check engine OPEL VECTRA 1988 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1988, Model line: VECTRA, Model: OPEL VECTRA 1988Pages: 525, PDF Size: 58.26 MB
Page 146 of 525

42Where applicable, screw the pressure-
proportioning valves into the base of the
cylinder.
43Refit the master cylinder, as described in
Section 15.
17Master cylinder (ABS) -
general
The master cylinder fitted to models with
ABS cannot be dismantled, and no attempt
should be made at overhaul.
If faulty, the complete unit must be
renewed, as described in Section 15.
18Vacuum servo - description
and testing
Description
1The vacuum servo is fitted between the
brake pedal and the master cylinder, and
provides assistance to the driver when the
pedal is depressed, reducing the effort required
to operate the brakes. The unit is operated by
vacuum from the inlet manifold. With the brake
pedal released, vacuum is channelled to both
sides of the internal diaphragm. However,
when the pedal is depressed, one side of the
diaphragm is opened to atmosphere, resulting
in assistance to the pedal effort. Should the
vacuum servo develop a fault, the hydraulic
system is not affected, but greater effort will be
required at the pedal.
Testing
2The operation of the servo can be checked
as follows.
3With the engine stopped, destroy the
vacuum in the servo by depressing the brake
pedal several times.
4Hold the brake pedal depressed and start
the engine. The pedal should sink slightly as
the engine is started.
5If the pedal does not sink, check the servo
vacuum hose for leaks.
6If no defects are found in the vacuum hose,
the fault must lie in the servo itself.7No overhaul of the servo is possible, and if
faulty, the complete unit must be renewed.
19Vacuum servo - removal and
refitting
4
Note: During the 1989 model year, some
vehicles were produced with the brake pedal
height incorrectly set, resulting in the brake
pedal resting approximately 15.0 mm (0.6 in)
above the clutch pedal instead of 4.0 mm
(0.16 in below). The correct pedal height can
be set by adjusting the vacuum servo
operating fork dimension, as described in
paragraphs 15 and 16
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Working inside the vehicle, remove the
lower trim panel from the driver’s footwell.
3Disconnect the wiring plug from the brake
lamp switch, then twist the switch anti-
clockwise and remove it from its bracket.
4Pull the spring clip from the right-hand end
of the servo fork-to-pedal pivot pin.
5Using a pair of pliers, pull back the end of
the pedal return spring from the pedal, to
enable the servo fork-to-pedal pivot pin to be
removed. Withdraw the pivot pin.
6Remove the windscreen cowl panel, as
described in Chapter 11, then remove the
windscreen wiper motor and linkage as
described in Chapter 12.7Remove the coolant expansion tank as
described in Chapter 3.
8Pull the vacuum pipe from the brake servo.
9Unscrew the two securing nuts, and
carefully withdraw the brake master cylinder
from the studs on the servo. Move the master
cylinder forwards slightly, taking care not to
strain the brake pipes.
10Remove the two plugs covering the servo
securing bolts from the cowl panel (see
illustrations).
11Using a Allen key or hexagon bit, unscrew
the servo securing bolts and remove them
completely, then lift the servo from the
bulkhead (see illustrations).
12If desired, the mounting bracket can be
removed from the servo by unscrewing the
four securing nuts. Note that the bracket will
stick to the servo, as it is fitted with sealing
compound.
13The servo cannot be overhauled, and if
faulty, the complete unit must be renewed.
Refitting
14Before refitting the servo, check that the
operating fork dimension is correct as follows.
15Measure the distance from the end face of
the servo casing to the centre of the pivot pin
hole in the end of the operating fork. The
distance should be 144.0 mm (5.6 in). To
make accurate measurement easier, insert a
bolt or bar of similar diameter through the
pivot pin hole, and measure to the centre of
the bolt or bar (see illustration).
Braking system 9•15
19.11A Unscrew the securing bolts . . .19.15 Measuring the servo operating fork
dimension using a bolt inserted through
the pivot pin hole19.11B . . . and withdraw the servo
19.10B . . . to expose the servo securing
bolts19.10A Remove the plugs . . .
9
Page 147 of 525

16If adjustment is necessary, slacken the
locknut, turn the fork to give the specified
dimension, then tighten the locknut.
17Where applicable, coat the contact faces
of the servo and the mounting bracket with
sealing compound, then refit the bracket to
the servo, and tighten the securing nuts to the
specified torque.
18Coat the threads of the servo securing
bolts with locking fluid, then fit the servo to
the bulkhead and tighten the securing bolts.
19Refit the securing bolt cover plugs to the
cowl panel.
20Refit the master cylinder to the servo, and
tighten the securing nuts to the specified
torque.
21Reconnect the vacuum pipe to the servo.
22Refit the coolant expansion tank, as
described in Chapter 3.
23Refit the windscreen wiper motor and
linkage as described in Chapter 12, then refit
the windscreen cowl panel.
24Further refitting is a reversal of removal.
On completion, test the operation of the
servo, as described in Section 18.
20ABS hydraulic modulator -
removal and refitting
4
Note: Refer to Section 2, and the note at the
beginning of Section 3, before proceeding
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the brake fluid reservoir cap, and
secure a piece of polythene over the filler
neck with a rubber band, or by refitting the
cap. This will reduce the loss of fluid during
the following procedure.
3Remove the securing screw, and withdraw
the plastic cover from the hydraulic
modulator.
4Remove the two clamp screws, and lift off
the modulator wiring harness clamp (see
illustration).
5Disconnect the modulator wiring plug,
levering it from the socket with a screwdriver if
necessary.6Unscrew the brake fluid pipe union nuts,
and disconnect the pipes from the modulator.
Be prepared for fluid spillage, and plug the
open ends to prevent dirt ingress and further
fluid loss. Move the pipes just clear of the
modulator, taking care not to strain them.
7Unscrew the three modulator securing nuts
(see illustration), then tilt the modulator
slightly, and withdraw it upwards from its
bracket, sufficiently to gain access to the
earth lead securing nut at the front lower edge
of the modulator.
8Unscrew the securing nut and disconnect
the earth lead, then withdraw the modulator
from the vehicle, taking care not to spill brake
fluid on the vehicle paintwork.
9If a new modulator is to be fitted, pull the
two relays from the top of the old modulator,
and transfer them to the new unit. No attempt
must be made to dismantle the modulator.
Refitting
10Before refitting the modulator, check that
the bolts securing the mounting bracket to the
body panel are tight, and that the modulator
rubber mountings are in good condition.
Renew the rubber mountings if necessary.
11Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
12Make sure that the earth lead is
reconnected before fitting the modulator to its
mounting bracket.13On completion, remove the polythene
sheet from the brake fluid reservoir filler neck,
and bleed the complete brake hydraulic
system, as described in Section 3.
14Check that the ABS warning lamp
extinguishes when first starting the engine
after the modulator has been removed. At the
earliest opportunity, take the vehicle to a
Vauxhall dealer, and have the complete
system tested, using the dedicated ABS test
equipment.
21ABS wheel sensors - removal
and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Front wheel sensor
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant front roadwheel bolts
and apply the handbrake. Jack up the front of
the vehicle, and support on axle stands (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”) positioned
under the body side members. Remove the
roadwheel.
3Unclip the sensor wiring connector from the
retaining clip under the wheel arch, then
separate the two halves of the wiring
connector, prising them apart with a
screwdriver if necessary (see illustration).
4Using a Allen key or hexagon bit, unscrew
the bolt securing the wheel sensor to its
mounting bracket, then carefully lever the
sensor from the bracket using a screwdriver
(see illustration). Recover the seal ring.
Refitting
5Examine the condition of the seal ring, and
renew if necessary.
6Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
7Smear a little grease on the sensor casing
before fitting it to the bracket.
8Do not fully tighten the roadwheel bolts until
the vehicle is resting on its wheels.
9Check that the ABS warning lamp
extinguishes when first starting the engine
after a wheel sensor has been removed. At
9•16Braking system
20.4 ABS hydraulic modulator (cover
removed)
1 Wiring harness
clamp screws2 Earth lead
3 Relays
21.3 Front wheel sensor wiring under
wheelarch - DOHC model
1 ABS sensor connector
2 Disc pad wear sensor wiring connector
21.4 ABS front wheel sensor securing bolt
(arrowed) - DOHC model20.7 ABS hydraulic modulator securing
screws (arrowed)
Page 148 of 525

the earliest opportunity, take the vehicle to a
Vauxhall dealer, and have the complete
system tested, using the dedicated ABS test
equipment.
Rear wheel sensor
Removal
10Disconnect the battery negative lead.
11Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel.
12Unclip the sensor wiring connector from
the retaining clip on the rear underbody, then
separate the two halves of the wiring
connector, prising them apart with a
screwdriver if necessary (see illustration).
13Note the routing of the sensor wiring, and,
where applicable, release it from the clips on
the underbody.
14Using a Allen key or hexagon bit, unscrew
the bolt securing the wheel sensor to the
trailing arm (or the mounting bracket on
DOHC models), then carefully lever the sensor
from its location using a screwdriver (see
illustration). Recover the seal ring.
Refitting
15Proceed as described in paragraphs 5 to 9
inclusive.
22ABS electronic control
module - removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
ABS-2E systems
Removal
1Ensure that the ignition is switched off, then
disconnect the battery negative lead.
2The control module is located under a
cover in the passenger sill, to the left-hand
side of the seat.
3Extract the three securing screws, and lift
the cover from the control module. Note that
two of the screws are covered by plastic trim
plugs. 4Lift the control module from its recess, then
release the retaining clip and disconnect the
module wiring plug. Withdraw the module
(see illustrations).
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
6Check that the ABS warning lamp
extinguishes when first starting the engine
after the module has been removed. At the
earliest opportunity, take the vehicle to a
Vauxhall dealer, and have the complete
system tested, using the dedicated ABS test
equipment.
ABS-2EH systems
Removal
7Ensure that the ignition is switched off, then
disconnect the battery negative lead.
8Remove the cover from the hydraulic
modulator.
9Disconnect both the wiring harness and
solenoid valve connectors.
10Relays can only be removed from control
units that have slanted covers (see
illustration). The relays for the solenoid valve
and pump motor, if removable, can now be
removed. If the unit has a flat cover, and is
faulty, the whole unit will have to be replaced.
11Undo fixing bolts and remove the control
unit.
Refitting
12Refitting is a reversal of removal. Refer
also to paragraph 6.
23ABS relays (ABS-2E systems
only) - removal and refitting
2
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding.
For ABS-2EH system relays, refer to
paragraphs 7 to 12, in Section 22.
Solenoid valve and pump motor
relays
Removal
1The solenoid valve and pump motor relays
are mounted on the hydraulic modulator.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Remove the securing screw and withdraw
the plastic cover from the hydraulic
modulator.
4Pull out the appropriate relay. The small
relay is for the solenoid valve, and the large
relay is for the pump motor.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
6Check that the ABS warning lamp
extinguishes when first starting the engine
after a relay has been removed. At the earliest
opportunity, take the vehicle to a Vauxhall
dealer, and have the complete system tested,
using the dedicated ABS test equipment.
Surge arrester relay
Removal
7The surge arrester relay is located in the
relay box at the left rear of the engine
compartment.
Braking system 9•17
22.4A Lift out the ABS control module . . .22.10 ABS-2EH control unit
1 Slanted cover type 2 Flat cover type22.4B . . . and release the wiring plug
retaining clip - ABS-2E system
21.14 ABS rear wheel sensor (arrowed) -
DOHC model21.12 ABS rear wheel sensor wiring
connectors (arrowed) on rear underbody -
DOHC model`
9
Page 154 of 525

4B
General
Injection system type:
C16 NZ, C16 NZ2, X16 SZ and C18 NZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multec Central Fuel Injection
20 NE, C20 NE and 20 SEH, (up to 1990) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M4.1
20 NE, C20 NE and 20 SEH, (from 1990) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M1.5
20 XEJ and C20 XE, (up to 1993) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M2.5
C20 XE (from 1993) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M2.8
X20 XEV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Simtec 56.1
Fuel tank capacity:
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63.0 ± 2 litres
Fuel octane rating *
Leaded . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98 RON (4-star)
Unleaded (refer to Chapter 5) * . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95 RON (Premium)
* Note
: Models fitted with a catalytic converter (engine code prefixed by ‘C’ or ‘X’), must only be operated on unleadedfuel.
Idle settings
Idle speed:
C16 NZ and X16 SZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 80 rpm
C16 NZ2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 880 ± 80 rpm
C18 NZ
Manual transmission models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 880 ± 80 rpm
Automatic transmission models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 830 ± 80 rpm
20 NE, C20 NE and 20 SEH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 80 rpm
20 XEJ and C20 XE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 940 ± 80 rpm
X20 XEV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 160 rpm
Note:Idle speed adjustment is not possible on these models, for information only
Chapter 4 Part B:
Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models
Air box - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Air cleaner - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Air filter element - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
Airflow meter (if fitted) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Air mass meter (if fitted) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Air temperature sensor (later models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . .7
Air temperature control - description and testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Depressurising the fuel system - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Electronic Control Unit (ECU) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Fuel filter (‘In-tank’ fuel pump models) - removal and refitting . . . . . .10
Fuel filter (‘Out-of-tank’ fuel pump models) - removal and refitting . . .9
Fuel flow damper - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Fuel injection system - precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Fuel injector (Multec system) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Fuel injector (Multec system) - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Fuel injectors (except Multec system) - removal and refitting . . . . . .28
Fuel pressure regulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Fuel pump - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Fuel pump (‘In-tank’ fuel pump models) - removal and refitting . . . .13
Fuel pump (‘Out-of-tank’ fuel pump models) - removal and refitting .12
Fuel pump relay - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14Fuel tank - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Fuel tank filler pipe - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Fuel tank sender unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Hot film mass airflow meter - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Idle air control stepper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Idle mixture - checking and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Idle speed adjuster - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Inlet manifold (DOHC models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Inlet manifold (SOHC with Multec) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .39
Inlet manifold (SOHC without Multec) - removal and refitting . . . . . .38
Knock sensor and module (X16 SZ models) - removal and refitting .36
Knock sensor (Simtec system) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .37
System testing - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Throttle body (except Multec system) - removal and refitting . . . . . .31
Throttle body (Multec system) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Throttle cable - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Throttle pedal - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 4A
Throttle position sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Throttle potentiometer - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Throttle valve potentiometer - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
4B•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 155 of 525

Idle settings (continued)
Idle mixture (CO content):
20 NE and 20 SEH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.0 max.
20 XEJ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.7 to 1.2%
All other models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.3 % (at 2800 to 3200 rpm)
Fuel Pressure (regulator vacuum hose connected)
Multec . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.76 bar
Motronic 4.1:
Feed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.3 to 2.7 bar
Return . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.3 to 1.5 bar
Motronic 1.5:
Feed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.8 to 2.2 bar
Return . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.3 to 1.5 bar
Motronic 2.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.0 to 2.2 bar
Motronic 2.8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.2 to 2.7 bar
Simtec 56.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .not available
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
All specifications as for carburettor models except for the following:
Bracket, tank vent valve to coolant flange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Fuel distributor pipe to inlet manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Fuel flow damper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Fuel injector retainer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Fuel pressure regulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.52
Fuel pump clamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Idle air control stepper motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.52
Knock sensor (X16 SZ) to block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1310
Oxygen sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Throttle body mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Throttle body upper-to-lower section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64.5
Throttle potentiometer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21.5
Throttle valve housing to inlet manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
1General description
General
1All engines available within the Cavalier
range can be operated on unleaded petrol.
Refer to Chapter 5 for further details. Note
that models fitted with a catalytic converter
must only be operated on unleaded petrol,
and leaded petrol must not be used. Models
with catalytic converter can be identified by
the engine code, which is prefixed by the
letter ‘C’ or ‘X’.
Multec system
Note: There is no provision for the adjustment
or alteration of the idle speed; if checking the
idle speed, remember that it may vary
constantly under ECU control.
2The Multec system is essentially a simple
method of air/fuel metering, replacing the
carburettor with a single injector mounted in a
throttle body. This type of system is therefore
also known as Throttle Body Injection (TBi),
Central Fuel Injection (CFi) or single-(or
mono-) point injection. The whole system is
best explained if considered as three
sub-systems, these being fuel delivery, air
metering and electrical control.
3The fuel delivery system incorporates the
fuel tank (with the electric fuel pumpimmersed inside it), the fuel filter, the fuel
injector and pressure regulator (mounted in
the throttle body), and the hoses and pipes
connecting them. When the ignition is
switched on (or when the engine is cranking,
on X16 SZ engines) the pump is supplied with
voltage, by way of the pump relay and fuse
11, under the control of the Electronic Control
Unit (ECU). The pump feeds through the fuel
filter to the injector. Fuel pressure is controlled
by the pressure regulator, which lifts to allow
excess fuel to return to the tank.
4The air metering system includes the inlet air
temperature control system and the air
cleaner, but its main components are in the
throttle body assembly. This incorporates the
injector, which sprays fuel onto the back of the
throttle valve, the throttle potentiometer. This
is linked to the throttle valve spindle and sends
the ECU information on the rate of throttle
opening by transmitting a varying voltage. The
idle air control stepper motor is controlled by
the ECU to maintain the idle speed.
5The electrical side of the fuel injection
system consists of the ECU and all the
sensors that provide it with information, plus
the actuators by which it controls the whole
system’s operation. The basic method of
operation is as follows; note that the ignition
system is controlled by the same ECU.
6The manifold absolute pressure sensor is
connected by a hose to the inlet manifold.
Variations in manifold pressure are converted
into graduated electrical signals that are usedby the ECU to determine the load on the
engine. The throttle valve potentiometer is
explained above.
7Information on engine speed and
crankshaft position comes from the distributor
on C16 NZ engines and from the crankshaft
speed/position sensor on C16 NZ2, X16 SZ
and C18 NZ engines.
8An odometer frequency sensor provides the
ECU with information on the vehicle’s road
speed, and the coolant temperature sensor
provides it with the engine temperature. A
knock sensor located in the cylinder block
between cylinders 2 and 3 on the X16 SZ
engine provides additional information to the
ECU by detecting pre-ignition (detonation)
during the combustion process.
9All these signals are compared by the ECU
with set values pre-programmed (mapped)
into its memory. Considering this information,
the ECU selects the response appropriate to
those values. It controls the ignition amplifier
module by varying the ignition timing as
required. The fuel injector is controlled by
varying its pulse width the time the injector is
held open, to provide a richer or weaker
mixture, as appropriate. The idle air control
stepper motor controls the idle speed. The
fuel pump relay controls the fuel delivery and
the oxygen sensor, accordingly. The mixture,
idle speed and ignition timing are constantly
varied by the ECU to provide the best settings
for cranking, starting and engine warm-up
(with either a hot or cold engine), idling,
4B•2Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models
Page 157 of 525

31This engine is also fitted with an EGR
(exhaust gas recirculation) valve and
secondary air injection (AIR - Air Injection
Reactor), to conform to the latest European
exhaust emission limits (as from 1996). The
EGR returns a specific amount of exhaust gas
into the combustion process. This in turn
reduces the formation of nitrogen oxides
(No
x). The secondary air injection system has
an electrically driven air pump that injects air
into the exhaust manifold, reducing the
amount of CO and HC emissions.
2Fuel injection system -
precautions
The fuel injection system is pressurised,
therefore extra care must be taken when
disconnecting fuel lines. When disconnecting
a fuel line union, loosen the union slowly, to
avoid a sudden release of pressure that may
cause fuel to spray out.
Fuel pressure checking must be entrusted
to a Vauxhall dealer, or other specialist, who
has the necessary special equipment.
3System testing - general
3
General
1Apart from basic electrical tests, there is
nothing that can be done by the owner to test
individual fuel system components.2If a fault arises, check first that it is not due
to poor maintenance. Check that the air
cleaner filter element is clean, the spark plugs
are in good condition and correctly gapped.
Check also that the engine breather hoses are
clear and undamaged and that the throttle
cable is correctly adjusted. If the engine is
running very roughly, check the compression
pressures (Chapter 1) and remember the
possibility that one of the hydraulic tappets
might be faulty, producing an incorrect valve
clearance.
3If the fault is thought to be due to a dirty
injector, it is worth trying one of the
established injector-cleaning treatments
before renewing, perhaps unnecessarily, the
injector.
4If the fault persists, check the ignition
system components (as far as possible).
5If the fault is still not eliminated, work
methodically through the system, checking all
fuses, wiring connectors and wiring, looking
for any signs of poor connections, dampness,
corrosion, dirt or other faults.
6Once the system components have been
checked for signs of obvious faults, take the
vehicle to a Vauxhall dealer for the full system
to be tested on special equipment.
7Do not attempt to “test” any component,
but particularly the ECU, with anything other
than the correct test equipment, available at a
Vauxhall dealer. If any of the wires to be
checked lead to a component such as the
ECU, always first unplug the relevant
connector from the system components so
that there is no risk of the component being
damaged by the application of incorrect
voltages from test equipment.
4Air cleaner - removal and
refitting
2
Note:If ‘round type’ air filter is fitted, follow
procedure in Chapter 4A.
Removal
1Unclip the coolant expansion tank hose
from the air cleaner cover, and move it to one
side out of the way.2Loosen the clamp screw and disconnect
the air trunking from the airflow meter (see
illustration).
3Disconnect the battery negative lead, then
disconnect the wiring plug from the airflow
meter.
4Release the two securing clips from the left-
hand side of the air cleaner cover, and
unscrew the two captive securing screws
from the right-hand side, then lift off the
cover.
5Lift out the filter element.
6Loosen the preheat hoses, fastening nuts.
7Undo the nuts securing the 2 rubber block
studs which are secured through the lower
half of the air cleaner housing.
8Some models are fitted with an inlet air
resonance box, to reduce induction noise.
This box is located under the wheel arch, and
connects to a pipe on the air inlet tube.
9The resonance box must be removed
before the air inlet tube can be removed. To
do this, first apply the handbrake, then jack up
the front of the vehicle, and support securely
on axle stands placed under the body side
members.
10Remove the securing screws, and
withdraw the lower splash shield from the
wing to expose the resonance box.
11Unscrew the single securing screw, and
pull the resonance box from the connector
tube (see illustrations).
12If desired, the air inlet tube can be
removed after pulling off the connector tube
from under the wing (see illustration).
4B•4Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models
4.12 Removing the resonance box
connector tube4.11B . . . and withdraw the resonance box4.11A Remove the securing screw . . .
4.2 Loosening the air trunking clamp
screw at the airflow meter
Warning: Many of the
procedures in this sub-Section
require the removal of fuel lines
and connections that may result
in some fuel spillage. Before carrying out
any operation on the fuel system refer to
the precautions given in Safety first! at
the beginning of this Manual and follow
them implicitly. Petrol is a highly
dangerous and volatile liquid, and the
precautions necessary when handling it
cannot be overstressed.
Page 158 of 525

4B
13Manipulate the air inlet tube to release the
securing lugs from the front body panel. This
is a tricky operation, and patience will be
required. For improved access, the headlamp
can be removed, as described in Chapter 12.
Refitting
14Refitting of all components is a reversal of
removal, noting that the air cleaner element
fits with the rubber locating flange uppermost.
5Air box - removal and refitting
2
Removal
1The air box, if fitted, is secured by two or
three bolts to the top of the throttle body.
Take note of the routing and connections of
the inlet air temperature control system
vacuum pipes.
2Disconnect the engine breather hose from
the air box and the vacuum pipe from the
rearmost of the throttle body’s three unions
(see illustration).
3Do not lose the sealing ring as the air box is
withdrawn.
Refitting
4On refitting, ensure that the sealing ring is
seated correctly in the slot in the underside of
the air box, tighten the screws, and reconnect
the vacuum pipe and breather hose (see
illustrations).
6Air temperature control -
description and testing
3
Description
1Fitted to models with Multec systems, air
temperature is controlled by a thermac switch
(thermostat), mounted in the air box. When
the engine is started from cold, the switch is
closed to allow inlet manifold depression to
act on the air temperature control valve in the
air cleaner assembly. This uses a vacuum
servo in the valve assembly to draw a flap
valve across the cold air inlet thus allowing
only (warmed) air from the exhaust manifold to
enter the air cleaner.2As the temperature of the exhaust warmed
air in the air box rises, a bi-metallic strip in the
thermac switch deforms. This opens the
switch to shut off the depression in the air
temperature control valve. The flap is then
lowered gradually across the hot air inlet. Until
the engine is fully warmed up to normal
operating temperature, only cold air from the
front of the vehicle is entering the air cleaner.
Testing
3To check the system, allow the engine to
cool down completely, then remove the air
cleaner cover; the flap valve should be
securely seated across the hot air inlet. Start
the engine. The flap should immediately rise to
close off the cold air inlet. It should then lower
steadily as the engine warms until it is
eventually seated across the hot air inlet again.
4To check the thermac switch, disconnect
the control valve vacuum pipe from the switch
union (on the rear face of the air box) when the
engine is running. With the engine cold, full
inlet manifold depression should be felt
sucking at the union; none at all should be felt
when the engine is fully warmed up.
5To check the air temperature control valve,
remove the air cleaner cover; the flap valve
should be securely seated across the hot air
inlet. Disconnect the control valve vacuum
pipe from the switch union on the rear face of
the air box and suck hard on its end; the flap
should rise to shut off the cold air inlet.
6If either component is faulty, it must be
renewed. This means renewing the air cleaner
lower casing to obtain a new air temperature
control valve, or renewing the air box in the
case of the thermac switch.
7Air temperature sensor (later
models) - removal and
refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the wiring plug at the inlet air
temperature sensor.
3Release the hose clips and remove the air
trunking then remove the inlet air temperature
sensor from the trunking.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal but ensure
that the air trunking is connected to the
airflow meter as shown (see illustration).
8Depressurising the fuel
system - general
2
General
1The fuel system consisting of the
tank-mounted fuel pump, the fuel filter, the
fuel injector and the pressure regulator in the
throttle body. Metal pipes and flexible hoses
of the fuel lines connect these components.
All these contain fuel that will be under
pressure while the engine is running and/or
while the ignition is switched on.
2The pressure will remain for some time after
the ignition has been switched off and must
be relieved before any of these components
are disturbed.
3Remove either the fuel pump fuse (num-
ber 11) or the fuel pump relay and start the
engine. Allow the engine to idle until it cuts
out. Turn the engine over once or twice on the
starter to ensure that all pressure is released,
then switch off the ignition.
4Do not forget to refit the fuse or relay when
work is complete.
Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models 4B•5
5.4B Do not overtighten the air box
screws
7.4 Removing the intake air temperature
sensor from the air trunking - later models
5.4A Ensure the sealing ring is located in
the air box groove5.2 Vacuum pipe connections to air box
A To throttle body B To air cleaner
Warning: The following
procedures will merely relieve
the pressure in the fuel system.
Remember that fuel will still be
present in the system components, so
take precautions before disconnecting
any of them. Refer to Section 2.
Page 159 of 525
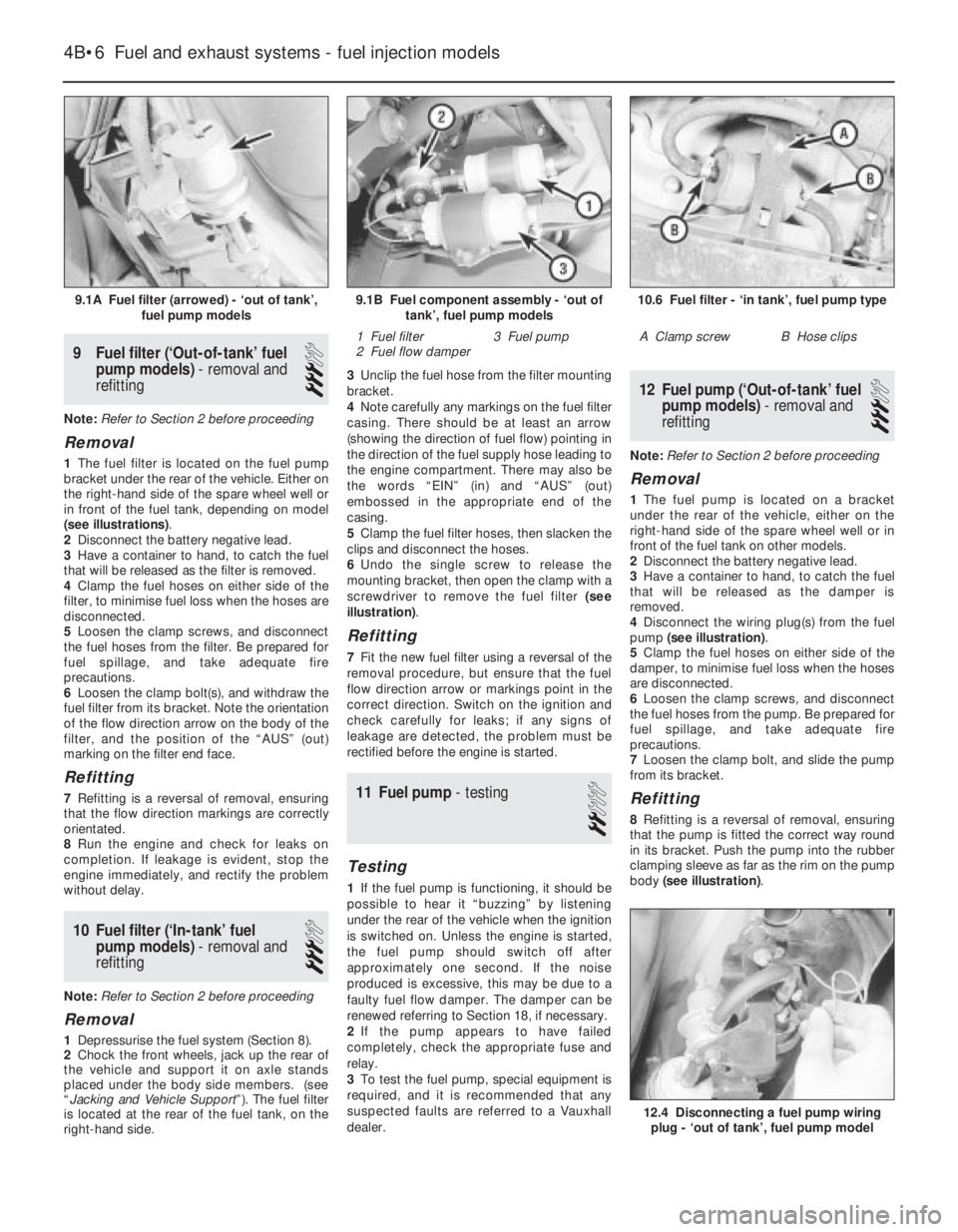
9Fuel filter (‘Out-of-tank’ fuel
pump models) - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1The fuel filter is located on the fuel pump
bracket under the rear of the vehicle. Either on
the right-hand side of the spare wheel well or
in front of the fuel tank, depending on model
(see illustrations).
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Have a container to hand, to catch the fuel
that will be released as the filter is removed.
4Clamp the fuel hoses on either side of the
filter, to minimise fuel loss when the hoses are
disconnected.
5Loosen the clamp screws, and disconnect
the fuel hoses from the filter. Be prepared for
fuel spillage, and take adequate fire
precautions.
6Loosen the clamp bolt(s), and withdraw the
fuel filter from its bracket. Note the orientation
of the flow direction arrow on the body of the
filter, and the position of the “AUS” (out)
marking on the filter end face.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the flow direction markings are correctly
orientated.
8Run the engine and check for leaks on
completion. If leakage is evident, stop the
engine immediately, and rectify the problem
without delay.
10Fuel filter (‘In-tank’ fuel
pump models) - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1Depressurise the fuel system (Section 8).
2Chock the front wheels, jack up the rear of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands
placed under the body side members. (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”). The fuel filter
is located at the rear of the fuel tank, on the
right-hand side.3Unclip the fuel hose from the filter mounting
bracket.
4Note carefully any markings on the fuel filter
casing. There should be at least an arrow
(showing the direction of fuel flow) pointing in
the direction of the fuel supply hose leading to
the engine compartment. There may also be
the words “EIN” (in) and “AUS” (out)
embossed in the appropriate end of the
casing.
5Clamp the fuel filter hoses, then slacken the
clips and disconnect the hoses.
6Undo the single screw to release the
mounting bracket, then open the clamp with a
screwdriver to remove the fuel filter (see
illustration).
Refitting
7Fit the new fuel filter using a reversal of the
removal procedure, but ensure that the fuel
flow direction arrow or markings point in the
correct direction. Switch on the ignition and
check carefully for leaks; if any signs of
leakage are detected, the problem must be
rectified before the engine is started.
11Fuel pump - testing
2
Testing
1If the fuel pump is functioning, it should be
possible to hear it “buzzing” by listening
under the rear of the vehicle when the ignition
is switched on. Unless the engine is started,
the fuel pump should switch off after
approximately one second. If the noise
produced is excessive, this may be due to a
faulty fuel flow damper. The damper can be
renewed referring to Section 18, if necessary.
2If the pump appears to have failed
completely, check the appropriate fuse and
relay.
3To test the fuel pump, special equipment is
required, and it is recommended that any
suspected faults are referred to a Vauxhall
dealer.
12Fuel pump (‘Out-of-tank’ fuel
pump models) - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1The fuel pump is located on a bracket
under the rear of the vehicle, either on the
right-hand side of the spare wheel well or in
front of the fuel tank on other models.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Have a container to hand, to catch the fuel
that will be released as the damper is
removed.
4Disconnect the wiring plug(s) from the fuel
pump (see illustration).
5Clamp the fuel hoses on either side of the
damper, to minimise fuel loss when the hoses
are disconnected.
6Loosen the clamp screws, and disconnect
the fuel hoses from the pump. Be prepared for
fuel spillage, and take adequate fire
precautions.
7Loosen the clamp bolt, and slide the pump
from its bracket.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the pump is fitted the correct way round
in its bracket. Push the pump into the rubber
clamping sleeve as far as the rim on the pump
body (see illustration).
4B•6Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models
9.1A Fuel filter (arrowed) - ‘out of tank’,
fuel pump models10.6 Fuel filter - ‘in tank’, fuel pump type
A Clamp screwB Hose clips
12.4 Disconnecting a fuel pump wiring
plug - ‘out of tank’, fuel pump model
9.1B Fuel component assembly - ‘out of
tank’, fuel pump models
1 Fuel filter
2 Fuel flow damper3 Fuel pump
Page 160 of 525

4B
9Run the engine and check for leaks on
completion. If leakage is evident, stop the
engine immediately, and rectify the problem
without delay.
13Fuel pump (‘In-tank’ fuel
pump models) - removal and
refitting
3
Removal
1Depressurise the fuel system (Section 8),
then remove and refit the fuel filler cap to
ensure that the pressure is equalised inside
and outside the tank.
2Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
3Fold forwards the rear seat cushion. Peel
back the floor covering beneath it, then
remove the cover plug from the vehicle floor
to reach the pump mountings (see
illustration).
4Noting exactly how it is connected, and
making your own marks or notes to ensure
that it can be reconnected the same way
round, disconnect the wiring plug from the
pump.
5Release the securing clip and disconnect
the fuel hose from the pump. Clamp or plug
the hose to prevent the loss of fuel and the
entry of dirt.
6Undo the pump mounting bracket screws,
then withdraw the mounting bracket and
pump assembly from the tank. Note the
position of the sealing ring and discard it, then
cover the tank opening as a safety measure
and to prevent the entry of dirt.
7If the pump is to be renewed, first move it to
a clean working area and carry out the
following.
8Prise off the filter at the base of the pump
assembly, then release the securing clamp
and disconnect the mounting
bracket-to-pump fuel hose.
9Making your own marks or notes to ensure
that they can be reconnected the same way
round, unsolder the wires connecting the
pump to the mounting bracket.
10Press the pump out of the rubber sleeve.
Refitting
11Reassembly and refitting are the reverse
of the removal and dismantling procedures,
noting the following points.a)Ensure that the pump is seated correctly
in the sleeve and that the hose is securely
fastened.
b)Ensure that the wires are correctly
reconnected and securely soldered.
c)Always renew the pump mounting
bracket’s sealing ring.
d)Apply a few drops of sealing compound
(i.e. Vauxhall part no. 90485251) to the
threads of the screws, then tighten them
securely, but take care not to distort the
sealing ring.
14Fuel pump relay - renewal
2
The relay is mounted in the engine
compartment relay box (Chapter 12). Where
more than one relay is fitted, the fuel pump
relay is the one with the black base.
15Fuel tank filler pipe - removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1Syphon out any remaining fuel in the tank
into a clean container that is designed for
carrying petrol and is clearly marked as such.
2Raise the bottom edge of the seal
surrounding the filler neck and undo the single
securing screw beneath.
3Chock the front wheels, jack up the rear of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
placed under the body side members.
4Unscrew the single filler pipe mounting bolt
from the underbody, then work along the
length of the pipe, cutting or releasing any
clips or ties securing other pipes or hoses to
it. Releasing their clips, disconnect the filler
and vent hoses from the pipe’s lower end and
the small-bore vent hoses from the unions at
its upper end.
5Having ensured that all components have
been removed or disconnected which mightprevent its removal, manoeuvre the pipe away
from the vehicle’s underside.
6To check the operation of the pipe’s
anti-leak valve, invert the filler pipe and fill the
lower union (now uppermost) with petrol. If
the valve is functioning correctly, no petrol will
leak from the other union. If petrol leaks from
the other union the valve is faulty and the
complete filler pipe must be renewed.
Refitting
7Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following.
a)Check the condition of all hoses and
clips, renewing any components that are
found to be worn or damaged
b)When reconnecting the small-bore vent
hoses to the unions at the pipe’s upper
end, connect the hose from the charcoal
canister to the uppermost union and the
vent hose from the tank itself to the lower
union (see illustration).
c)Replacing any that were cut on removal
use the clips or ties provided to secure
any other pipes or hoses to the filler pipe.
d)Check carefully for signs of leaks on
refilling the tank; if any signs of leakage
are detected, the problem must be
rectified immediately.
16Fuel tank - removal and
refitting
4
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
SOHC models
1The procedure is similar as for models with
carburettors. Refer to Chapter 4A, however
note the following:
a)Depressurise the fuel system (Section 8).
b)On models with C16 NZ and X16 SZ
engines, disconnect the exhaust system
from the manifold.
c)When working on the fuel tank sender
unit, note that there is only one hose to be
disconnected.
Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models 4B•7
15.7 Vent hose connections at fuel tank
filler pipe
A Charcoal canister hose
B Tank vent hose
13.3 Fuel pump - ‘in-tank’, fuel pump
model
A Wiring connector
B Fuel hose clampC Mounting bracket
screws
12.8 Fuel pump clamping sleeve should
rest against rim (arrowed)
Page 161 of 525

d)Disconnect the fuel pump hose and wiring
as described in Section 12.
e)When releasing the tank mounting straps,
note that the fuel filter must either be
moved aside or removed completely,
whichever is most convenient
f)One of the fuel hoses connects to a pipe
in the side of the tank.
DOHC models
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Siphon out any remaining fuel in the tank
through the filler pipe. Siphon the fuel into a
clean metal container that can be sealed.
4Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
placed under the body side members (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
5Open the fuel filler flap, then pull back the
rubber seal to expose the fuel filler pipe
securing screw (see illustration). Remove the
screw.
6Release the fuel tank vent hoses from the
clips on the underbody.
7Support the weight of the fuel tank on a
jack, with an interposed block of wood.
8Unscrew the securing bolts from the tank
mounting straps. Then remove the straps and
lower the tank sufficiently to enable the fuel
hoses, vent hoses and fuel tank sender unit
wiring to be disconnected (see illustration).
9Disconnect the vent hoses and the fuel tank
sender unit wiring. Note the positions of the
vent hoses as an aid to refitting.
10Disconnect the fuel hoses from the tank and
the fuel tank sender unit, making a note of the
hose positions for use when refitting. Be
prepared for fuel spillage, and take adequate fire
precautions. Plug the open ends of the hoses, to
prevent dirt ingress and further fuel loss.
11Lower the fuel tank, and withdraw it from
under the vehicle.
12If the tank contains sediment or water, it
may be cleaned out using two or three rinses
with clean fuel. Shake vigorously using
several changes of fuel, but before doing so,
remove the fuel tank sender unit, as described
in Section 17. This procedure should be
carried out in a well-ventilated area, and it is
vital to take adequate fire precautions - refer
to the “Safety first!” Section at the beginning
of this manual for further details.
Refitting
13Any repairs to the fuel tank should be
carried out by a professional.
14Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that all hoses are reconnected to their correct
locations as noted during removal.
15On completion, fill the fuel tank, then run
the engine and check for leaks. If leakage is
evident, stop the engine immediately, and
rectify the problem without delay.
17Fuel tank sender unit -
removal and refitting
3
Note:Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
SOHC models
1Remove the fuel tank, (refer to Section 16),
if necessary. Note that there is only one hose
connected to the sender unit. This must also
be disconnected from the union on the inside
of the unit before it can be withdrawn
completely from the tank (see illustration).
DOHC models
2Remove the fuel tank, as described in
Section 16.
3Make alignment marks on the sender unit
and the fuel tank so that the sender unit can
be refitted in its original position.
4To remove the sender unit, an improvised
tool must be used which engages with thecut-outs in the sender unit retaining ring. The
Vauxhall special tool KM-673 for this purpose
is shown (see illustration).
5Withdraw the unit carefully, to avoid
bending the float arm.
6Recover the sealing ring.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
8Renew the sealing ring.
9Ensure that the marks made on sender unit
and fuel tank before removal are aligned.
10Refit the fuel tank, (Section 16).
18Fuel flow damper - removal
and refitting
3
Note:Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1The fuel flow damper is located on the fuel
pump bracket under the rear of the vehicle, on
the right-hand side of the spare wheel well or
in front of the fuel tank, depending on model
(see illustration). The damper is positioned in
the fuel feed line between the fuel pump and
the fuel filter, and its purpose is to reduce
pressure fluctuations in the fuel return line,
thus reducing noise levels.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Have a container to hand, to catch the fuel
that will be released as the damper is
removed.
4B•8Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models
16.5 Fuel filler pipe securing screw
(arrowed) - models with semi-trailing arm
rear axles17.1 Fuel level sender unit - models with
semi-independent rear axles
18.1 Fuel flow damper - models with semi-
trailing arm rear axles17.4 Vauxhall special tool KM-673 for
removing fuel level sender units
16.8 Fuel tank mounting - models with
semi-trailing arm rear axles
1 Strap securing bolt 2 Vent hose securing