fuel RENAULT SCENIC 2011 J95 / 3.G Engine And Peripherals Siemens Injection User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: RENAULT, Model Year: 2011, Model line: SCENIC, Model: RENAULT SCENIC 2011 J95 / 3.GPages: 329, PDF Size: 1.71 MB
Page 20 of 329

13B-20
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Function13B
The exhaust system is fitted with an exhaust gas treatment system consisting of (in order):
●A shell casing containing an oxidation catalytic converter to treat hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide, the volume
and positioning of which is identical to K9K Step 2 without a particle filter.
●A fuel injector supplied by a second fuel circuit which is independent of the main fuel circuit.
●A second casing containing an oxidation catalytic converter and a particle filter positioned under the vehicle floor.
EXHAUST GAS TREATMENT
Operating principle
Regeneration consists of burning the particles accumulated in the filter. When oxygen is present, regeneration
by particle combustion occurs naturally when the exhaust gas temperature reaches 570°C.
This temperature is very different to the temperatures observed in the normal operating range of a common rail
engine. In town, the engine does not produce much heat and the exhaust gas temperature varies between 250°C
and 300°C. Whatever the driving conditions may be, a particle filter regeneration program should be developed
without an effect on driving pleasure.
A differential pressure sensor monitors the status of the particle filter (particle weight) and triggers regeneration.
Regeneration is performed by specific injection regulation (phased injection and post-injection) which brings the
temperature of the exhaust gas to between 550 °C and 650 °C at the particle filter inlet.
Regeneration lasts at least 30 minutes and is carried out every 165 miles (275 km) (minimum interval between 2
successful regenerations).
Certain types of customer driving (mainly urban driving) may cause the particle filter to accumulate a significant
quantity of particles. This amount of soot may impair customer experience: poor vehicle performance due to
excessive pressure in the exhaust system.
This driving type may cause the speed request (Vdiag 45 and 49 only) warning light to come on when the particle
weight reaches 30.8 g or after 10 regeneration failures or if the distance between each regeneration reaches
111 0 m il es (1850 km). The customer is asked to drive in a certain way (see vehicle handbook).
However, this warning may be misinterpreted or taken to be a vehicle fault. The vehicle must not be returned to the
garage after such a warning; if the vehicle is taken back to the garage and accepted for repair, the mechanic should
carry out After-Sales regeneration.
PARTICLE FILTER INJECTOR PROGRAM
The particle filter injector is clamped in place inside a cooling cylinder head, which itself is attached to the output
cone of the first oxidation catalytic converter. The coolant flows into the cylinder head via a take-off pipe on the
cooling system and leaves via a hose connected to the turbocharger.
This injector is used to replace post injection in areas of low load and low flow.
This injector is supplied by an additional electric fuel pump.
The electric fuel pump is:
●controlled by a relay during each regeneration phase or purge,
●integrated into the suction module submerged in the tank,
●connected to the second fuel circuit.
Page 22 of 329

13B-22
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Function13B
High pressure pump:
The pump draws in fuel from the tank, which passes through a fuel filter and supplies the fuel injectors.
Rail pressure sensor:
This sensor is fitted to the rail and shows the pressure inside the rail.
Rail pressure regulator:
This component regulates the high pressure of the fuel in the injection system.
Fuel flow regulator:
This component regulates the fuel flow of the injection system.
Fuel temperature sensor:
This sensor measures the temperature of the fuel arising from the pump and injector return.
Piezoelectric injectors:
These injectors enable rapid, precise metering of the quantity of fuel injected, with excellent injection process
repetitiveness.
Vacuum pump:
The vacuum pump is driven by the camshaft. The pump provides the vacuum required to operate the following
components: control solenoid valve, brake servo.
Control solenoid valve:
The solenoid valve connects the vacuum pump and the control diaphragm of the turbocharger blades.
Turbocharger:
The turbocharger is used to supply the engine with more air.
Intake air pressure sensor:
This sensor measures the pressure at the turbocharging air cooler output before the damper valve.
Turbocharger pressure sensor:
This sensor measures the pressure at the turbocharging air cooler output before the damper valve.
Air mass flow meter:
The flowmeter measures the amount of fresh air which goes back into the engine.
EGR valve:
The exhaust gas recirculation enables nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions to be reduced significantly.
EGR position sensor:
The sensor gives the position of the EGR solenoid valve.
Damper valve (Vdiag 44, 45, 48, 49 and 4D only):
The damper valve is used:
– During regeneration in order to control the flow of fresh air.
– When the engine is switched off, to dampen the engine which helps stop the engine.
– When inoperative, the damper valve is by default in the fully open position.
Particle filter:
The particle filter retains the particles for destruction during regeneration, avoiding propagation of these particles in
the atmosphere (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only).
Page 23 of 329

13B-23
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Function13B
TDC sensor:
The angular position is measured using a magneto-inductive sensor triggered by machined teeth on the flywheel.
This sensor gives the engine speed and the position of the crankshaft for injection.
Camshaft sensor:
This sensor gives a signal to perform the injection cycle. When the piston of cylinder 1 is at top dead centre, either at
the end of the compression stroke or at the end of the exhaust stroke, the camshaft sensor enables a distinction to
be made between these two states.
Electric coolant pump:
The electric coolant pump is activated when the coolant temperature has reached a significant temperature
threshold when the engine has stopped.
The role of the electric water pump is to cool the turbocharger when the engine stops (Vdiag 45, 49 only).
Refrigerant pressure sensor:
The role of the sensor is to measure the refrigerant fluid pressure in the air conditioning circuit.
Electric fuel pump:
The pump is controlled by a relay during each regeneration or purge phase; it is submerged in the tank and is
connected to the secondary fuel circuit only.
Coolant temperature sensor:
The engine coolant temperature sensor informs the computer about the engine coolant temperature.
Air temperature sensor:
The air temperature sensor is fitted in the inlet manifold and informs the computer about the temperature of the air
sucked up by the engine.
Turbocharging pressure sensor solenoid valve:
This solenoid valve operates the turbocharger wastegate pneumatic circuit to lower the turbocharging pressure.
Catalytic converter:
Its role is to convert pollutant gases into harmless gases.
Catalytic converter downstream temperature sensor:
This sensor gives the temperature of the exhaust gas at the catalytic converter output.
Turbine upstream temperature sensor:
This sensor gives the temperature of the exhaust gas at the turbine inlet.
Particle filter downstream temperature sensor:
This sensor gives the exhaust gas temperature at the particle filter outlet (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only).
Particle filter upstream temperature sensor:
This sensor gives the exhaust gas temperature at the particle filter inlet (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only).
Particle filter differential pressure sensor:
A differential pressure sensor monitors the status of the particle filter (particle weight) and triggers regeneration.
The role of the sensor is to inform the computer of the pressure difference between particle filter inlet and outlet
(Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only).
Page 24 of 329

13B-24
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Function13B
Cruise control/speed limiter on/off switch:
This switch turns the cruise control/speed limiter on or off.
Water in diesel fuel sensor (optional):
This sensor indicates if water is present in the diesel.
Fan unit relay:
This relay actuates the motor-driven fan assemblies when a temperature threshold has been exceeded.
Accelerator potentiometer:
The accelerator potentiometer informs the computer about the position of the accelerator pedal (engine load).
Brake pedal switch:
The brake pedal switch informs the computer about the pedal status.
Clutch pedal switch:
The clutch pedal switch informs the computer about the pedal status.
Particle filter injector:
The particle filter injector is a low pressure injector. This injector allows the temperature of the second catalytic
converter to be raised to assist with regeneration of the particle filter (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only).
Only on Kangoo 2: an evaporator plate is present at the particle filter injector outlet, at the level of the bracket
between the exhaust pipe and the catalytic converter.
Heating elements:
The heating elements heat the engine coolant to enhance user comfort (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only).
Heater plugs:
The heater plugs preheat the combustion chamber so that the explosion of the fuel mixture occurs under the best
conditions to start the engine.
Page 30 of 329

13B-30
MR-372-J84-13B050$312.mif
V17
13B
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Configurations and programming
SPECIAL COMMANDS
SC001: Write saved data.
Use this command after replacing or (re)programming the computer (if the data has been saved using command
SC003).
SC003: Save computer data.
This command enables the computer operating data, the engine adaptives, to be recorded.
Use this command before replacing or (re)programming a computer.
SC013: Enter VIN.
This command permits manual entry of the vehicle's VIN into the computer.
Use this command each time the computer is replaced or (re)programmed.
SC017: Particle filter regeneration.
The regeneration command is used to burn particles which have accumulated in the filter.
Run this command when the particle filter is clogged.
SC040: Speed limiter (Kangoo II only).
This command enables the vehicle's speed to be restricted to a certain speed.
Use this command at the customer's request.
SC041: Modification of the commercial vehicle idle speed (Kangoo II only).
This command enables the idle speed for vehicles such as refrigerated vehicles, ambulances etc. to be increased or
decreased.
CONFIGURATION READING
LC005: Gearbox type.
Manual gearbox or automatic transmission/sequential gearbox
LC009: Air conditioning.
With or without.
LC065: Water in diesel fuel sensor.
With or without.
LC120: Cruise control.
With or without.
LC121: Speed limiter.
With or without.
MR-372-J84-13B050$312.mif
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
Page 32 of 329
13B-32
MR-372-J84-13B050$351.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Fault summary table13B
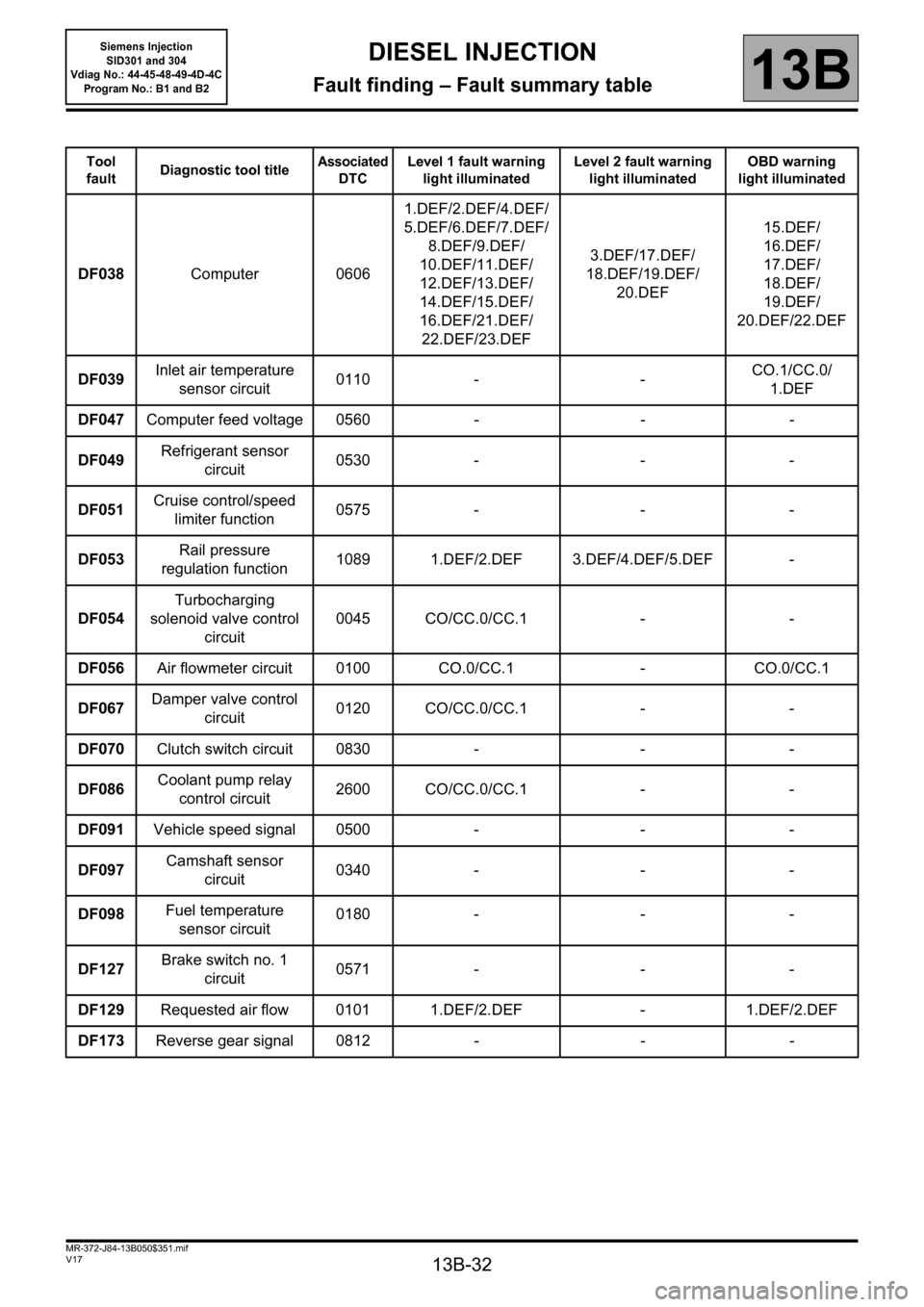
Tool
faultDiagnostic tool titleAssociated
DTCLevel 1 fault warning
light illuminatedLevel 2 fault warning
light illuminatedOBD warning
light illuminated
DF038Computer 06061.DEF/2.DEF/4.DEF/
5.DEF/6.DEF/7.DEF/
8.DEF/9.DEF/
10.DEF/11.DEF/
12.DEF/13.DEF/
14.DEF/15.DEF/
16.DEF/21.DEF/
22.DEF/23.DEF3.DEF/17.DEF/
18.DEF/19.DEF/
20.DEF15.DEF/
16.DEF/
17.DEF/
18.DEF/
19.DEF/
20.DEF/22.DEF
DF039Inlet air temperature
sensor circuit0110 - -CO.1/CC.0/
1.DEF
DF047Computer feed voltage 0560 - - -
DF049Refrigerant sensor
circuit0530 - - -
DF051Cruise control/speed
limiter function0575 - - -
DF053Rail pressure
regulation function1089 1.DEF/2.DEF 3.DEF/4.DEF/5.DEF -
DF054Turbocharging
solenoid valve control
circuit0045 CO/CC.0/CC.1 - -
DF056Air flowmeter circuit 0100 CO.0/CC.1 - CO.0/CC.1
DF067Damper valve control
circuit0120 CO/CC.0/CC.1 - -
DF070Clutch switch circuit 0830 - - -
DF086Coolant pump relay
control circuit2600 CO/CC.0/CC.1 - -
DF091Vehicle speed signal 0500 - - -
DF097Camshaft sensor
circuit0340 - - -
DF098Fuel temperature
sensor circuit0180 - - -
DF127Brake switch no. 1
circuit0571 - - -
DF129Requested air flow 0101 1.DEF/2.DEF - 1.DEF/2.DEF
DF173Reverse gear signal 0812 - - -
Page 34 of 329
13B-34
MR-372-J84-13B050$351.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Fault summary table13B
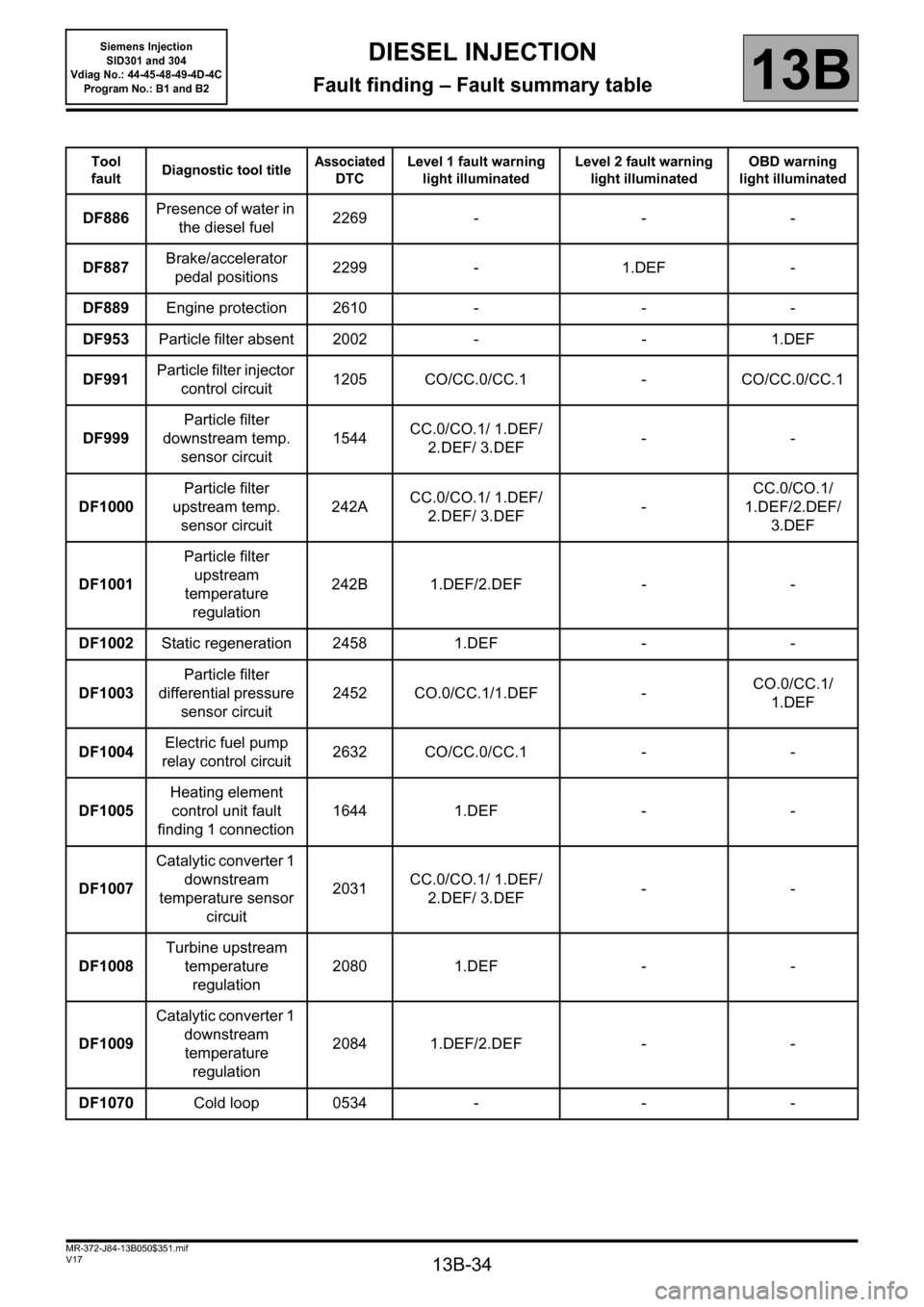
Tool
faultDiagnostic tool titleAssociated
DTCLevel 1 fault warning
light illuminatedLevel 2 fault warning
light illuminatedOBD warning
light illuminated
DF886Presence of water in
the diesel fuel2269 - - -
DF887Brake/accelerator
pedal positions2299 - 1.DEF -
DF889Engine protection 2610 - - -
DF953Particle filter absent 2002 - - 1.DEF
DF991Particle filter injector
control circuit 1205 CO/CC.0/CC.1 - CO/CC.0/CC.1
DF999Particle filter
downstream temp.
sensor circuit1544CC.0/CO.1/ 1.DEF/
2.DEF/ 3.DEF--
DF1000Particle filter
upstream temp.
sensor circuit242ACC.0/CO.1/ 1.DEF/
2.DEF/ 3.DEF-CC.0/CO.1/
1.DEF/2.DEF/
3.DEF
DF1001Particle filter
upstream
temperature
regulation 242B 1.DEF/2.DEF - -
DF1002Static regeneration 2458 1.DEF - -
DF1003Particle filter
differential pressure
sensor circuit 2452 CO.0/CC.1/1.DEF -CO.0/CC.1/
1.DEF
DF1004Electric fuel pump
relay control circuit 2632 CO/CC.0/CC.1 - -
DF1005Heating element
control unit fault
finding 1 connection 1644 1.DEF - -
DF1007Catalytic converter 1
downstream
temperature sensor
circuit 2031CC.0/CO.1/ 1.DEF/
2.DEF/ 3.DEF--
DF1008Turbine upstream
temperature
regulation 2080 1.DEF - -
DF1009Catalytic converter 1
downstream
temperature
regulation 2084 1.DEF/2.DEF - -
DF1070Cold loop 0534 - - -
Page 53 of 329
13B-53
MR-372-J84-13B050$390.mif
V17
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Interpretation of faults
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No. 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
13B
DF026
PRESENT
OR
STOREDCYLINDER 1 INJECTOR CONTROL CIRCUIT
CC : Short circuit
CO : Open circuit
1. DEF: Line in open circuit
2. DEF: Open circuit or internal electronic fault
NOTESConditions for applying the fault finding procedure to a stored fault:
The fault is declared present after a road test.
If the fault is present:
– Engine speed and torque are restricted.
–The level 1 warning light is lit.
–The OBD warning light is illuminated.
– Loss of performance, operation on minimum of 2 cylinders.
Use CLIO III, MODUS, MEGANE II ph2, SCENIC II ph2 and KANGOO II Wiring
diagrams Technical Note.
Check the connection and condition of the connector for injector no. 1, component code193 (see MR 392, 385,
364, 370 and 417, Mechanical, 13B, Diesel injection, Diesel fuel injector: Removal - Refitting) and the
injection computer connector, component code120 (see MR 392, 385, 364, 370 and 417, Mechanical, 13B,
Diesel injection, Diesel injection computer: Removal - Refitting).
If the connectors are faulty and if there is a repair procedure (see Technical Note 6015A, Repairing electrical
wiring, Wiring: Precautions for repair) repair the connector(s); otherwise, replace the wiring.
Check the insulation, continuity and the absence of interference resistance on the following connections:
–3KW between components 193 and 120,
–3CR between components 193 and 120.
If the connection(s) are faulty and there is a repair method (see Technical Note 6015A, Repairing electrical
wiring, Wiring: Precautions for repair), repair the wiring, otherwise replace it.
Measure at ambient temperature (approx. 20°C), allow the engine to cool down for at least 30 minutes.
Measure the resistance between connections 3KW and 3CR for injector 1, component code 193.
If the resistance is not between 150 kΩ and 250 kΩ, replace injector 1 (see MR 392, 385, 364, 370 and 417,
Mechanical, 13B, Diesel injection, Diesel injector: Removal - Refitting).
Apply test 7 Incorrect injection quantity.
If the fault is still present, contact the Techline.
AFTER REPAIRDeal with any faults displayed by the diagnostic tool.
Clear the computer fault memory.
Carry out a road test followed by another check with the diagnostic tool.
SID301_V44_DF026 / SID304_V45_DF026 / SID301_V48_DF026 / SID304_V49_DF026 / SID304_V4D_DF026 / SID301_V4C_DF026
Page 58 of 329
13B-58
MR-372-J84-13B050$390.mif
V17
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Interpretation of faults
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No. 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
13B
DF039
PRESENT
OR
STOREDINLET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT
CC.0 : Short circuit to earth
CO.1 : Open circuit or short circuit to +12 V.
1. DEF: Micro-breaks
NOTESProcessing priority in the event of a number of faults:
Deal with fault DF011 Sensor supply voltage no. 1 first if it is present or stored.
Conditions for applying the fault finding procedure to a stored fault:
The fault is declared present after the ignition has been switched on for at least
10 seconds.
If the fault is present:
The air temperature has a default value, which is PR059 Inlet air temperature =
40°C.
Illumination of OBD fault warning light on the instrument panel.
Special notes:
The inlet air temperature sensor is integrated into the air flowmeter.
Use CLIO III, MODUS, MEGANE II ph2, SCENIC II ph2 and KANGOO II Wiring
diagrams Technical Note.
Check the connection and condition of the connector for the flowmeter, component code799 (see MR 392, 364,
370 and 417, Mechanical, 12A, Fuel mixture, Air flowmeter: Removal - Refitting).
If the connector is faulty and there is a repair procedure (see Technical Note 6015A, Electrical wiring repair,
Wiring: Precautions for repair), repair the connector, otherwise replace the wiring.
Check the connection and condition of the injection computer connector, component code 120 (see MR 392,
385, 364, 370 and 417, Mechanical, 13B, Diesel injection, Diesel injection computer: Removal - Refitting).
If the connector is faulty and there is a repair procedure (see Technical Note 6015A, Electrical wiring repair,
Wiring: Precautions for repair), repair the connector, otherwise replace the wiring.
Measure the resistance of the air temperature sensor between connections 3ABQ and 3DW of the air
flowmeter component code 799.
If the resistance measured is not:
3553Ω
flowmeter: Removal - Refitting)
Check the insulation, continuity and the absence of interference resistance on the following connections:
–3ABQ
, between components799 and 120,
–3DW between components 799 and 120.
If the connection(s) are faulty and there is a repair method (see Technical Note 6015A, Repairing electrical
wiring, Wiring: Precautions for repair), repair the wiring, otherwise replace it.
If the fault is still present, contact the Techline.
AFTER REPAIRDeal with any faults displayed by the diagnostic tool.
Clear the computer fault memory.
Carry out a road test followed by another check with the diagnostic tool.
SID301_V44_DF039 / SID304_V45_DF039 / SID301_V48_DF039 / SID304_V49_DF039 / SID304_V4D_DF039 / SID301_V4C_DF039
Page 62 of 329
13B-62
MR-372-J84-13B050$390.mif
V17
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Interpretation of faults
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No. 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
13B
DF053
PRESENT
OR
STORED
RAIL PRESSURE REGULATION FUNCTION
1. DEF: Regulator closed
2. DEF: Regulator open
3. DEF: Regulator open
4. DEF: Regulator closed
5. DEF: Faulty component: Pressure or flow regulator
6. DEF: Pressure regulation oscillation
7. DEF: Flow regulation oscillation
NOTESProcessing priority in the event of a number of faults:
Deal with fault DF098 Fuel temperature sensor circuit or DF007 Rail pressure
sensor circuit first, if the fault is present or stored.
Conditions for applying the fault finding procedure to a stored fault:
The fault is considered present when the engine is running.
Special notes:
Possible engine stoppage with illumination of Level 1 or Level 2 warning light or
loss of performance with illumination of the Level 1 warning light.
Apply test 1 Low pressure fuel supply system check.
Apply test 2 Internal fuel transfer pump check (ITP).
Apply test 3 High pressure fuel pressure solenoid valve check.
Apply test 4 Check high-pressure pump (HPP) and fuel flow solenoid valve.
Apply test 5 Rail high pressure regulation circuit check.
Apply test 6 Major leak in open injectors/injectors.
Apply test 7 Incorrect injection quantity.
If the fault is still present, contact the Techline.
AFTER REPAIRDeal with any faults displayed by the diagnostic tool.
Clear the computer fault memory.
Clear RZ004 Pressure regulation adaptives
Carry out a road test followed by another check with the diagnostic tool.
SID301_V44_DF053 / SID304_V45_DF053 / SID301_V48_DF053 / SID304_V49_DF053 / SID304_V4D_DF053 / SID301_V4C_DF053