automatic transmission Seat Alhambra 2015 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SEAT, Model Year: 2015, Model line: Alhambra, Model: Seat Alhambra 2015Pages: 305, PDF Size: 5.46 MB
Page 147 of 305
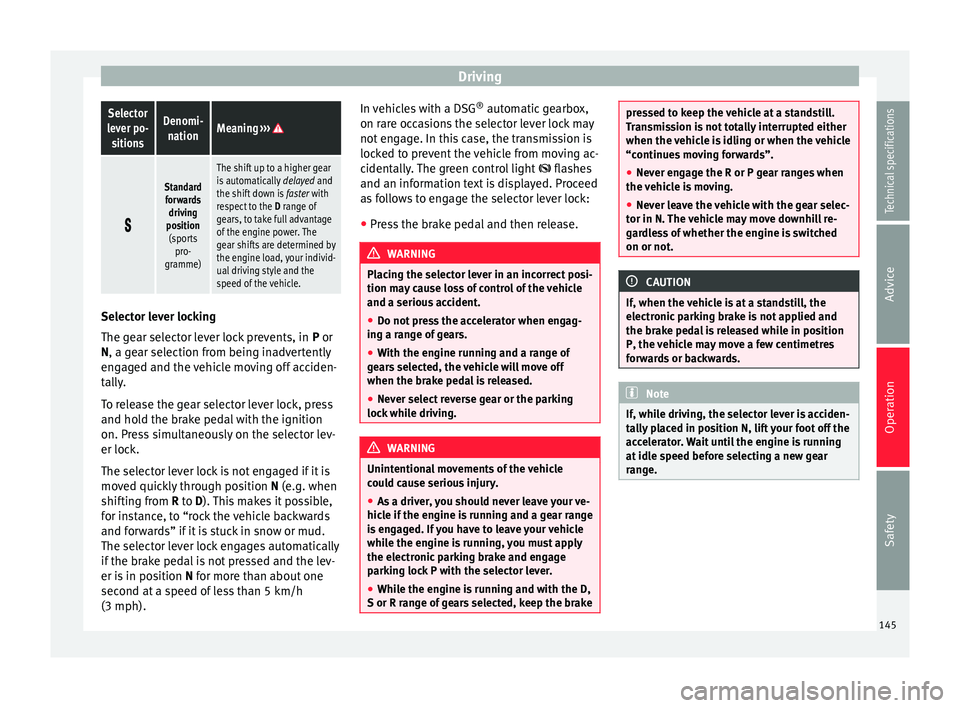
DrivingSelector
lever po- sitionsDenomi- nationMeaning ›››
Standard
forwards driving
position (sports pro-
gramme)
The shift up to a higher gear
is automatically delayed and
the shift down is faster with
respect to the D range of
gears, to take full advantage
of the engine power. The
gear shifts are determined by
the engine load, your individ-
ual driving style and the
speed of the vehicle. Selector lever locking
The gear selector lever lock prevents, in
P or
N , a gear selection from being inadvertently
en
gaged and the vehicle moving off acciden-
tally.
To release the gear selector lever lock, press
and hold the brake pedal with the ignition
on. Press simultaneously on the selector lev-
er lock.
The selector lever lock is not engaged if it is
moved quickly through position N (e.g. when
shiftin
g from R to D). This makes it possible,
for instance, to “rock the vehicle backwards
and forwards” if it is stuck in snow or mud.
The selector lever lock engages automatically
if the brake pedal is not pressed and the lev-
er is in position N
for more than about one
second at a speed of less than 5 km/h
(3 mph). In vehicles with a DSG
®
automatic gearbox,
on rare occasions the selector lever lock may
not engage. In this case, the transmission is
locked to prevent the vehicle from moving ac-
cidentally. The green control light flashes
and an inform
ation text is displayed. Proceed
as follows to engage the selector lever lock:
● Press the brake pedal and then release. WARNING
Placing the selector lever in an incorrect posi-
tion may cause loss of control of the vehicle
and a serious accident.
● Do not press the accelerator when engag-
ing a range of gears.
● With the engine running and a range of
gears selected, the vehicle will move off
when the brake pedal is released.
● Never select reverse gear or the parking
lock while driving. WARNING
Unintentional movements of the vehicle
could cause serious injury.
● As a driver, you should never leave your ve-
hicle if the engine is running and a gear range
is engaged. If you have to leave your vehicle
while the engine is running, you must apply
the electronic parking brake and engage
parking lock P with the selector lever.
● While the engine is running and with the D,
S or R range of gears selected, keep the brake pressed to keep the vehicle at a standstill.
Transmission is not totally interrupted either
when the vehicle is idling or when the vehicle
“continues moving forwards”.
●
Never engage the R or P gear ranges when
the vehicle is moving.
● Never leave the vehicle with the gear selec-
tor in N. The vehicle may move downhill re-
gardless of whether the engine is switched
on or not. CAUTION
If, when the vehicle is at a standstill, the
electronic parking brake is not applied and
the brake pedal is released while in position
P, the vehicle may move a few centimetres
forwards or backwards. Note
If, while driving, the selector lever is acciden-
tally placed in position N, lift your foot off the
accelerator. Wait until the engine is running
at idle speed before selecting a new gear
range. 145
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 155 of 305
Driving
automatically. The control lamp will not light
up in this case . For the sake of the environment
Even when the emission control system is
working perfectly, there may be a smell of
sulphur under certain conditions. This de-
pends on the sulphur content of the fuel be-
ing used. Driving abroad
In some countries, certain safety regulations
and requirements are in force relating to ex-
haust gas emissions, which differ from the
technical characteristics of the vehicle. Be-
fore travelling abroad, SEAT recommends you
consult a technical service about the legal re-
quirements and the following points:
●
Does the vehicle need technical modifica-
tions for driving abroad, for example, adjust-
ment of the headlamps?
● Does the vehicle have all the tools, diag-
nostics equipment and spare parts required
for inspections and repairs?
● Are there any SEAT dealers in the destina-
tion country?
● For petrol vehicles: Is unleaded petrol avail-
able at the right octane rating?
● For diesel engines: Is diesel fuel available
with a low sulphur content? ●
Are a suitable engine oil ( ››› page 218) and
other engine fluids complying with SEAT
specifications available in the destination
country?
● Will the navigation system fitted at the fac-
tory operate correctly in the destination coun-
try with the available navigation data?
● Are special tyres required in the destination
country? CAUTION
SEAT does not accept liability for any damage
to the vehicle due to the use of a lower quali-
ty fuel, an inadequate service or the non-
availability of genuine spare parts. Driving along flooded roadways
To prevent damage to the vehicle when driv-
ing through water, for example, along a floo-
ded road, please observe the following:
● Check the depth of the water before enter-
ing the flooded zone. The water should never
come above the lower edge of the bodywork
››› .
● Do not drive faster than a pedestrian.
● Do not stop in the water, use reverse gear
or switch off the engine.
● Oncoming traffic will cause waves which
raise the level of the water, making it difficult
to cross the water. WARNING
When driving through water, mud, melted
snow, etc., please remember that due to
damp or frozen brake discs and shoes in win-
ter, the braking effect may be delayed, there-
fore the required braking distance is greater.
● “Dry the brakes and remove ice” by braking
carefully. Ensure that you are not endanger-
ing other road-users or breaking traffic regu-
lations in the process.
● After driving through water, avoid sudden
sharp manoeuvres. CAUTION
● Driving through flooded areas may severely
damage vehicle components such as the en-
gine, transmission, drive train or electrical
system.
● Never drive through salt water as salt cau-
ses corrosion. Always rinse any parts of the
vehicle which have been in contact with salt
water. 153Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 156 of 305

Operation
Driver assistance systems
Braking and stability systems Brake assist systems The brake assist systems ESC, ABS, BAS, ASR
and EDL only operate when the ignition is
switched on. They contribute significantly to
increasing active safety.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
ESC reduces the risk of skidding and increa-
ses the vehicle stability by braking individual
wheels under specific driving conditions. ESC
detects critical handling situations, such as
understeer, oversteer and wheelspin on the
driven wheels. The system stabilises the ve-
hicle by braking individual wheels or by re-
ducing the engine torque.
The ESC has limits. It is important to realise
that the ESC is also subject to the laws of
physics. ESC will not be able to deal with all
situations with which drivers may be faced.
For example, if the road surface changes sud-
denly then ESC will not be useful in all cases.
If the vehicle suddenly enters a section cov-
ered by water, mud or snow then ESC will not
provide assistance in the same way as on dry
ground. If the vehicle loses its grip on the
ground and moves on a film of water (“aqua-
planing”), the ESC will not be able to assist the driver to control the vehicle as the loss of
adherence with the road surface will prevent-
ing braking and steering. If the vehicle is
driven through series of bends at high
speed, the ESC will not always be as effec-
tive: the vehicle reaction to aggressive driv-
ing is not the same as at reduced speeds.
When driving with a trailer, ESC does not pro-
vide the same amount of vehicle control as
without a trailer.
Adjust your speed and driving style to road,
traffic and weather conditions. ESC cannot
push the limits of the laws of physics; im-
prove the transmission available or maintain
the vehicle on the road if a lack of driver at-
tention creates an inevitable situation. Other-
wise, ESC assists in maintaining vehicle con-
trol in extreme situations and uses the move-
ments of the steering made by the driver to
maintain the vehicle moving in the desired
direction. If the vehicle is driven at such a
speed that it will leave the road before ESC
can intervene then the system cannot pro-
vide assistance.
The ABS, BAS, ASR and EDL systems are in-
corporated into the ESC. The ESC is always
on. The ESC should only be turned off using
the ASR button
›››
Fig. 134 when traction is
in s
ufficient. Always remember to turn on the
ASR once more when the vehicle has traction
again. Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
ABS can prevent the wheels from locking dur-
ing braking until just before the vehicle stops
thus helping the driver to steer the vehicle
and maintain control. This means that, even
during full braking, the risk of skidding is re-
duced:
● Press and hold the brake pedal fully. Do not
remove your foot from the brake pedal or re-
duce braking force!
● Do not “pump” the brake pedal, or reduce
braking force!
● Maintain vehicle direction when braking
fully.
● When the brake pedal is released or when
the brake force is reduced, ABS is turned off.
ABS control can be observed by vibration of
the brake pedal and noise. You should never
expect
the ABS to reduce the braking dis-
tance under
any circumstances. This distance
will increase when driving on gravel, recent
snow or on icy and slippery ground.
When driving on loose ground, the all-terrain
configuration of the ABS is automatically
turned on. When ABS is activated, the front
wheels may lock briefly. This shortens the
braking distance in off-road situations as the
wheels are prevented from digging into loose
surfaces. All-terrain ABS only intervenes
when driving in a straight line. When the
154
Page 194 of 305
Advice
Check first with a specialised workshop that
understands the technical possibilities of in-
stallation if you wish to use a two-way radio
with a transmitting power of over 10 watts.
SEAT recommends taking your car in for tech-
nical service.
All legal requirements, together with the in-
structions for the use of two-way radios must
be observed. WARNING
If the two-way radio is not securely fastened
in position, it could be sent flying around the
vehicle in the event of sharp braking, sudden
manoeuvres or accident, causing injury.
● While driving, two-way radios must be se-
curely fastened in position, outside the radi-
us of action of the airbags, or safely stowed
away. WARNING
When using a two-way radio without a con-
nection to an exterior aerial, the maximum
permitted levels of electromagnetic radiation
may be exceeded. This is also the case if the
aerial has not been correctly installed.
● You should only use a two-way radio inside
the vehicle if it has first been correctly con-
nected to an exterior aerial. Information stored by the control
units
Your vehicle is fitted at the factory with a ser-
ies of electronic control units responsible for
the engine and gearbox management. In ad-
dition, the control units supervise the per-
formance of the exhaust gas system and the
airbag systems.
Therefore, while the vehicle is being driven,
these electronic control units are continuous-
ly analysing the vehicle data. In the event of
faults or deviations from the theoretical val-
ues, only this data is stored. Normally, the
warning lamps on the instrument panel light
up in the event of faults.
This data can only be read and analysed us-
ing special equipment.
The storing of the data allows specialised
workshops to detect and repair faults. Stored
data may include:
● Data relating to the engine or the gearbox
● Speed
● Direction of travel
● Braking force
● Detection of seat belt
The vehicle control units never record conver-
sations held by passengers in the vehicle.
In vehicles equipped with an emergency call
function via the mobile phone or other appli- ances connected in the vehicle, it is possible
to send the vehicle position. If the control
unit records an accident with airbag activa-
tion, the system may automatically send a
signal. This will depend on the network oper-
ator. Normally, transmission is only possible
in areas with good coverage.
Event Data Recorder
The vehicle is
not
fitted with an event data re-
c or
der.
An event data recorder temporarily stores the
vehicle information. Therefore, in the event of
an accident, it is possible to obtain detailed
information about how the accident occur-
red. For example, in vehicles with airbag sys-
tems, data relating to speed of impact, seat
belt status, seat positions and airbag activa-
tion times may be stored. The volume of data
depends on the manufacturer.
Event data recorders can only be mounted
with authorisation from the vehicle owner
and, in some countries, they are governed by
local legislation.
Reprogramming control units
On the whole, all the data required for the
component management is stored in the con-
trol units. The programming of certain con-
venience functions, such as the turn signals,
individual door opening and instructions on
the display can be modified using special
192
Page 259 of 305

Emergencies
Towing vehicles with an automatic gearbox
Note the following for a towed vehicle:
● Make sure the gear selector lever is in the N
position.
● Do not drive faster than 50 km/h (30 mph).
● Do not tow further than 50 km (30 miles).
● If a breakdown truck is used, the vehicle
must be towed with the front wheels raised.
Note the following instructions for towing
four all-wheel drive vehicles.
Instructions for towing all-wheel drive
vehicles
All-wheel drive vehicles can be towed using a
toolbar or tow rope. If the vehicle is towed
with the front or rear axle raised, the engine
must be turned off to avoid transmission
damage.
For vehicles with a double clutched DSG ®
(di-
rect shift gearbox) the instructions for towing
vehicles with an automatic gearbox apply
››› page 257 .
Sit uation
s in which the vehicle should not be
towed
In the following cases, the vehicle should not
be towed but transported on a trailer or spe-
cial vehicle:
● If the vehicle gearbox does not contain lu-
bricant due to a fault. ●
If the vehicle battery is flat and, as a result,
the electronic steering lock and electronic
parking brake cannot be disengaged if ap-
plied.
● If the vehicle to be towed has an automatic
gearbox and the distance to be covered is
greater than 50 km (30 miles). Note
● The vehicle can only be towed if the elec-
tronic parking brake and steering lock are de-
activated. If the vehicle has no power supply
or there is an electric system fault, the en-
gine must be started using jump leads to de-
activate the electronic parking brake and
electronic steering lock.
● Vehicles with the Keyless Access locking
and ignition system should only be towed
with the ignition connected since, otherwise,
the electronic steering lock will not unlock. Fitting the front towline anchorage
Fig. 194
On the right-hand side of the front
bumper: Screw in the towline anchorage. The location for the removable towline an-
chorage is on the right-hand side of the front
bumper
››› Fig. 194 .
The t o
wline anchorage should always be kept
in the vehicle.
Note the instructions for towing ››› page 256.
To fit the towline anchorage
● Take the towline anchorage from the vehi-
cle tool kit ››› page 244.
● Pre
ss on the upper cover and carefully re-
move it forwards. Allow the cover to hang.
● Screw in the towline anchorage into its po-
sition anticlockwise as far as it will go
›
›› Fig. 194 ››› . Use a suitable tool to firmly
tighten the towline anchorage in its location. »
257
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety