throttle PONTIAC FIERO 1988 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 1988, Model line: FIERO, Model: PONTIAC FIERO 1988Pages: 1825, PDF Size: 99.44 MB
Page 16 of 1825
- -
GENERAL INFORMATION OA-13
LIST OF AUTOMOTIVE ABBREVIATIONS
WHICH MAY
BE USED IN THIS MANUAL
A-6 - Axial 6 Cyl. A C Compressor AIC - Air Conditioning
ACC - Auto'matic Climate Control
EMF
- Electromotive Force PAIR - Pulse Air Injection Reaction System
EMR - Electronic Module Retard
P B - Power Brakes
EOS - Exhaust Oxygen Sensor
PCV - Positive Crankcase Ventilation
ESC - Electronic Spark Control
PECV - Power Enrichment Control Valve
APT
- Adjustable Part Throttle
AT - Automatic Transmission
ATC - Automatic Temperature Control
ATDC
- After Top Dead Center
FMVSS
- Federal Motor Vehicle Safety BAR0 - Barometric Absolute Pressure Sensor
Ft. Lb. - Foot Pounds (Torque)
Bat. + - Positive Terminal FWD - Front Wheel Drive
- Four Wheel Drive
BHP - Brake Horsepower 4 x 4 - Four Wheel Drive
BP - Back Pressure
BTDC - Before Top Dead Center
HD - Heavy Duty HE1 - High Energy Ignition
Cat. Conv. - Catalytic Converter
CC - Catalytic Converter
- Cubic Centimeter - Converter Clutch
CCC - Computer Command Control
HVM
- Heater-Vent-Module
IAC
- ldle Air Control CCOT - Cycling Clutch (Orifice) Tube IC - Integrated Circuit CCP - Controlled Canister Purge
ID - Identification
C.E. - Check Engine - Inside Diameter
CEAB - Cold Engine Airbleed ILC - Idle Load Compensator
CEMF - Counter Electromotive Force I/P - Instrument Panel
CID - Cubic Inch Displacement ISC - Idle Speed Control CLOOp - Closed Loop
CLCC - Closed Loop Carburetor Control km - Kilometers
CP
- Canister Purge kmiL - Kilometers Liter (mpg) Cu. In. - Cubic Inch kPa - Kilopascals
CV - Constant Velocity
Cyl.
- Cylinder(s)
L-4 - Four Cylinder In-Line (Engine)
DBB - Dual Bed Bead L-6 - Six Cylinder In-Line (Engine)
DBM - Dual Bed Monolith
LF - Left Front DEFl - Digital Electronic Fuel Injection LR - Left Rear DFI - Digital Fuel Injection
Diff. - Differential Man. Vac. - Manifold Vacuum Distr. - Distributor MAP - Manifold Absolute Pressure
EAC
- Electric Air Control Valve
EAS - Electric Air Switching Valve MPG - Miles Per Gallon
ECC - Electronic Comfort Control
MPH - Miles Per Hour
ECM - Electronic Control Module MT - Manual Transmission
N.m - Newton Metres (Torque)
Emission Control
Fig. 014-15 -- Common Abbreviations
Page 18 of 1825

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION OB-1
SECTION OB
NTENANCE AND LUBR
CONTENTS
Maintenance Schedule, Gasoline .............................................. OB-l
Maintenance Schedules I and 11 .............................................. OB-2
Owner Inspections
......................................................... OB-3
Recommended Fluids and Lubricants ......................................... OB-6
PASSENGER CAR MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
VEHICLES
WITH GASOLINE ENGINE
NORMAL CAR USE ITEM 4
The maintenance services contained in Schedules I Carburetor or Throttle Body Mounting Bolt
and 11 are based on the assumption that your car will be Torque* used as designed:
Check torque of mounting bolts and/or nuts. @ To carry passengers and cargo within the limits
shown on the Tire Placard located on the edge of the ITEM 5 driver's door.
@ On reasonable road surfaces within legal driving Engine Idle Speed Adjustment*
limits. (Engines
without Idle Speed Control or Idle Air
Control) - Adjust to specifications shown on the under- @ On unleaded gasoline.
hood label. If no specifications are shown on the label, no
adjustment is necessary. Calibrated test equipment must
EXPLANATION OF SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE be used. SERVICES
The services listed in Maintenance Scheduies I and ITEM 6
11 are further explained below. When the following main- ~i~~ and wheel aotation tenance services are performed, make sure all parts are
replaced and all necessary repairs are done before driving To equalize wear and obtain maximum tire life,
your car. Be sure to use the proper fluid and lubricants as rotate in accordance with patterns shown in Owner's
shown in Figure OB-2. Manual.
ITEM 1
Engine Oil and Oil Filter Change*
ALWAYS USE SFICC OR SF/CD ENERGY CON-
SERVING OILS OF PROPER VISCOSITY
- Also.
always change oil and filter as soon as possible after
driving in a dust storm. See your Owner's Manual for
further details.
ITEM 2
Chassis Lubrication
Lubricate all grease fittings in suspension and steer-
ing linkage. Lubricate
transmissionltransaxle shift
linkage, parking brake cable guides, underbody contact
points and linkage. Also lubricate clutch cross shaft lever
every
30,000 miles (50 000 km) on rear-wheel-drive cars
only.
ITEM 3
Carburetor Choke and Hoses*
If your car is equipped with a carburetor, verify that
choke and vacuum break work properly and are within
specifications. Correct any binding caused by damage or
gum on the choke shaft. Inspect hoses for proper hookup,
cracks, chafing or decay. Correct as necessary.
Vacuum or A.I.R. Pump Drive Belt Inspection*
When a separate belt is used to drive the vacuum or
A.I.R.
pump, inspect it for cracks, fraying, wear and
proper tension. Adjust or replace as needed.
ITEM 8
Cooling System Service*
Drain, flush and refill system with new coolant. See
your Owner's Manual
for further details.
ITEM 9
Wheel Bearing Repack (Rear-Wheel-Drive Cars
Only Except Corvette)
Clean and repack front wheel bearings at each brake
relining or 15,000 miles
(25 000 km), whichever comes
first, when car is used in such service as police, taxi or
door-to-door delivery. If you do not use your car in such
service, clean and repack bearings at each brake relining
or 30,000 miles
(50 000 km), whichever comes first.
Corvette models do not require wheel bearing repack.
Page 22 of 1825

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION OB-5
Throttle linkage inspection -- Inspect for inter-
ference, binding, damaged or missing parts.
Engine drive belts inspection - Inspect all
belts for cracks, fraying and wear. Adjust or replace as
needed.
Rear axle service (if equipped) - Check gear
lubricant level and add if needed. For cars equipped with a
limited slip rear axle, fluid does not require changing
(except Caprice and Corvette
- change fluid and required
additive at first
7,500 miles (12 500 km). See your
Owner's Manual or "Recommended Fluids
& Lubricants
Chart" in this section.
IF YOU USE YOUR GAR TO PULL A TRAILER,
CHANGE GEAR LUBRICANT EVERY 7,500 MILES
(12 500 KM).
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Power antenna - Clean and then lubricate power
antenna mast. The proper lubricant as shown in Figure
OB-2 should be used.
AT LEAST ONCE A YEAR
Lap and shoulder belts condition and opera-
tion
- Inspect belt system, including webbing, buckles,
latch plates, retractors, guide loops and anchors.
Moveable head restraint operation - On cars
with moveable restraints, make sure restraints stay in the
desired position. (See adjustment instructions in your
Owner's Manual.)
Seatback latch and recliner operation on
cars equipped
with recliner seat --- Be sure seat-
backs latch on those cars with folding seats using mechan-
ical latches. Make sure the recliner is holding by pushing
and pulling on the top of the
seatback while it is reclined.
See your Owner's Manual for seat operating information.
Spare tire and jack storage- Be alert to rattles
in rear of car. Make sure the space tire, all jacking equip-
ment, any tire inflator and any covers or doors are securely
stowed at all times. Oil jack ratchet or screw mechanism
after each use.
Key lock service - Lubricate key lock cylinder at
least annually.
Body lubrication service - Lubricate all body
door hinges including the tailgate or hatchback lid (if
equipped). Also lubricate the body hood, fuel door and
rear compartment hinges and latches including interior
glove box and counsel doors, and any folding seat
hardware.
"Fansmissionltransaxle neutral or clutch
starl switch operation
CAUnON: Before pedorming the follow-
ing safety switch check, be sure to have
enough room around the car. Then, firmly
apply both the parking brake (see your
Owner's Manual for procedure) and the
regular brakes. Do not use the accelerator pedal.
If the engine
starls, be ready to turn
off the ignition promptly. Take these pre-
cautions because the car could move
without warning and possibly cause per-
sonal injury or properly damage. On auto-
matic transmissionltransaxle cars, try to
starl the engine in each gear. The starler
should crank only in "Park" or "Neutral."
On manual transmissionltransaxle cars,
place the
shiR lever in "Neutral," push the
clutch halfway and try to starl. The starler
should crank only when the clutch is fully
depressed.
Steering column lock operation
- While
parked, try to turn key to "Lock" in each gear range. The
key should turn to "Lock" only when gear is in "Park" on
automatic or "Reverse" on manual
transmissionltransax-
le. On cars with key release lever, try to turn key toULock"
without depressing the lever. The key should turn to
"Lock" only with the key lever depressed. On all vehicles,
the key should come out only in "Lock."
Parking brake and transmissionltransaxle
"Park" mechanism operation
CAUT1ON:Before checking the holding
ability of the parking brake and automatic
transmissionltransaxle "Park" mecha-
nism, park on a fairly steep hill with
enough room for movement in the down-
hill direction. To reduce the risk of person-
al injury or property damage, be prepared
to apply the regular brakes promptly if the
car begins to move.
To check the parking brake, with the engine running and
transmission/transaxle in "Neutral." slowly remove foot
pressure from the regular brake pedal (until the car is held
by only the parking brake).
To check the automatic transmissionltransaxle "Park"
mechanism holding ability, release all brakes after shift-
ing the transmissionltransaxle to "Park."
ljnderbody flushing - At least every spring,
tlush from the underbody with plain water any corrosive
materials used for ice and snow removal and dust control.
Take care to thoroughly clean any areas where mud and
other debris can collect.
Sediment packed in closed areas
of the vehicle should be loosened before being flushed.
Engine cooling system service - Inspect
coolant and freeze protection. If dirty or rusty, drain, flush
and refill with new coolant. Keep coolant
at the proper
mixture as specified in your Owner's Manual. This pro-
vides proper freeze protection. corrosion inhibitor level
and engine operating temperature. Inspect hoses and re-
place if cracked. swollen or deteriorated. Tighten hose
clamps. Clean outside of radiator and air conditioning
condensor. Wash radiator filler cap and neck.
To help
ensure proper operation. a pressure test of both the cooling
system and cap is also recommended. (See maintenance
schedule charts in Figure
OB-l for the recommended
coolant change interval.)
Page 47 of 1825
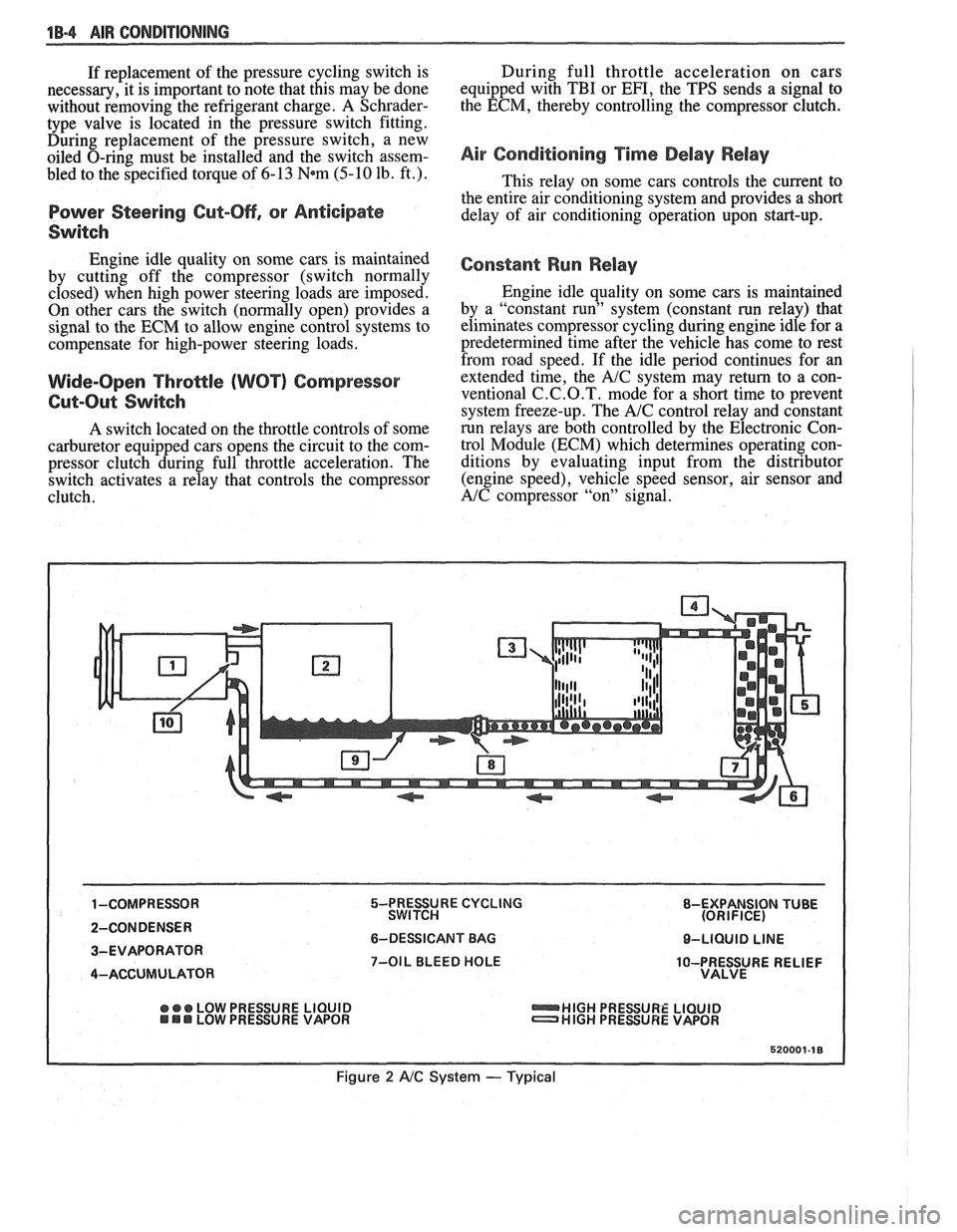
18-4 AIR CONDITIONING
If replacement of the pressure cycling switch is
necessary, it is important to note that this may be done
without removing the refrigerant charge.
A Schrader-
type valve is located in the pressure switch fitting.
During replacement of the pressure switch, a new
oiled O-ring must be installed and the switch assem-
bled to the specified torque of
6- 13 N*m (5- 10 lb. ft.).
Power Steering Gut-OH, or Anticipate
Switch
Engine idle quality on some cars is maintained
by cutting off the compressor (switch normally
closed) when high power steering loads are imposed.
On other cars the switch (normally open) provides a
signal to the ECM to allow engine control systems to
compensate for high-power steering loads.
Wide-Open Tkroale (WOT) Compressor
Cut-Out
Switch
A switch located on the throttle corltrols of some
carburetor equipped cars opens the circuit to the com-
pressor clutch during full throttle acceleration. The
switch activates a relay that controls the compressor
clutch. During full throttle acceleration
on cars
equipped with TBI or
Em, the TPS sends a signal to
the ECM, thereby controlling the compressor clutch.
Air Conditioning Time Delay Relay
This relay on some cars controls the current to
the entire air conditioning system and provides a short
delay of air conditioning operation upon start-up.
Constant Run Relay
Engine idle quality on some cars is maintained
by a "constant run" system (constant run relay) that
eliminates compressor cycling during engine idle for a
predetermined time after the vehicle has come to rest
from road speed.
If the idle period continues for an
extended time, the
A/C system may return to a con-
ventional C.C.O.T. mode for a short time to prevent
system freeze-up. The
A/C control relay and constant
run relays are both controlled by the Electronic Con-
trol Module (ECM) which determines operating con-
ditions by evaluating input from the distributor
(engine speed), vehicle speed sensor, air sensor and
A/C compressor "on" signal.
5-PRESSURE CYCLING 8-EXPANSION TUBE
SWITCH (ORIFICE)
6-DESSICANT BAG O-LIQUID LINE
7-OIL BLEED HOLE
10-PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
@ ee LOW PRESSURE LIQUID HIGH PRESSURE LIQUID LOW PRESURE VAPOR HIGH PRESSURE VAPOR
Figure 2 A/C System - Typical
Page 257 of 1825

481-4 REAR AXLE
Gear Noise
Gear noise (whine) is audible from 20 to 55 mph
under four driving conditions:
1. Light Acceleration - Accelerate slowly.
2. Road Load
- Car
driving load or constant speed.
3. Float - Using enough throttle to keep the car from
driving the engine
- car slows down gradually but
engine still pulls slightly.
4. Coast - Throttle closed and car in gear.
Bearing Noise
Bad bearings generally produce more of a rough
growl or grating sound, rather than the whine typical
of gear noise. Bearing noise frequently "wow-wows" at
bearing rpm, indicating a defective pinion or rear axle
case side bearing. This noise could easily be confused
with rear wheel bearing noise. Inspect and replace as
required.
Rear Wheel Bearing Noise
A rough rear wheel bearing produces a noise
which continues with car coasting at low speed and
transmission in neutral. Noise may diminish some by
gentle braking. With rear wheels jacked up, spin rear
wheels by hand while listening at hubs for evidence of
rough (noisy) wheel bearing.
Knock At Low Speeds
Low speed knock can be caused by worn
universal joints or a side gear hub counterbore in a case
that has worn oversize. Inspect and replace universal
joint or case and side gear as required.
Backlash Clunk
Excessive clunk with acceleration and deceleration
is caused by worn differential pinion gear shaft, excessive
clearance between axle shaft and side gear splines, exces-
sive clearance between side gear hub and counterbore in
case, worn pinion and side gear teeth, worn thrust washers
and excessive drive pinion and ring gear backlash. Re-
move worn parts and replace as required, selecting close
fitting parts when possible. Adjust pinion and ring gear
backlash.
DIAGNOSIS
1. Noise
is the same in "Light Acceleration" or
"Coast".
a. Road noise.
b. Tire noise.
c. Front wheel bearing noise.
d. Rear axle bearing noise.
2. Noise changes on a different type of road.
a. Road noise.
b. Tire noise.
3. Noise tone lowers as car speed is lowered.
a. Tire noise.
b. Front
wheel bearings and rear axle bearings.
c. Gear noise.
4. Similar noise is produced with car standing and
driving. a.
Engine noise.
b. Transmission noise.
c. Exhaust noise.
5. Vibration.
a. Rough rear axle bearing.
b. Unbalanced or damaged propeller shaft.
c. Tire unbalance.
d. Worn universal joint in propeller shaft.
e. Mis-indexed propeller shaft at pinion
flange.
f. Pinion flange runout too great.
6. A knock or click approximately every two
revolutions of the rear wheel.
a. A rear axle bearing.
b. Worn case.
7. Noise most pronounced on turns.
a. Rear axle side gear and pinion noise,
differential gear noise.
b. Axle bearings.
8. A continuous low pitch whirring or scraping
noise starting at relatively low speed.
a. All bearing noise.
9. Drive noise, coast noise or float noise.
a. Ring
and pinion gear noise.
b. Front
pinion bearing noise, coast or drive.
c. Axle bearing noise.
10. Clunk
on
acceleration or deceleration.
a. Worn
rear axle pinion shaft splines.
b. Side
gear hub counterbore in case worn
oversize.
c. Worn U-joints.
d. Excessive transmission backlash.
e. Worn axle shaft splines.
11. Chatter on turns.
a. Wrong
lube in rear axle.
b. Clutch
cone worn or spalled.
12. Clunk
or knock on rough road operation.
a. Worn suspension bushings.
PRE-REPAIR INVESTIGATION AND TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
A carefull diagnosis of the rear axle prior to
disassembly will often reveal valuable information as to
the extent and type of repairs or adjustments necessary.
Since frequent causes of axle noises are improper
backlash, pinion bearing pre-load, or side bearing
pre-load, or a combination, a few simple adjustments
may be all that are necessary to correct a problem.
Before disassembling the rear axle, the following
checks should be made with the results recorded and
analyzed: 1) Backlash;
2) Total Assembly Preload; 3)
Tooth Contact Pattern Test; 4) Fluid Level; and 5)
Fluid Contamination.
If axle shaft end play is excessive then check
bearings, retainer, and bolts securing backing plate.
The axle bearings could be worn and need replacement.
The four bolts or nuts securing the brake backing plate
may be loose, stripped, or missing. If the inner bearing
retainer worked loose it must be replaced.
Use care at all times to keep dirt and other foreign
matter, such as grinder dust, soot or sand, away from
differential to prevent possibility of subsequent failure.
Page 276 of 1825

REAR AXLE 4B-3
Noise which originates in other places cannot be
corrected by adjustment or replacement of parts in the
differential. It should also be remembered that rear
axle gears, like any other mechanical device, are not
absolutely quiet and should be accepted as being
commercially quiet unless some abnormal noise is
present.
To make a systematic check for axle noise under
standard conditions, observe the following:
1. Select a level smooth asphalt road to reduce tire
noise and body drumming.
2. Check rear axle lubricant to assure correct level,
then drive car far enough to thoroughly warm up
rear axle lubricant.
3. Note speed and RPM at which noise occurs. Then
stop car and with automatic transmission in neutral,
run engine slowly up and down through engine speeds, corresponding to car speed at which noise
was most pronounced, to determine if it is caused by
exhaust, muffler roar or other engine conditions.
4. Tire noise changes with different road surfaces,
but rear axle noise does not. Temporarily
inflating all tires to approximately 50 pounds
pressure for
test purposes only will materially
alter noise caused by tires, but will not affect noise
caused by rear axle. Rear axle noise usually stops
when coasting at speeds under 30 miles per hour;
however, tire noise continues, but with lower
tone, as car speed is reduced. Rear axle noise
usually changes when comparing acceleration
and coast, but tire noise remains about the same.
Distinguish between tire noise and rear axle noise
by noting if noise varies with various speeds or
sudden acceleration and deceleration; exhaust
and axle noise show variations under these
conditions while tire noise remains constant and
is more pronounced at speeds of 20 to 30 miles
per hour. Further check for tire noise by driving
car over smooth pavements or dirt roads (not
gravel) with tires at normal pressure. If noise is
caused by tires, it will noticeably change or
disappear and reappear with changes in road
surface.
5. Loose or rough front wheel bearings will cause
noise which may be confused with rear axle
noises; however, front wheel bearing noise does
not change when comparing drive and coast.
Light application of brakes while holding car
speed steady will often cause wheel bearing noise
to diminish, as this takes some weight off the
bearing. Front wheel bearings may be easily
checked for noise by jacking up the wheels and
spinning them, also by shaking wheels to
determine if bearings are loose.
6. Rear suspension rubber bushings and spring
insulators dampen out rear axle noise when
correctly installed. Check to see that no metallic
contact exists between the spring and spring
opening in frame or between upper and lower
control arm bushings and frame or axle housing
brackets.
Metal-to-metal contact at those points
may result in telegraphing road noise and normal axle
noise which would not be objectionable if
dampened by bushings.
AXLE NOISES
Gear Noise
After the noise has been determined as being in
the
axle by following the above appraisal procedure,
the type of axle noise should be determined to aid in
maki~~g repairs if necessary.
Gear noise (whine) is audible from 20 to
55 mph
under four driving conditions:
1. Drive - Acceleration or heavy pull.
2. Road Load - Car driving load or constant speed.
3. Float
- Using
enough throttle to keep the car from
driving the engine
- car slows down gradually but
engine still pulls slightly.
4. Coast
- Throttle closed and car in gear. Gear
noise most frequently has periods where noise is
more prominent, usually 30 to 40 mph and 50 to
55 mph.
Bearing Noise
Bad bearings generally produce more of a rough
growl or grating sound, rather than the whine typical
of gear noise. Bearing noise frequently "wow-wows" at
bearing rpm, indicating a defective pinion or rear axle
case side bearing. This noise could easily be confused
with rear wheel bearing noise. Inspect and replace as
required.
Rear Wheel Bearing Noise
A rough rear wheel bearing produces a noise
which continues with car coasting at low speed and
transmission in neutral. Noise may diminish some by
gentle braking. With rear wheels jacked up, spin rear
wheels by hand while listening at hubs for evidence of
rough (noisy) wheel bearing.
I(noclc At Low Speeds
Low speed knock can be caused by worn
universal joints or a side gear hub counterbore in a case
that has worn oversize. Inspect and replace universal
joint or case and side gear as required.
Baclclash Clunk
Excessive clunk with acceleration and
deceleration is caused by worn differential pinion shaft,
excessive clearance between axle shaft and side gear
splines, excessive clearance between side gear hub and
counterbore in case worn pinion and side gear teeth,
worn thrust washers and excessive drive pinion and
rear gear backlash. Remove worn parts and replace as
required, selecting close fitting parts when possible.
Adjust pinion and ring gear backlash.
REAR AXLE STANDARD AND LIMITED-SLIP
1. Noise is the same in "Drive" or "Coast".
a. Road noise.
b. Tire noise.
c. Front wheel bearing noise.
Page 290 of 1825

REAR AXLE 48-1 7
approached. No further tightening should be
attempted until the pre-load has been checked.
7. Check pre-load by using an inch pound torque
wrench.
NOTICE: After pre-load has been checked, final
tightening should be done very carefully. For
example, if when checking, pre-load was found to
be 0.6
N-m (5 lbs. in.), any additional tightening
of the pinion nut can add many additional pound
inch of torque. Therefore, the pinion nut should be
further tightened only a little at a time and the
pre-load should be checked after each slight
amount of tightening. Exceeding pre-load
specifications will compress the collapsible spacer
too far and require the installation of a new
collapsible spacer.
While observing the preceeding note, carefully set
pre-load at 2.7 to 3.6
N-m (24 to 32 1b.in.) on new
bearings or 1.0 to 1.4
N m (8 to 12 1b.in.) on used
bearings.
8. Rotate pinion several times to assure that
bearings have been seated. Check pre-load again.
If pre-load has been reduced by rotating pinion,
reset pre-load to specifications.
Rear Axle Backlash Adjustment
1. Install rear axle case into carrier, using shims as
determined by the side bearing pre-load
adjustment.
2. Rotate rear axle case several times to seat
bearings, then mount dial indicator. Use a small
button on the indicator stem so that contact can
be made near heel end of tooth. Set dial indicator
so that stem is in line as nearly as possible with
gear rotation perpendicular to tooth angle for
accurate backlash reading.
3. Check backlash at three or four points around
ring gear. Lash must not vary over
.05mm (.002")
around ring gear. Pinion must be held stationary
when checking backlash. If variation is over
.05mm (.002") check for burrs, uneven bolting
conditions or distorted case flange and make
corrections as necessary.
4. Backlash at the point of minimum lash should be
between .13 and
.23mm (.005" and ,009") for all
new gears.
5. If backlash is not within specifications, correct by
increasing thickness of one shim and decreasing
thickness of other shim the same amount. This
will maintain correct rear axle side bearing
pre-load.
For each
.03mm (.001") change in backlash
desired, transfer
.05mm (.002") in shim
thickness. To decrease backlash
.03mm (.00lU),
decrease thickness of right shim .05mm (.002")
and increase thickness of left shim .05mm (.
002 "). To increase backlash .05mm (.002 ")
increase thickness of right shim .10mm (.004")
and decrease thickness of left shim .10mm (.
004"). 6.
When backlash is correctly adjusted, remove both
bearing caps and both shim packs.
Keep packs in their respective position, right or
left side.
Select a shim
.10mm (.004") thicker than the one
removed from the left side, then insert left side
shim pack between the spacer and the left bearing
race. Loosely install bearing cap.
7. Select a shim
.10mm (.004") thicker than the one
removed from right side and insert between the
spacer and the right bearing race. It will be
necessary to drive the right shim into position
(Fig. 614).
8. Torque to 75 Nem (55 1b.ft.).
9. Recheck backlash
and correct if necessary.
10. Install axles (See Rear Axle Installation).
11.
Use sealant 1052366 or cover gasket
only.
Install cover and torque cover bolts to 27
N-m (20 1b.ft.).
12. Fill rear axle to proper level with the specified
lubricant. Refer to specifications.
LIMITED SLIP REAR AXLE (GONE TYPE)
The cone-type limited-slip differential has several
definite operating characteristics. An understanding of
these characteristics is necessary as an aid to diagnosis.
The clutch energizing force comes from the
thrust side of the gears. Consequently, a free spinning
wheel may not have enough resistance to drive torque
to apply the clutch cones. If this occurs, apply the
parking brake a few notches which will provide enough
resistance to energize the clutch cones.
Energizing the clutch cones is independent of
acceleration; therefore, a very slow application of the
throttle on starting is recommended to provide
maximum traction by preventing "break away" of
either rear wheel.
Improper operation is generally indicated by cone
slippage or grabbing. Sometimes this produces a
chatter or whirring sound. However, these sounds do
not always indicate failure as they could be produced
from a lack of proper lubrication. For example, under
certain conditions where one wheel is on
a very slippery
surface and the other on dry pavement, wheel spin can
occur if over acceleration is attempted. Continued
spinning may cause audible noise, such as a whirring
sound, due to the cones lacking sufficient lubricant.
This does not necessarily indicate failure of the unit.
During regular operation (straight ahead driving)
when both wheels rotate at equal speeds, there is an
approximately equal driving force delivered to each
wheel. When cornering, the inside wheel delivers extra
driving force causing slippage in both clutch cones.
Consequently, the operational life of the limited slip
unit is dependent upon equal rotation of both wheels
during straight ahead operation. If wheel rotation for
both rear wheels is not equal during straight ahead
operation, the limited-slip unit will constantly be
functioning as if the vehicle were cornering. This will
impose constant slippage on the clutch cones and will
eventually lead to abnormal wear on the clutch cones.
Therefore, it is important that there be no excessive
differences in the rear wheel tire sizes, air pressures, or
Page 346 of 1825

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION 6-1
SECTION 6
NE GENERAL NFORMAT
Description ............................................................... 6 TBI ...................................... .. ...... 6E2 ................ Engine Mechanical Multi Port Fuel Injection (MPFI) 6E3 -
............................................... 2.8L V-6 ....................................................... 6A2 Exhaust Systems 6F
5.OL V-8 ......................................................... 6A3 ~~~~~~l ~~f~~~~ti~~ ..................................... 6-2
............................ Engine Cooling ...................................................... 6B Engine Performance Diagnosis 6-3 ............................. Engine Fuel 6C Engine Mechanical Diagnosis
6-3 ........................................................... ................................... Engine Knock Diagnosis 6-4
Engine Electrical ................................................... 6D Compression Test ...................................... ... 6-5
................... Driveability and Emission Controls ...................... 6E Oil Leak Detection .. ..................... 6-5
ALL NEW GENERAL MOTORS VEHICLES ARE CERTIFIED BY THE UNITED STATES
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY AS CONFORMING TO THE REQUIREMENTS OF
THE REGULATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF AIR POLLUTION FROM NEW MOTOR VEHICLES.
THlS CERTIFICATION IS CONTINGENT ON CERTAIN ADJUSTMENTS BEING SET TO
FACTORY STANDARDS. IN MOST CASES, THESE ADJUSTMENT POINTS EITHER HAVE
BEEN PERMANENTLY SEALED AND/OR MADE INACCESSIBLE TO PREVENT
INDISCRIMINATE OR ROUTINE ADJUSTMENT IN THE FIELD. FOR
THlS REASON, THE
FACTORY PROCEDURE FOR TEMPORARILY REMOVING PLUGS, CAPS, ETC., FOR
PURPOSES OF SERVICING THE PRODUCT MUST BE STRICTLY FOLLOWED AND,
WHEREVER PRACTICABLE, RETURNED TO THE ORIGINAL INTENT OF THE DESIGN.
DESCRIPTION OF: SECTION 6
SECTION 6A - ENGINE MECHANICAL used for each carburetor. TBI units are described in
This section general contains information on the Section 6E.
mechanical parts of the engine, such as block,
crankshaft, pistons, valve train, and camshaft, that are
common to most engines. Overhaul procedures,
removal and replacement procedures, and
s~ecifications are also covered. Subsections furnish
detailed information on each specific engine. Service
SECTION 6D - ENG l N E ELECTRICAL
information is also given that relates to that engine's
use in each
Carline. Specific subsections are: Items
covered in this section are battery,
generator, starter, primary and secondary ignition,
6A2
- 2.8L V-6 Engine
engine wire harness, spark plugs and wires, and
6A3
- 5.OL V-8 Engine
ignition switch.
SECTION 6B - ENGINE COOLING
Engine cooling system components such as
radiator, water pump, thermostat, and cooling fan, are
covered in this section. Accessory drive belts are also
covered, along with cooling system capacities.
SECTION 6C - FUEL SYSTEM
This section contains information on all the parts
of the fuel system
except the carburetor, or Throttle
Body Injection unit (TBI) itself. Items covered are fuel
tank, fuel pump, and fuel lines. Specific subsections are
SECTION 6E - DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
This section covers emission control systems
general information, and diagnostic procedures which
will lead to repairing performance and driveability
related problems for gasoline engine equipped vehicles.
All emission components are covered, as well as all
removal and replacement procedures. Instructions on
use of special tools are also given. Specific sections are:
6E
- Driveability and Emissions
6E2
- Fuel Injection (TBI)
Page 350 of 1825

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION 6-5
INSTRUMENT PANEL OIL WARNING LAMP "ON" AT IDLE
1. Oil cooler, or oil or cooler line restricted. Remove 2. Oil pump pressure low. See oil pump repair
restrictions in cooler or cooler line. procedures
in Section
6A.
ENGINE COMPRESSION EST
COMPRESSION TEST
Important
e Disconnect the "BAT." terminal from the - HE1 distributor or ignition module.
To determine if the valves or pistons are at fault,
a test should be made to determine the cylinder
compression pressure. When checking cylinder
compression, the throttle and choke should be open, all
spark plugs removed, and the battery at or near full
charge. The lowest reading cylinder should not be less
than
70% of the highest and no cylinder reading
should be less than
689 kPa (100 PSI). This
should be done with four
"puffs" per
cylinder.
Normal - Compression builds up quickly and
evenly to specified compression on each cylinder.
Piston Rings - Compression low on first
stroke, tends to build up on following strokes, but does
not reach normal. Improves considerably with addition
of oil.
Valves - Low on first stroke, does not tend to
build up on following strokes. Does not improve much
with addition of oil.
Use approximately three squirts from a plunger
type oiler.
Page 359 of 1825
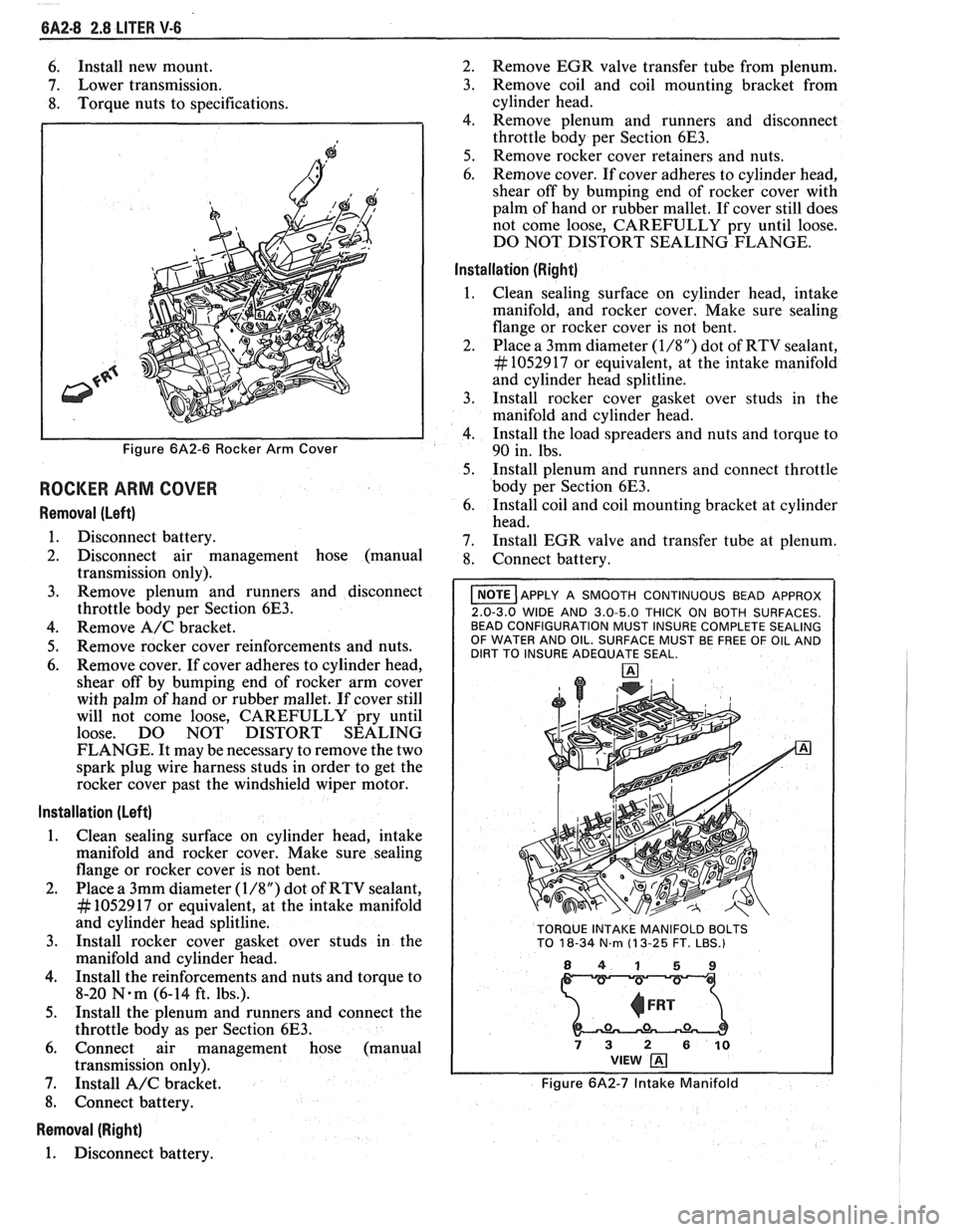
6A2-8 2.8 LITER V-6
6. Install new mount.
7. Lower transmission.
8. Torque nuts to specifications.
Figure 6A2-6 Rocker Arm Cover
ROCKER ARM COVER
Removal (Left)
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Disconnect air management hose (manual
transmission only).
3. Remove plenum and runners and disconnect
throttle body per Section
6E3.
4. Remove A/C bracket.
5. Remove rocker cover reinforcements and nuts.
6. Remove cover. If cover adheres to cylinder head,
shear off by bumping end of rocker arm cover
with palm of hand or rubber mallet. If cover still
will not come loose, CAREFULLY pry until
loose. DO NOT DISTORT SEALING
FLANGE. It may be necessary to remove the two
spark plug wire harness studs in order to get the
rocker cover past the windshield wiper motor.
Installation (Left)
1. Clean sealing surface on cylinder head, intake
manifold and rocker cover. Make sure sealing
flange or rocker cover is not bent.
2. Place a 3mm diameter
(1/8") dot of RTV sealant,
# 1052917 or equivalent, at the intake manifold
and cylinder head splitline.
3. Install rocker cover gasket over studs in the
manifold and cylinder head.
4. Install the reinforcements and nuts and torque to
8-20
N.m (6-14 ft. lbs.).
5. Install the plenum and runners and connect the
throttle body as per Section
6E3.
6. Connect air management hose (manual
transmission only).
7. Install
A/C bracket.
8. Connect battery.
Removal (Right)
1. Disconnect battery. 2.
Remove EGR valve transfer tube from plenum.
3. Remove coil and coil mounting bracket from
cylinder head.
4. Remove plenum and runners and disconnect
throttle body per Section
6E3.
5. Remove rocker cover retainers and nuts.
6. Remove cover. If cover adheres to cylinder head,
shear off by bumping end of rocker cover with
palm of hand or rubber mallet. If cover still does
not come loose, CAREFULLY pry until loose.
DO NOT DISTORT SEALING FLANGE.
Installation (Right)
Clean sealing surface on cylinder head, intake
manifold, and rocker cover. Make sure sealing
flange or rocker cover is not bent.
Place a 3mm diameter
(1/8") dot of RTV sealant,
# 1052917 or equivalent, at the intake manifold
and cylinder head splitline.
Install rocker cover gasket over studs in the
manifold and cylinder head.
Install the load spreaders and nuts and torque to
90 in. lbs.
Install plenum and runners and connect throttle
body per Section
6E3.
Install coil and coil mounting bracket at cylinder
head.
Install EGR valve and transfer tube at plenum.
Connect battery.
I NOTE ]APPLY A SMOOTH CONTINUOUS BEAD APPROX
2.0-3.0 WIDE AND 3.0-5.0 THICK ON BOTH SURFACES.
BEAD CONFIGURATION MUST INSURE COMPLETE SEALING
OF WATER AND OIL. SURFACE MUST BE FREE OF OIL AND
DIRT TO INSURE ADEQUATE SEAL.
TORQUE INTAKE MANIFOLD BOLTS
TO
18-34 N.m (1 3-25 FT. LBS.)
841 59
73 2 610 VIEW
Figure 6A2-7 Intake Manifold