warning light OPEL VECTRA 1988 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1988, Model line: VECTRA, Model: OPEL VECTRA 1988Pages: 525, PDF Size: 58.26 MB
Page 15 of 525

12
Wiper blades
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 ins. Champion X-4803
Fuses
Rating:
Red . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 A
Blue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 A
Yellow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 A
Green . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 A
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Airbag unit to steering wheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Airbag control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Brackets, passenger airbag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 16
Passenger airbag to bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 6
Steering to column . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Chapter 12
Body electrical systems
Aerial - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Aerial mast, electric - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Airbag - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Airbag contact unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Airbag control unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Airbag unit, drivers side - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
Airbag unit, passengers side - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Anti-theft alarm - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Anti-theft alarm system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . .54
Bracket, passenger airbag unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .60
Brake lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Central door locking components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .46
Check control system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . .21
Cigarette lighter - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Clock - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Courtesy lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Direction indicator/lighting switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .5
Electric door mirror switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Electric window components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Electric window controls - programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Electrical fault-finding - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Exterior lamp bulbs - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Facia panel switches - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Front indicator lamp unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Front foglamp - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Fuses and relays - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Handbrake “on” warning lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . .13
Headlamp aim adjustment motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .26
Headlamp dim-dip system - general, removal and refitting . . . . . . . .28
Headlamp unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Headlamp washer fluid non-return valve - removal and refitting . . . .43Headlamp wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Headlamps - alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Heated front seats - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Horn(s) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Ignition switch and lock cylinder - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .4
Instrument panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Instrument panel components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Interior lamp bulbs - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Interior lamps - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Luggage compartment lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . .11
Number plate lamp - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Oil pressure warning lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .14
Radio/cassette player - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Rear lamp unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Reversing lamp switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 7A
Side repeater lamp - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Speakers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Speedometer cable - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Steering wheel (with airbag) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Sunroof motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Sunroof operating switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Tailgate wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Trip computer components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Wash/wipe switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Washer fluid reservoir - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Washer nozzles - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Washer pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Windscreen wiper motor and linkage - removal and refitting . . . . . . .38
Wiper arms - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Wiper blades - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Wiring diagrams - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
12•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 16 of 525

1General information and
precautions
The electrical system is of 12-volt negative
earth type. Power for the lights and all
electrical accessories is supplied by a
lead/acid type battery, which is charged by
the alternator.
This Chapter covers repair and service
procedures for the various electrical
components not associated with engine.
Information on the battery, alternator and
starter motor can be found in Chapter 5.
It should be noted that, before working on
any component in the electrical system, the
battery negative terminal should first be
disconnected, to prevent the possibility of
electrical short-circuits and/or fires.
Whenever the occasion arises, carefully
check the routing of the wiring harness,
ensuring that it is correctly secured by the
clips or ties provided so that it cannot chafe
against other components. Carefully check
points such as the clutch cable bracket,
clutch housing and harness support bracket,
the inlet manifold, the horn mounting bracket,
the starter motor terminals, and the rear
bumper and number plate lamp.
If evidence is found of the harness having
chafed against other components, repair the
damage and ensure that the harness is
secured or protected so that the problem
cannot occur again.
2Electrical fault-finding -
general information
Note:Refer to the precautions given in “Safety
first!” (at the beginning of this manual) and to
Section 1 of this Chapter before starting work.
The following tests relate to testing of the main
electrical circuits, and should not be used to
test delicate electronic circuits (such as anti-
lock braking systems), particularly where an
electronic control module is used.
A typical electrical circuit consists of an
electrical component, any switches, relays,
motors, fuses, fusible links or circuit breakers
related to that component, and the wiring and
connectors that link the component to boththe battery and the chassis. To help to
pinpoint a problem in an electrical circuit,
wiring diagrams are included at the end of this
Chapter.
Before attempting to diagnose an electrical
fault, first study the appropriate wiring
diagram, to obtain a complete understanding
of the components included in the particular
circuit concerned. The possible sources of a
fault can be narrowed down by noting
whether other components related to the
circuit are operating properly. If several
components or circuits fail at one time, the
problem is likely to be related to a shared fuse
or earth connection.
Electrical problems usually stem from
simple causes, such as loose or corroded
connections, a faulty earth connection, a
blown fuse, a melted fusible link, or a faulty
relay (refer to Section 3 for details of testing
relays). Visually inspect the condition of all
fuses, wires and connections in a problem
circuit before testing the components. Use
the wiring diagrams to determine which
terminal connections will need to be checked,
to pinpoint the trouble-spot.
The basic tools required for electrical fault-
finding include the following:
a)a circuit tester or voltmeter (a 12-volt bulb
with a set of test leads can also be used
for certain tests).
b)a self-powered test light (sometimes
known as a continuity tester).
c)an ohmmeter (to measure resistance).
d)a battery.
e)a set of test leads.
f)a jumper wire, preferably with a circuit
breaker or fuse incorporated, which can
be used to bypass suspect wires or
electrical components.
Before attempting to locate a problem with
test instruments, use the wiring diagram to
determine where to make the connections.
To find the source of an intermittent wiring
fault (usually due to a poor or dirty
connection, or damaged wiring insulation), a
“wiggle” test can be performed on the wiring.
This involves wiggling the wiring by hand, to
see if the fault occurs as the wiring is moved.
It should be possible to narrow down the
source of the fault to a particular section of
wiring. This method of testing can be used in
conjunction with any of the tests described in
the following sub-Sections.
Apart from problems due to poor
connections, two basic types of fault can
occur in an electrical circuit - open-circuit, or
short-circuit.
Open-circuit faults are caused by a break
somewhere in the circuit, which prevents
current from flowing. An open-circuit fault will
prevent a component from working, but will
not cause the relevant circuit fuse to blow.
Short-circuit faults are caused by a “short”
somewhere in the circuit, which allows the
current flowing in the circuit to “escape” along
an alternative route, usually to earth. Short-
circuit faults are normally caused by abreakdown in wiring insulation, which allows a
feed wire to touch either another wire, or an
earthed component such as the bodyshell. A
short-circuit fault will normally cause the
relevant circuit fuse to blow.
Finding an open-circuit
To check for an open-circuit, connect one
lead of a circuit tester or voltmeter to either
the negative battery terminal or a known good
earth.
Connect the other lead to a connector in
the circuit being tested, preferably nearest to
the battery or fuse.
Switch on the circuit, remembering that
some circuits are live only when the ignition
switch is moved to a particular position.
If voltage is present (indicated either by the
tester bulb lighting or a voltmeter reading, as
applicable), this means that the section of the
circuit between the relevant connector and
the battery is problem-free.
Continue to check the remainder of the
circuit in the same fashion.
When a point is reached at which no
voltage is present, the problem must lie
between that point and the previous test point
with voltage. Most problems can be traced to
a broken, corroded or loose connection.
Finding a short-circuit
To check for a short-circuit, first disconnect
the load(s) from the circuit (loads are the
components that draw current from a circuit,
such as bulbs, motors, heating elements, etc.).
Remove the relevant fuse from the circuit,
and connect a circuit tester or voltmeter to the
fuse connections.
Switch on the circuit, remembering that
some circuits are live only when the ignition
switch is moved to a particular position.
If voltage is present (indicated either by the
tester bulb lighting or a voltmeter reading, as
applicable), this means that there is a short-
circuit.
If no voltage is present, but the fuse still
blows with the load(s) connected, this indicates
an internal fault in the load(s).
Finding an earth fault
The battery negative terminal is connected
to “earth” (the metal of the
engine/transmission and the car body), and
most systems are wired so that they only
receive a positive feed. The current returning
through the metal of the car body. This means
that the component mounting and the body
form part of that circuit. Loose or corroded
mountings can therefore cause a range of
electrical faults, ranging from total failure of a
circuit, to a puzzling partial fault. In particular,
lights may shine dimly (especially when
another circuit sharing the same earth point is
in operation). Motors (e.g. wiper motors or the
radiator cooling fan motor) may run slowly,
and the operation of one circuit may have an
affect on another. Note that on many vehicles,
earth straps are used between certain
components, such as the engine/transmission
and the body, usually where there is no metal-
12•2Body electrical systems
Warning: Before carrying out
any work on the electrical
system, read through the
precautions given in “Safety
first!” at the beginning of this manual, and
in Chapter 5.
Caution:If the radio/cassette player fitted
to the vehicle is one with an anti-theft
security code, as the standard unit is, refer
to “Radio/cassette player anti-theft system
- precaution”in the Reference Section of
this manual before disconnecting the
battery.
Page 18 of 525

5Direction indicator/lighting
switch - removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Turn the steering wheel as necessary to
expose the two front steering column shroud
securing screws, which are covered by plastic
caps. Prise out the caps and remove the
screws.
3Remove the three securing screws from the
underside of the lower column shroud, then
remove both the upper and lower shrouds.
4Disconnect the wiring plug from the switch.
5Depress the switch retaining clip, and
withdraw the switch from the housing.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal.
6Wash/wipe switch - removal
and refitting
2
Proceed as described in Section 5.
7Facia panel switches -
removal and refitting
2
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Lighting switch
Removal
2Turn the switch to the “dipped beam on”
position, then insert a small screwdriver or rod
through the hole in the bottom of the switch
knob to depress the knob retaining clip. Pull
the knob from the switch (see illustration).
3Press the two now-exposed switch
securing clips towards the switch spindle,
then pull the switch from the facia and
disconnect the wiring plug (see illustrations).
4Note that the switch assembly cannot be
dismantled, and if any part of the switch is
faulty, the complete assembly must be
renewed.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Push-button switches
Removal
6First check beneath the switch, if there is a
small hole in the facia, insert a slim
screwdriver or metal rod into it. Release the
switch retaining spring clip by pressing it
upwards against the switch, then remove the
switch and disconnect its wiring. If there is no
hole, remove the switch by prising it out of the
facia using a small screwdriver. Lever gently
under the switch’s lower edge (use adhesive
tape or a piece of card to protect the facia’s
finish). Disconnect the switch wiring plug and
withdraw the switch (see illustration).
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Headlamp aim adjustment
switch
8The procedure is as described for push-
button switches.
Hazard warning switch
Removal
9Using a screwdriver, carefully prise the cap
from the switch (see illustration).
10Using a screwdriver with a piece of card
under the blade to avoid damage to the facia
trim, prise the ventilation nozzle from the
facia.
11Prise the switch from the facia and
disconnect the wiring (see illustration).
Refitting
12Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Heater blower motor switch
Removal
13Remove the heater control panel, as
described in Chapter 11.
14Disconnect the wiring plug from the
switch, if not already done.
15Prise the switch out from the rear of the
heater control panel.
Refitting
16Refitting is a reversal of removal, but refer
to Chapter 11, when refitting the heater
control panel.
12•4Body electrical systems
7.2 Using a thin rod to depress the
lightning switch knob retaining clip
7.3B . . . then pull the switch from the facia
7.11 Withdrawing the hazard warning
flasher switch from the facia7.9 Prising the cap from the hazard
warning flasher switch7.6 Prising a push-button switch from the
facia
7.3A Press the switch securing clips
towards the switch spindle . . .
Page 19 of 525

8Electric door mirror switch -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Prise the plastic surround from the door
interior handle.
3Free the trim panel from the top edge of the
door by releasing the securing clips. This can
be done using a screwdriver, but it is
preferable to use a forked tool, to minimise
the possibility of damage to the trim panel and
the clips.
4Note the position of the mirror switch wiring
connector in the bracket at the top of the
door, then separate the two halves of the
connector.
5Prise the switch from the door trim panel,
and feed the wiring through the panel.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the wiring is correctly routed, so as not to
foul the door interior handle mechanism.
9Sunroof operating switch -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Prise the courtesy lamp from the roof trim
panel, and disconnect the wiring.
3Remove the two trim panel securing
screws, and withdraw the trim panel from the
roof, disconnecting the wiring from the
sunroof operating switch.
4Release the securing clips, then pull the
switch from the rear face of the trim panel.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
10Courtesy lamp switch -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Open the door and remove the switch
securing screw.
3Withdraw the switch from the door pillar,
and pull the wiring out sufficiently to prevent it
from springing back into the pillar.4Disconnect the wiring and remove the
switch.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
11Luggage compartment lamp
switch - removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Open the boot lid or tailgate, as applicable,
and remove the switch securing screw.
3Withdraw the switch from the body panel,
and pull the wiring out sufficiently to prevent it
from springing back into the body.
4Disconnect the wiring and remove the
switch.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
12Brake lamp switch - removal
and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the lower trim panel from the
driver’s footwell.
3Disconnect the wiring plug from the brake
lamp switch, then twist the switch
anti-clockwise and remove it from its bracket.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
13Handbrake “on” warning
lamp switch - removal and
refitting
3
For access to the switch, the handbrake
lever must be removed. Removal and refitting
of the switch is described as part of the
handbrake lever removal and refitting
procedure, in Chapter 9.
14Oil pressure warning lamp
switch - removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2The switch is screwed into the oil pump, on
the inlet manifold side of the engine. On 1.4
and 1.6 litre (except C16 NZ2), models the
switch projects at right-angles to the
crankshaft axis, while on C16 NZ2, 1.8 and
2.0 litre models it is parallel to the crankshaft
(see illustration).
3In most cases the switch can be reached
quite easily from above. However, on some
models access will be easier if the front of the
vehicle is jacked up and supported on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
(ensure that the handbrake is securely
applied) and the front right-hand roadwheel is
removed.
4Disconnect the switch wire and use a
spanner to unscrew the switch (see
illustration). As you withdraw the switch,
swiftly plug the hole in the oil pump to
minimise the loss of oil and to prevent the
entry of dirt.
Refitting
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; tighten the switch securely but do
not overtighten it, reconnect its wire, then
check and if necessary top-up the oil level, as
described in Chapter 1. Wash off any spilt oil
and check for leaks when the engine is
restarted.
15Cigarette lighter - removal
and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Slide the ashtray/cigarette lighter assembly
from the facia, then disconnect the wiring and
slide the illumination bulb from the cigarette
lighter.
Body electrical systems 12•5
14.4 Unscrewing the oil pressure warning
lamp switch -
SOHC model (engine removed)14.2 Oil pressure warning lamp switch
(arrowed) viewed from underneath vehicle
- SOHC model
12
Tape the wiring to the door
pillar, to prevent if falling
back into the door pillar.
Alternatively, tie a piece of
string to the wiring to retrieve it.
Page 20 of 525
3To remove the cigarette lighter assembly,
simply pull it from the illumination ring
assembly. If desired, the illumination ring
assembly can be removed, by pulling it from
the housing after depressing the retaining
clips.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
16Clock - removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Using a thin-bladed screwdriver, carefully
prise the clock from the facia panel.
3Disconnect the wiring plugs and withdraw
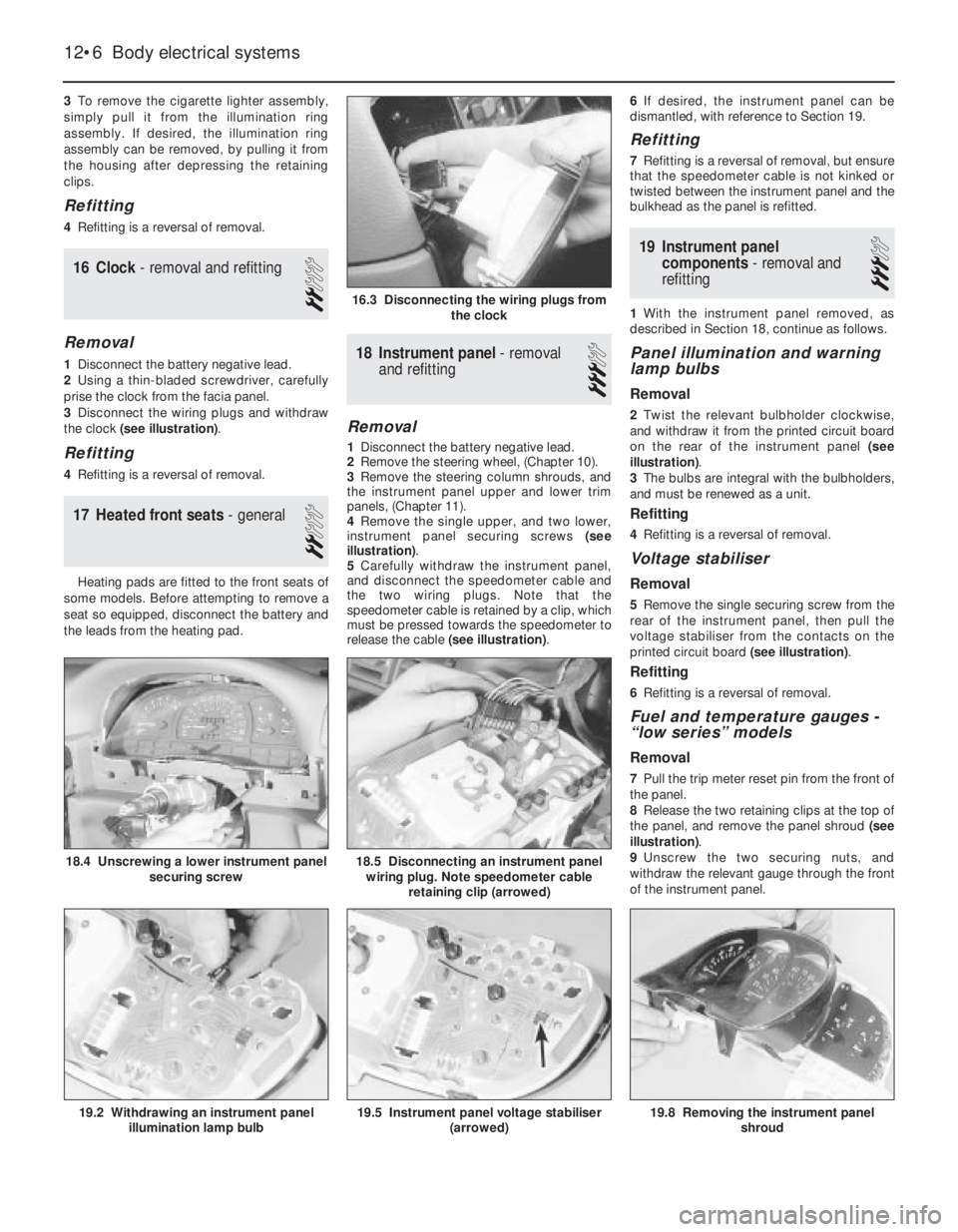
the clock (see illustration).
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
17Heated front seats - general
2
Heating pads are fitted to the front seats of
some models. Before attempting to remove a
seat so equipped, disconnect the battery and
the leads from the heating pad.
18Instrument panel -removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the steering wheel, (Chapter 10).
3Remove the steering column shrouds, and
the instrument panel upper and lower trim
panels, (Chapter 11).
4Remove the single upper, and two lower,
instrument panel securing screws (see
illustration).
5Carefully withdraw the instrument panel,
and disconnect the speedometer cable and
the two wiring plugs. Note that the
speedometer cable is retained by a clip, which
must be pressed towards the speedometer to
release the cable (see illustration).6If desired, the instrument panel can be
dismantled, with reference to Section 19.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the speedometer cable is not kinked or
twisted between the instrument panel and the
bulkhead as the panel is refitted.
19Instrument panel
components - removal and
refitting
3
1With the instrument panel removed, as
described in Section 18, continue as follows.
Panel illumination and warning
lamp bulbs
Removal
2Twist the relevant bulbholder clockwise,
and withdraw it from the printed circuit board
on the rear of the instrument panel (see
illustration).
3The bulbs are integral with the bulbholders,
and must be renewed as a unit.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Voltage stabiliser
Removal
5Remove the single securing screw from the
rear of the instrument panel, then pull the
voltage stabiliser from the contacts on the
printed circuit board (see illustration).
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Fuel and temperature gauges -
“low series” models
Removal
7Pull the trip meter reset pin from the front of
the panel.
8Release the two retaining clips at the top of
the panel, and remove the panel shroud (see
illustration).
9Unscrew the two securing nuts, and
withdraw the relevant gauge through the front
of the instrument panel.
12•6Body electrical systems
16.3 Disconnecting the wiring plugs from
the clock
18.5 Disconnecting an instrument panel
wiring plug. Note speedometer cable
retaining clip (arrowed)
19.8 Removing the instrument panel
shroud19.5 Instrument panel voltage stabiliser
(arrowed)19.2 Withdrawing an instrument panel
illumination lamp bulb
18.4 Unscrewing a lower instrument panel
securing screw
Page 24 of 525

27Headlamps -alignment
2
1Correct alignment of the headlamp beams
is most important, not only to ensure good
vision for the driver, but also to protect other
drivers from being dazzled.
2Accurate alignment should be carried out
using optical beam setting equipment.
3In an emergency, adjustments may be
made by turning the adjustment screws
shown (see illustrations). If an adjustment is
made, the alignment should be checked using
beam setting equipment at the earliest
opportunity.
4All 1992-on models are fitted with the
headlamp aim adjustment system, operated
through the facia-mounted switch (see
illustration).
a)Position ‘0’, is for correct alignment if just
the driving seat is occupied.
b)Position ‘1’, if all seats are occupied.
c)Position ‘2’, if all seats occupied and
luggage.
d)Position ‘3’, for just driver and luggage.
28Headlamp dim-dip system -
general, removal and refitting
3
General
1The system (where fitted) is governed by the
dim-dip control unit mounted either behind
and above the glovebox (early models), or
behind the main fuse panel (later models).
2The control unit uses the oil pressure
warning lamp circuit to ensure that, when theengine is running and the sidelamps are
switched on, reduced current is fed to the
headlamp dipped-beam circuits. This lights
the headlamps with approximately one-sixth
of their normal power so that the vehicle
cannot be driven using sidelamps alone.
3To locate the dim-dip control unit, open the
main fuse panel covering flap and unclip it
from its bottom and top mountings (Section 3).
Then use a torch to see whether the unit is
fastened to the plastic bracket behind the facia
and fuse panel. The unit is usually rectangular,
of black plastic, and can be identified by the
colours of the five wires leading to it (see
applicable wiring diagram).
Removal
4If the unit can be seen, remove the driver’s
side lower facia and footwell trim panels
(Chapter 11), then unscrew the four retaining
screws and lower the plastic bracket until the
control unit can be detached.
5If the unit cannot be seen, remove the
glovebox assembly (Chapter 11). The unit will
be fastened to the underside of the facia top
surface.
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
26Headlamp aim adjustment
motor - removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Remove the headlamp, (Section 25).
2Twist the motor clockwise to release it from
the headlamp, then carefully disconnect the
motor from the balljoint (see illustrations).
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the motor is correctly engaged with the
balljoint.
12•10Body electrical systems
26.2A Headlamp aim adjustment motor
(headlamp removed)
27.4 The headlamp aim adjustment switch
- 1992-on models
27.3B Headlamp alignment adjustment screws - models with
electric aim adjustment
A Vertical adjustment screw B Horizontal adjustment screw27.3A Headlamp alignment adjustment screws - models without
electric aim adjustment
A Vertical adjustment screw B Horizontal adjustment screw
26.2B Headlamp aim adjuster balljoint
(arrowed)
Page 33 of 525
53Anti-theft alarm - general
1Certain models are fitted with an anti-theft
alarm as standard equipment.
2The alarm system is triggered by door,
bonnet and boot lid/tailgate mounted
switches, and by ultrasonic sensors mounted
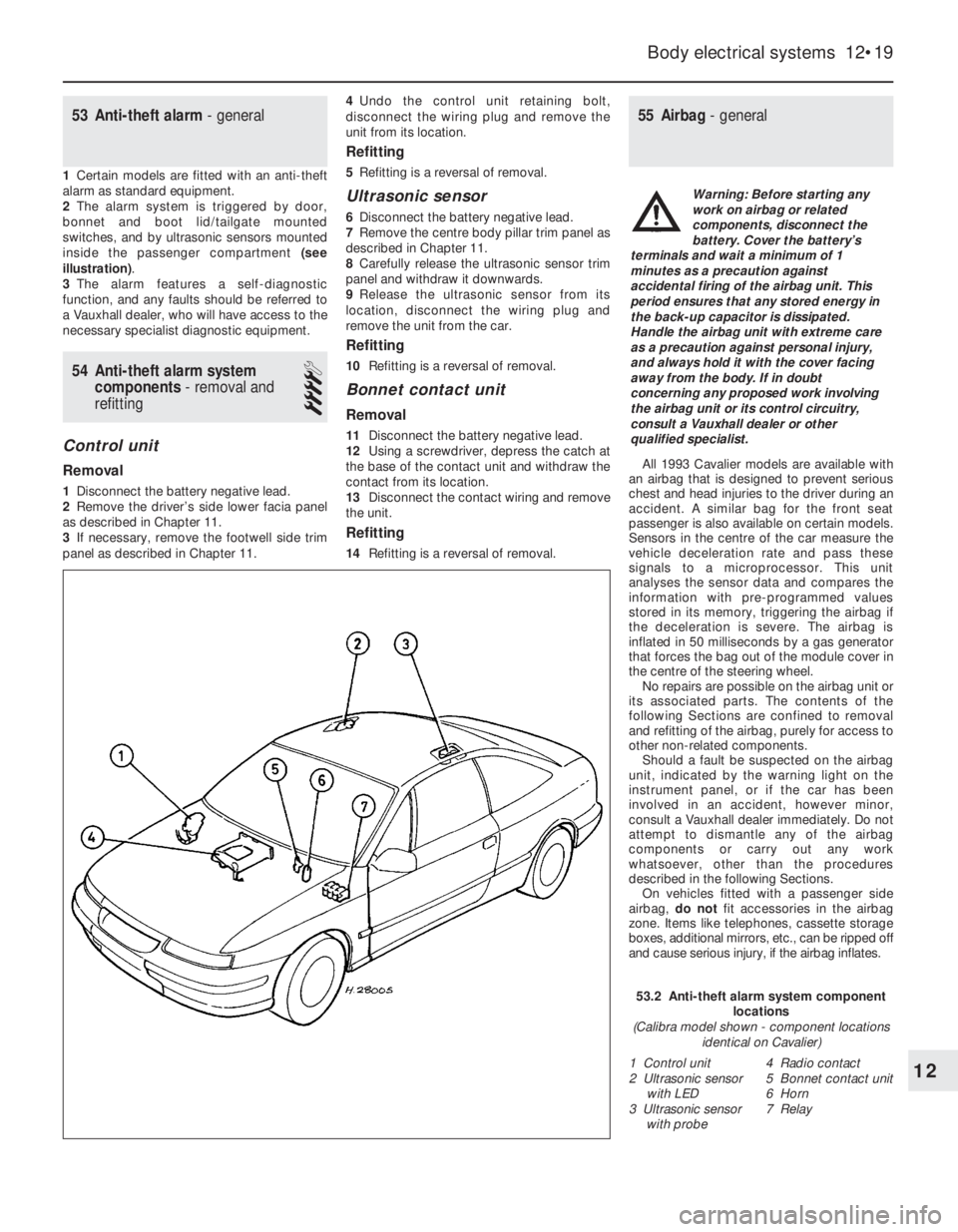
inside the passenger compartment (see
illustration).
3The alarm features a self-diagnostic
function, and any faults should be referred to
a Vauxhall dealer, who will have access to the
necessary specialist diagnostic equipment.
54Anti-theft alarm system
components -removal and
refitting
4
Control unit
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the driver’s side lower facia panel
as described in Chapter 11.
3If necessary, remove the footwell side trim
panel as described in Chapter 11.4Undo the control unit retaining bolt,
disconnect the wiring plug and remove the
unit from its location.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Ultrasonic sensor
6Disconnect the battery negative lead.
7Remove the centre body pillar trim panel as
described in Chapter 11.
8Carefully release the ultrasonic sensor trim
panel and withdraw it downwards.
9Release the ultrasonic sensor from its
location, disconnect the wiring plug and
remove the unit from the car.
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Bonnet contact unit
Removal
11Disconnect the battery negative lead.
12Using a screwdriver, depress the catch at
the base of the contact unit and withdraw the
contact from its location.
13Disconnect the contact wiring and remove
the unit.
Refitting
14Refitting is a reversal of removal.
55Airbag - general
All 1993 Cavalier models are available with
an airbag that is designed to prevent serious
chest and head injuries to the driver during an
accident. A similar bag for the front seat
passenger is also available on certain models.
Sensors in the centre of the car measure the
vehicle deceleration rate and pass these
signals to a microprocessor. This unit
analyses the sensor data and compares the
information with pre-programmed values
stored in its memory, triggering the airbag if
the deceleration is severe. The airbag is
inflated in 50 milliseconds by a gas generator
that forces the bag out of the module cover in
the centre of the steering wheel.
No repairs are possible on the airbag unit or
its associated parts. The contents of the
following Sections are confined to removal
and refitting of the airbag, purely for access to
other non-related components.
Should a fault be suspected on the airbag
unit, indicated by the warning light on the
instrument panel, or if the car has been
involved in an accident, however minor,
consult a Vauxhall dealer immediately. Do not
attempt to dismantle any of the airbag
components or carry out any work
whatsoever, other than the procedures
described in the following Sections.
On vehicles fitted with a passenger side
airbag, do notfit accessories in the airbag
zone. Items like telephones, cassette storage
boxes, additional mirrors, etc., can be ripped off
and cause serious injury, if the airbag inflates.
Body electrical systems 12•19
12
53.2 Anti-theft alarm system component
locations
(Calibra model shown - component locations
identical on Cavalier)
1 Control unit
2 Ultrasonic sensor
with LED
3 Ultrasonic sensor
with probe4 Radio contact
5 Bonnet contact unit
6 Horn
7 Relay
Warning: Before starting any
work on airbag or related
components, disconnect the
battery. Cover the battery’s
terminals and wait a minimum of 1
minutes as a precaution against
accidental firing of the airbag unit. This
period ensures that any stored energy in
the back-up capacitor is dissipated.
Handle the airbag unit with extreme care
as a precaution against personal injury,
and always hold it with the cover facing
away from the body. If in doubt
concerning any proposed work involving
the airbag unit or its control circuitry,
consult a Vauxhall dealer or other
qualified specialist.
Page 35 of 525
4Disconnect the plug connections.
5Unbolt the six M6 nuts from the two side
brackets.
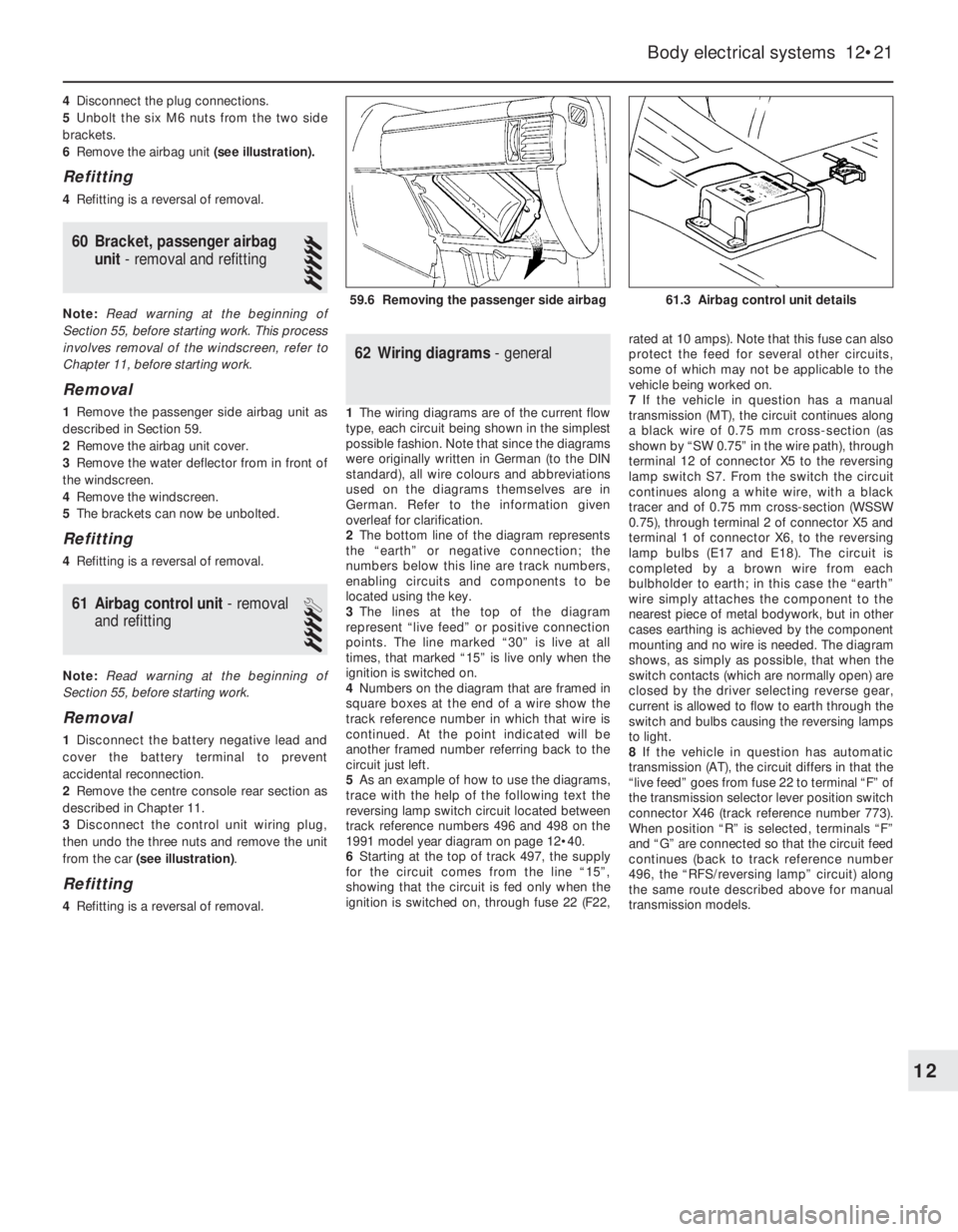
6Remove the airbag unit (see illustration).
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
60Bracket, passenger airbag
unit - removal and refitting
5
Note: Read warning at the beginning of
Section 55, before starting work. This process
involves removal of the windscreen, refer to
Chapter 11, before starting work.
Removal
1Remove the passenger side airbag unit as
described in Section 59.
2Remove the airbag unit cover.
3Remove the water deflector from in front of
the windscreen.
4Remove the windscreen.
5The brackets can now be unbolted.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
61Airbag control unit - removal
and refitting
4
Note: Read warning at the beginning of
Section 55, before starting work.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead and
cover the battery terminal to prevent
accidental reconnection.
2Remove the centre console rear section as
described in Chapter 11.
3Disconnect the control unit wiring plug,
then undo the three nuts and remove the unit
from the car (see illustration).
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
62Wiring diagrams -general
1The wiring diagrams are of the current flow
type, each circuit being shown in the simplest
possible fashion. Note that since the diagrams
were originally written in German (to the DIN
standard), all wire colours and abbreviations
used on the diagrams themselves are in
German. Refer to the information given
overleaf for clarification.
2The bottom line of the diagram represents
the “earth” or negative connection; the
numbers below this line are track numbers,
enabling circuits and components to be
located using the key.
3The lines at the top of the diagram
represent “live feed” or positive connection
points. The line marked “30” is live at all
times, that marked “15” is live only when the
ignition is switched on.
4Numbers on the diagram that are framed in
square boxes at the end of a wire show the
track reference number in which that wire is
continued. At the point indicated will be
another framed number referring back to the
circuit just left.
5As an example of how to use the diagrams,
trace with the help of the following text the
reversing lamp switch circuit located between
track reference numbers 496 and 498 on the
1991 model year diagram on page 12•40.
6Starting at the top of track 497, the supply
for the circuit comes from the line “15”,
showing that the circuit is fed only when the
ignition is switched on, through fuse 22 (F22,rated at 10 amps). Note that this fuse can also
protect the feed for several other circuits,
some of which may not be applicable to the
vehicle being worked on.
7If the vehicle in question has a manual
transmission (MT), the circuit continues along
a black wire of 0.75 mm cross-section (as
shown by “SW 0.75” in the wire path), through
terminal 12 of connector X5 to the reversing
lamp switch S7. From the switch the circuit
continues along a white wire, with a black
tracer and of 0.75 mm cross-section (WSSW
0.75), through terminal 2 of connector X5 and
terminal 1 of connector X6, to the reversing
lamp bulbs (E17 and E18). The circuit is
completed by a brown wire from each
bulbholder to earth; in this case the “earth”
wire simply attaches the component to the
nearest piece of metal bodywork, but in other
cases earthing is achieved by the component
mounting and no wire is needed. The diagram
shows, as simply as possible, that when the
switch contacts (which are normally open) are
closed by the driver selecting reverse gear,
current is allowed to flow to earth through the
switch and bulbs causing the reversing lamps
to light.
8If the vehicle in question has automatic
transmission (AT), the circuit differs in that the
“live feed” goes from fuse 22 to terminal “F” of
the transmission selector lever position switch
connector X46 (track reference number 773).
When position “R” is selected, terminals “F”
and “G” are connected so that the circuit feed
continues (back to track reference number
496, the “RFS/reversing lamp” circuit) along
the same route described above for manual
transmission models.
Body electrical systems 12•21
61.3 Airbag control unit details59.6 Removing the passenger side airbag
12
Page 36 of 525

12•22Body electrical systems
Explanations of abbreviations used in wiring diagrams
ABSAnti-lock braking system
ACAir conditioning
AZVTrailer hitch
ATAutomatic transmission
ATCAutomatic temperature control
BRTrip (on-board) computer
CCCheck control system
CRCCruise control
DDiesel
DSTheft protection
DTTurbo Diesel
DWAAnti-theft warning system
DZMTachometer
EFCElectric folding roof (Convertible)
EKSPinch guard (electric windows)
EMPRadio
EUREuronorm (emission control standard)
engine
EZ + ElPlus ignition system (with self-
diagnosis)
EZVEcotronic
FHElectric windows
GBGreat Britain
HSHeated rear window
HWRear window wiper
HZGHeating
HRLLuggage compartment lampINSInstrument panel
IRLCourtesy lamps
KATCatalytic converter
KBSWiring harness
KVContact breaker distributor
L3.1Bosch Jetronic fuel injection system
LCDLiquid crystal display (LCD)
instruments
LHDLeft-hand drive
4WDFour-wheel-drive
LWRHeadlamp aim adjustment
M1.5Bosch Motronic M1.5 engine
management system
M2.5Bosch Motronic M2.5 engine
management system
MOTMotronic (general)
MTManual gearbox
MULMultec fuel injection system
NNorway
NSFront foglamps
NSLRear foglamps
OELOil level/pressure check system
OPTOptional equipment
PBSLPark and brake shift block
(automatic transmission, selector
lever in position ‘P’)P/NPark/neutral (automatic transmission)
POTPotentiometer
RCRear suspension level control
system
RFSReversing lamps
RHDRight-hand drive
SSweden
SDSunroof
SHHeated seats
SRAHeadlamp washers and wipers
TANKFuel level sender unit
TDTurbo Diesel
TEMPTemperature gauge
TFLDaytime driving lamps
TKSCourtesy lamp (door pillar) switches
TSZITransistorised ignition (inductive-
triggered) system
VGSCarburettor
WEGOdometer frequency/roadspeed
sensor
WHRRear suspension level control
system
WSWarning buzzer
ZVCentral locking
ZYLCylinder
Colour codes
BLBlue
HBLLight blue
BRBrown
GEYellow
GRGrey
GNGreenRTRed
WSWhite
SWBlack
LILilac
VIViolet
Wiring identification
Example: GEWS 1.5
GE -Wire basic colour
WS -Wire tracer colour
1.5 -Wire cross-section in mm
2
Note: Not all items shown are fitted to all models. Refer to Section 62 (Chapter 12) for details of diagram usage.
Page 37 of 525
Wiring diagrams 12•23
12
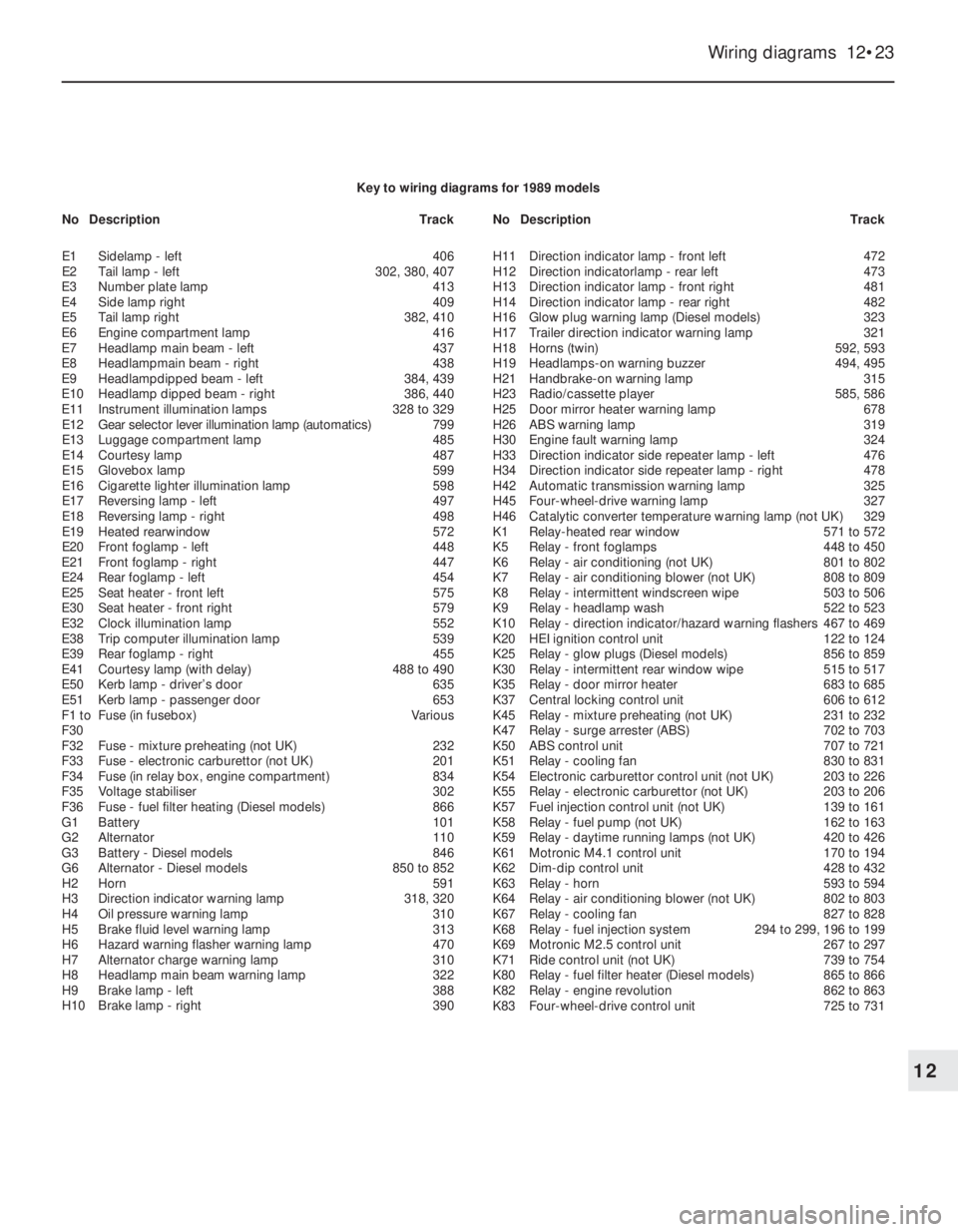
Key to wiring diagrams for 1989 models
E1Sidelamp - left406
E2Tail lamp -left302, 380, 407
E3Number plate lamp413
E4Side lamp right409
E5Tail lamp right382, 410
E6Engine compartment lamp416
E7Headlamp main beam - left437
E8Headlampmain beam - right438
E9Headlampdipped beam - left384, 439
E10Headlamp dipped beam - right386, 440
E11Instrument illumination lamps328 to 329
E12Gear selector lever illumination lamp (automatics)799
E13Luggage compartment lamp485
E14Courtesy lamp487
E15Glovebox lamp599
E16Cigarette lighter illumination lamp598
E17Reversing lamp - left497
E18Reversing lamp - right498
E19Heated rearwindow572
E20Front foglamp -left448
E21Front foglamp - right447
E24Rear foglamp - left454
E25Seat heater -front left575
E30Seat heater - front right579
E32Clock illumination lamp552
E38Trip computer illumination lamp539
E39Rear foglamp - right455
E41Courtesy lamp (with delay)488 to 490
E50Kerb lamp - driver’s door635
E51Kerb lamp - passenger door653
F1 toFuse (in fusebox)Various
F30
F32Fuse - mixture preheating (not UK)232
F33Fuse - electronic carburettor (not UK)201
F34Fuse (in relay box, engine compartment)834
F35Voltage stabiliser302
F36Fuse - fuel filter heating (Diesel models)866
G1Battery101
G2Alternator110
G3Battery - Diesel models846
G6Alternator - Diesel models850 to 852
H2Horn591
H3Direction indicator warning lamp318, 320
H4Oil pressure warning lamp310
H5Brake fluid level warning lamp313
H6Hazard warning flasher warning lamp470
H7Alternator charge warning lamp310
H8Headlamp main beam warning lamp322
H9Brake lamp - left388
H10Brake lamp - right390H11Direction indicator lamp - front left472
H12Direction indicatorlamp - rear left473
H13Direction indicator lamp - front right481
H14Direction indicator lamp - rear right482
H16Glow plug warning lamp (Diesel models)323
H17Trailer direction indicator warning lamp321
H18Horns (twin)592, 593
H19Headlamps-on warning buzzer494, 495
H21Handbrake-on warning lamp315
H23Radio/cassette player585, 586
H25Door mirror heater warning lamp678
H26ABS warning lamp319
H30Engine fault warning lamp324
H33Direction indicator side repeater lamp - left476
H34Direction indicator side repeater lamp - right478
H42Automatic transmission warning lamp325
H45Four-wheel-drive warning lamp327
H46Catalytic converter temperature warning lamp (not UK)329
K1Relay-heated rear window571 to 572
K5Relay - front foglamps448 to 450
K6Relay - air conditioning (not UK)801 to 802
K7Relay - air conditioning blower (not UK)808 to 809
K8Relay - intermittent windscreen wipe503 to 506
K9Relay - headlamp wash522 to 523
K10Relay - direction indicator/hazard warning flashers467 to 469
K20HEI ignition control unit122 to 124
K25Relay - glow plugs (Diesel models)856 to 859
K30Relay - intermittent rear window wipe515 to 517
K35Relay - door mirror heater683 to 685
K37Central locking control unit606 to 612
K45Relay - mixture preheating (not UK)231 to 232
K47Relay - surge arrester (ABS)702 to 703
K50ABS control unit707 to 721
K51Relay - cooling fan830 to 831
K54Electronic carburettor control unit (not UK)203 to 226
K55Relay - electronic carburettor (not UK)203 to 206
K57Fuel injection control unit (not UK)139 to 161
K58Relay -fuel pump (not UK)162 to 163
K59Relay - daytime running lamps (not UK)420 to 426
K61Motronic M4.1 control unit170 to 194
K62Dim-dip control unit428 to 432
K63Relay - horn593 to 594
K64Relay - air conditioning blower (not UK)802 to 803
K67Relay -cooling fan827 to 828
K68Relay -fuel injection system294 to 299, 196 to 199
K69Motronic M2.5 control unit267 to 297
K71Ride control unit (not UK)739 to 754
K80Relay -fuel filter heater (Diesel models)865 to 866
K82Relay - engine revolution862 to 863
K83Four-wheel-drive control unit725 to 731 NoDescriptionTrackNoDescriptionTrack