suspension and SteeringCheck for damaged, loose or missing parts, or parts
showing visible signs of excessive wear or lack of
lubrication in front and rear suspension and steering
system. Questionable parts noted should be replaced
without delay.
Safety Checks to be Performed by OwnerListed below are the safety checks that should be
made by the owner (items a thru t). These checks
should be made at least every 4 months or
6,ooOmiles, whichever occurs first, or more often when the
need is indicated. Any deficiencies should be brought
to the attention of your dealer or another service
outlet, as soon as possible, so the advise of a qualified
mechanic is available regarding the need for repairs
or replacements.
A. Steering Column Lock
_ Check for proper operat-
ion by attempting to turn key to LOCK position and
turning steering wheel with car stationary. Steering
wheel should turn as long as key remains in lock.
When key is removed steering wheel should lock.
Key should be removable only in LOCK position.
B. Lap and Shoulder Belts
- Check belts, buckles,
retractors and anchors for cuts, fraying or weakened
portions, loose connections, damage, and for proper
operation. Check to make certain that anchor
mounting bolts are tight.
C. Steering
- Be alert to any changes in steering
action. The need for inspection or servicing may
beindicated by “hard” steering, excessive free play or
unusual sounds when turning or parking.
D. Windshield Wipers and Washers
- Check operat-
ion of wipers, as well as condition and alignment of
Page 222 of 625

WHEELS AND TIRES3G- 55
WHEELS AND TIRES
CONTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION: (Not Applicable)
DIAGNOSIS:
Car
RoughnessandVibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .AbnormalTireWear
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS:
Demounting and Mounting Tubeless Tires
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .Wheel
andTireBalance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAJOR REPAIR: (Not Applicable)
SPECIFICATIONS:
Specifications
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Page No.
3G-55
3G-58
3G-6136-6236-62
DIAGNOSIS
CAR ROUGHNESS AND VIBRATIONinflation pressures and perform tire inspection, in-
cluding removal of any foreign material on tire tread
or wheel large enough to upset balance.
Possible Causes
To assist in the diagnosis and correction of some of
the more stubborn cases of tire vibration and rough-
ness conditions that may be encountered, the follow-
ing information is offered:Tire inflation pressure recommendations are very
important at all times and particularly so on all ride
complaints. Raising or lowering tire pressures to
“improve” mileage or traction should not be at-
tempted.
VIBRATION, or a quivering motion condition, no-
ticeable by feel through the steering column, steering
wheel, floor
p&n, or by hood and fender shake, usu-
ally originates from the front wheels and tires. Front
end vibration, when caused by unbalanced front
wheels, can be generally felt as steering wheel “nib-ble”.Next, road-test the car with the owner, if possible,
and have the owner explain the specific ride disturb-
ance.After road-testing, raise car on hoist and proceed to
isolate the offending tire/wheel assembly.
Reproducing the Disturbance
A vibration felt through the seats as a side-to-side
disturbance can usually be attributed to the rearIn an attempt to reproduce the disturbance ex-
wheels and tires.perienced in the ride, a wheel spinner can be used on
the front wheels of the car.
Both front and rear vibration can be noticed mainly
at highway speeds, usually over 60 mph.The rear wheels may be spun by placing car in
“Drive” with engine running.
ROUGHNESS, noticeable primarily at speeds be-
tween 40 and 65 mph, can be felt (and occasionally
heard), and is due to certain irregularities in the tire.
Roughness usually sets up a “trembling” feel or a
shuddering effect.When spinning rear wheels, never exceed a speedom-
eter speed of 35 mph with a standard rear axle assem-
bly, or 75 mph on one with a positive traction rear
axle. Excessive speeds may cause damage to the rear
axle assembly.
Road-Test With Owner
When a ride complaint is encountered, first checkJack up both rear wheels by placing the jack under
the differential housing. Spin one wheel and tire with
the opposite wheel held from rotating by holding the
Page 227 of 625

36. 601973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
severe or careless driver. Rapid acceleration and de-celeration, severe application of brakes, taking turns
at excessive speed, high-speed driving, and striking
curbs or other obstructions which lead to misalign-
ment are driving habits which will shorten the life of
any tire.hiaintenance of proper inflation pressure and peri-
odic interchanging of tires to equalize wear are
within the control of the driver. Underinflation
raises the internal temperature of a tire greatly due
to the continual friction caused by the flexing of the
side walls. Tire squealing on turns is an indication of
underinflation or excessive speed on the turns. A
combination of underinflation, high road tempera-
tures, and high-speed driving will quickly ruin the
best tire made.
High speed on straight highways or expressways nor-
mally causes more rapid wear on the rear than on thefront tires, although cupping of front tires can result
if the tires are not periodically switched from wheel
to wheel. Driving turns and curves at too high a rate
of speed causes the front tires to wear much faster
than the rear tires.
An inspection of the tires, together with information
as to locality in which the car has been operated willusually indicate whether abnormal wear is due to the
operating conditions described above or to mechani-cal faults which should be corrected.
The various types of
abnormal tire wear and their
causes are described in the following paragraphs.
Shoulder or Underinflation Tread WearWhen a tire is underinflated, the side walls and
shoulders of the tread carry the load, while the centerof tread folds in or compresses due to the low inter-
nal air pressure. This action causes the shoulders to
take all of the driving and braking load, resulting in
much faster wear of shoulders than of the center of
tread. See Figure 3G-7. For maximum results in han-dling, riding and tire life, tire inflation pressures
should never be allowed to go below the specified
minimum pressure.
Continuous high-speed driving on curves, right and
left, may produce tread wear very similar to underin-flation wear and might very easily be mistaken for
such. Side thrust when rounding turns causes wear
on the sides of tire tread. In making a turn to the left,especially at high speeds, the outside shoulder of the
right tire and the inside shoulder of the left tire take
the side thrust and naturally receive the most wear.
The only possible correction is to advise slower
speeds on curves. Do not increase tire inflation pres-
sures beyond specified limits, as this will cause centeror over-inflation wear. See paragraph below.
Canter or Overinflation Tread Wear
Excessive wheel camber, either positive or negative,causes the tire to run at such an angle to the road
surface that one side of the tread wears much more
than the other. See Figure
3G-7.When tire inflation pressures are maintained within
the specified limits, the tire will make a full contact
across the entire width of tread, thereby distributing
the wear evenly over the total surface of the tread
area.
Cross or Toe Tread WearWhen the front wheels have an excessive amount of
either toe-in or toe-out, the tires are actually draggedsideways when they travel straight down the road
and cross wear or scraping action takes place rapidly
wearing away the tread of tires. This cross wear con-dition will usually produce a tapered or feathered
edge on the ribs of the tire tread. See Figure
3G-7.In most cases, this can be detected by rubbing the
hand across the tire tread.
If the tapered or feathered edges are on the inner
sides of the ribs on one of both sides, it indicates thatone or both tires have excessive toe-in, while the
same condition in the outer sides of ribs indicates
excessive toe-out. Usually, excessive toe-in causes
excessive tire wear on the outer edge of the right
front tire and toe-out causes tire wear on the inner
edge of the left front tire. See Section 3C for toe-in
correction.Cornering wear caused by high-speed driving on
curves (see following paragraph) sometimes has the
appearance of toe wear. Care must be used to distin-guish between these two types of wear so that the
proper corrective measures will be used.
Side or Camber WearExcessive wheel camber, either positive or negative,
causes the tire to run at such an angle to the road
surface that one side of the tread wears much more
than the other. See Figure
3G-7.The amount or angle of the camber wear will be
governed by the amount of positive or negative cam-ber. Tire tread wear very similar in appearance to
camber wear may be caused by driving on turns at
excessive speeds. This “cornering” tread wear (see
paragraph below) cannot be corrected by change of
camber angle.
Adjustments for specified camber are covered in Sec-
tion 3C.
Page 228 of 625

WHEELS AND TIRES3G- 61Cornering Tread WearThe modern independently-sprung automobile al-
lows the driver to negotiate turns at a high rate of
speed with a greater feeling of safety. This fact is
responsible for a comparatively new type of tread
wear that can easily be mistaken for toe or camber
wear.When a car is making a turn, the tires are supposed
to be rolling in a circle. When the turn is made at
high speed, however, centrifugal force acting on the
car causes the tires to be distorted sideways and to
slip or skid on the road surface. This produces a
diagonal cross type of wear, which in severe cases
will result in a fine or sharp edge on each rib of the
tire treads.
Cornering wear can be distinguished from toe or
camber wear by the rounding of the outside shoulder
of the tire and by the roughening of tread surface in
this section denoting severe abrasion. See Figure
3G-7.No alignment or tire pressure cahnge can be made
that will relieve cornering wear. Only the driver can
effect a cure and that is by slowing down on curves.
Heel and Toe Tread WearHeel and toe wear is a saw-tooth effect with one end
of each tread block worn more than the other.
The end which wears is the one that first grips the
road when the brakes are applied. High-speed driv-
ing and excessive “se of the brakes will cause this
type of irregular tire wear. This type of wear will
occur on any type of block tread design. See Figure3G-7.
Heel and toe wear is not so prevalent on the rear tires
because of the propelling action which creates a
counteracting force which wears the opposite end of
the tread block. These two stresses on the rear tires
wear the tread blocks in opposite directions and re-
sult in more even wear while on the front tires, the
braking stress is the only one which is effective. This
may be counteracted by interchanging tires.
A small amount of irregular wear, slightly
saw-toothed in appearance, at the outer segments of tires
is a normal condition and is due to the difference in
circumference between the center and the outer
edges of the tire tread. This saw-toothed appearance,
however, will be exaggerated by underinflation, im-
proper toe-in, or both.Cupped or Scalloped Type Tire Wear
Cupping or scalloping is associated with wear on acar driven mostly at highway speeds without recom-
mended tire rotation. Factors which promote cup-
ping include underinflation, incorrect toe-in setting
or camber setting, and steady highway speeds on
smooth, paved surfaces as opposed to gravel or
rough asphalt.
The following recommendations suggest action that
may be taken to help prevent cupping.
1. Rotate tires as recommended in Figure
3G-6.2. Frequently inspect front tires for irregular wear
due to underinflation, improper toe-in setting, or
camber setting. Regardless of the original cause of
cupped tread wear on either front tire, no alignment
or balance job, however perfect, can prevent future
excessive wear of the spots. Once a front tire acquires
flat or cupped spots, additional wear will continue at
a rapid rate. At the time of correction, however, the
cupped tire should be interchanged with a rear tire
on which the tread runs true. The cupped tire will,
to a certain degree, true itself on a rear wheel.
Although not normally the cause of cupping, the
following factors can contribute to the problem.
Looseness of parts in the suspension system, such as
worn steering knuckle ball joints, loose wheel bear-
ings, inoperative shock absorbers, and any excessive
looseness throughout the steering system all tend to
allow the front wheels to kick around and, if any of
the wheel alignment factors are incorrect, irregular
spotty tire tread wear of one type or another may
result.
Wobble or runout of a tire, either front or rear, due
to bent wheel or to tire being improperly mounted
will cause uneven wear.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTSDEMOUNTING AND MOUNTING
TUBELESS TIRESDue to “se of symmetrical rims, tires must be
mounted over the narrow rim shoulder i.e., over out-
side rim flange.
When demounting a tubeless tire “se care to avoid
damaging the rim-seal ridges on tire beads DO NOT
USE TIRE IRONS TO FORCE BEADS A WA Y
FROM WHEEL RIM FLANGES.
When tire is removed, inspect it carefully to deter-
mine whether loss of air was caused by puncture or
by improper
tit of beads against rim flanges. If im-
proper fit is indicated, check wheel as follows: Do
not reuse dented rims.
Page 229 of 625

3G- 621973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
1. Clean rims thoroughly, using No. 3 coarse steel
wool to remove all oxidized rubber, soap solution,
etc. Remove rust with wire brush.2. Inspect butt weld and other areas of rim contactedby tire beads to make certain there is no groove or
high spot. Remove any groove or high spot by tiling
smooth.
3. Inspect valve stem and replace it if damaged.
Make certain that valve stem is properly installed to
provide an air tight joint.
4. Before mounting a tubeless tire on a wheel, mois-
ten a cloth with mounting compound or soap solu-
tion and wipe rim-seal ridges of both beads to remove
all foreign substances.
5. Moisten base of both beads with mounting com-
pound or soap solution to help beads snap into place
when tire is inflated. Start tire over rim flange at
point opposite valve stem.
6. Inflate tire until both beads are firmly seated
against rim flanges and temporarily over inflate.
Leak test wheel and tire assembly and if satisfactory,
reduce to recommended pressure.
SPECIFICATIONSWHEEL AND TIRE BALANCE
Wheel and tire balance is the equal distribution of the
weight of the wheel and tire assembly around the axis
of rotation. Wheel unbalance is the principal cause of
tramp and general car shake and roughness and con-
tributes somewhat to steering troubles.
The original balance of the tire and wheel assembly
may change as the tire wears. Severe acceleration,
severe brake applications, fast cornering and side slip
wear the tires out in spots and often upset the origi-
nal balance condition and make it desirable to rebal-
ance the tire and wheel as an assembly. Tire and
wheel assemblies should be rebalanced after punc-
tures are repaired.
Because of the speed at which cars are driven, it is
necessary to test the wheel and tire assembly for
dynamic balance. Dynamic balancing of a wheel and
tire assembly must be done on a machine designed to
indicate out-of-balance conditions while the wheel is
rotating on the car. Since procedures differ with dif-
ferent machines, the instructions of the equipment
manufacturer must be carefully followed.
General SpecificationsWheels
Opel 1900
- Manta and GT ,._......,,,._.................,...,,..............................~,,,.................... 5.J x 13
Tires
1900 - Manta __.......,,___.,...,,..,.....,,....,,...........,...,,.,,...,.........,,..................,....................... 165-13
GT . . . . . . . ..__........_..............,...,,........,,,...,,..........,....,..,,...,,........,..................,,,.....................165-13
Tire Size and Pressures (Pounds Per Square Inch
Cold)
ModelTire Size51.53.54.57
165-1357R.57L165-13
77
165-13Recommended(Standard
PressureInflation)
FrontRear24
PSI32PSI23
PSI26PSI
19PSI23
PSI
NOTE:
1.Tire inflation pressures may increase as much as 6 pounds per square inch
when hot.
2.For continuous high-speed operation (over 75 MPH), increase tire inflation
pressures 4 pounds per square inch over the recommended pressures up to a
maximum of 30 pounds per square inch cool for 4 ply rating tires. When the
4 psi pressure adjustment for sustained high speed with maximum vehicle load
Page 230 of 625

WHEELS AND TIRES36-63would require inflation pressures above the maximum allowable, speed must be
limited to 75 miles per hour.
3.Cool tire inflation pressure: After vehicle has been inoperative for 3 hours
or more, or driven less than one mile. Hot tire inflation pressure: After vehicle
has been driven
10 miles or more at 60-70 MPH.
4.Vehicles with luggage racks do not have a vehicle load limit greater than
specified.
5. When towing trailers, the allowable passenger and cargo load must be
reduced by an amount equal to the trailer tongue load on the trailer hitch.
Torque SpecificationWheelNuts
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65lb.ft.
IFigure 3G-8 Wheel and Tire - Exploded View
Page 622 of 625

Subject
Page NumbelSubjectPage Number4.Speed Manual I..
Clutch
Detent Cable Adjustment
:Differential
Directional Signal Switch
Repair Opel 1900 & Manta
Repair GT
:Disassembly of
4.Speed Manual Transmission
DistributorFunction of Valves and Hydraulic Control Units
Opel
3.Speed Automatic.................
74-21
Fuse Chart..............................lG-56
Fusible Link.............................
lA-8Specifications.
Point Replacement..
..,78-127A-
17c-9148-73E-393E-4878.23
1C-26
1 c-20
GEGas Tank See Fuel Tank
General Specifications
Engine...............................6A-28
Opel 3.Speed Automatic
.................7C-134
Transmission, Manual.,
..................78-33
Clutch...............................7A-7
Body................................ZA-4
Governor Drive Gear
Opel
3.Speed Automatic.................7C-103
Grille
Opel 1900 & Manta.....................8A-7
GT..................................8A-6 Electrically Heated Rear Window
Engine
General Description
Cooling System
Lubrication System
Trouble Diagnosis
Exhaust Manifold
Exhaust System
Removal and Installation
External Oil Leaks,
Opel 3 Speed Automatic
FFast Idle Adjustment
..................
Filter-Engine Oil
......................
Fluid Checking Procedure Transmission
Opel 3Speed Automatic.............
Frame-Opel 1900 & Manta.............
Frame
GT-Opel......................
SWVOOpel Xipeed Automatic...........
Front Suspension
Opel1900&Manta.................
GT..............................
Front Wheel Alignment................
Front Wheel Bearing Adjustment
All Series.........................
Fuel Gauge
Trouble Diagnosis
Opell$OO&Manta...............
GT............................
Fuel Pump Operation..................
Fuel System
Fuel Tank (Opel 1900 & Manta)
.......
Fuel Lines (Opel 1900 & Manta)
.......
Fuel Tank
(GT)....................
Fuel Gauge Tank Unit
(GT)...........
Fuel Lines
(GT)....................
Fuel Tank Removal and Installation....
Cleaning Tank.....................
lH-576A-268-326A-46A-66A-126D-427C-816E-51
oc-77C~Bl2B-826-77c-1003A-23A-23C-223A-4
HHazard Warning Flasher
....................lG-55
Headlamp Aiming
.........................1 F-46
Headlamp Switch
Opel 190.0 & Manta
.....................1 F-46
Headlamp Mechanism GT
..................8A-2
Heater System Opel 1900 &Manta
Trouble Diagnosis
......................9A-11
Description and Operation
................9A-10
Adjustments and Minor Service............9A-12
Removal and Installation
.................9A-12
Specifications..........................$A-16
Heater System GT
Trouble Diagnosis
......................9A-4
Description and Operation
................9A-2
Adjustments and Minor Service
............9A-4
Removal and Installation.................9A-5
Specifications..........................$A-9Horn
Operation.............................lG-54
Hydraulic Operation
Opel
3.Speed Automatic.................7C-64
IIdentification Number Vehicle...............
OA-1ldle.Adjustment
..........................6E-51
Inflation Pressures, Tires.
...................36-62
Ignition Coil
Specifications.
.........................
lC-26Identification, Engine
......................
OA-1Ignition System
Timing...............................
lC-20Instrument Panel Parts Removal