RENAULT TWINGO 2009 2.G Electrical Equipment - Multiplexing Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: RENAULT, Model Year: 2009, Model line: TWINGO, Model: RENAULT TWINGO 2009 2.GPages: 33, PDF Size: 0.18 MB
Page 1 of 33
8Electrical equipment
V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$TOC.mif
V3
88B
"The repair procedures given by the manufacturer in this document are based on the
technical specifications current when it was prepared.
The procedures may be modified as a result of changes introduced by the
manufacturer in the production of the various component units and accessories from
which his vehicles are constructed."
V3
All rights reserved by Renault s.a.s.
Edition Anglaise
Copying or translating, in part or in full, of this document or use of the service part
reference numbering system is forbidden without the prior written authority of
Renault s.a.s.
© Renault s.a.s. 2008
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Introduction 88B - 2
Fault finding – List and location of components 88B - 8
Fault finding – Operating diagram 88B - 10
Fault finding – Function 88B - 12
Fault finding – Defect and safe modes 88B - 16
Fault finding – Configuration 88B - 17
Fault finding – Interpretation of faults 88B - 20
Fault finding – Fault finding chart 88B - 28
Page 2 of 33

88B-2V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$010.mif
88B
INTRODUCTION
Description of the multiplex network:
The multiplex network consists of a twisted pair of wires connected to several vehicle computers.
These two wires are called multiplex line H and multiplex line L.
Depending on the vehicle options, there is a single multiplex network.
–the Vehicle multiplex line (injection, anti-lock braking system/electronic stability program, instrument panel, air
conditioning, rev counter, sequential gearbox, UCH, airbag/pretensioners) is always present,
–the Multimedia multiplex line (navigation, radio, display, hands-free telephone) depending on the vehicle options.
Data is exchanged by the computers on the Vehicle multiplex line and Multimedia multiplex line networks at a
communication speed of 500 kbit/s.
The Vehicle multiplex line network has two computers, each with an internal resistance of 120ΩΩ Ω Ω
(network terminating resistors):
–the injection computer,
–the airbag computer.
The Multimedia multiplex line network has two computers, each with an internal resistance of 120ΩΩ Ω Ω
(network terminating resistors):
–the A2/A3 display,
–the radio.
PURPOSE
–The purpose of the multiplex network test is to determine the computers present on the vehicle's multiplex network
as well as the cause of possible inter-computer communication faults.
–It also serves to determine the functions installed in the vehicle which are often housed in various computers
(distributed functions, e.g.: Air conditioning, Security access, etc.).
–The test also checks the condition of multiplex network segments.
–The multiplex network test can also run fault finding on computers disconnected from the multiplex network; this
provides an overview of the vehicle's electronic layout. Note:
The Vehicle and Multimedia multiplex line networks support fault finding using the RENAULT tool.
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Introduction
Page 3 of 33

88B-3V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$010.mif
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Introduction88B
MULTIPLEX NETWORK OPERATION TEST
Vehicle computer power supply for fault finding:
Depending on the type of vehicle equipment, proceed as follows:
To cut off + after ignition feed, proceed as follows:
This step is the essential starting point for any computer fault finding procedure.
It ensures that the network is correctly connected at the terminals of each computer and that the signal is correctly
sent to it and received by it. This function also reads the number of faults present in the computers.
The multiplex network test function is started after the user selects the vehicle then selects the Test
computers icon.
After the network check, the other functions become accessible.Standard key/radio frequency key, switch on the ignition with the key.
Standard key/radio frequency key, switch off the ignition with the key.
Page 4 of 33

88B-4V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$010.mif
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Introduction88B
MULTIPLEX NETWORK TEST PROCEDURE
–Establish dialogue with the computers storing the vehicle configuration (read identification).
–Read the vehicle configuration in the two computers that store the multiplex network configuration (UCH and
Airbag) for the Vehicle multiplex line network.
–Read the vehicle configuration in the computer that stores the multiplex network configuration (A2/A3 display
computer) for the Multimedia multiplex line network.
–List of computers which support fault finding read from the two configuration computers.
–Computer interrogation.
–Physical (electrical) measurements on the multiplex line network.
IMPORTANT
There are three diagnostic lines, depending on the vehicle options:
Fault finding on the computer using the vehicle multiplex network:
–Injection systems,
–ABS or ABS/ESP or vehicle speed computer (depending on the vehicle equipment),
–UCH,
–Automatic transmission (depending on the vehicle equipment),
–Lighting (depending on the vehicle equipment),
–Instrument panel,
–Airbag/pretensioners,
–Climate control (depending on the vehicle equipment),
–Driving school unit (depending on the vehicle equipment),
–LPG injection (depending on the vehicle equipment).
Fault finding on computers using the multimedia multiplex network (depending on the vehicle equipment):
–Radio (R1-08 or R2-08),
–Multimedia interface (A2/A3 display),
–Multimedia connection (C-box).
Fault finding on the computer using the K line (depending on the vehicle equipment):
–Parking distance control and power-assisted steering.
Page 5 of 33

88B-5V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$010.mif
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Introduction88B
If the following error messages appear during a multiplex network test:
–Communication cannot be established with some computers: check their supply and their diagnostic line
before rerunning the test: the network topology is visible. Check to see if there are many computers that have not
been configured: update the multiplex network according to the computers present on the vehicle (see Multiplex
network configuration).
–Incorrect configuration of computers that support fault finding: check the configuration before rerunning
a test: the network topology is not visible, a network configuration is requested (see Multiplex network
configuration).
–Incorrect configuration: check the computer configuration before rerunning a test: the network topology is
not visible, a network configuration is requested (see Multiplex network configuration).
ACQUISITION AND DISPLAY OF THE RESULTS
The acquisition screen is made up of a bar graph which changes when the various initialisation, acquisition and data
analysis stages are updated.
At the end of the test, the tool displays a screen with the test result.
How to read the topological diagram:
The results display screen consists of three screens:
–the upper zone: fault finding procedure result message,
–the left-hand centre zone: topological diagram (not always available),
–the right-hand centre zone: interpretation of the results from the various vehicle computers and list.
COMPUTERS
–Valid: green border, green lettering.
–Not detected: red border, red lettering.
–Do not support fault finding: black border, black lettering.
–Not recognised: red border, red lettering + exclamation mark.
SEGMENTS
–Valid: green dash.
–Faulty: red dash.
–Cannot support fault finding: black dash.
Page 6 of 33

88B-6V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$010.mif
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Introduction88B
Interpreting test result charts
On the Faults tab, the computers are organised into the following groups:
–Not detected if the computer failed to respond to the tool's identification request.
Within the undetected category, the computers are subdivided into Stores multiplex network configuration
and Does not store multiplex network configuration.
–Not recognised if the computer is detected but cannot be identified from its response.
On the Information tab, the computers are organised and listed as follows:
–Cannot support fault finding, if the computer cannot support fault finding with the tool and therefore was not
queried.
–Valid if the computer responded correctly to the tool's request.
If the Proceed icon in the bottom right-hand corner is selected, a new screen will appear with the following tab:
Under the Results tab the computers are organised into the following groups:
–Faulty if the computer is known and has a non-zero number of faults.
–OK if the computer was detected, recognised and has no faults.
–Not recognised if the computer was detected but could not be identified from its response.
–Not detected if the computer can support fault finding but failed to respond.
FUNCTION TESTING
The function test can be accessed by clicking on the List of functions icon.
–The vehicle function tests screen resembles the multiplex network test screen with a diagram of the network layout
if this is known and displayed.
–The Function tab displays the different computers involved in the functions, which may be distributed over several
computers.
Examples for the Vehicle multiplex line network:
•Air conditioning: UCH, INJ, and CLIM.
•Access - Safety: UCH and INJ
•Wiping: UCH
•Lighting: UCH
Examples for the Multimedia multiplex line network:
•Radio.
•Multimedia interface (A2/A3 display)
•Multimedia connection (C-box)
–The Info tab displays the other possible functions found on the vehicle concerned.
–Selecting a function from the list of functions enables computers not involved in this function to be shaded, thus
indicating the computers involved in this function.
–The Fault finding button runs fault finding on the function selected from the list.
Page 7 of 33

88B-7V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$010.mif
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Introduction88B
REPAIR HELP
Help with detecting computer or faulty segment:
If the multiplex network is completely frozen, this command can isolate multiplex network segments and thereby
rule out those that respond properly to the tool. This makes it easier to pinpoint the cause of the fault.
The algorithm for help with locating faults is intended for dealing with electrical faults present solely in the multiplex
line; it is therefore essential that connectors and computers not attached to the multiplex line V are not taken into
consideration.
A test for multiplex network faults by using physical measurements:
When a multiplex network segment has a short circuit, the computers can no longer communicate with each other or
with the diagnostic tool. At this point, the network test is not operational.
The CLIP tool can identify several types of faults by taking electrical measurements on the multiplex line H and
multiplex line L multiplex network. It can detect a multiplex line L / multiplex line H short circuit, a multiplex line L /
+12 V short circuit, a multiplex line H / +12 V short circuit, and a multiplex line H / earth short circuit.
By disconnecting the connectors then the computers, it is possible to determine or indicate the segment causing the
fault on the multiplex network.
Page 8 of 33
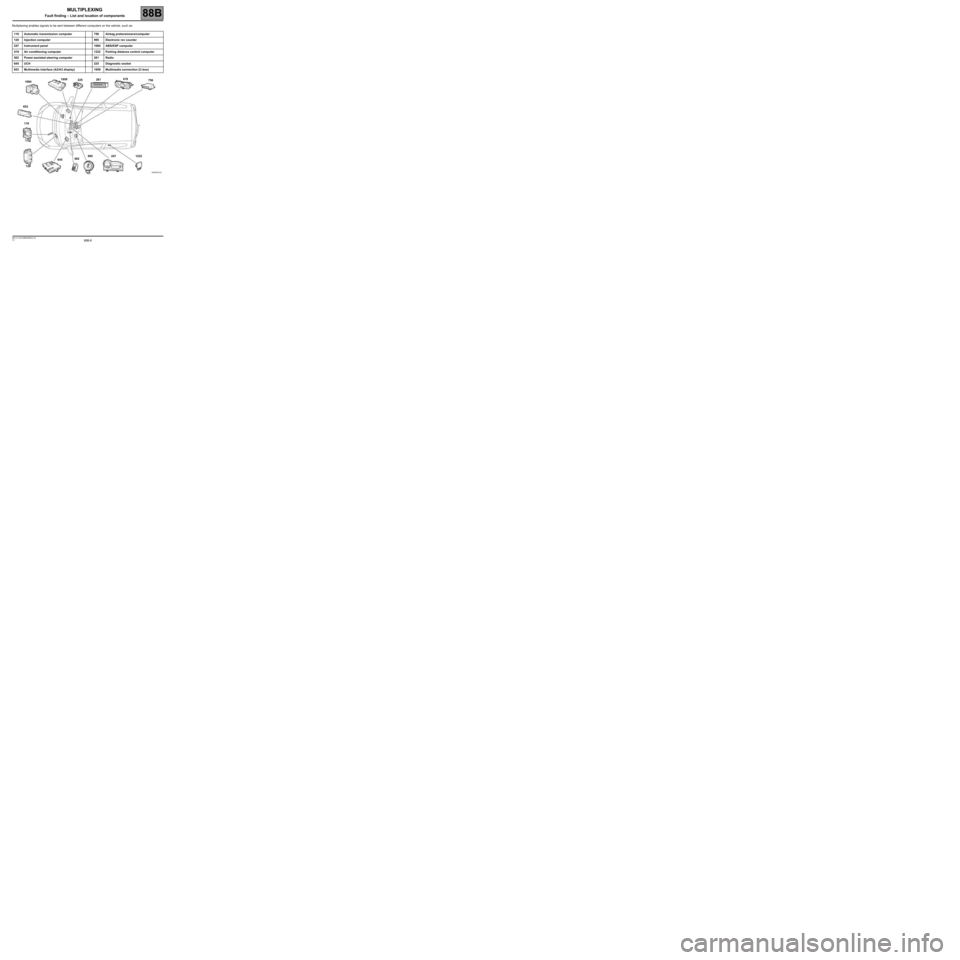
88B-8V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$020.mif
88B
Multiplexing enables signals to be sent between different computers on the vehicle, such as:
119 Automatic transmission computer 756 Airbag pretensioners/computer
120 Injection computer 995 Electronic rev counter
247 Instrument panel 1094 ABS/ESP computer
419 Air conditioning computer 1222 Parking distance control computer
502 Power-assisted steering computer 261 Radio
645 UCH 225 Diagnostic socket
653 Multimedia interface (A2/A3 display) 1959 Multimedia connection (C-box)
1222 247 995
502
645
120 119 65310941959
225261419
756
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – List and location of components
Page 9 of 33

88B-9V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$020.mif
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – List and location of components88B
1222
995
261
645
756
502 120 119 10942251959653247
419
Page 10 of 33
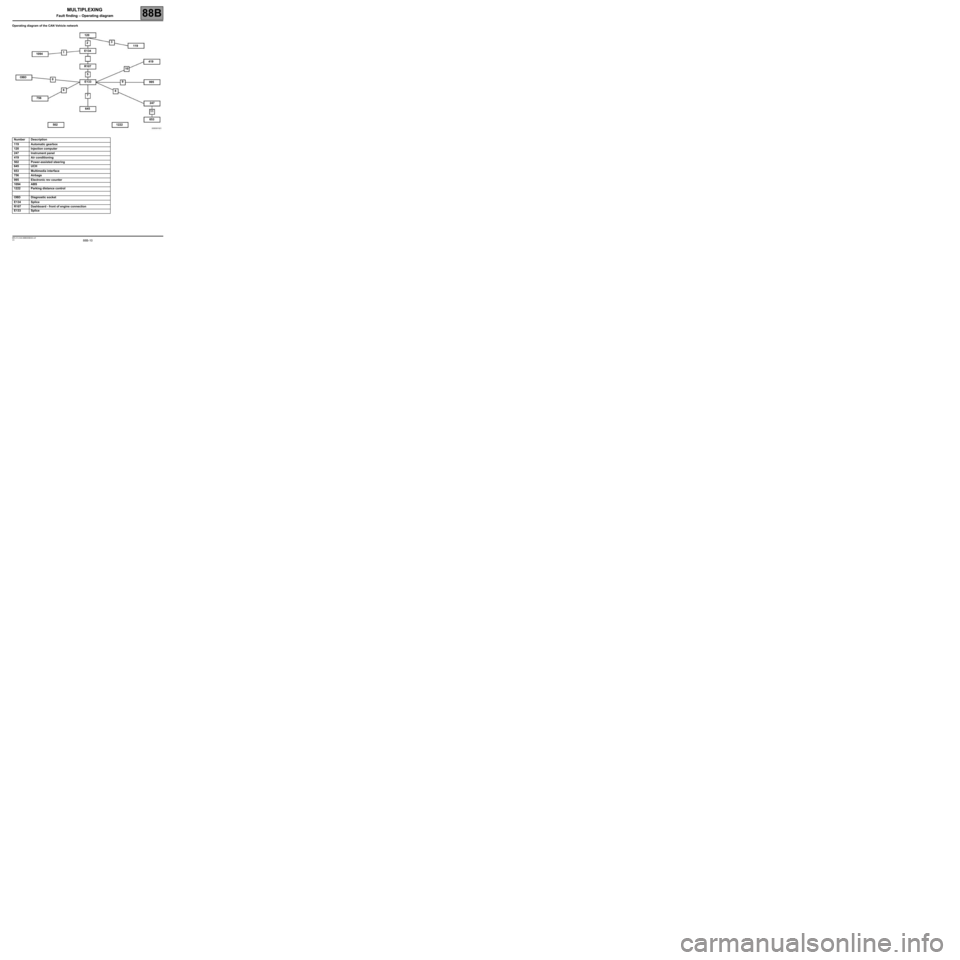
88B-10V3 MR-413-X44-88B000$030.mif
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Operating diagram88B
Operating diagram of the CAN Vehicle network
Number Description
119 Automatic gearbox
120 Injection computer
247 Instrument panel
419 Air conditioning
502 Power-assisted steering
645 UCH
653 Multimedia interface
756 Airbags
995 Electronic rev counter
1094 ABS
1222 Parking distance control
OBD Diagnostic socket
E134 Splice
R107 Dashboard - front of engine connection
E133 Splice
120
010
11 123
5
6
7 89 OBDE134
E133 R107
645 1094119
419
995
247
653
1222 502 756
MULTIPLEXING
Fault finding – Operating diagram